Using traditional financial systems requires verification by a central authority that serves as a validator and transaction intermediary. This structure imposes several limitations on financial services in traditional systems, including geographical and time-based restrictions.
Satoshi Nakamoto, by creating Bitcoin, introduced a solution where transactions would not require third-party approval and could be carried out directly between peers. Therefore, Bitcoin effectively addresses problems such as double spending and centralization.

Problems in Digital Financial Systems Before Bitcoin
Digital financial systems prior to the invention of Bitcoin had two significant issues of centralization and double-spending. To solve these problems, individuals had to rely on intermediaries such as banks to process their transactions.
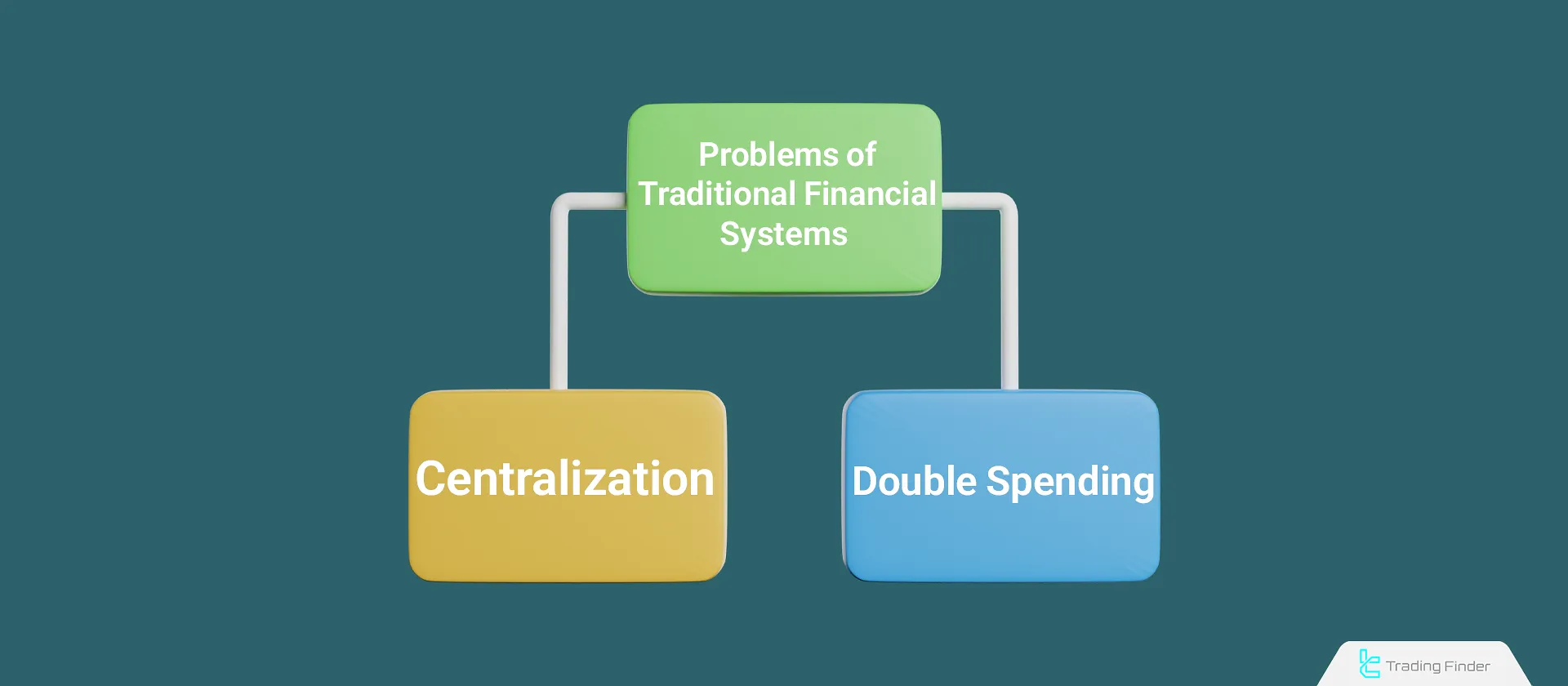
The double-spending problem refers to the ability to spend the same digital asset more than once. For example, if someone creates an image file of a one-dollar bill, they could copy it infinitely and use it across various platforms.
