Monetary policy, with its direct impact on liquidity, reduces or increases inflation. The way monetary policy affects economic inflation depends on the type (tools) and direction (contractionary or expansionary) of the policy.
Moreover, implementing monetary policy may lead to a boom or recession in various economic sectors by changing societal consumption patterns.
What is Monetary Policy?
Monetary policies refer to the set of actions the central bank takes to create stability in the labor market and control inflation (the central bank's dual mandate).
These policies have a significant impact on economic indicators and are implemented through the following tools:
- Interest Rate: The cost of borrowing money for a specified period;
- Open Market Operations: The central bank’s control over liquidity through buying and selling securities;
- Reserve Requirement: The percentage of bank deposits held by the central bank.
Contractionary and Expansionary Monetary Policy
Contractionary and expansionary monetary policies have completely different effects on the economy. The central bank implements these policies depending on its goal (reducing inflation or stimulating the labor market) and the existing economic conditions.
Parameter | Contractionary | Expansionary |
Impact on Inflation | Decreases | Increases |
Impact on Economic Growth | Limits economic growth | Encourages economic growth |
Execution Time | Requires controlling inflation | Requires stimulating economic growth |
Tools | Increased interest rates, reducing asset balance | Decreased interest rates, quantitative easing policy |
In addition to monetary policies, the hawkish or dovish stance of the central bank’s president can also influence inflation and inflation expectations.
Note: Neutral monetary policy is one of the monetary policy types. This policy is executed when inflation is within the central bank's target range and keeps inflation at an equilibrium level.
The Impact of Monetary Policies on Inflation
Monetary policies change the level of liquidity and therefore have a direct impact on inflation. However, the impact of monetary policies on inflation depends on their type and objectives.
The Impact of Expansionary Monetary Policy on Inflation
In expansionary monetary policy, the central bank increases liquidity by lowering interest rates or purchasing securities (increasing the balance sheet - quantitative easing).
According to the monetary base formula for inflation, the action tends to be inflationary and is usually aimed at boosting economic growth and improving the labor market (reducing unemployment).
Note: According to the monetary base formula for inflation, inflation will occur if the money supply increases more than the supply of goods.
Example of the Impact of Expansionary Monetary Policy on Inflation
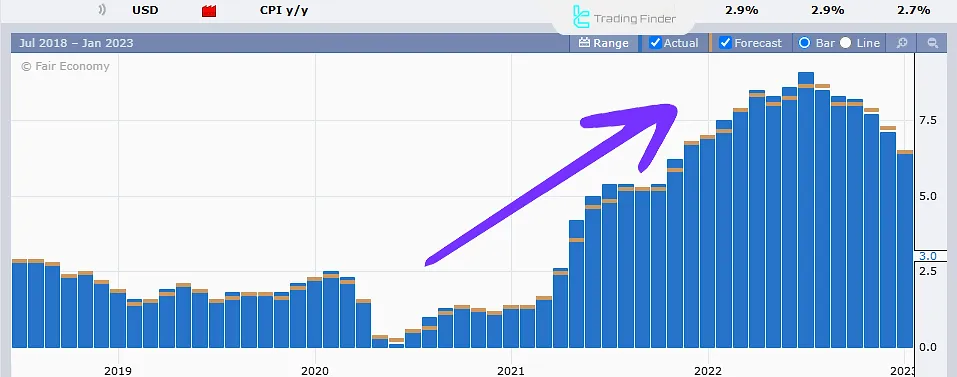
For instance, in 2020, in response to the recession caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, central banks adopted expansionary monetary policy, which led to a sharp increase in inflation.
The Federal Reserve's expansionary monetary policy at the beginning of 2020, which included lowering interest rates and purchasing securities (quantitative easing), was implemented by the central bank.
This policy led to a significant increase in inflation, reaching approximately 9%.
However, expansionary policies are not always implemented with the intensity seen in 2020.
The impact of monetary policies on inflation varies depending on the strength and duration of their implementation.
The Impact of Contractionary Monetary Policy on Inflation
Contractionary monetary policy raises borrowing costs (interest rates), reducing liquidity.
This demonstrates the impact of interest rates on inflation, as higher rates directly reduce liquidity and suppress demand.
