Interest rates are a key tool for central banks to implement monetary policy, and changes ininterest rates create significant fluctuations in financial markets.
Typically, increasing interest rates leads to currency strengthening, while decreasing interest ratescausescurrency weakening. Additionally, expectations of interest rate changes also influence the market.

Under normal conditions, an increase in interest rates is implemented with the aim of restraining demand and controlling inflationary pressures.
This process enhances the attractiveness of returns on assets denominated in the domestic currency and ultimately leads to a strengthening of the currency’s value.
Conversely, a reduction in interest rates lowers the returns on monetary assets, increases incentives for capital outflows, and leads to currency depreciation.
Why Are Interest Rates Important in Financial Markets?
Changes in interest rates play a crucial role in financial markets because they directly impact inflation, economic growth, and unemployment rates. Changes in these factors lead to either the strengthening or weakening of currencies.
According to academic definitions, interest rates can be defined as the "value of money"; the interest rate is the cost of borrowing money. This means the borrower must repay the borrowed amount plus the interest rate or borrowing cost.
For example, assume the interest rate is 5%, and you borrow 1000$. In this case, you must repay 1000$ plus 5% of it (50$). Actually, the 50$ is the cost of borrowing.
To monitor interest rates of various economies, you can use TradingFinder interest rate tool.
The Interest Rate Impact on Economic Trends and Indicators
Changes in interest rates affect liquidity, consumer demand, and economic growth. Increasing interest rates reduces inflation and economic growth, acting as a constraint on the economy. Conversely, lowering borrowing costs supports economic growth, but it may also lead to increased inflation.
The table below shows the relationship between interest rates and key economic indicators:
Indicators | Result of Lowering Interest Rates | Result of Increasing Interest Rates |
Inflation | Increase | Decrease |
Economic Growth | Increase | Decrease |
Unemployment Rate | Decrease | Increase |
You can track economic reports from the economic calendar on the TradingFinder website.
The Relationship Between Interest Rates and Inflation
Decreasing or increasing interest rates directly affects liquidity and inflation. Lower borrowing costs increase liquidity, leading to higher consumer demand, resulting in increased inflation.
Additionally, according to the monetary root of the inflation formula, if the money supply exceeds the supply of goods, inflation occurs.
Conversely, increasing borrowing costs reduces liquidity, and limits demand, and lower demand leads to reduced inflation.
The Relationship Between Interest Rates and Economic Growth
According to the expenditure approach in calculating GDP (Gross Domestic Product), demand is one of the factors influencing economic growth.
Any action that suppresses demand, such as increasing interest rates or reducing liquidity, leads to a decline in economic growth. Conversely, any action that stimulates demand, such as lowering interest rates or increasing liquidity, boosts economic growth.
The table below examines the relationship between interest rates and GDP growthand economic growth based on the expenditure approach to GDP:
Analytical Dimension | Effect of Interest Rate Increase | Effect of Interest Rate Decrease | Relation to GDP Expenditure Components |
Aggregate Demand | Reduction in aggregate demand due to higher borrowing costs and lower willingness to consume | Increase in aggregate demand as a result of lower borrowing costs and stimulated consumption | Household consumption, investment |
Investment | Decline in business investment caused by higher financing costs and reduced project viability | Growth in investment driven by cheaper access to credit | Productive investment |
Government Spending | Inflation and demand control through tighter government spending | Lower borrowing costs and expansion of government development expenditures | Government expenditure |
Net Exports | Appreciation of the national currency and a decline in exports following interest rate hikes | Currency depreciation and improved export capacity following interest rate cuts | Exports and imports |
Economic Growth | Slower economic growth due to reduced demand, lower investment, and pressure on production | Higher economic growth resulting from demand stimulation, production expansion, and increased investment | Overall outcome of GDP expenditure components |
Note: The expenditure approach in calculating GDP is based on the following factors:
- Trade Balance
- Government Expenditures
- Consumer Demand
- Investment in Productio
The Relationship Between Interest Rates and Unemployment Rates
The unemployment rate has an inverse relationship with economic growth; Increased economic growth leads to a lower unemployment rate.
