After the 2008 financial crisis and the emergence of weaknesses in traditional and centralized financial systems, a concept called Bitcoin was introduced to the world through a 9-page whitepaper titled "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System," written by an anonymous individual under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto.

This whitepaper discusses the problems of centralized financial systems and outlines Bitcoin's solution to address them.
Bitcoin provides a platform where all financial transactions are conducted peer-to-peer, fully decentralized, and without intermediary intervention.
What Is Bitcoin and How Does It Work?
Bitcoin is a blockchain created by an anonymous individual named Satoshi Nakamoto. The Bitcoin blockchain is a Distributed Ledger, meaning that all members (nodes) have access to the recorded data on the blockchain and are connected through cryptographic techniques.
The native currency of this blockchain, named after the blockchain itself (Bitcoin), is traded in the cryptocurrency market under the ticker symbol BTC. All Bitcoin transactions are conducted on the blockchain in a completely decentralized and peer-to-peer manner. As a result, there is no centralized authority managing these transactions.
What Is the Bitcoin Whitepaper?
This whitepaper was published in 9 pages under the title "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System."
In the introduction of the whitepaper, Satoshi Nakamoto refers to the weaknesses of traditional financial systems such as intermediaries, high costs, and more.
In the following sections, the Bitcoin whitepaper explains how this financial system operates, including transaction mechanisms, the Proof of Work consensus algorithm, and concludes with a computational example that demonstrates Bitcoin’s security.

What Is Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC)?
Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC) is a version of Bitcoin that operates on the Ethereum blockchain (ERC-20) and was created by the Ethereum team to facilitate decentralized services.
Essentially, Wrapped Bitcoin is the same Bitcoin running on the Ethereum blockchain, but using smart contracts, it offers more functionality than the original Bitcoin blockchain.
What Is the Bitcoin Blockchain?
The Bitcoin blockchain is a data and information registry. On this blockchain, a vast network of computers and servers around the world—interconnected globally—records and stores Bitcoin transaction data.
Anyone, anywhere in the world, can become part of this network by installing the Bitcoin software on their personal computer. As a result, each transaction is stored across all these devices, making it virtually impossible to alter or delete transactions.
Block Hash in the Bitcoin Network
In a blockchain, blocks are linked together like a chain. Therefore, to identify and review each block, it must contain unique information. This information is known as the block hash.
Why Is the Block Hash Important?
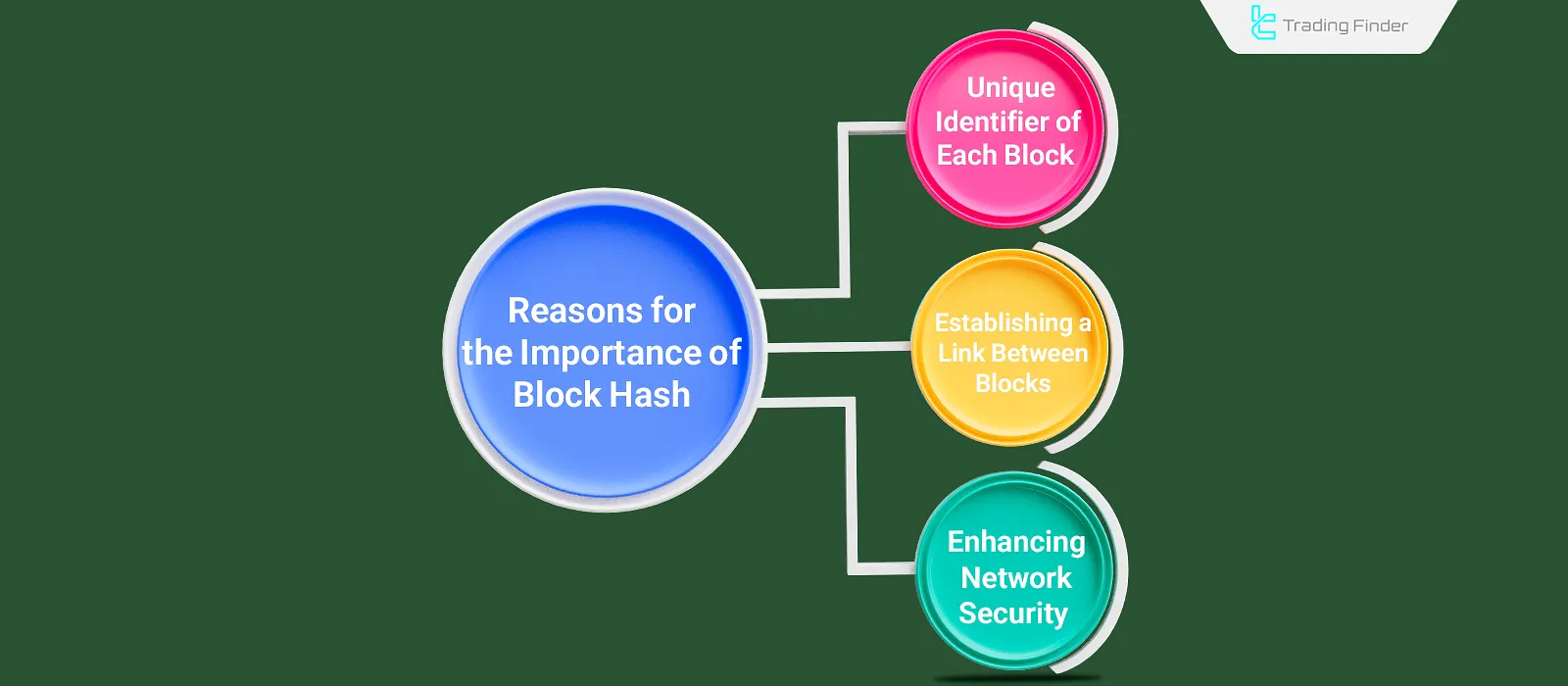
The block hash is highly significant due to its role in creating a unique identifier for each block, linking blocks, ensuring network security, and more.