To prevent such occurrences, people had to trust a central authority like a bank, and this trust naturally created the concept of centralization.
Comparison of the Digital Financial System Before Bitcoin and After Bitcoin:
Topic | Situation before Bitcoin | Situation after Bitcoin |
Transaction control structure | Dependent on a central authority for recording and verifying transactions | Peer to peer verification without the need for an intermediary or central authority |
Double Spending possibility (Double Spending) | Very high; due to the ability to copy digital assets | Almost zero; through simultaneous data storage across millions of nodes |
Security and data protection | Centralized; a single point is sufficient for attack and manipulation | Distributed; attacking the network is almost impossible |
Asset ownership | Dependent on banks and intermediary companies; possibility of freezing | Full ownership of assets through private keys |
Transaction transparency | Limited; users do not have access to transaction information | Full transparency; the ability to review the history of all transactions |
Time limitations | Banking services limited to business hours | 24 hours operation without interruption |
Global access | Limited; especially for individuals without bank accounts or official documents | Access for everyone with only internet and a wallet |
Transaction costs | Variable and often high fees, especially international | Uniform and predictable fees worldwide |
Transfer speed | Slow; especially in cross border transactions | Fast; transaction confirmation within minutes |
Risk of censorship or transaction stoppage | High; possibility of stopping, rejecting, or restricting by banks | Almost zero; transactions are censorship resistant |
The Role of Bitcoin in Eliminating the Need for Trust (Trustless System)
In traditional financial systems, users are forced to trust a central authority for every transaction. This trust includes data storage, transaction verification, and fraud prevention.
Bitcoin eliminated this requirement by designing a "Trustless" system; meaning that users can conduct transactions and store assets without trusting a specific person or organization.
This mechanism ensures that even if a single computer or a group of nodes behaves maliciously, the network structure remains unaffected and transactions are executed with full security.
A Simple Example of the Double Spending Problem in Digital Assets
When a digital asset exists, copying it is extremely easy. Imagine someone creates a digital image of a 1 dollar banknote. This file can be sent across multiple platforms without limitation, with no distinction between the original version and the copied versions.
This ability to copy allows a single asset to be spent multiple times; an issue that never occurs with physical assets. This problem was one of the most fundamental challenges of digital financial systems before Bitcoin and required a solution that could prevent the repetition of a transaction.
In the Double Spending tutorial article on the Investopedia website, this concept is explained in full:
How does Bitcoin Solve the Double Spending Problem
In traditional systems, all transaction information is recorded and stored in the ledger of a central authority. As a result, every transaction required approval from this entity.
Bitcoin introduced the concept of the Distributed Ledger, offering a solution where financial transactions could be carried out peer-to-peer without requiring the approval of a central authority. This process prevents double spending in a fully decentralized way.
How Does Bitcoin’s Distributed Ledger Work?
The Distributed Ledger, utilizing blockchain technology, records all transactions in a file that is replicated across thousands of computers worldwide. Thus, it becomes practically impossible to alter this information.
All versions of this file are continuously synchronized, and all users can view and verify these records.
How Did Bitcoin Make Transaction Forgery and Manipulation Impossible?
The Bitcoin blockchain structure stores transactions in the form of blocks, where each block is connected to the previous one using a cryptographic hash.
This chain-based connection means that any change in a single transaction would require altering all subsequent blocks; a process that is practically impossible due to the existence of thousands of copies of the blockchain across the world.
For this reason, no individual or entity can manipulate transaction records or inject false data into the network.
The Role of Mining Difficulty in Preventing Attacks
The Bitcoin network uses a mechanism called Mining Difficulty to prevent attacks and maintain security. This mechanism determines how much computational power miners must use to produce a new block.
An increase in mining difficulty significantly raises the cost and required power to attack the network. This is precisely how bitcoin fixes this, and it is one of the key reasons why Bitcoin is considered one of the most secure financial networks in the world.
Other Problems Solved by Bitcoin
The existence of a central authority as the validator of transactions led to other issues, such as censorship of information, restricted access, and complications with cross-border transactions, among others.