Thus, lowering borrowing costs and increasing liquidity is effective in reducing the unemployment rate. Conversely, increasing borrowing costs and putting pressure on producers leads to a higher unemployment rate. Example of rising unemployment due to increased borrowing costs:
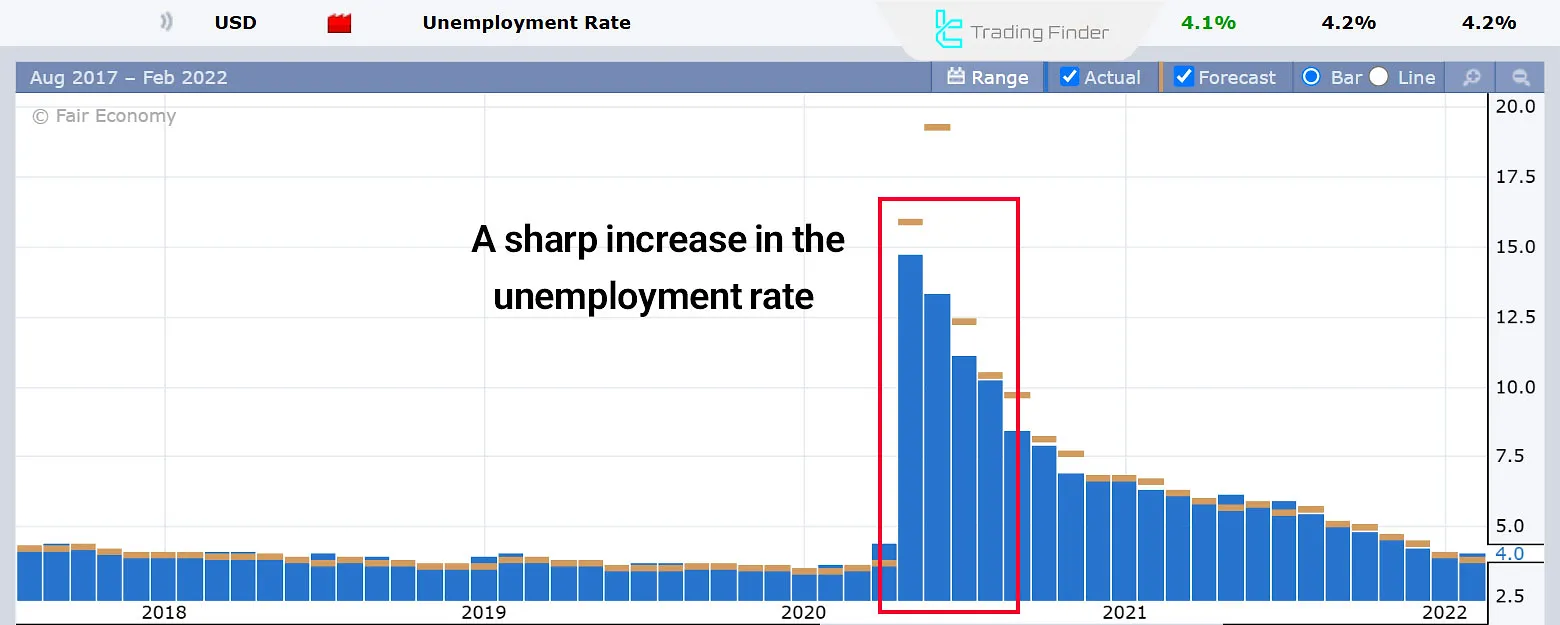
At the beginning of 2020, following the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, the US unemployment rate increased sharply (image above). To combat the recession and reduce unemployment, the Federal Reserve lowered interest rates, as shown in the image below.