Key Roles of the Block Hash:
- Unique Identifier for Each Block: The hash creates a unique ID through mathematical functions, allowing each block to be independently identified and reviewed on the blockchain;
- Linking Blocks: The hash of each block is stored in the next block, thus forming the blockchain structure;
- Network Security: Any change in the contents of a block alters its hash, enabling the network to detect unauthorized modifications.
How Is a Block Hash Generated?
To generate a block hash, all data from the previous block—such as the previous hash, timestamp, block number, etc.—is included in the new block. This data is then processed by miners, and the output is a 256-bit value known as the block hash.
What Is a Network Node in the Bitcoin Blockchain?
A network node (Node) refers to the various computers and servers connected to the Bitcoin blockchain. Each one plays a role in maintaining the blockchain’s security by serving as a communication point.
In the context of Bitcoin’s Distributed Ledger, data and records are stored across all blockchain nodes, eliminating any chance of tampering. Thus, nodes are fundamental to the security of the blockchain.
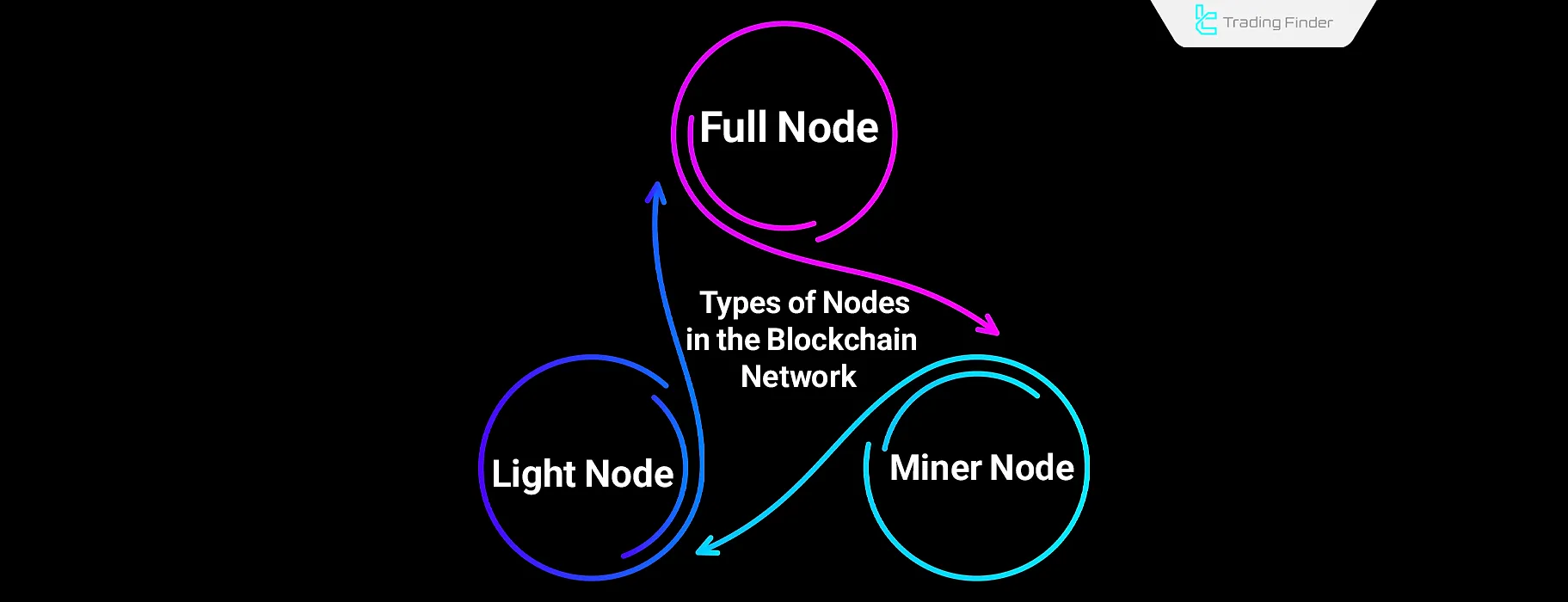
Types of Nodes in the Bitcoin Blockchain
Nodes in the Bitcoin (BTC) network are generally divided into three categories:
- Full Node: This type of Bitcoin blockchain node downloads and stores all the network’s data and history, and is categorized into two types of Archival Node and Pruned Node;
- Light Node: These nodes only download the block headers and rely on full nodes for complete information;
- Miner Node: Miner nodes are responsible for validating transactions and mining Bitcoin by solving complex mathematical problems.