Example of the Impact of Contractionary Monetary Policy on Inflation
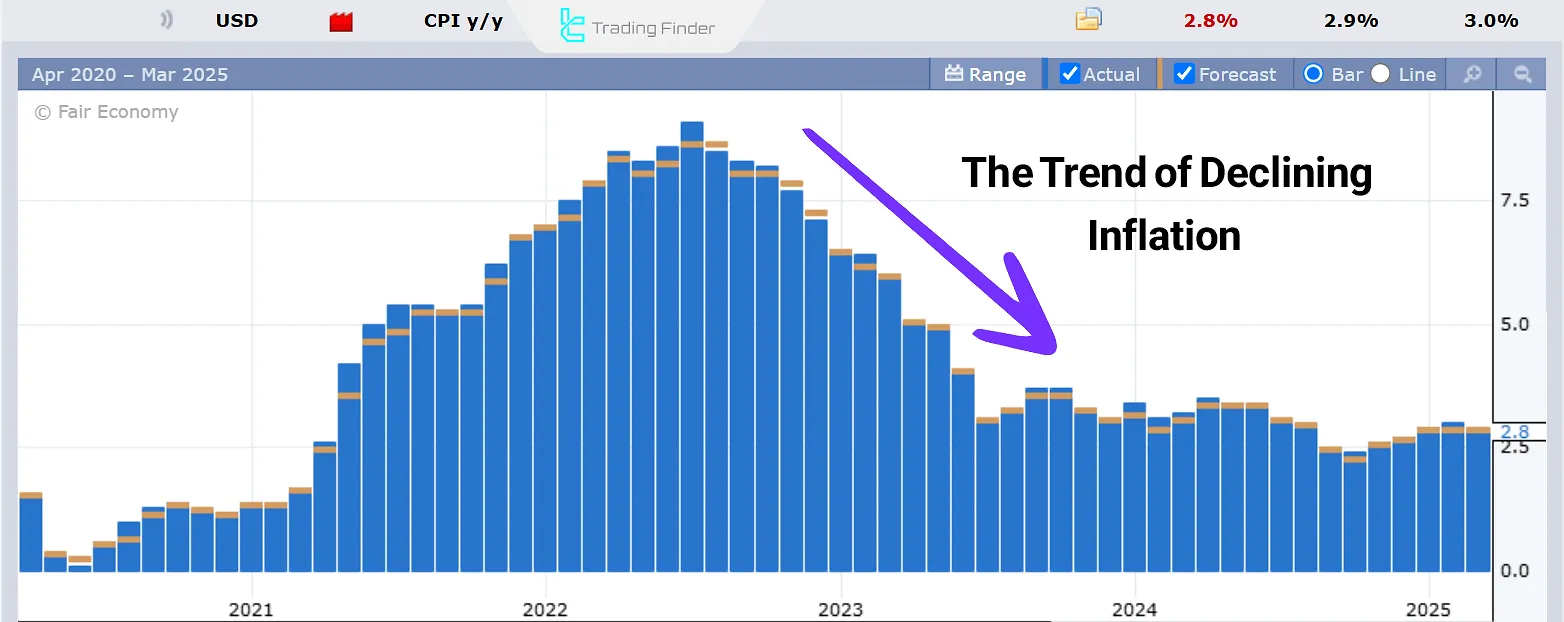
The Federal Reserve’s increase in interest rates in 2022, aimed at controlling inflation, is a good example of contractionary monetary policy and its impact on inflation.
As a result of the sharp rise in interest rates, inflation fell from around 9% back to the 2% range.
Duration of the Impact of Monetary Policies on Inflation
Monetary policies typically take several months to affect economic indicators.The delay in the impact of interest rates on inflation is often due to the time it takes for rate changes to affect consumer behavior and loan structures.
For example, the Federal Reserve started raising interest rates and implementing contractionary policy in March 2022, but the downward trend in inflation began approximately five months later (in August).