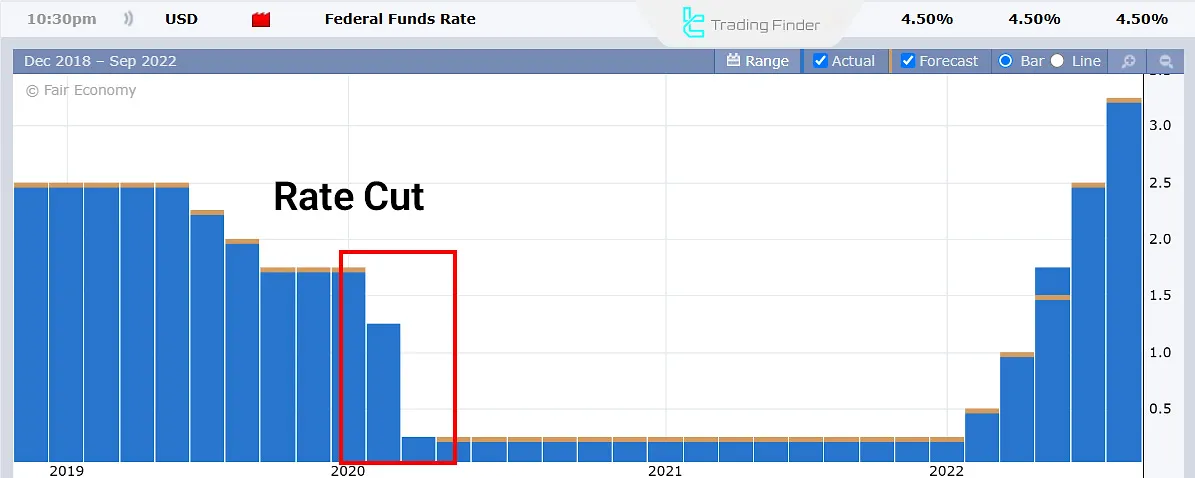
What Factors Influence Changes in Interest Rates?
Implementing changes and setting interest rates is the responsibility of the central bank. Considering their dual mandate (controlling unemployment and inflation) and monitoring economic data, central banks adjust interest rates.
Central banks consider the following data when setting interest rates:
- Inflation: If inflationary pressures are felt in the economy, the central bank will raise interest rates to control inflation (contractionary monetary policy);
- Unemployment Rate: If the unemployment rate rises, the central bank lowers interest rates to stimulate the economy and reduce unemployment (expansionary monetary policy).
Analysis of the Impact of Interest Rates on Financial Markets
Changes in Interest rate impact are among the most influential and critical factors in financial markets.
These changes have significant effects on currencies, equities, commodities, and other financial instruments.
An interest rate represents the cost paid for borrowing money and is determined based on decisions made by central banks. In general, changes in interest rates can lead to substantial fluctuations in financial markets and influence investment decisions as follows:
The Effect of Interest Rates on the Forex Market
Interest rates have a direct relationship with currency values in the Forex market. When central banks raise interest rates, investment returns in that currency increase, which attracts foreign investors and leads to a strengthening of the currency.
Conversely, a reduction in interest rates can result in currency depreciation, as investment returns decline and investors tend to shift their capital toward currencies with higher interest rates.
For more information on the impact of interest rates on financial markets, you can also refer to the educational article on How Interest Rates Affect Financial Markets on sjb-global.com.
Impact of Interest Rates on Financial Markets
Changes in interest rates directly influence capital flows across financial markets by altering the relative return on investment between economies.
When a central bank adjusts its policy rate, it reshapes yield expectations for fixed-income instruments, banking products, and leveraged assets, prompting institutional and retail investors to rebalance portfolios across currencies and asset classes.
The Effect of Interest Rates on Forex
As the money supply increases, the currency's value decreases; Conversely, as the money supply decreases, the currency's value increases.
According to this principle, increasing borrowing costs strengthens the currency. Conversely, lowering borrowing costs weakens the currency.
Interest Rate Impact on the Stock Market
The effect of interest rates on the stock market is such that increasing borrowing costs suppresses demand, making it harder to obtain loans, and putting pressure on producers.
Thus, during periods of contractionary policy or increased borrowing costs, the Interest rates and stock marketmoves away from prosperous days.