Difference Between a Node and a Miner in the Bitcoin Blockchain
In general, a Miner is considered a type of node. However, there are key differences in their roles and functions in the Bitcoin blockchain.
Parameters | Node | Miner |
Main Role | Stores and maintains information in the blocks | Processes and mines new blocks |
Hardware Requirements | No need for high-end hardware | Requires powerful hardware |
Reward System | Usually not rewarded | Earns rewards for mining new blocks |
Bitcoin Network Security
The Bitcoin blockchain is built upon mathematical formulas and computations. To this day, it has not experienced any successful hacks or security breaches. This level of security is based on the Proof of Work consensus mechanism and a decentralized architecture.
Proof of Work (PoW) Consensus Mechanism
The Proof of Work (PoW) is a decentralized method for validating transactions and mining new blocks. In this system, miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles to create a new block.
The first miner to successfully solve the puzzle:
- Adds the block to the blockchain
- Receives the block reward and transaction fees inside the new block
How Does PoW Ensure Bitcoin’s Security?
Through this mechanism, all Bitcoin (BTC) transactions are validated without intermediaries, in a fully decentralized manner. All verifications are conducted by the participants of the network.
To attack the Bitcoin network, a hacker would need more than 51% of the total mining power. Given the vast scale and global distribution of miners, such an attack is virtually impossible.
Moreover, since miners take approximately 10 minutes to validate and add a new block, an attacker would have only that limited time before the next block is generated—further reducing the chance of successful intrusion.
What Is the Lightning Network?
The Lightning Network is a scalability solution for Bitcoin. It introduces a second layer on top of the Bitcoin blockchain to manage small transactions.
Only the final result of these microtransactions is recorded on the main blockchain, which greatly increases transaction speed.
- Lower transaction fees
- Faster confirmations
- Off-chain processing (outside the main blockchain)
These are some of the key advantages of the Lightning Network.
What Is Bitcoin Halving?
Bitcoin halving is a method for controlling the supply of Bitcoin and preventing inflation caused by excessive issuance. Approximately every four years, and after the creation of 210,000 blocks, the block reward and Bitcoin production rate are reduced by 50%.
The first halving occurred in 2012, reducing the block reward from 50 BTC to 25 BTC. Following the most recent halving in 2024, the reward for each new block was reduced to 3.125 BTC.

How Does Halving Affect the Price of Bitcoin?
Generally, a reduction in the supply of an asset leads to an increase in its value, provided that demand also increases.
During previoushalving events, the price of Bitcoin (BTC) experienced notable growth, indicating a rise in demand following each halving.
History of Bitcoin
Bitcoin was not the first attempt to apply blockchain technology or to create a decentralized monetary system. Earlier projects such as Bit Gold and Flooz had similar ambitions. Studying these projects helps us better understand the position and innovations brought by Bitcoin.
Additionally, analyzing the activities of Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin's anonymous creator, reveals deeper insights into the concept and design of this digital currency.
Failed Projects Before Bitcoin
The history of Bitcoin predates its whitepaper, which was published in 2008. Bitcoin is the result of various achievements in the cryptographic field, aimed at countering the monopoly of governments over financial systems.
Before Bitcoin, there were multiple unsuccessful attempts to create the first cryptocurrency, including DigiCash, Bit Gold, and Flooz—all of which ultimately failed.

- DigiCash: Launched in 1983, DigiCash aimed to create a digital money system. Despite its innovative approach, it faced challenges such as lack of mainstream adoption, leading to its bankruptcy in 1998;
- Bit Gold: Proposed in 1998 by Nick Szabo, Bit Gold is often considered a direct precursor to Bitcoin. While the project was never implemented, it had a significant influence on Bitcoin’s design;
- Flooz: Flooz was a payment system for online shopping launched in the late 1990s. Users could purchase credits with traditional currency and spend them in online stores. However, due to lack of merchant adoption, the project was shut down in 2001.
Who is Satoshi Nakamoto?
Satoshi Nakamoto is the pseudonym of the individual or group who published the Bitcoin (BTC) whitepaper in 2008. As such, Satoshi Nakamoto is credited with solving the fundamental issue of double spending in a decentralized manner.
This pseudonymous entity was active in the field of blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies until 2011 and could be contacted via email. However, more than 15 years after the launch of Bitcoin, their true identity remains unknown.
Satoshi Nakamoto ultimately disappeared in 2011 after sending an email to another cryptocurrency developer that read: “I’ve moved on to other things.” Since then, there has been no trace of them.
It is estimated that Satoshi Nakamoto owns approximately 1 million Bitcoins, and the potential sale of this amount would deal a significant blow to the entire cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Bitcoin’s Connection to the 2008 Financial Crisis
In 2008, the financial crisis in the United States and Europe led to major disruptions such as the bankruptcy of large banks like Lehman Brothers, over 8 million people losing their jobs, and the closure of more than 2.5 million businesses. These events exposed critical flaws in the centralized financial system.
Therefore, in 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto proposed the Bitcoin whitepaper as a solution to prevent such crises from reoccurring—offering a fully decentralized approach to conducting financial operations.
