Dovish stance refers to expansionary monetary policy, aimed at stimulating economic growth, which often leads to the depreciation of the related currency.
A dovish stance is usually favorable for risky assets such as cryptocurrencies and stocks. In contrast, a hawkish stance describes a contractionary monetary policy, implemented to control economic inflation and generally results in currency appreciation.
Hawkish stances by the Federal Reserve often lead to corrections in risk markets.

What Do Hawkish and Dovish Mean?
Hawkish and Dovish are financial market terms used to describe central banks’ monetary policy positions.
The term Hawkish comes from “hawk” – a symbol of aggression and firmness, while Dovish comes from “dove” – a symbol of peace and softness.
What’s the Difference Between Hawkish and Dovish Policies?
The term hawkish describes tightening monetary policy, whereas dovish refers to easing monetary policy.
These stances serve different goals and have varying implementations and effects on the economy.
A dovish stance aims to stimulate economic growth and is typically executed by lowering interest rates or pausing hikes (holding rates during an upward trend).
In contrast, a hawkish stance aims to reduce inflation and is commonly carried out by raising interest rates or halting rate cuts (holding rates steady during a downward trend).
Comparison Table: Hawkish and Dovish Stances:
Parameter | Hawkish | Dovish |
Objective | Controlling or reducing inflation | Stimulating economic growth |
Central Bank Policy | Contractionary | Expansionary |
Interest Rate | Increasing interest rate | Decreasing interest rate |
Impact on Economic Growth | Slows economic growth | Boosts economic growth |
Impact on Inflation | Reduces inflation | Increases inflation |
Impact on Currency | Strengthens the currency | Weakens the currency |
Inflation Expectations | Lowers inflation expectations | Raises inflation expectations |
When Are Hawkish or Dovish Policies Implemented?
Hawkish and Dovish stances are opposite and have different economic implications; therefore, they are executed at different times with specific goals:
When Dovish Policies Are Adopted (Shifting from Hawkish to Dovish Stance)
- Weak economic growth
- Disinflation or deflation crisis
- Weak labor market and high unemployment rate
- Interest rates that hinder growth (above the neutral rate)
When Hawkish Policies Are Adopted (Shifting from Dovish to Hawkish Stance)
- Inflation exceeding the central bank’s target
- Overheated labor market (fueling inflation risks)
- Low interest rates (below the neutral range)
Identifying the Central Bank’s Stance in Interest Rate Meetings
When a central bank moves toward an expansionary monetary policy or aims to soften a tightening policy, it adopts a Dovish stance. For instance, in its Market statements and speeches, it may use language that implies rate cuts, affecting market sentiment and expectations accordingly.
Conversely, a Hawkish stance is evident when a central bank signals tightening policy or a reduction in easing measures (such as halting rate cuts).
In this case, speeches and official statements contain language suggesting interest rate hikes or other contractionary measures.
Hawkish and Dovish Tone in Central Bank Speeches
The tone of the central bank governor during interest rate decision speeches can reveal whether the stance is Hawkish or Dovish.
Example of Determining Central Bank Stance in a Speech
For instance, the Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ) adopted a Hawkish stance during its May 2024 meeting to control inflation and reduce inflation expectations. It signaled that rate cuts may not occur until the second half 2025.
