Market makers refer to traders or financial entities such as central banks, large commercial companies and banks that significantly impact market trends with their massive capital. Individuals known as market makers are the main players in the market. With their high capital, advanced trading tools, and precise information, they steer the market in their desired direction.
Market makers, through the integration of market depth data, pending order structures, institutional open positions, and liquidity behavior, formulate price movement scenarios and then, by applying targeted pressure on order concentration points, liquidity zones, and stop loss clusters, organize order distribution at their desired levels.

The Role of the Market Maker in the Real Structure of the Forex Market
The real structure of the Forex market consists of a decentralized network of major banks, financial institutions, hedge funds, liquidity providers, and market makeranalysis, each of which plays a direct and active role in shaping price flow.
This dynamic structure, through continuous interaction among institutional participants, enables order distribution, risk transfer, and price formation at the interbank level, and coordinates the path of capital movement across all layers of the market.
Market makers operate at the core of this network and, by aggregating incoming orders from diverse sources including tier-one banks, institutional trading desks, ECN platforms, and the order flow of corporate clients, generate and adjust the market’s reference prices in real time.
This process is based on the analysis of market depth, supply and demand balance, pending order structure, and simultaneous management of trading portfolio risk, resulting in price formation that is reflected across all trading platforms such as MetaTrader, cTrader, and Trading View.
The Working Process of Market Makers
Market makers form the core of the price discovery process in the Forex market and, by simultaneously processing liquidity data, order behavior, and supply and demand balance, adjust the market’s price structure at every moment as follows:
- Setting bid and ask prices based on order depth and order flow;
- Managing order imbalance risk through hedging in the interbank market;
- Absorbing short-term volatility arising from supply and demand imbalance within the liquidity layer;
- Enabling the rapid execution of large orders without causing a breakdown in the price structure.
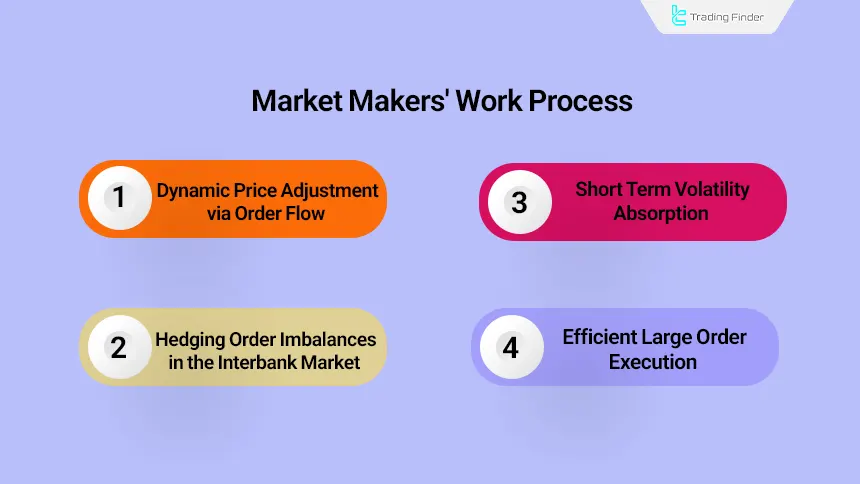
As a result of this mechanism, the prices that a retail trader observes in the trading environment are a direct reflection of the real time decisions, pricing algorithms, and risk management policies of market makers within the global Forex liquidity network.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Market Makers for the Forex Market
market makeralgorithm by playing a central role in liquidity provision and the architecture of price behavior, exert a profound impact on all layers of the Forex market, and their presence shapes trade execution pathways, risk distribution, and the price discovery process at the interbank level.