Bitcoin Pizza Day
On May 22, 2010, a Florida-based programmer named Laszlo Hanyecz posted an offer on the BitcoinTalk forum, stating that he was willing to pay 10,000 Bitcoins in exchange for two large pizzas; A British man accepted the offer.
At that time, the value of the Bitcoins used in the transaction was around $41, but due to the exponential price growth of Bitcoin, the current value of those Bitcoins is now over $1 billion.
This date is annually celebrated by the crypto community as the anniversary of the first real-world transaction using Bitcoin.
How Is Bitcoin Mined?
Bitcoin is a decentralized network that is not controlled by any individual or centralized entity. Therefore, the verification and execution of transactions on this network are carried out by machines called miners.
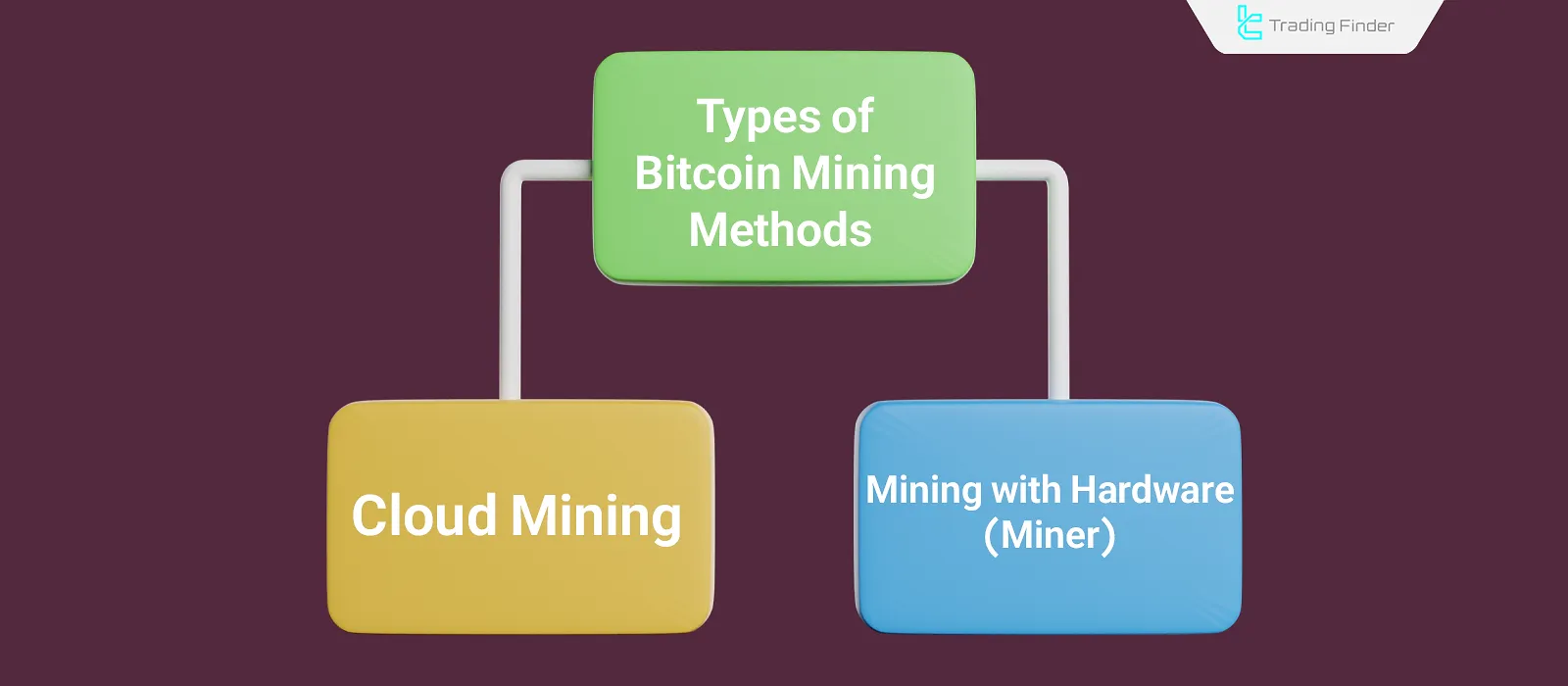
Types of Mining Methods
Bitcoin is generated through a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus algorithm. In this method, the blockchain issues a certain amount of Bitcoin as a reward for the creation and confirmation of a block. The miner who successfully creates and verifies a new block receives this reward.
Mining with Devices (Miners)
In the Bitcoin system, each block contains a unique hash. Miners use their computational power to search for the correct hash that confirms the block.
The miner who first finds the correct hash gets to confirm the block and receives the blockchain reward. Additionally, the transaction fees from the confirmed block also go to the miner who validates it.
BTC Cloud Mining
In general, there is only one true method of mining Bitcoin, and that is using miners to participate in the Proof-of-Work algorithm. However, certain platforms possess high computational power, giving them a greater chance of successfully confirming blocks.
These platforms have made their computational power available for rent to the public. This means that individuals, without needing to purchase mining equipment, can earn income from Bitcoin mining by paying a fee to rent the computing resources of these platforms.
How to Buy and Store Bitcoin?