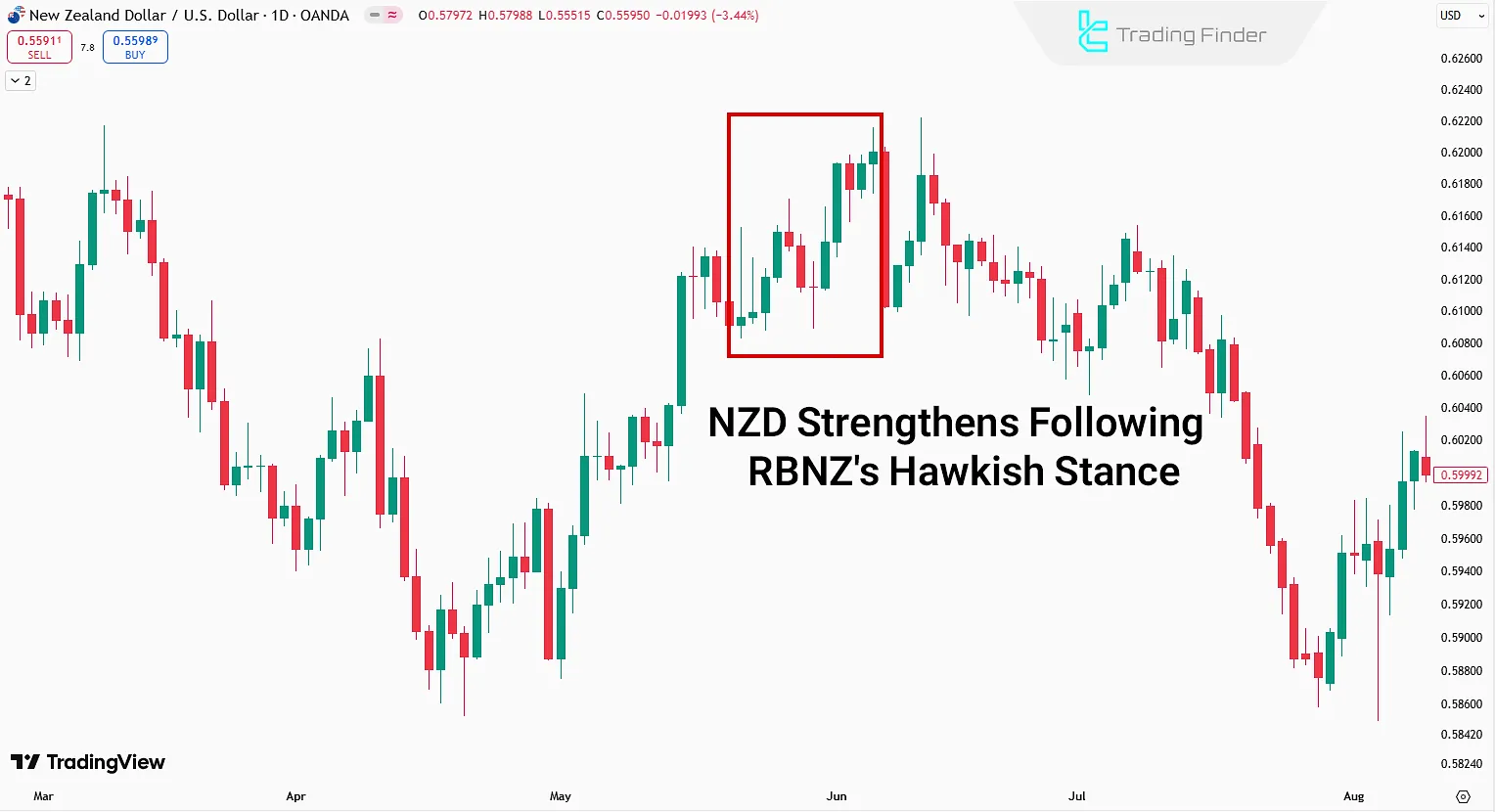
Hawkish and Dovish in Central Bank Projections
Central banks regularly update their economic projections on every quarter. Traders compare the new projections with the previous ones to evaluate whether the stance has become more Hawkish or Dovish.
Example: Analyzing the Federal Reserve’s Projections
The image below compares the Federal Reserve’s December 2024 projection with that of September 2024.
