The stock market and Forex market differ in terms of nature, trading hours, leverage, fees, and fundamental analysis methods. Traders in the Forex market examine all factors affecting the global economy and currency prices.
In contrast, stock traders not only consider macroeconomic factors )such as production, economic growth, and the labor market(, but also develop expertise in analyzing financial statements and assessing the intrinsic value of equities.

What is the Forex Market?
Forex refers to the global market for trading currency pairs. For example, the US Dollar against the Euro is displayed in Forex as "EUR/USD," buying it means buying the Euro against the Dollar.
In Forex, traders speculate under CFD (Contract for Difference) agreements without owning the underlying asset. Therefore, trading EUR/USD means profiting from price fluctuations.
The two sided nature of the Forex market allows traders to profit from both rising and falling prices without any limitation on market direction; whereas in many stock markets, profitability is effectively dependent on the price appreciation of the asset.
Additionally, the daily trading volume of Forex, which is estimated at over 7.5 trillion dollars. Creates a level of liquidity that enables order execution with minimal price slippage and without the formation of trading queues, and this characteristic turns Forex into a highly efficient environment for short term trading and precise risk management.
What is the Stock Market?
In the stock market, shares of companies are bought and sold. For example, by buying Apple shares, you become a partial company owner and share in its profits and losses based on the number of shares purchased. In essence, by buying shares, you will own the asset.
In addition to ownership rights, the structure of the stock market causes the price performance of each share to be directly dependent on the company’s financial condition, management decisions, the state of the relevant industry, and the firm’s economic outlook.
Therefore, in order to make successful decisions in the stock market, a trader is inevitably required to conduct deep fundamental analysis, examine financial statements, profitability reports, and macroeconomic factors.
Those interested in using educational material on the differences between the stock market and Forex in financial markets should refer to the instructional video of the “Mindfully Trading” channel on YouTube:
In the Forex market, the main analytical focus is placed on countries’ macroeconomic variables, central banks’ monetary policies, and international liquidity flows, which shape the movement path of currency pairs.
Comparison of Stocks and Forex
forex vs stock market trading are two markets with different natures, where all parameters (trading hours, leverage offered, liquidity level, and the type of fundamental analysis) differ. Comparison of stocks and Forex at a glance:
| Feature | Forex | Stocks |
| Nature | Trading currency pairs | Trading company shares |
| Trading Hours | 24/5 | Determined by the stock exchange |
| Leverage | High (usually up to 1:500) | Lower than Forex (e.g., up to 1:5) |
| Liquidity | Very high (daily $7 trillion) | Varies depending on the stock |
| Fundamental Analysis | Global economy analysis | Macroeconomic analysis, financial statements, and commodity markets |
These forex vs stock market trading structural differences cause the trading style, investment time horizon, and risk management model in each of these two markets to differ fundamentally.
In the stock market, the primary focus is on analyzing companies’ financial statements, industry conditions, and domestic economic factors, whereas in the Forex market, decision making is formed based on countries’ macroeconomic variables, central banks’ monetary policies, and international liquidity flows.
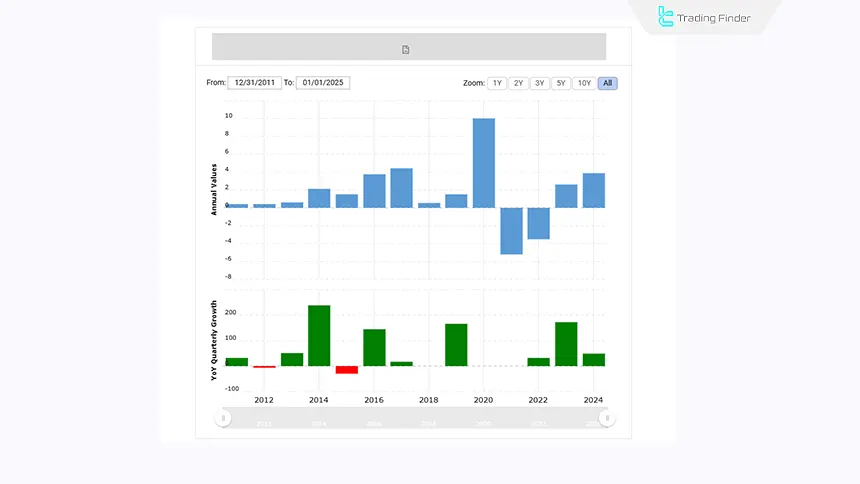
The image below shows a view of Tesla’s annual profit and loss index over the period from 2012 to 2024:
On the other hand, the very high liquidity of Forex, round the clock activity, and the possibility of using trading leverage turn this market into a dynamic environment for active traders, while the stock market provides a more suitable platform for structured and long term investment.