In the early days of Bitcoin, before the emergence of cryptocurrency exchanges, Bitcoin transactions were conducted entirely on a peer-to-peer basis. Individuals would post their buy or sell requests, along with their proposed prices, in Bitcoin online forums.
In 2010, MT.Gox became the first cryptocurrency exchange, enabling the buying and selling of Bitcoin in exchange for fiat currencies.
Top Exchanges for Buying Bitcoin
Over time, with the advancement of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, numerous crypto exchanges emerged worldwide. These platforms not only facilitate the buying and selling of cryptocurrencies but also offer a range of additional services. Below is a list of the top cryptocurrency Centralize exchanges in 2025:
Bitcoin Wallet
The system used to store Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies is called a wallet. Given the significance of Bitcoin in the crypto market, most wallets support the storage of Bitcoin.
Due to the decentralized nature of Bitcoin, the full responsibility of safeguarding the assets lies with the owner.
Types of Bitcoin Wallets
Bitcoin wallets are generally categorized into two types: hardware wallets and software wallets. These two types differ in terms of security, ease of use, and other features.
Types of Bitcoin Wallets:
- Software Wallet: A software or hot wallet is an online application or platform used to store Bitcoin, where the private keys are kept online;
- Hardware Wallet: A hardware or cold wallet is a physical device for storing Bitcoin, where the private keys are stored offline.
What Are the Key Features of Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is considered an effective solution to the challenges of traditional financial systems due to its features such as decentralization, limited supply, and high security.

Decentralization
Traditional financial systems store all data in a central ledger—completely centralized and lacking transparency. In contrast, Bitcoin stores all information on the blockchain in a fully decentralized manner across all connected nodes, eliminating intermediaries in financial operations.
Limited Supply
The supply of Bitcoin is inherently limited. Ultimately, there will only ever be 21 million Bitcoins, and no further production or mining of this asset will be possible. As a result, Bitcoin serves as a deflationary store of value, since rising demand does not lead to an increase in supply.
Transparency
All data and transactions on theBitcoin blockchain are publicly accessible. Therefore, anyone with a personal computer and an internet connection can inspect the contents of various blocks. This characteristic makes Bitcoin highly transparent.
High Security
The computational power required to hack or tamper with the Bitcoin blockchain is extremely high, making such actions virtually impossible. Additionally, the fast block generation time of Bitcoin further prevents any form of intrusion or manipulation.
No Need for Identity Verification
Using the Bitcoin blockchain does not require users to submit any personal identification. However, purchasing or selling Bitcoin through centralized exchanges may involve KYC procedures.
These identity verification steps are not related to Bitcoin itself but are enforced according to each exchange’s internal policies. Therefore, the only data recorded on the Bitcoin blockchain is the wallet address where the Bitcoin is stored.
Irreversibility of Transactions
Due to the immutable nature of the Bitcoin blockchain, once a transaction is made, it cannot be reversed or canceled. In other words, the full responsibility for transactions lies with the wallet owner, and in case of any error, there is no possibility to undo or cancel the transaction.
No Border Limitations
The use of Bitcoin is not restricted by geography. This means that Bitcoin is a global asset, not tied to any specific country or government, and is accessible for use by people worldwide.
Uses of Bitcoin
Thanks to its various features—such as limited supply, decentralization, and high security—Bitcoin has multiple applications in the world of finance. Below are three of the main financial use cases of Bitcoin.
Store of Value (Investment)
The supply of Bitcoin (Bitcoin) is limited to 21 million units under any circumstances. This means that when demand for Bitcoin increases, its supply remains unchanged, leading to an increase in the value and price of Bitcoin.
Currently, gold is considered the best store of value by the general public. However, a significant portion of gold reserves remains undiscovered, which means that in reality, its supply is not limited. Therefore, Bitcoin, with its limited supply, is regarded as a more suitable store of value compared to gold.
Online Payment Tool Without Using Identity Information
Bitcoin (Bitcoin), as a secure and peer-to-peer payment method, is used for purchasing goods and services online. Today, with the progress of Bitcoin and the increasing public trust in this asset, the number of stores and websites that support Bitcoin as a payment method is on the rise.
International Transfer
The lack of a defined concept of borders in the structure of Bitcoin makes this asset suitable for cross-border transfers. Bitcoin allows transfers to be made to any account at any time of day or night. This means that the fastest way to transfer assets internationally is by using the Bitcoin blockchain.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Bitcoin
The advantages of Bitcoin include security, transparency, deflationary nature, and more. On the other hand, there are factors that have created disadvantages for Bitcoin (Bitcoin). Among the most important of these are issues like scalability, price volatility, and technical complexity.
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Decentralization | Price volatility |
Deflationary property | Technical complexity |
Transparency | Irreversibility of transactions |
High transaction speed | Negative environmental impact from mining |
Cross-border transactions | Scalability |
High liquidity | Potential for illegal activities |
Full control over assets | Lack of full public acceptance |
What Is the Difference Between Fiat Currency and Bitcoin?
Bitcoin, in general, differs from fiat currencies in several aspects, including control and centralization, backing, supply, security, and more.