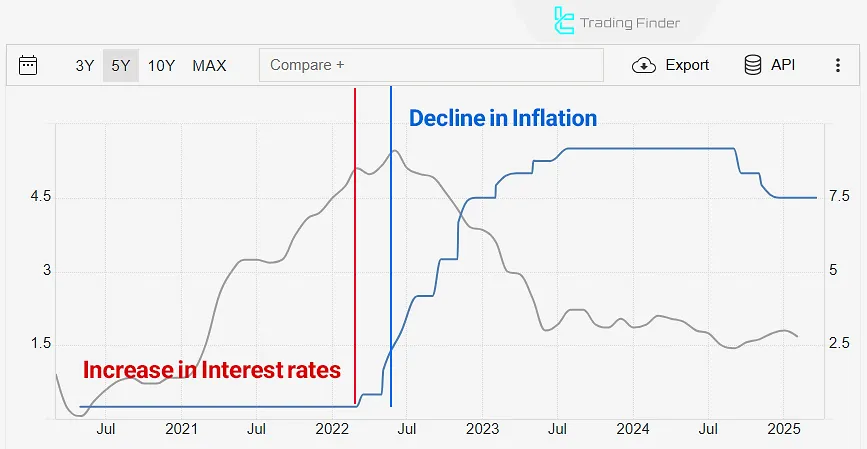
In the chart, the delay in the effect of interest rates on inflation is evident in the difference between the start of interest rate increases and contractionary policy (in red) and the start of the downward trend in inflation (in blue).
Why Is the Impact of Monetary Policy on Inflation Delayed?
The main reason for the delay in the effect of monetary policy on the economy is that changes in interest rates take time to influence the banking system, as well as consumer and producer behavior.
Delay in the Application of New Interest Rates on Existing Loans
After the central bank announces new interest rates, they apply to new loans, but many previous loans have fixed rates or revision periods.
For example, mortgage and commercial loan rates are usually reviewed every three months, six months, or annually.
In other words, the new interest rates may be applied during the next review period.
Also, bank deposits are considered with the previous rate until the end of their term.
Diminishing Effect of Monetary Policy by External Factors
Certain external factors, such as commodity prices, political relations, supply chain risks, and imports, can influence the economy and diminish the effect of monetary policy.
For example, if supply shortages and cost-push factors cause inflation, monetary policy will have a reduced impact.
Consumer and Producer Behavior
Before impacting inflation, monetary policy first affects consumer and producer behavior.
For example, in expansionary monetary policy, increased liquidity leads to an increase in purchasing power and demand.
As a result, with the rise in producer sales, prices gradually increase.
In contrast, during the implementation of contractionary policy, producers consider whether the weak demand is temporary or permanent.
If weak demand persists, companies may reduce their prices.
The Differing Impact on Different Sectors of the Economy
The effect of monetary policy on different sectors and goods is not uniform.
For example, reducing inflation in goods dependent on imported raw materials is more difficult due to exchange rate fluctuations, and the effect of monetary policy on them requires more time.
Example of the Impact of Monetary Policy on Inflation
During economic crises such as war, economic recession, or stagflation, the impact of monetary policy may take longer to become evident. For example:
- The 1980 U.S. inflation crisis: The impact of contractionary policy lasted 1.5 to 2 years;
- The 2008 recession: During the 2008 financial crisis, the impact of expansionary policy became visible in 2010;
- The severe inflation in the Turkish economy after COVID-19: Following a reduction in interest rates, lending and investment increased, but after a few months, Turkey experienced severe inflation and a collapse of the lira.
Changing Consumption Patterns During the Implementation of Monetary Policy
During the implementation of either expansionary or contractionary monetary policy, consumption patterns may change because consumers' demand for goods might vary according to their financial situation.
For example, if expansionary monetary policy leads to high inflation and reduced purchasing power, consumers may prefer to buy cheaper substitute goods.
Changing Consumption Patterns Based on Price Elasticity of Demand
Goods whose demand changes with price fluctuations (such as luxury goods or travel services) are considered to have high price elasticity.
On the other hand, inelastic goods (e.g., water, electricity, internet, and medicine) are not affected by price changes, but in inflationary conditions, they put economic pressure on consumers.
Why Is It Important to Pay Attention to Consumption Patterns in Investment?
In fundamental analysis, examining the details of inflation reports and forecasting their future trends is crucial.
Additionally, predicting the boom or recession in various sectors of the economy is essential for stock market investment.
For example, during contractionary policy, there may be a decrease in demand for new cars or luxury vehicles.
If the global contractionary cycle is implemented (after the COVID-19 crisis in the years 2022 to 2024), the export of luxury cars will also face challenges.
Conclusion
Controlling inflation is one of the central bank’s main responsibilities, done through tools like interest rates and open market operations.
By adjusting liquidity, the central bank influences inflation and consumer demand, though the effects often appear with a delay.
The delay is caused by factors such as slow transmission of new interest rates, external influences, and changes in consumer and producer behavior. These shifts can impact economic cycles and lead to booms or recessions in specific sectors.