The Impact of Interest Rates on the Commodities Market
Changes in interest rates have wide ranging effects on the commodities market.
Commodities include assets such as gold, oil, silver, copper, natural gas, and other raw materials whose values are directly influenced by Monetary policy impact and interest rate decisions.
Interest rates, particularly through their effects on currency values and investment capital flows, can create significant price volatility in these commodities as outlined below:

Interest Rate Increases and Declining Commodity Prices
When central banks raise interest rates, borrowing costs for investors and consumers increase. This typically leads to reduced demand for commodities such as oil, precious metals, and other raw materials.
In addition, higher interest rates can strengthen major currencies such as the US dollar, which in turn causes commodities denominated in dollars, such as oil and gold, to decline in price.
Those interested in learning more about how interest rates affect financial markets can use the educational video from the YouTube channel “This Will Make You Rich”:
The Impact of Interest Rate Increases on the Dollar
When the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, returns on dollar denominated investments such as bonds and bank deposits increase on a relative basis. This higher yield attracts foreign investors to US financial markets.
As demand for dollar-based assets rises, the US dollar strengthens against other currencies. Foreign investors require dollars to purchase these assets, which increases demand and leads to further dollar appreciation.
Interest Rate Cuts and Rising Commodity Prices
When a central bank lowers interest rates, borrowing costs decline and demand increases for commodities that require large scale investment. In particular, for assets such as oil and precious metals, lower interest rates can boost demand and result in higher prices.
Moreover, interest rate cuts typically weaken major currencies, which supports higher prices for commodities such as gold, as gold acts as a safe haven asset against currency depreciation.
The Effect of Interest Rates on Gold
Gold, [the long-standing competitor to fiat currency], is affected by changes in interest rates. Increasing interest rates leads to a correction in gold prices, while decreasing interest rates causes gold to rise.
Note: The effect of interest rates on gold appears in the long term, and other factors also influence gold's trend.
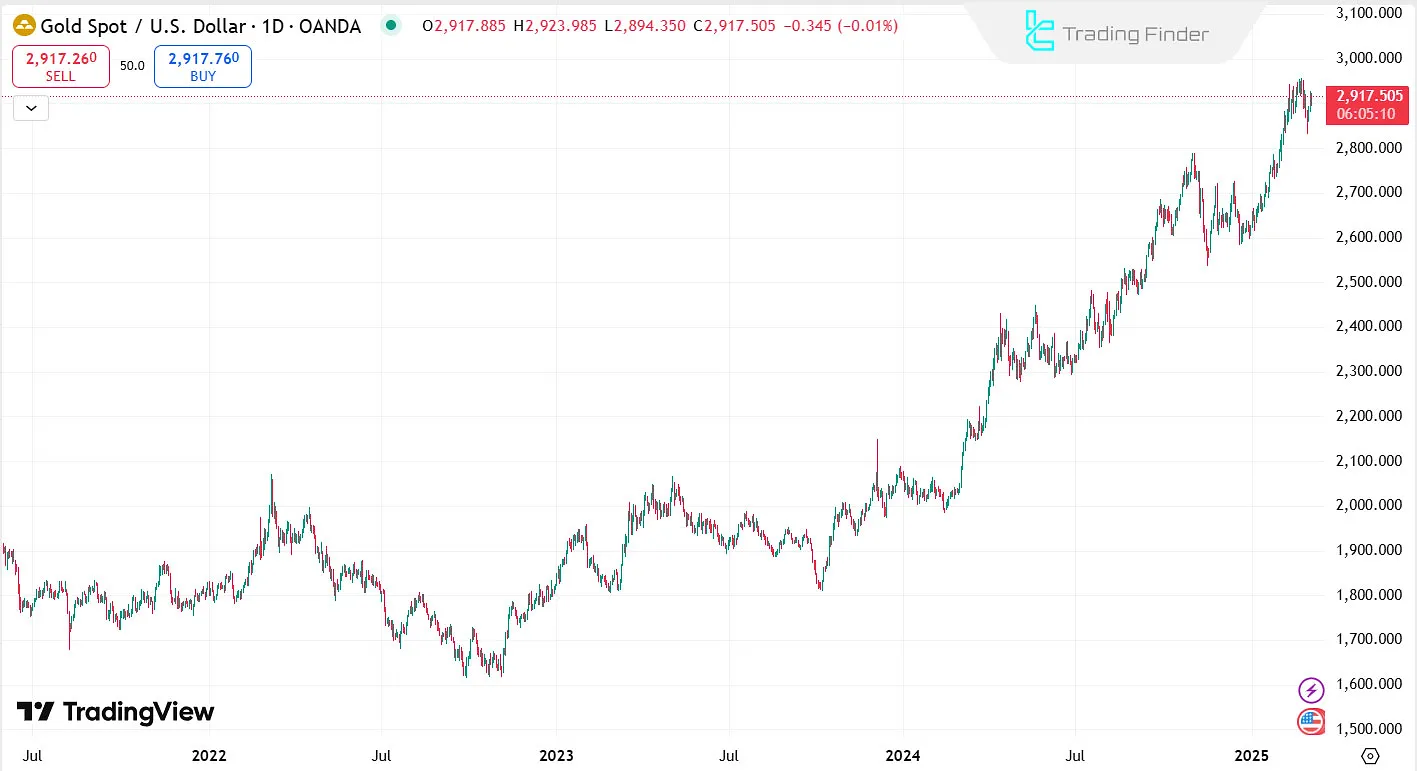
Gold's trend in 2023 and 2024 was driven by geopolitical tensions, proving that rising interest rates alone cannot determine the trend.
Introduction of the Forex Factory Calendar Indicator for Analyzing Interest Rate Changes in Financial Markets