Trading Hours in the Stock Market and Forex
When comparing Forex vs Stocks, Forex markets operate 24 hours a day, whereas stock markets have fixed trading hours.
Comparison of stocks and Forex in terms of trading hours:
Parameter | Stocks | Forex |
Start Time | Varies by country (usually 8-9:30 AM on business days) | Monday 0:00 (UTC) |
End Time | Varies by country (usually 3-5:30 PM) | Friday 23:59 (UTC) |
Business Days | 5 days a week | 5 days a week |
Trading Costs [Spread, Commission, Fees, Slippage, and Swap]
In the stock market, trading costs are usually charged in the form of buying and selling fees, brokerage commissions, and in some markets, transaction taxes, and these costs are directly deducted from the trader’s final profit.
In contrast, in the Forex market, the main portion of trading costs is applied in the form of the spread, meaning the difference between the buying and selling price, and in some accounts, as a fixed commission.
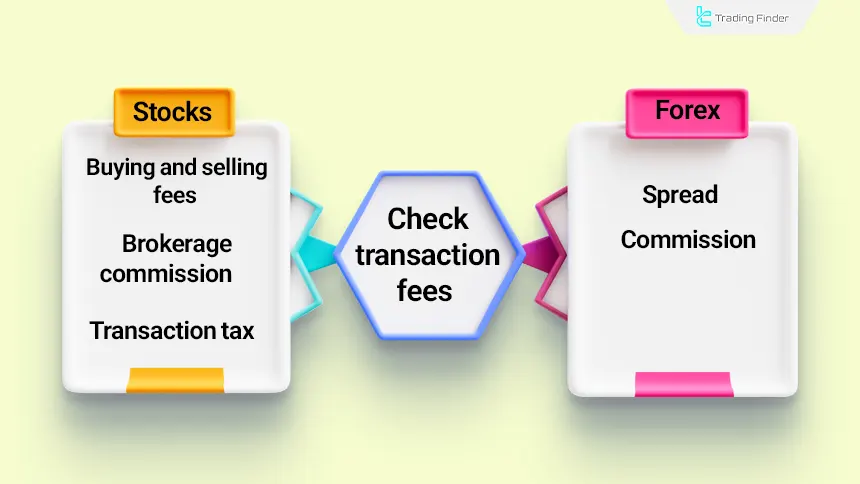
Comparison of stocks and Forex in terms of broker and brokerage costs:
Cost Type | Forex | Stocks |
Spread | Varies by currency pair, usually lower than stocks | Varies by stock and brokerage, usually higher than Forex |
Commission | No commission in many brokers | Varies based on trade volume or number of shares purchased |
Swap | Varies by currency pair and position | No overnight fees (except for margin trading or ETFs) |
Taxes | In some countries | In some countries |
Leverage
Leverage allows traders to trade with multiples of their capital. This tool multiplies profits and losses and increases risk.
In the Forex market, the possibility of using high leverage is one of the structural characteristics of this market, which allows a trader to control a larger trading volume with a small amount of capital.
However, just as leverage increases profit potential, it proportionally intensifies the probability of capital loss, and in the case of improper risk management, it can lead to irrecoverable losses.
