Expectations in financial markets are a key driver of price volatility before the actual data is released. In fact, traders buy or sell based on their market expectations and forecasts for future data, and this behavior often drives market fluctuations. Market expectations can stem from anticipated economic or political events, interest rate changes, or other influential factors in financial markets.
For this reason, the market’s reaction to an important piece of news sometimes forms before its official release and may even move in the opposite direction after the actual data is announced. Because prices have already reflected expectations in advance, the true measure of impact is considered to be the difference between market expectations and the final outcome.
Types of Expectations in Financial Markets and Differences in Their Impact
Expectations in financial markets are not considered a uniform and fixed concept and, depending on the time horizon and the type of information, take different forms.
Understanding the types of expectations enables traders to interpret market reactions more accurately and make more rational decisions. The table below provides a detailed review of the types of financial market expectations:
Expectation category | Type of expectations | Basis of formation | Method of impact on the market | Sample variables and events |
From the time-horizon perspective | Short-term expectations | Information and news close to the present time | Creating rapid volatility and increasing emotional behavior in prices | Monthly inflation rate, employment report, interest rate decisions, immediate economic data |
From the time-horizon perspective | Long-term expectations | Analysis of structural trends and macro policies | Influencing sustainable price trends and asset valuation | Future monetary policies, economic growth, demographic and technological trends |
From the formation perspective | Rational expectations | Logical analysis of available information and estimation of probable scenarios | Increasing market efficiency and rapid reflection of information in prices | Data-based forecasts, economic models, fundamental analysis |
From the formation perspective | Adaptive expectations | Reliance on past experiences and patterns | Delay in adapting to new conditions and the possibility of behavioral bias | Continuation of previous price trends, delayed reaction to policy changes |
Market Expectations vs. Actual Data
To identify market volatility after a data release, one must examine the forecasts' proximity to the actual figures. Economic reports are usually listed with three parameters:
- Previous
- Forecast
- Actual
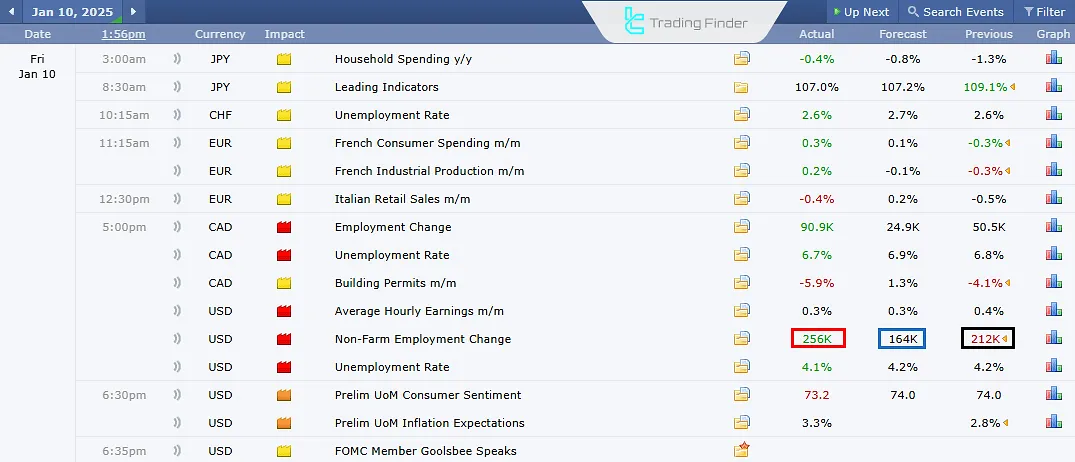
In this image, the previous (black), expectations (blue), and actual (red) values for the NFP (Non-Farm Payroll) data for December 2024 are shown. Here’s what each of these terms means:
- Previous: The previous report of the same data; used for comparison with the new release and sometimes revised upon the latest release;
- Forecast (Expectations): Analysts’ predictions. The market moves based on this estimate before the actual data is released;
- Actual: The official number reported by the respective institution.
How do Expectations Turn Into Price Movements?
The impact of expectations on price is a multi-stage process and does not occur suddenly. First, analysts, banks, and financial media present possible scenarios. With the repetition of these analyses, a dominant expectation, or market consensus, is formed.
In the next stage, traders adjust their positions based on this consensus before the event occurs. Finally, when the actual data is released, the market reacts not to the news itself but to the degree of difference between it and prior expectations.
This is why sometimes the release of positive data can lead to a price decline; because that news has already been priced into market expectations.