This structure simultaneously provides traders with a set of advantages and operational limitations as follows:
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Continuous liquidity provision | Manipulation of short term price structure |
Reduction of price slippage | Creation of liquidity traps |
Stabilization of price structure | Lack of transparency in execution decisions |
Ability to execute large orders | Increased complexity of price behavior |
Efficient shaping of the price discovery process | Efficient shaping of the price discovery process |
The Difference Between Market Makers and Broker Market Makers
The fundamental difference between a market maker and a broker market maker originates from the nature of their role, the level of influence in the market, the revenue model, and their position within the liquidity chain, and understanding this distinction is of vital importance for analyzing the real structure of the Forex market as follows:
Comparison Component | Market Maker | Broker Market Maker |
Position in market structure | Institutional participant at the macro layer of the interbank liquidity network | Trade executor at the retail layer of the market |
Primary role | Price architecture, price discovery, and systematic risk management | Managing the execution of retail traders’ orders |
Impact on price behavior | Direct and structural impact on price trends across all timeframes | Indirect impact limited to the level of order execution |
Pricing source | Price generation based on institutional order flow and interbank liquidity | Receiving and distributing prices from liquidity providers or dealing desks |
Operational capital | Extremely large and at the level of global banks and financial institutions | More limited and dependent on the broker’s business model |
Access to the interbank market | Direct access to tier one banks and liquidity providers | Indirect access through liquidity provision agreements |
Risk management | Managing order imbalances through hedging (Hedging) in the interbank market | Managing the risk of client positions at the internal broker level |
Counterparty to the trade | Rarely the direct counterparty of the retail trader | In many cases the direct counterparty of the retail trader |
Transparency of execution model | Processes and pricing algorithms are confidential and institutional | More transparent execution model and observable within client contracts |
Level of market influence | Very high and decisive in shaping market movement structure | Limited to the framework of interaction with retail traders |
Economic objective | Stabilizing liquidity flow and managing macro level financial system risk | Generating revenue from spreads, commissions, and managing client positions |
Short Term Price Structure Adjustment by Market Makers
Market makers, by continuously adjusting bid and ask prices based on order depth, order flow, and the condition of interbank liquidity, guide the path of capital movement across different timeframes.
This process causes price behavior to go beyond a simple reaction to supply and demand and transform into an engineered mechanism in which liquidity release, risk transfer, and the formation of accumulation and distribution phases are carried out with high precision.
Absorption of Volatility and Stability of Market Structure by Market Makers
From an operational perspective, market makers absorb short term volatility arising from order imbalances within the liquidity layer, neutralize volume shocks resulting from the entry of large orders, and enable the execution of large trades without the collapse of the price structure.
This performance preserves the behavioral stability of the market and prevents the formation of disorderly and destructive price movements.
Origin of Price Behavioral Patterns in Market Maker Logic
Price behavioral patterns such as liquidity sweep, stop hunts, the creation of imbalance zones, and the formation of structural reversal points originate directly from the execution logic of market makers.
Those interested in using market makeranalysis education in financial markets should use the educational video of the channel “One Minute Economics” on YouTube:
For this reason, advanced analytical approaches such as Smart Money Concepts and the ICT trading style interpret price behavior as a reflection of the coordinated decisions of market makers within the global Forex liquidity network.
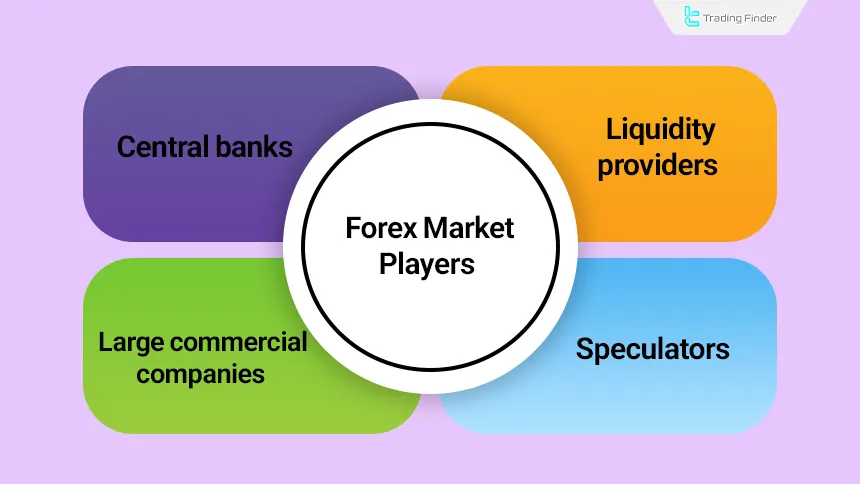
Who Are the Forex Market Players?
From central banks to retail traders with limited capital, every influential individual in the market is considered a player. Forex market players include:
- Central Banks
- Liquidity Providers
- Large Commercial Companies
- Speculators (Hedge Funds and Individual Traders)
Central Banks
Central banks significantly impact currency pair fluctuations by setting monetary policy and controlling liquidity levels.
For example, a contractionary monetary policy, such as raising interest rates, reduces liquidity, leading to currency strengthening. Traders can identify differences in monetary policies between two economies and trade the relevant currency pair.
However, central banks do not only influence the market through monetary policy; sometimes, they verbally or monetarily intervene to steer the market in line with their objectives.