Feature | Bitcoin | Fiat Currencies |
Control | Completely decentralized | Controlled by banks and governments |
Backing | Limited supply and demand | Mostly backed by gold, silver, or government trust |
Volatility | High volatility due to the liquidity of the crypto market | Lower volatility compared to crypto markets |
Transparency | High transparency and access to transaction data anytime | Controlled by banks and governmental regulatories |
Geographic restriction | No geographic restriction | Limited to the country’s territory |
Supply | Limited to 21 million units | Controlled by central banks and governments |
What Is the Difference Between Bitcoin and Other Cryptocurrencies?
Bitcoin (Bitcoin), as the first cryptocurrency in the world, has fewer technological capabilities compared to newer blockchain projects. Therefore, it is not possible to implement new and diverse features—resulting from advancements in blockchain technology—such as decentralized applications, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), etc., on the Bitcoin blockchain.
What Is the Difference Between Ethereum and Bitcoin?
A few years after the creation of Bitcoin, Vitalik Buterin, Charles Hoskinson, and Gavin Wood examined the limitations of the Bitcoin blockchain and, in an effort to enhance the functionality of cryptocurrencies, introduced Ethereum and the concept of smart contracts.
Bitcoin and Ethereum differ significantly in terms of use cases. Specifically, Bitcoin is primarily considered a deflationary asset and store of value, while Ethereum is seen as a platform for accessing a wide range of decentralized services.
Feature | Bitcoin | Ethereum |
Mining Algorithm | Proof of Work (PoW) | Proof of Stake (PoS) |
Supply | Limited | Unlimited |
Scalability | 7 transactions per second | 30 transactions per second |
Upgradability | Not supported | Supported |
Application | Store of value | Use of diverse decentralized services |
What Is the Difference Between Stablecoins and Bitcoin?
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies pegged to a fiat currency such as the US dollar, and their value is not influenced by crypto market volatility. Therefore, these currencies are mostly used as intermediaries in cryptocurrency transactions.
In general, stablecoins differ from Bitcoin (Bitcoin) in almost every aspect, such as liquidity, price volatility, primary purpose, backing, and more.
Feature | Bitcoin | Stablecoins |
Transaction Speed | Relatively low | High |
Backing | Limited supply and market demand | Typically backed by a reputable company or fiat currency |
Price Stability | Affected by crypto market volatility | Unaffected by crypto market volatility |
Purpose | Addressing issues in traditional financial systems | Facilitating crypto transactions as a medium of exchange |
What is the Future Outlook for Bitcoin?
For Bitcoin to achieve mass adoption and reach its full potential, it must overcome various challenges such as the role of governments and financial institutions, regulatory impacts, investment by influential companies, and more.
What Are the Impacts of Regulation, Governments, and Financial Institutions on the Future of Bitcoin?
Governments and financial institutions have a major influence on shaping the future of Bitcoin. Therefore, analyzing aspects such as tax regulations, restrictions, and the legal status of Bitcoin in countries that significantly impact the global economy can provide a clearer picture of Bitcoin’s future trajectory.
Bitcoin ETF Funds
From the inception of Bitcoin (Bitcoin), numerous requests have been submitted to create Bitcoin ETF funds, but for various reasons, these requests were not approved at the time.
Over time, Bitcoin ETFs have been approved and launched in various countries. However, the most notable event was the approval of a Bitcoin ETF in 2023 by the SEC in the United States, which was accompanied by a significant influx of capital into Bitcoin.
The creation of Bitcoin ETF funds has allowed Bitcoin shares to be traded on stock exchanges without the complexities of blockchain, thereby increasing public adoption and credibility of Bitcoin.
Bitcoin Dominance in the Cryptocurrency Market
Bitcoin dominance refers to the ratio of Bitcoin’s market value to the total value of the cryptocurrency market. The higher this ratio is, the more influence Bitcoin has on the overall market volatility.
Bitcoin generally holds a large share of the crypto market dominance, meaning that other cryptocurrencies tend to follow Bitcoin’s price movements.
For example, when the price of Bitcoin rises, other cryptocurrencies often experience price increases as well, depending on their respective conditions.