The Forex Factory Calendar indicator on the MetaTrader platform serves as a critical macroeconomic intelligence interface for professional analysts and active traders.
It enabling precise monitoring of high-impact economic events that systematically influence global financial markets. This tool consolidates time-sensitive fundamental data into a structured release framework.
It allowing market participants to anticipate periods of heightened volatility and liquidity expansion across currency pairs, indices, commodities, and correlated assets.
By delivering comprehensive coverage of essential macroeconomic metrics such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth rates, labor market statistics including unemployment and participation rates, central bank policy decisions.
It interest rate announcements, and inflation indicators such as CPI and PPI, the indicator equips traders with high-quality fundamental inputs.
These inputs strengthen macroeconomic interpretation, enhance forecasting accuracy, and improve the alignment between fundamental analysis, market execution, and risk control frameworks.
Through real-time synchronization with scheduled economic releases, traders can align technical execution models with macro-driven volatility cycles.
This alignment enhances risk management calibration and optimizes trade timing across both short-term speculative strategies and long-term macro positioning.
By displaying economic events as vertical lines on the chart, this tool allows users to observe the impact of economic news on financial markets.
For example, the release of economic news related to the US dollar can have a significant effect on gold prices and various currency pairs.
The Forex Factory Calendar indicator also offers filtering capabilities across different trading symbols, allowing users to view only events related to specific currencies such as the US dollar or the euro.
In addition, after each news release, the indicator automatically removes the corresponding event line from the chart.
Other features of this indicator include customizable settings for different news impact levels, alert displays, and color configurations for news with varying degrees of importance.
This tool is considered a highly useful option for intermediate and advanced traders who seek in depth market analysis based on economic events.
- Download the Forex Factory Calendar indicator for MetaTrader 4
- Download the Forex Factory Calendar indicator for MetaTrader 5
Expectations of Interest Rate Changes in Forex
Currencies will strengthen if market participants expect an interest rate hike during the upcoming central bank meeting. Impact of Interest Rate Changes on Forex:
- Expectations of Rising Interest Rates: Strengthen the related currency and increase risk aversion in the market;
- Expectations of Falling Interest Rates: Weaken the related currency and increase risk appetite in the market.