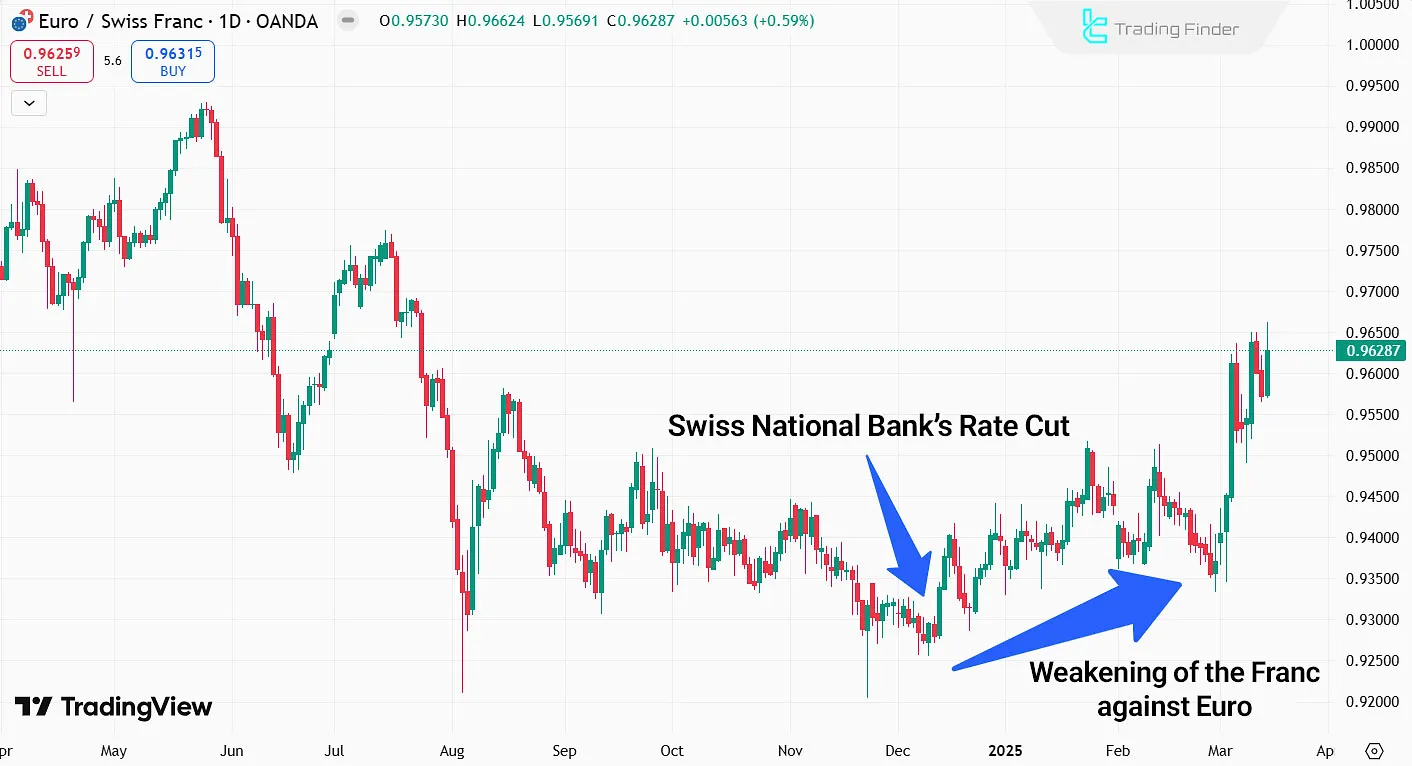
Example of of Central Banks Impact in Forex
For example, the Swiss National Bank, in order to prevent excessive strengthening of the Swiss franc and the intensification of recessionary risks and inflation reduction.
Publicly signaled monetary intervention in the market and, simultaneously with the implementation of an interest rate cut policy, directed the expectations of institutional participants toward a structured weakening of the franc.
This combined approach caused capital flows, speculative positions, and liquidity behavior in the interbank market to rapidly align with the policymaker’s objective, resulting in the weakening of the franc in accordance with the central bank’s macro strategy.
This example clearly demonstrates that macro players such as central banks, acting as institutional market makers.
Through the use of monetary policy tools, strategic communications, and expectations management, not only alter the path of exchange rates but also redesign the entire architecture of price behavior on a global scale.
Large Banks and Liquidity Providers
Large banks and liquidity providers (Liquidity Providers) are market makers who engage in currency buying and selling as part of market-making activities. Their activities (in terms of orders) can be observed in COT reports.
Continuous high-volume trading allows them to earn significant income from the spread (difference between the Bid and Ask prices).
Banks and liquidity providers, by offering Bid and Ask prices, engage in market making and influence short-term market fluctuations.
Electronic Liquidity Providers (ELPs)
Electronic Liquidity Providers use artificial intelligence and complex trading algorithms to inject liquidity into financial markets.