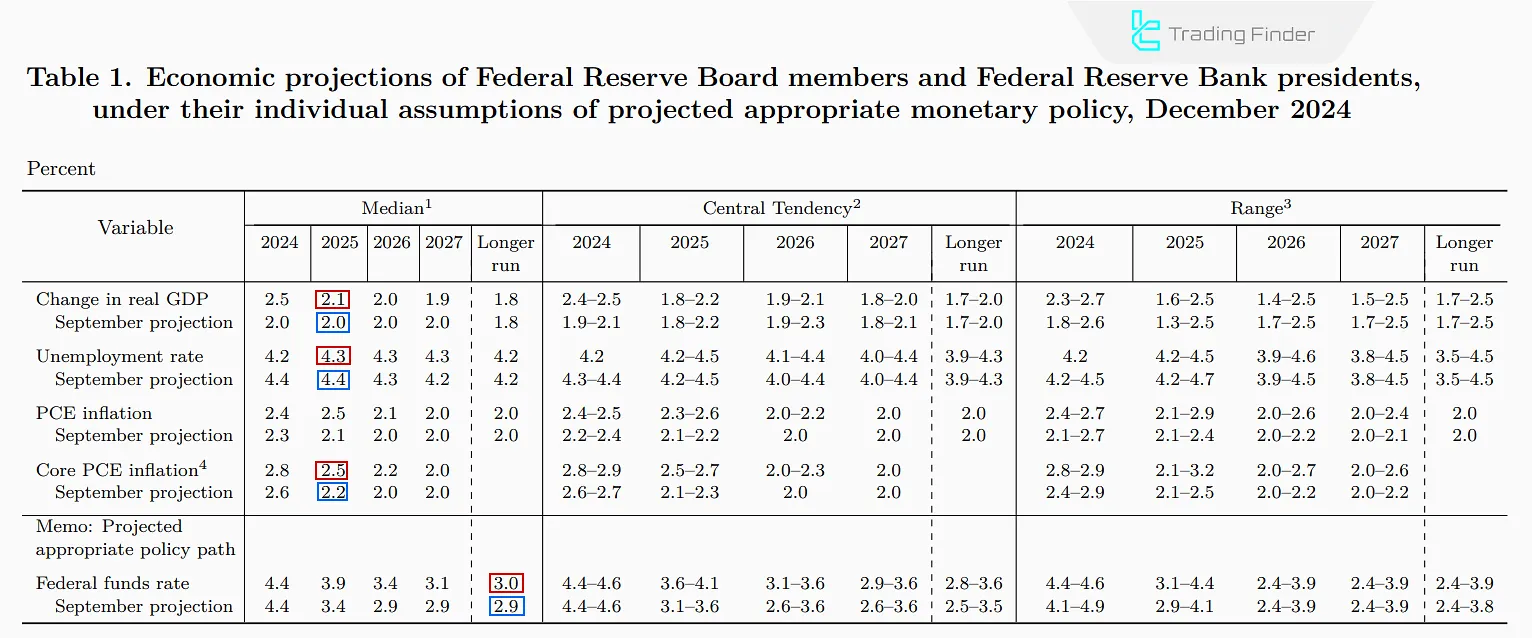
The December projection introduced several Hawkish elements:
- Higher neutral interest rate: The Fed envisions a higher neutral rate;
- Rising inflation: The Fed plans to reduce the rate cuts to manage rising inflation better;
- Lower unemployment rate: This may drive wages up, potentially fueling inflation;
- Higher economic growth: could lead to more inflationary pressure, prompting the Fed to keep rates elevated.
All these projection changes are considered Hawkish, as they support stronger interest rates and a stronger US dollar.
How Do Hawkish and Dovish Policies Affect Financial Markets?
Hawkish and Dovish stances are implemented with different objectives, resulting in diverse market impacts.
Impact of a Dovish Stance on Financial Markets
A Dovish stance (expansionary) by the central bank aligns with easing policies and is generally welcomed by risk assets such as stocks and cryptocurrencies.
Easing policies boost liquidity by lowering interest rates, which supports risk markets. In other words, when interest rates are reduced—or even when the central bank governor signals a potential rate cut—the related currency in the Forex market tends to weaken, creating a favorable environment for risk assets.
Impact of a Hawkish Stance on Financial Markets
Conversely, a Hawkish stance reflects tightening policy, negatively impacting risk markets due to reduced liquidity.
The adverse effect of contractionary policy on risk assets stems from lower available liquidity. When consumers have less money for essential purchases, their willingness to invest in risk assets declines.
Example: Federal Reserve’s Hawkish Stance and Its Market Impact
Let’s examine the market reaction to the Federal Reserve’s extremely Hawkish stance in the December 18, 2024, meeting.