Expectations of US interest rate changes can be viewed on the CME FedWatch Tool website.
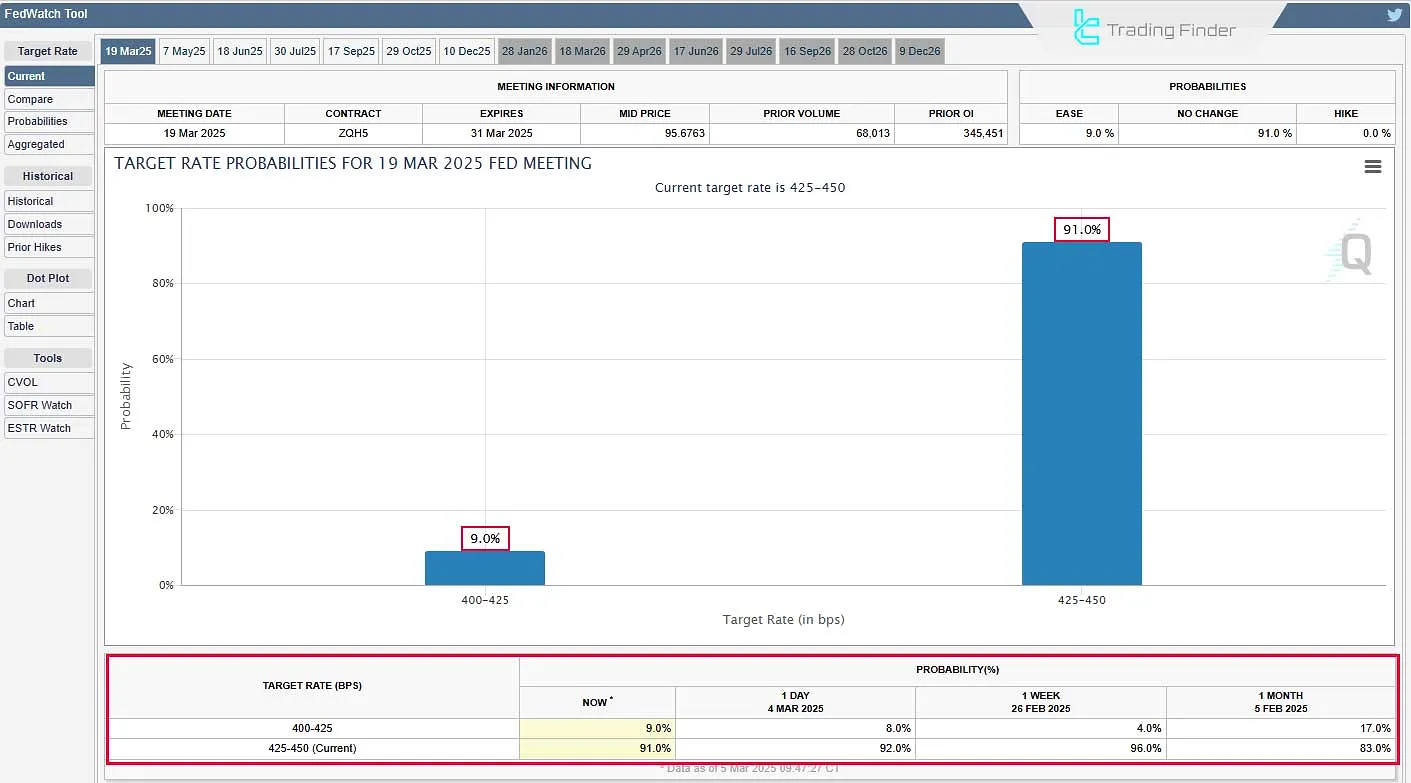
This image from the CME FedWatch Tool shows that, at this moment, 91.0% of the market expects interest rates to remain unchanged during the upcoming Federal Reserve meeting.