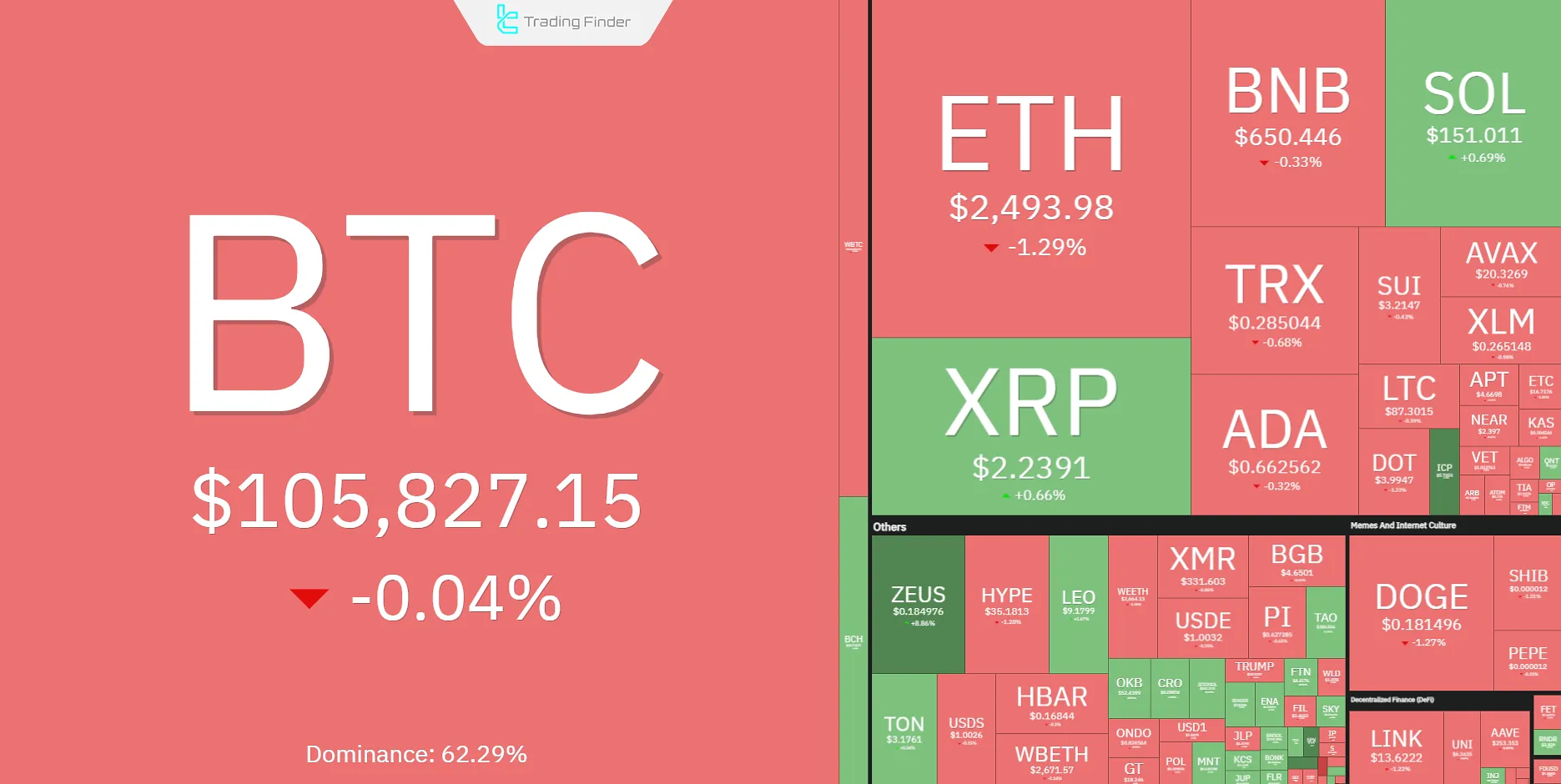
The Relationship Between Bitcoin Dominance and Tether
Theoretically, there is a logical relationship between Bitcoin dominance and Tether dominance, which is primarily dependent on traders' confidence in the crypto market.
- Bullish Market Scenario: As the market grows and trader confidence increases, they convert Tether into Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. This leads to an increase in Bitcoin dominance and a decrease in Tether dominance;
- Bearish Market Scenario: In a declining market, traders lose confidence and convert their Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies into Tether to hedge against further losses. This results in a decrease in Bitcoin dominance and an increase in Tether dominance.
How to Transfer and Move Bitcoin?
The ability to transfer and move Bitcoin (Bitcoin) is exclusive to the individual who has access to the private key of the wallet.
Although the method of creating and confirming a transaction may vary from one wallet to another, the overall process for transferring Bitcoin follows a standard set of steps.
Steps to transfer Bitcoin from one wallet to another:
- Obtain the destination wallet address;
- Create a transaction to transfer Bitcoin to the received address;
- Sign and confirm the transaction using the private key by the wallet owner;
- Broadcast the transaction to the blockchain and have it confirmed by miners.
Is Bitcoin a Good Investment?
Generally speaking, due to its limited supply and strong functionality, Bitcoin is considered a suitable store of value for investment. However, investing in Bitcoin carries risks such as lack of universal acceptance and scalability limitations. Therefore, proper capital management and a defined trading strategy are essential when investing in Bitcoin.
Given its relatively lower liquidity and shorter history compared to other markets like Forex, Bitcoin experiences higher levels of volatility. Taking this into account and allocating only a reasonable portion of total capital can significantly reduce the investment risks associated with Bitcoin.
How to Get Free Bitcoin?
Currently, there are several methods for earning free Bitcoin by completing various tasks. These include:
Faucet Websites
In the early days of Bitcoin, faucet websites offered free Bitcoin as a way to introduce this innovation to the public.
In financial markets, faucet refers to drip income, meaning that the income from such sources is extremely minimal.
The mechanism of faucet sites works in such a way that by performing simple tasks—such as clicking a button repeatedly every few seconds or watching an advertisement video—you can earn small amounts of Bitcoin.
However, with the significant rise in Bitcoin’s price in recent years, the amount of Bitcoin these websites offer has become extremely low. Moreover, minimum withdrawal limits have made these platforms essentially unprofitable.
Reliable Faucet Sites:
- FreeBitco.in
- Fire Faucet
- Cointiply
- FaucetPay
Rewards Offered by Different Platforms
Various platforms attract users by offering small amounts of free Bitcoin during promotional events and advertising campaigns.