Example of Converting Expectations Into Price Movement
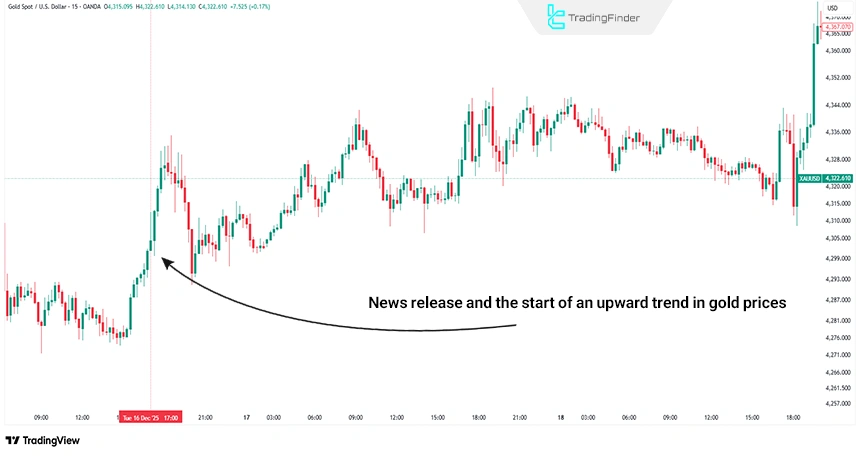
On December 16, 2025, before the release of US economic data, the market expected stronger data, which is usually negative for gold. This expectation had already been reflected in the price of gold.
However, the actual data was released weaker than expected and strengthened the probability of a more expansionary policy by the Federal Reserve. As a result, gold increased; because the market reacted not to the data itself but to its difference from prior expectations.
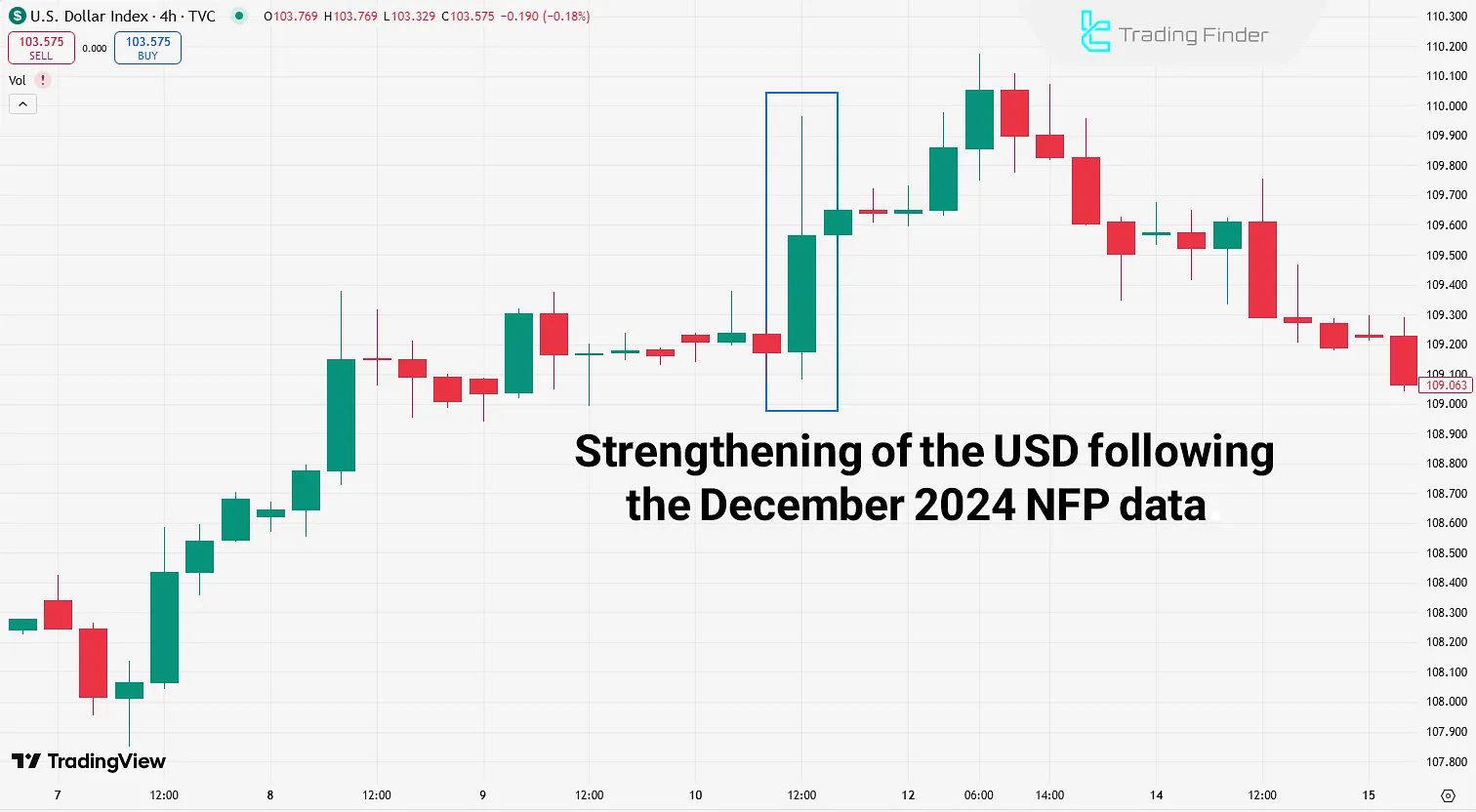
This reaction showed that the market did not react to the “inflation figure” itself, but rather to its difference from the formed expectations; even in the presence of data that was apparently considered negative.