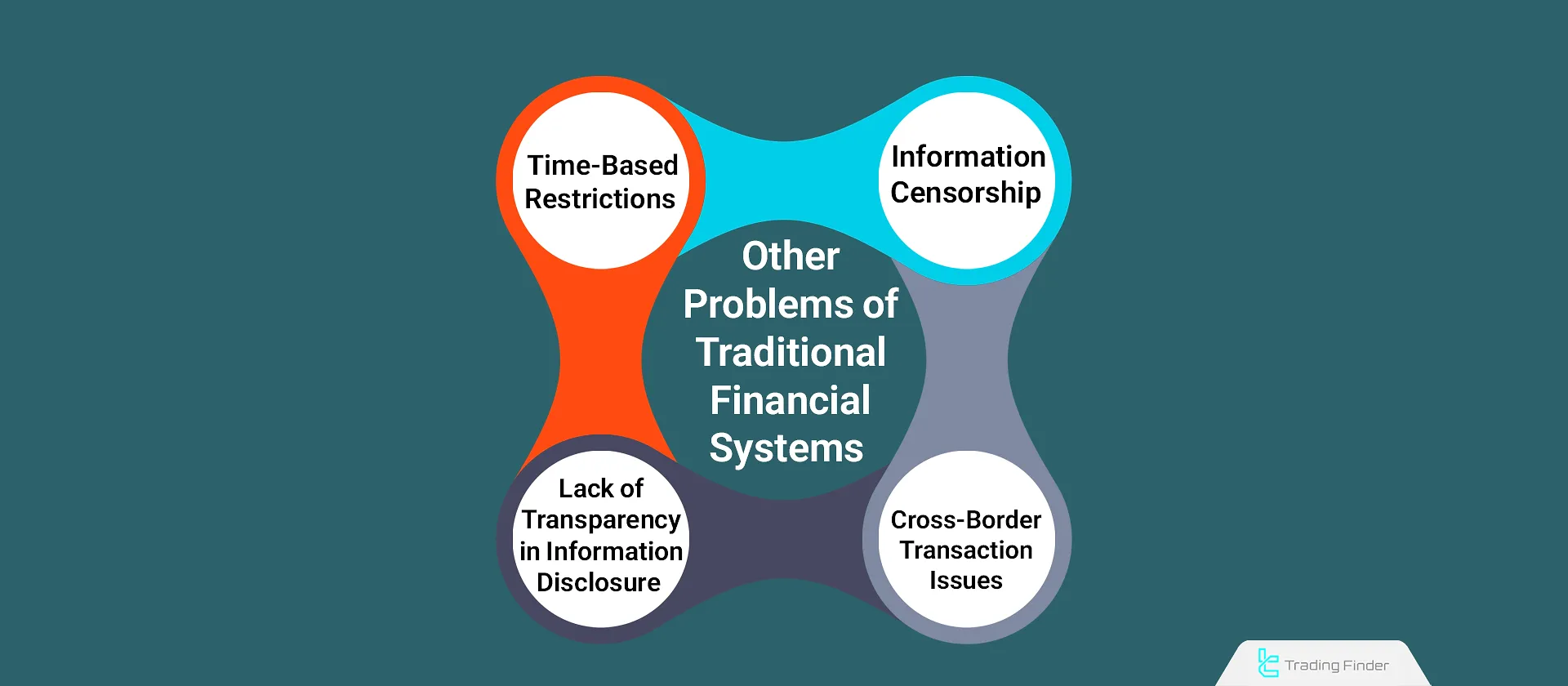
Issues in Traditional Financial Systems vs. Bitcoin's Solutions:
Problems of Traditional Financial Systems | Bitcoin’s Solutions |
Censorship and manipulation of information | Immunity to censorship due to data being stored on thousands of computers worldwide |
Time-based limitations in accessing financial services | 24/7 accessibility to Bitcoin services without any downtime |
High costs and legal hurdles for cross-border transactions | No concept of borders in Bitcoin’s system |
Lack of transparency in financial transactions | Full transparency and open access to review the history of all transactions |
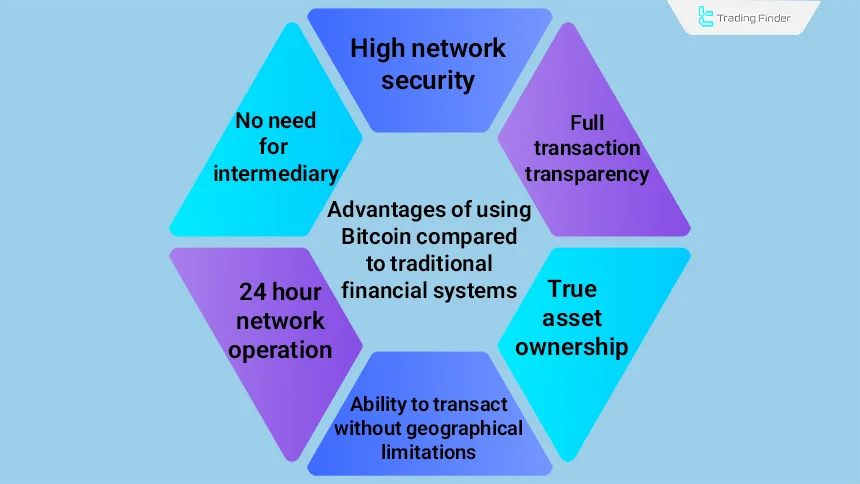
Advantages of Using Bitcoin Compared to Traditional Financial Systems
Using Bitcoin is not just a solution to the problems of financial systems; it also offers significant advantages that make the experience of using financial services simpler and faster for users. Some of the most important advantages include:
- No need for intermediaries: all transactions are conducted directly between users, with no need for banks, payment companies, or verification authorities;
- 24-hour network operation: unlike banks that are limited to business hours, the Bitcoin network operates continuously throughout the year;
- Ability to transact without geographical limitations: sending Bitcoin to any point in the world is exactly the same as a domestic transfer and is not dependent on country specific laws or banks;
- True ownership of assets: only the individual who holds the private key can execute transactions; therefore, there is no possibility of asset seizure or restriction;
- Full transaction transparency: all transactions are recorded on the blockchain, and reviewing transaction histories is possible for everyone;
- High network security: distributing data across thousands of nodes ensures that transaction censorship or manipulation is not possible.
The Problem of the Absence of a Global Payment System Before Bitcoin
Before the creation of Bitcoin, there was no unified system for sending money globally, and users were forced to navigate banking networks, country regulations, and varying fees.
Bitcoin created a global payment network in which asset transfers are not limited by country, bank, or geographical location. As a result, sending Bitcoin between individuals in two different countries is exactly the same as transferring it between two people in the same city.
The Problem of Heavy and Unpredictable Fees in the Banking System
