- TradingFinder
- Education
- Forex Education
- Brokers Education
Brokers Education
Choosing a broker directly impacts trade execution, transaction costs, and capital security. Brokers act as intermediaries between traders and financial markets, and their execution model affects order processing speed, spread and commission fees, and market liquidity access. Brokers operate under different execution models, including ECN (Electronic Communication Network), STP (Straight Through Processing), and Market Maker. Each of these models has a direct impact on spreads, commissions, and trade execution efficiency. On TradingFinder, traders can find detailed guides on evaluating brokers, comparing trading conditions, and avoiding risks such as spread manipulation, execution delays, and price slippage.
What Is an Islamic Forex Account? Swap-Free (Interest-Free) and Halal Trading in the Forex Market
In the Forex market, trades often remain open for more than one day and are therefore subject to overnight swaps. A swap...
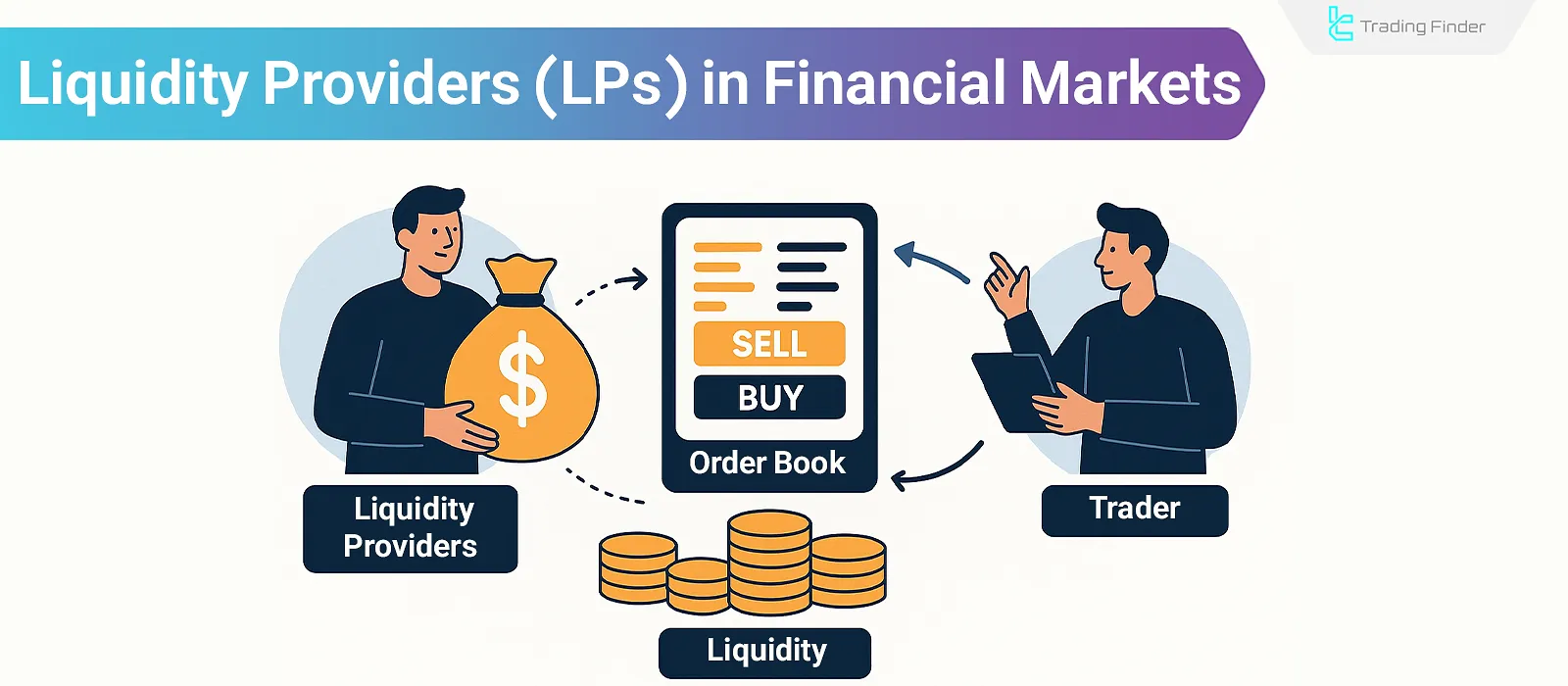
Liquidity Providers: How They Work and Why They Matter in Financial Markets
Liquidity Providers supply the required capital for trading in Forex, cryptocurrency, stock markets, and other markets. Liquidity...
STP Execution Model: Routing Trade Orders Directly to Liquidity Providers
In the Straight Through Processing (STP) model, the broker routes the client's order to a Liquidity Provider (LP) without internal...
Choosing a Forex Broker - Step-by-Step to Choose the Best Forex Broker
In financial markets such as Forex market, a broker acts as the intermediary between the trader and the market. To make the...