In this NFP case, where the actual data came in much stronger than expectations, the market reacted with a strong rally in the dollar.
Why Are Expectations Important?
The market always moves based on expectations around data or a specific event. Therefore, understanding and predicting market expectations is highly important for trading. For example, consider the dollar strengthening ahead of the 2024 U.S. elections.
Before the election, the U.S. dollar strengthened due to Trump’s threats of increasing import tariffs, raising concerns about economic inflation and interest rate reduction disruptions-even though he had not yet taken office and no tariffs were actually imposed.
People anticipated that Trump’s future policies would lead to a stronger dollar. As a result, demand for the dollar increased before any policy implementation.
The Role of Trader Psychology in Shaping Market Expectations
Market expectations are not only the result of economic analysis but are also strongly influenced by the collective psychology of traders. Herd behavior causes many market participants to follow prevailing expectations even if their personal analysis is different.
In addition, confirmation bias leads traders to seek information that supports their existing views. These factors can cause the market to overreact or underreact to news and play an important role in price volatility.
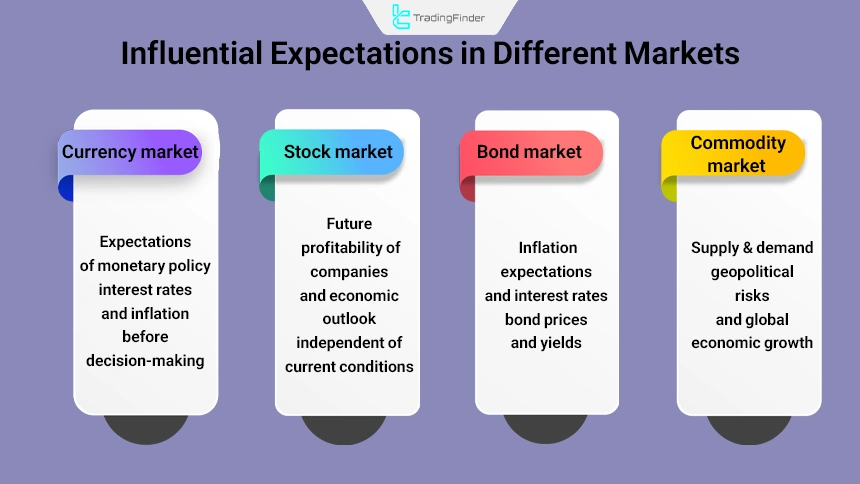
Expectations in Different Assets and Markets
Expectations play a key role in financial markets, but their mode of impact varies depending on the type of asset. Influential expectations in different markets:
- Currency market: Expectations related to monetary policy, interest rates, and inflation are decisive and can strengthen or weaken a currency even before decisions are implemented;
- Stock market: The main focus is on companies’ future profitability and economic outlook; therefore, price reactions are not necessarily aligned with current conditions;
- Bond market: Expectations of interest rates and inflation directly affect bond prices and their yields;
- Commodity market: Expectations of supply and demand, geopolitical risks, and global economic growth are the main drivers of price fluctuations.
What Does “Priced In” Mean in Financial Markets?
“Priced in” or “price being priced in” refers to the impact of expectations on price. For example, suppose economic data indicates that the Federal Reserve (the U.S. central bank) is likely to cut interest rates at its next meeting.
In this scenario, despite the rate cut not having occurred yet, market expectations for the change cause the U.S. dollar to weaken in the forex market. In fact, traders begin selling the dollar in advance. In this case, it’s said that “the interest rate cut is priced in.”