The table below illustrates the characteristics of the Forex and stock markets:
Feature | Forex | Stocks |
Maximum Leverage | Usually up to 1:1000 or more (depending on the broker and country) | Usually between 1:2 and 1:10 (depending on the stock and country) |
The currency pair market offers higher leverage, ranging from 1:50 to 1:500. However, leverage in Forex is subject to strict regulations; for example, in Europe, the maximum leverage allowed for retail traders is 1:30.
In the stock market, leverage is lower; however, higher leverage (e.g., 1:20) is offered in some CFD contracts.
Asset Diversity
In Forex, currency pairs are divided into three main categories. In the stock market, company shares, commodities, and ETFs are tradable.
In the Forex market, currency pairs are divided into three groups based on trading volume and the economic importance of countries, and this classification helps traders to accurately assess the level of liquidity, the degree of volatility, and the risk of each trading instrument.
In contrast, in the stock market, in addition to company shares, a wide range of assets such as commodities, bonds, indices, and exchange traded funds are also available to traders.
This diversity of instruments makes it possible to implement various investment strategies and portfolio management approaches.
For more information about the differences between the stock market and Forex in financial markets, you may also use the educational article on comparing the stock market and the Forex market on the website www.ig.com.

Types of Currency Pairs in Forex
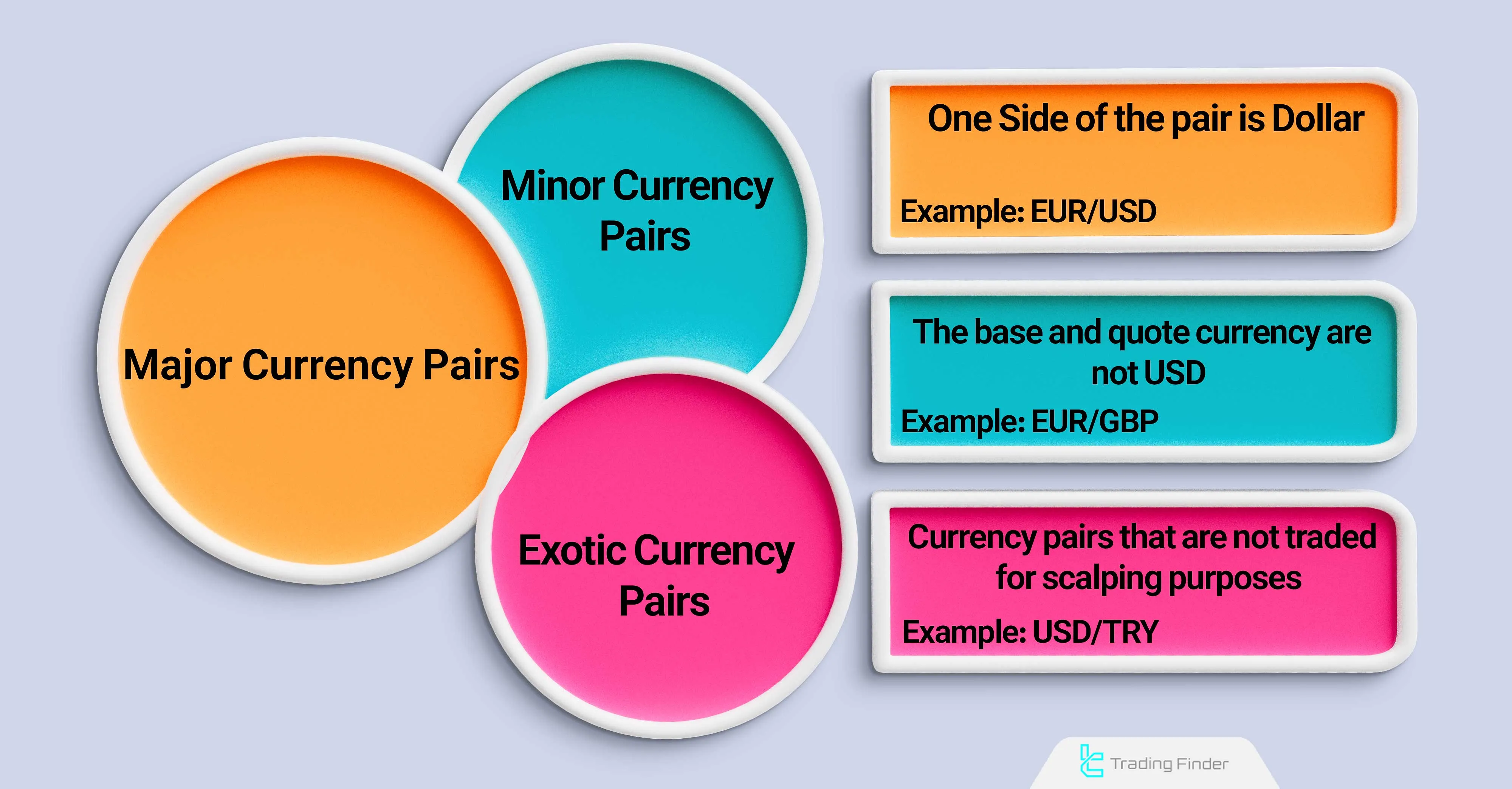