Banking networks rely on multiple institutions and country regulations to transfer money; a factor that increases fees and prolongs transaction times.
In contrast, Bitcoin network fees are determined by network conditions and are not related to the user’s country, bank, or account type. As a result, executing large or small transactions anywhere in the world is possible with predictable and transparent costs.
Solving the Problem of True Ownership of Digital Assets
In traditional digital financial systems, control over assets lies with banks and intermediary companies, and users do not have true ownership of their money. These entities can freeze, restrict, or even seize assets.
Bitcoin solves this problem through the use of private keys; a tool that only the owner can use to transfer assets. This has made Bitcoin one of the few digital assets where full ownership is genuinely held by users.
In the article on the problems that Bitcoin solved on the Kraken website, these issues are explained in full.
Security Limitations of Banking Systems and the Role of Bitcoin in Addressing them
Centralized banking systems, due to storing all information in a single location, are constantly exposed to cyberattacks, breaches, and sabotage. In such a structure, a single security failure can affect the data of millions of users.
Bitcoin, by using a vast network of nodes, has made centralized attacks almost impossible. Distributing data across thousands of computers has increased the security of transactions and assets and minimized the risk of intrusion or manipulation.
The Problem of Financial Service Downtime During Holidays and Bank Closures
In traditional financial systems, bank working hours are limited, and conducting transactions on holidays or weekends is not possible.
Unlike this structure, the Bitcoin network operates continuously throughout the year, allowing users to perform transactions at any hour of the day. This feature has made Bitcoin highly efficient in emergency situations or urgent transfers.
The Problem of Unstable Financial Regulations and their Impact on User Assets
In some countries, financial regulations change suddenly, and user assets may be frozen or bank accounts seized. With its decentralized structure, Bitcoin removes user assets from the direct control of governments and eliminates the possibility of unilateral seizure or freezing.
Bitcoin ownership is tied solely to the private key, and as long as this key remains in the user’s possession, the asset remains fully secure and accessible.