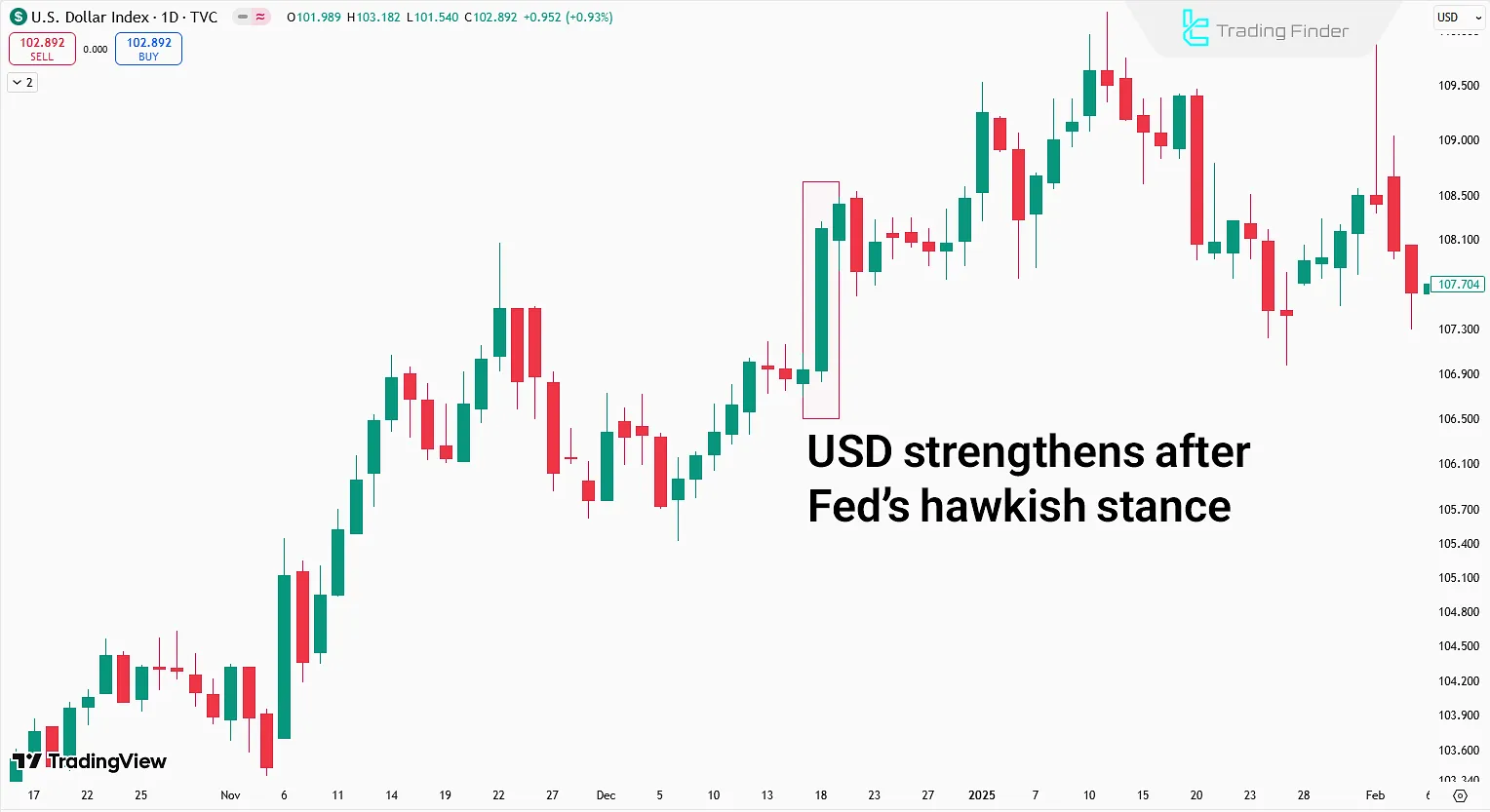
In this meeting, Fed Chair Jerome Powell used Hawkish language, stating:
“We are not ruling out the possibility of further interest rate hikes!”