In the Forex market, all trades are conducted based on currency pairs; these currency pairs, in terms of trading volume, liquidity, price stability, and risk level, are divided into the following three categories:
- Major currency pairs: one side of them is the dollar; such as EUR/USD;
- Minor currency pairs: neither the base nor the quote currency is the dollar; such as EUR/GBP;
- Exotic currency pairs: these are currency pairs that are not traded for the purpose of trading and speculation; rather, their transactions are carried out in global commerce.
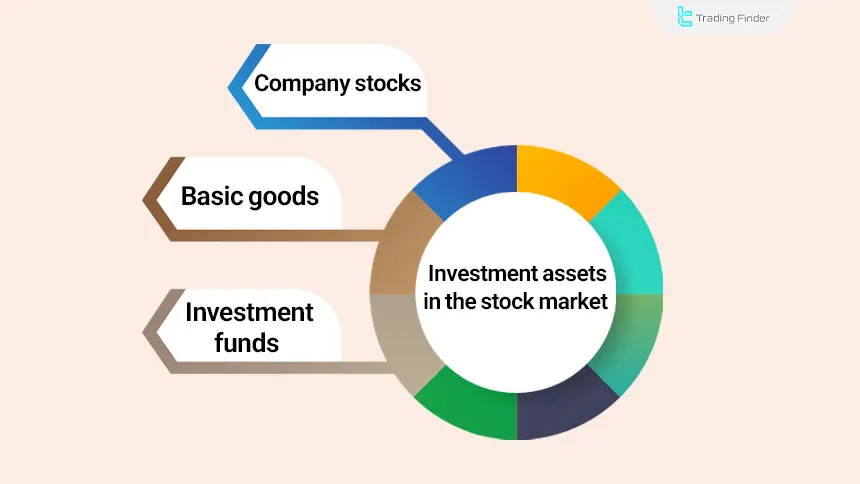
Types of Assets in the Stock Market
- Company Shares: By buying company shares, you become a partial owner and share in the profits and losses based on the volume of shares purchased;
- Commodities: Tradable assets typically consisting of natural resources, agricultural products, and metals;
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): Investment funds that include a mix of stocks, bonds, commodities, and other assets designed to diversify investment portfolios at low cost.
Fundamental Analysis
From a fundamental perspective, anything that affects macroeconomic indicators, such as economic data, central bank meetings, and even political risks like wars or elections, impacts currency pair trends and is analyzed in fundamental analysis of currency pairs.
In fundamental stock analysis, in addition to macroeconomic analysis, labor market conditions, and economic growth, financial statement analysis is also required. Financial statements examine the company's revenue and earnings per share.
A key difference in forex vs stock trading is that Forex trading is more influenced by global economic events, while stock trading is driven by company performance and industry trends.