Since markets are always anticipating future data, one can say that the market is constantly pricing in expectations of future data.
The educational article on price anticipation on the dreamwork.financial website provides additional explanations about price pricing, and interested readers can refer to it for more information.
Data Revisions
Just as newly released actual data is important, revisions of previous data (upward or downward) can also cause market volatility depending on how much they differ from the prior reports.
For instance, imagine it’s June, and Switzerland’s inflation trend is negative. The central bank's dovish stance, aiming to boost demand and restore inflation, weakens the Swiss franc.
However, if the inflation figure for the previous month (May) is revised upward from -0.2% to -0.1% alongside the June data release, the franc might temporarily strengthen-even though inflation remains negative and the dovish stance remains.
That’s because the inflation was less negative than market expectations.
Expectations Regarding Interest Rate Changes
Expectations in financial markets are not limited to economic data-they include political-economic events such as speeches by key government officials, geopolitical tensions, and central bank interest rate meetings.
Ahead of interest rate decisions, traders use available information to predict the outcome (increase, decrease, or no change). These predictions are what we call market expectations.
Economic data often shape these expectations. For example, if data show disinflation or a sharp decline ingrowth at the end of a tightening cycle, expectations for rate cuts increase-usually weakening the currency. The reverse also holds true.
Where to Track Market Expectations for Federal Reserve Rate Changes?
The CME FedWatch Tool is a reliable source for tracking expectations of interest rate changes by the Federal Reserve. This tool uses futures market interest rate data to display the probability of different scenarios of rate hikes, cuts, or pauses.
It guides traders to gain a clearer view of market expectations ahead of Federal Reserve meetings and to align their decisions with the prevailing outlook. For this reason, the CME FedWatch Tool is widely used in the fundamental analysis of financial markets.
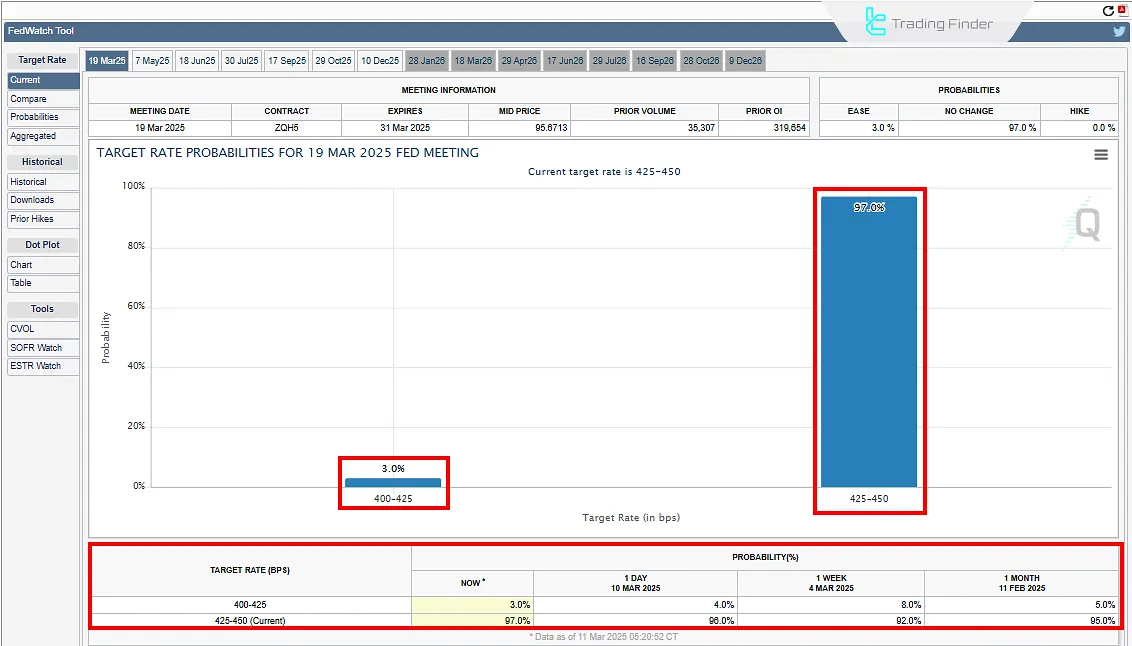
This image presents the market expectations from the CME FedWatch Tool. According to the snapshot, 97% of market participants expect the rate to remain unchanged at the next meeting, while only 3% expect a cut. Below the chart, changes in expectations over the past day, week, and month can also be observed.
The educational video from the UnfilteredForexx YouTube channel provides more comprehensive information on how to use and interpret the components of the CME FedWatch Tool, and interested users can watch it to learn more.