How Does Bitcoin Prevent Inflation?
Governments in different economic situations, like recessions, often resort to printing more money to boost the economy. However, this causes the value of money to decline, disrupts the balance between supply and demand, reduces purchasing power, and leads to inflation.
In contrast to fiat currencies that can be issued infinitely, Bitcoin has a fixed supply cap. The total supply is limited to 21 million units, and no authority, organization, or individual can increase this number beyond this limit. This feature turns Bitcoin into a deflationary asset.
In the Blockchain360 YouTube channel, the anti inflationary nature of Bitcoin is explained in video format:
Bitcoin and Solving the Problem of Supply Opacity in Fiat Currencies
In fiat currencies, people have no information about the real amount of money printing or future supply plans.
Decisions regarding increasing or decreasing the money supply are solely in the hands of the central bank. Bitcoin, by defining a fixed algorithm for block production and periodic reductions in mining rewards, has made its supply process completely transparent.
Everyone knows how much Bitcoin currently exists and how much will be produced in the future.
How Did Bitcoin Solve the Transparency Problem in Financial Networks?
In the Bitcoin network, all transactions are publicly visible, and anyone can review the history of asset transfers.
This feature, unlike traditional systems where financial information remains under the control of banks, has created a fully transparent and traceable system. This transparency not only prevents corruption but also reduces the risk of misuse of users’ financial data.
In the article explaining the role of transparency in the growth and trust building of financial services, it is examined in detail how transparency in fees, processing time, and payment tracking can affect user trust and retention.
Bitcoin and Solving Access Limitations in Developing Countries
In many countries, people are unable to use financial services due to the lack of banking infrastructure, government restrictions, or high account opening costs.
Bitcoin offers a simple and low-cost option for these individuals; all that is required is a smart device and an internet connection. With this structure, Bitcoin has become an important financial tool for millions of people in economically restricted countries.
How Did Bitcoin Solve the Problem of Complex Identity Verification in Banks?
In many banks, customers are required to go through complex identity verification processes to open accounts or perform various transactions.
This process is not only time consuming but may also be impossible for individuals without official documents. Bitcoin allows all users to create wallets and transfer assets without providing identity documents.
As a result, more people can access financial services without limitations.
Smart Money Digital Currency Divergence Indicator
The SMT Divergence indicator is designed based on Smart Money concepts to simultaneously analyze the behavior of correlated assets and identify moments when liquidity flow hides the true market direction from traders.
By analyzing three related assets such as BTC, ETH, and BCH, this tool reveals divergences that often precede trend weakening, corrections, or price reversals.
The signaling basis of this tool forms when one chart records a different direction compared to the other two symbols. This behavioral inconsistency usually indicates smart money inflows or outflows and shifts in power between buyers and sellers.
In an uptrend, when Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash form lower lows while Ethereum creates a higher high upon reacting to the indicator’s sensitive zone, a clear divergence appears among the three assets. Such a pattern usually signals a reduction in bearish momentum and the potential start of an upward move.
In a downtrend, when BTC and BCH show weak bullish reactions after hitting the marked level but ETH behaves inconsistently, the indicator warns of a possible weakening of the bullish trend and a transition of prices into a bearish phase.
The settings section of this tool includes options for selecting the three main analysis symbols, defining the distance between swing points, adjusting the High Low Divergence filter, and identifying the Pushed Symbol; a set of controls that makes it highly practical and precise for multi symbol analysts and correlation based strategies.
Overall, SMT Divergence, by examining coordination among BTC, ETH, and BCH, can reveal early signals of trend weakness, potential reversals, or short term corrections and help traders better understand the hidden forces behind market movements.
- Smart Money digital currency divergence MT4 indicator
- Smart Money digital currency divergence MT5 indicator
Conclusion
Traditional financial systems address the double-spending issue of digital assets by storing all transaction data in a centralized ledger and using it to validate and complete transactions. This centralized setup enabled system owners to manipulate, censor, or exploit data, demonstrating the inherent centralization in such systems.
Bitcoin, by introducing the concept of a Distributed Ledger, provided a decentralized solution to the double-spending problem. All transaction data is stored in the distributed ledger and replicated across millions of computers worldwide, making it resistant to censorship, manipulation, or misuse.