The mechanism of such events and campaigns is quite straightforward; by completing simple tasks like identity verification on the website or inviting friends, you receive Bitcoin as a reward.
Blockchain Games That Offer Bitcoin Rewards
Several games have been developed on different blockchain networks that reward users with cryptocurrencies in exchange for playing and progressing through levels.
Since the Bitcoin blockchain does not support smart contracts or the deployment of blockchain-based games, the Bitcoin rewards in such games are actually paid in Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC).
List of the top blockchain games with Bitcoin rewards:
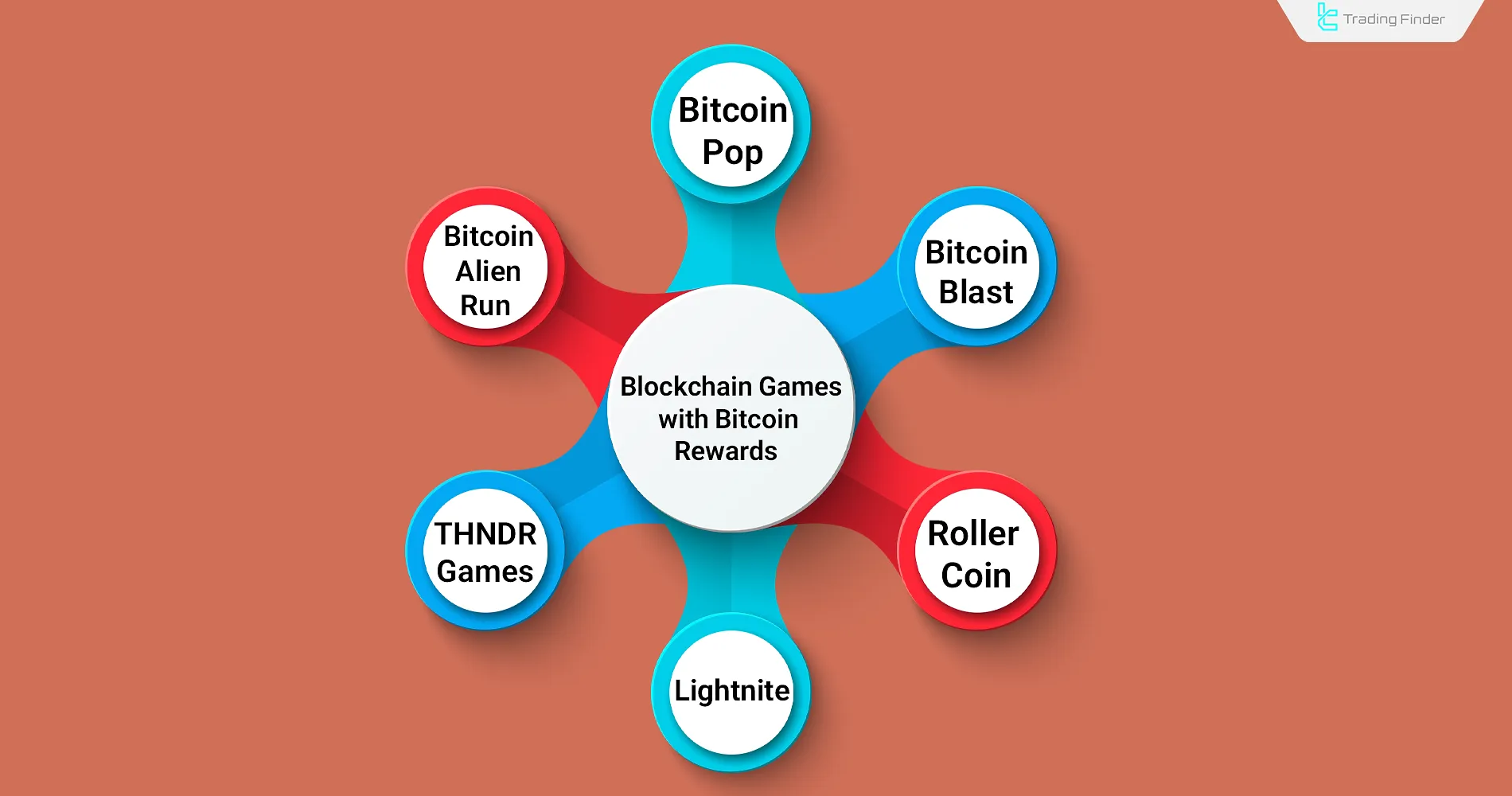
- Bitcoin Blast
- Bitcoin Pop
- Bitcoin Alien Run
- RollerCoin
- Lightnite
- THNDR Games
Conclusion
Bitcoin (BTC) is a solution to the double spending problem in a decentralized manner, introduced to the world in 2008 by a person under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. This project, utilizing the capabilities of blockchain technology, proposed a fully decentralized approach to financial operations, where transactions are conducted peer-to-peer, without intermediaries.
Bitcoin uses the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus algorithm for mining and maintaining the ecosystem. In this process, miners solve complex mathematical problems to validate and add a block to the blockchain.
Any miner who successfully mines a block receives the Bitcoin generated by the blockchain as a reward for verifying the transactions within that block.