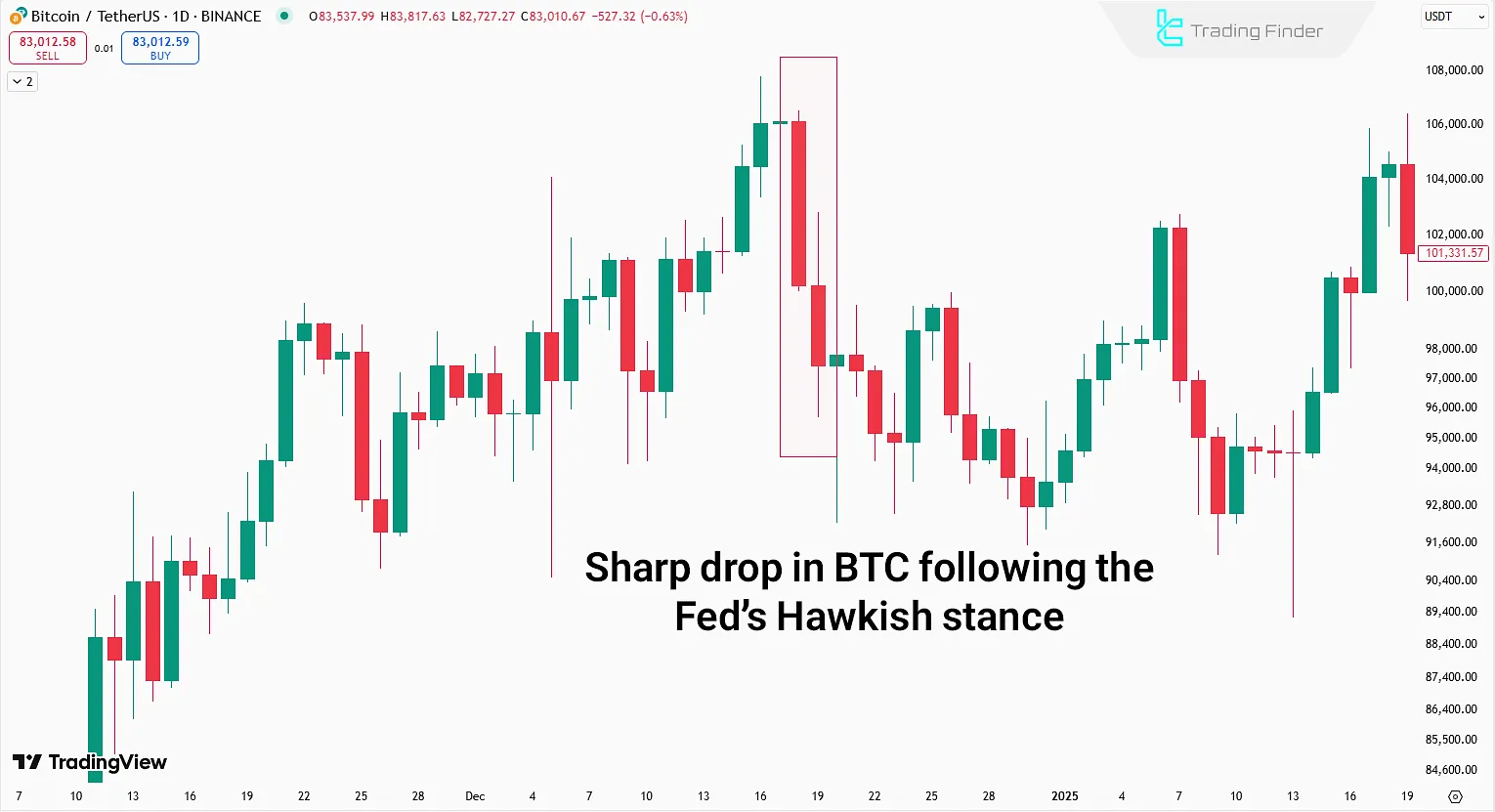
As seen, the Federal Reserve’s Hawkish stance during the meeting triggered a steep decline in Bitcoin (a typical risk asset).
Conclusion
Understanding the central bank’s stance can be achieved by analyzing the Hawkish and Dovish tone in the governor’s speeches and official statements.
Central banks’ economic projections include changes in inflation estimates, unemployment rates, the number of expected rate cuts, and the level of the neutral interest rate.
These changes can also reflect a Hawkish or Dovish stance, influencing medium-term currency trends in the Forex market.