How Can Market Expectations be Identified and Monitored?
To analyze market expectations, a trader should not rely on only one source. Combining several tools and signals can provide a more accurate picture of market sentiment. One of the most important sources is economic calendars, which display forecast values.
These figures represent the consensus of market expectations.
Statements by central bank officials, analytical reports from banks, and changes in bond yields also provide valuable information about future market expectations.
In addition, examining price reactions before news releases can show to what extent the market has already priced in a given scenario.
Common Mistakes Traders Make in Interpreting Market Expectations
One of the common analytical errors among traders is a simplistic interpretation of economic data, assuming that the release of any positive data will necessarily lead to an increase in an asset’s price.
In practice, however, the market reacts not to the data itself, but to the degree of deviation from prior expectations and forecasts. In addition, other common mistakes include:
- Ignoring market positioning before the news release: A significant part of the news impact is already reflected in price;
- Focusing only on the actual figure: Neglecting market consensus, analysts’ expectations, and pre-priced scenarios;
- Emotional entry after the initial price move: Increasing risk, slippage, and entries at unfavorable levels.

Forex Factory Economic Calendar Indicator in MetaTrader
The Forex Factory Economic Calendar indicator is one of the most practical news tools for traders in financial markets, enabling them to monitor macroeconomic data directly within the MetaTrader environment.
By focusing on influential events such as GDP growth rates, unemployment statistics, changes in central bank monetary policies, inflation indicators, and other fundamental reports, this indicator helps traders align their decisions with real global economic conditions.
From an analytical structure perspective, the Forex Factory Economic Calendar belongs to the category of news indicators and trading tools in MetaTrader and is designed for traders with an intermediate skill level.
This tool supports multi-timeframe analysis and is most commonly used in intraday trading (Day Trading), range-based volatility strategies, and breakout trades. Its target market is directly the Forex market and assets that are sensitive to economic news.
In bullish scenarios, positive news acts as a driver of price movement; for example, in XAU/USD, strong US data can cause gold to rise and become volatile, while weaker data creates selling pressure.
In bearish conditions, news also plays a decisive role. In the EUR/AUD pair, the release of an important economic report related to the euro can cause sharp short-term volatility, whether the result is above or below forecasts.
This rapid market reaction further highlights the importance of risk management during news releases. In terms of settings, the Forex Factory Economic Calendar indicator offers high flexibility for customization.
The user can set the importance level of news (High, Medium, Low), event colors, panel display or hide options, currency filters such as USD, EUR, GBP, JPY, and AUD, as well as the alert system including pop-up alerts, sound alerts, or email notifications according to their strategy.
It is even possible to define the time for removing events after their release.
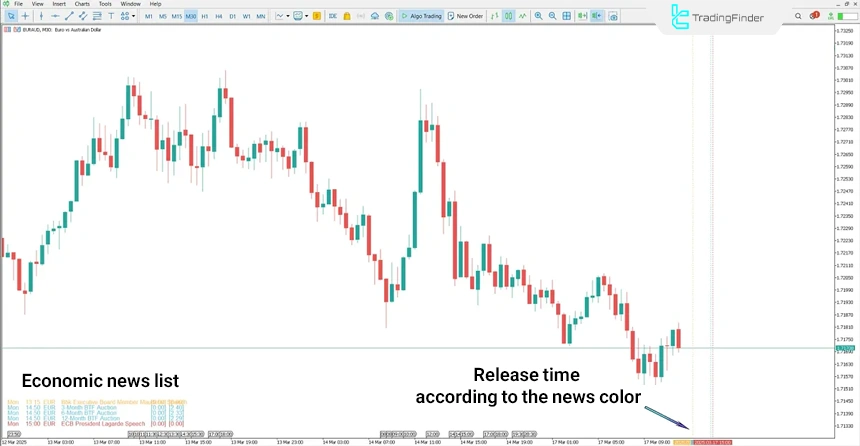
The Forex Factory Economic Calendar indicator allows fully customized settings for news importance levels, currency filters, event display, and alert types, and even the time for removing events after release can be adjusted.
Overall, it is a powerful tool for displaying economic events as vertical lines on the MetaTrader chart, which, through precise filtering and automatic removal of events after release, provides traders with a clear view of the impact of news on the market.
Conclusion
Expectations of future data often drive price fluctuations in financial markets. Traders act based on their market expectations and forecasts.
Upcoming data and events are continuously priced into the market; hence, traders should always pay attention to the impact of expectations on price.