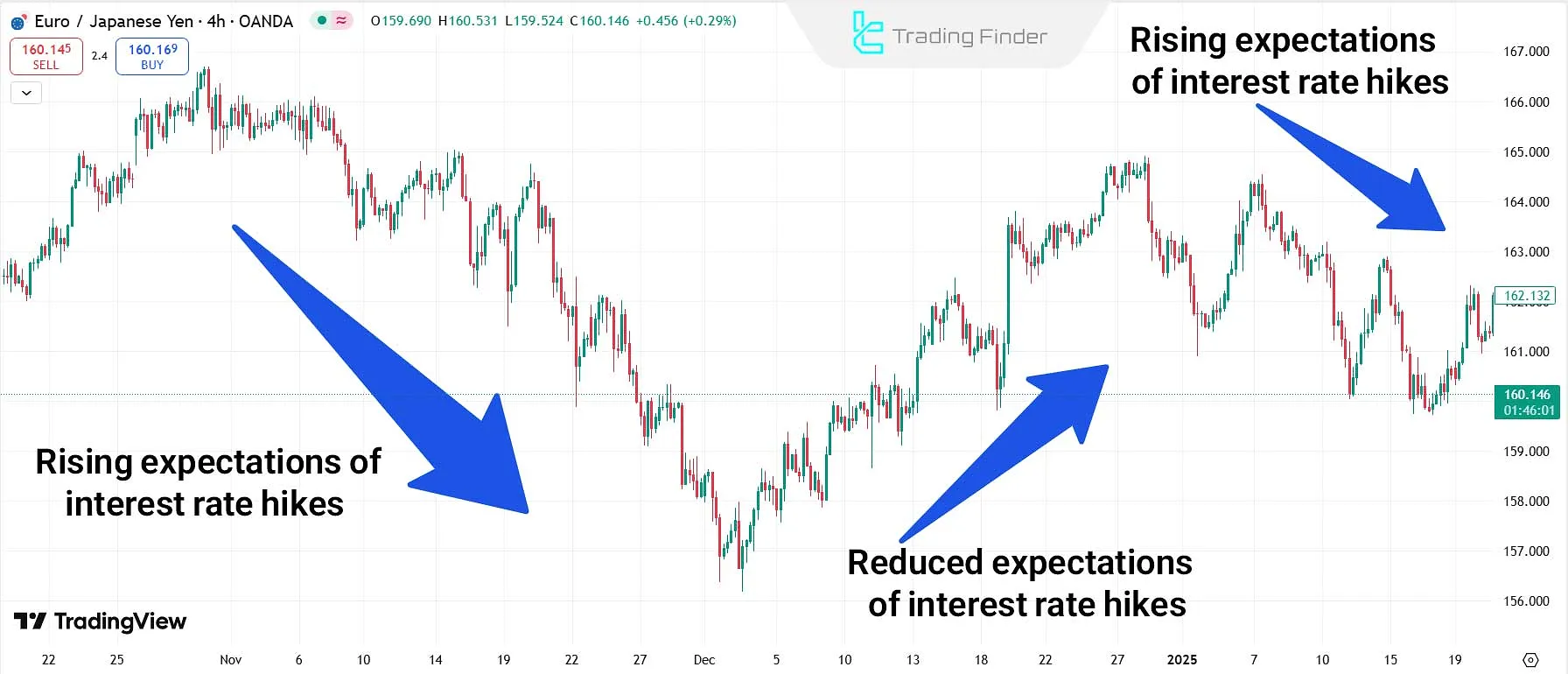
Example of the Impact of Interest Rate Expectations on the Market
As shown in the image below, with changes in market expectations for an interest rate hike by the BOJ (Bank of Japan), the Japanese yen has been significantly affected.
When the market expects an interest rate hike, the yen strengthens. However, when interest rates are expected to remain unchanged, the yen weakens.
Conclusion
Increasing interest rates limits economic growth by reducing liquidity and is a contractionary policy that strengthens currency.
Conversely, lowering interest rates increases liquidity, stimulates economic growth, and is an expansionary policy. This action leads to currency weakening.
By monitoring market expectations for interest rate changes, the direction of currency pairs can be predicted.