Liquidity and Market Depth
While Forex, with a daily trading volume of approximately $7 trillion, is the largest financial market, liquidity in stocks varies by market. Comparison table of stocks and Forex in terms of liquidity and trading volume:
Feature | Forex | Stocks |
Liquidity | Very high | Varies by stock and market |
Market Depth | Deep [high liquidity in all currency pairs] | Market depth depends on volume and type of stock |
Price Volatility | Usually high due to large trading volumes and global news | Lower volatility in some stock markets with price limits |
Trading Volume | Daily over $7 trillion | Varies by stock exchange, usually lower than Forex |
Example of the Difference Between the Stock Market vs Forex Market
Suppose a trader intends to trade on the appreciation of the US dollar. In the stock market, he must first identify companies that benefit from a stronger dollar, examine their financial statements, analyze the industry conditions, trade policies, and the company’s profitability outlook, and then select the appropriate stock.
This process may take days or even weeks, and his profitability will depend on the performance of that specific company.
However, in the Forex market, the same trader can directly trade the EUR/USD currency pair and, by selling this pair, take a position on the strengthening of the dollar.
If the dollar appreciates, the trade becomes profitable without the need to analyze the condition of a specific company or complex financial reports.
Moreover, if the trader’s analysis is incorrect, in the Forex market he can benefit from price declines as well by quickly closing the trade or even entering a reverse position, whereas in the stock market such flexibility does not exist, and in many exchanges profiting from falling prices is subject to structural limitations.
This example clearly shows that Forex is a fast, direct, and flexible environment for active trading, while the stock market is considered more suitable for analytical and long term investment.
Introduction of the Forex Profit Boost Indicator
The Forex Profit Boost indicator is designed as a multi market trend detection system that provides the capability to simultaneously analyze the price movement structure in Forex and Stock markets, cryptocurrencies, stocks, and commodities.
This trading tool, by combining two main analytical cores, namely the Moving Average and Bollinger Bands, creates an adaptive signaling framework that enables the trader to simultaneously identify trend direction, momentum strength, and potential price reversal zones.
The overlap of these two analytical models makes it possible to detect changes in market momentum phases before they fully appear in the price structure, allowing the trader to adjust entry and exit points with greater precision.
This adaptive structure plays an important role, especially in volatile markets where changes in price behavior occur in a non linear manner, in reducing false signals and increasing the quality of decision making.
The visual core of this indicator is based on a dynamic colored histogram whose changes directly reflect price behavior, movement acceleration, and the level of buying and selling pressure.
Changes in the color and height of the histogram bars indicate the market’s transition among the phases of accumulation, acceleration, saturation, and momentum weakening.
This graphical display, in addition to increasing decision making speed, creates precise alignment between price structure analysis and market psychology and effectively enhances trade execution quality.
The color sequence is algorithmically adjusted to clearly display the "Trend Continuation" and "Trend Reversal" phases.
When the market structure enters a bullish phase, the histogram bars appear in a combination of blue and yellow and display the increasing strength of buyers. In contrast, when the market turns into a bearish phase, this color spectrum changes to yellow and red, indicating the dominance of sellers.
Types of Assets in the Stock Market
The stock market encompasses a broad range of financial instruments and investment assets, each of which plays a different role in portfolio management, risk control, and return enhancement as follows:
- Company Shares: By buying company shares, you become a partial owner and share in the profits and losses based on the volume of shares purchased;
- Commodities: Tradable assets typically consisting of natural resources, agricultural products, and metals;
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): Investment funds that include a mix of stocks, bonds, commodities, and other assets designed to diversify investment portfolios at low cost.
Conclusion
The stock market and Forex have different natures. Forex is a suitable option if you are looking for a market with high liquidity, 24/5 trading, and high leverage.
On the other hand, if you have the necessary expertise for financial statement analysis and are looking for long-term investment with lower risk, the stock market is a suitable platform for trading.
As a result, choosing between these two markets should not be based merely on superficial appeal or the excitement of short term profit; rather, the level of financial knowledge, risk management capability, investment time horizon, and each trader’s tolerance for volatility play a decisive role in long term success.
Understanding the structural differences of these two markets, from pricing mechanisms to the behavior of the main participants, enables the trader to design his trading strategy with a data driven logic aligned with real market conditions.