These liquidity providers use automated algorithms to execute orders in the market; Algorithms continuously scan prices and place orders based on market conditions. Methods of income generation for electronic liquidity providers:
- Spread: The difference between buy and sell prices;
- Arbitrage between market maker broker: Profiting from price differences of an asset across different brokers;
- Receiving market-making fees from various brokers.
Large Commercial Companies
Transactions by large commercial companies drive changes in exchange rates. For example, the American company Apple needs to convert Dollars to Yuan to purchase raw materials from China.
In this transaction, Dollars are sold, and Yuan are bought, thereby it reduces the Dollar's value against the Yuan.
Companies also, through hedging operations, ensure that exchange rate fluctuations do not affect their profitability.
Hedging operations in commercial companies are as follows:
- Entering into forward contracts
- Options contracts
- Buying or selling in the spot market
- Futures transactions
Introduction of the Market Maker Model indicator
The Market Maker Model indicator is considered one of the advanced analytical tools for professional traders in financial markets, designed with a focus on market maker execution logic, price movement structure, and liquidity flow.
This indicator helps traders understand real price behavior beyond the surface level fluctuations of the market.
The core of the "MMXM" functionality is built upon the analysis of "Buyers" and "Sellers" behavior, the identification of liquidity zones, and the detection of structural market changes.
The indicator, by integrating key Smart Money concepts and patterns such as "FVG", "CHoCH", and "CISD", accurately plots them on the chart.
After the occurrence of "CHoCH" and the return of price to the "FVG" zone, if structural conditions are aligned, the indicator displays entry signals in a simple and visually understandable manner.
Also, when price collects liquidity by moving beyond specified levels, important zones are marked with purple arrows, indicating a change in the behavior of the main market participants.
- Download the Market Maker Model indicator for MetaTrader 4
- Download the Market Maker Model indicator for MetaTrader 5
In the bullish scenario, the indicator first identifies a bullish "FVG" on the higher timeframe. After price enters this zone and "CISD" occurs, the liquidity sweep process is completed, and with the closing of the confirmation candle, an appropriate buy position is introduced to the trader.
In the bearish scenario as well, after the formation of a bearish "FVG" and the occurrence of a valid "CHoCH", the return of price to this zone provides the conditions for issuing a sell signal.
The structure of the indicator settings is flexible and includes features such as displaying higher timeframe zones, managing chart color schemes, and the simultaneous display of breakouts.
Speculators (Individual Traders)
This group constitutes about 90% of trading volume and significantly impacts market fluctuations; Their goal is not hedging or commercial trading but identifying market trends through analysis to profit.
These traders, using their individual analyses, identify the market’s movement structure and align capital flow toward achieving returns.
As a result, their collective behavior becomes one of the key components in the formation of short term volatility and price behavioral cycles in the Forex market.
Hedge Funds
Hedge funds are forex market makers and are known as "smart money"; With their very high capital, algorithmic tools, and advanced technical analysis, they determine short-term market trends; their order directions can be tracked through COT reports on Tradingster.
For more information about market makers in financial markets, you can also use the Market maker education article on the website solutionshub.epam.com.
Market Maker Strategy
The Market Maker strategy is formed based on understanding the behavior of market makers and the method of liquidity distribution within the market structure. This approach, by focusing on patterns such as "Liquidity Sweep", "Stop Hunt", and "Imbalance Zones", identifies the real logic behind price movements.
In this strategy, price movement is interpreted not based on indicators, but as a reflection of the coordinated decisions of major market participants. Aligning trades with the macro liquidity flow is considered the core of decision making within the Market Maker style.
Understanding this structure makes the precise identification of entry and exit points possible under different market conditions.
Impact of Retail Traders on Liquidity Structure
Retail traders, by using fundamental analysis, technical analysis, sentiment analysis, and macroeconomic data, identify the dominant market directions and structure their trading decisions based on this analytical framework.
The widespread presence of this group at the retail layer of the market generates a continuous volume of order flow, which leads to an increase in the market’s nominal liquidity and strengthens the apparent depth of the order book.
Although this massive flow of retail orders does not possess the power to determine the price structure at the macro level, it acts as short term fuel for price movement and provides the necessary conditions for the execution maneuvers of institutional participants and market makers.
Conclusion
Central banks, liquidity providers, commercial companies, banks, hedge funds, and retail traders are the forex market players. Liquidity providers and hedge funds act as market makers, and market trends can be identified by tracking their orders.
Additionally, central banks influence the market through monetary policy, commercial companies through hedging operations, and hedge funds through profit-seeking activities.













