Harmonic patterns, based on Fibonacci ratios, are among the tools used in technical analysis. The ABCD pattern and the Three-Drive pattern are two harmonic patterns that can be used to identify reversal points and trend continuation signals.
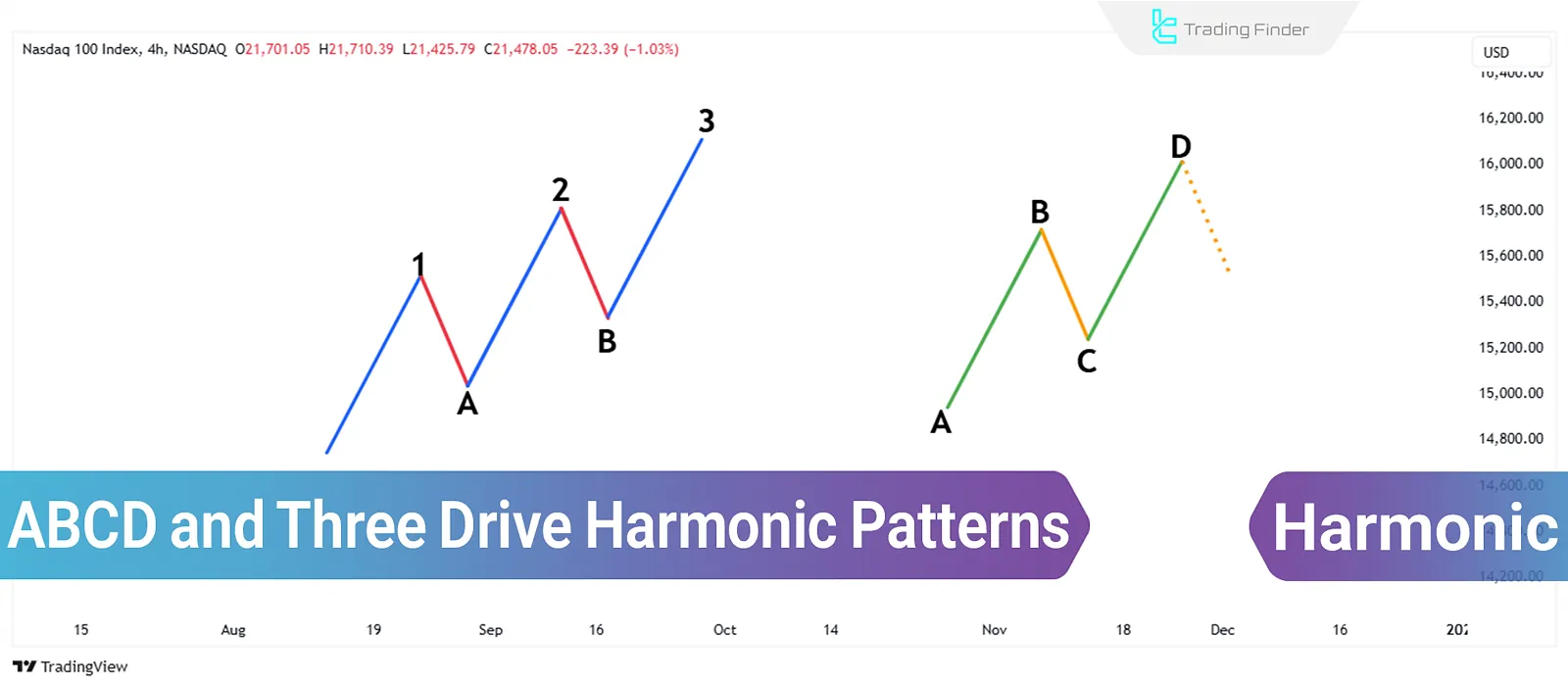
What is the ABCD Pattern?
The ABCD pattern is one of the most basic harmonic patterns. It consists of four main points:
- Two price movements (AB and CD)
- One corrective wave (BC)
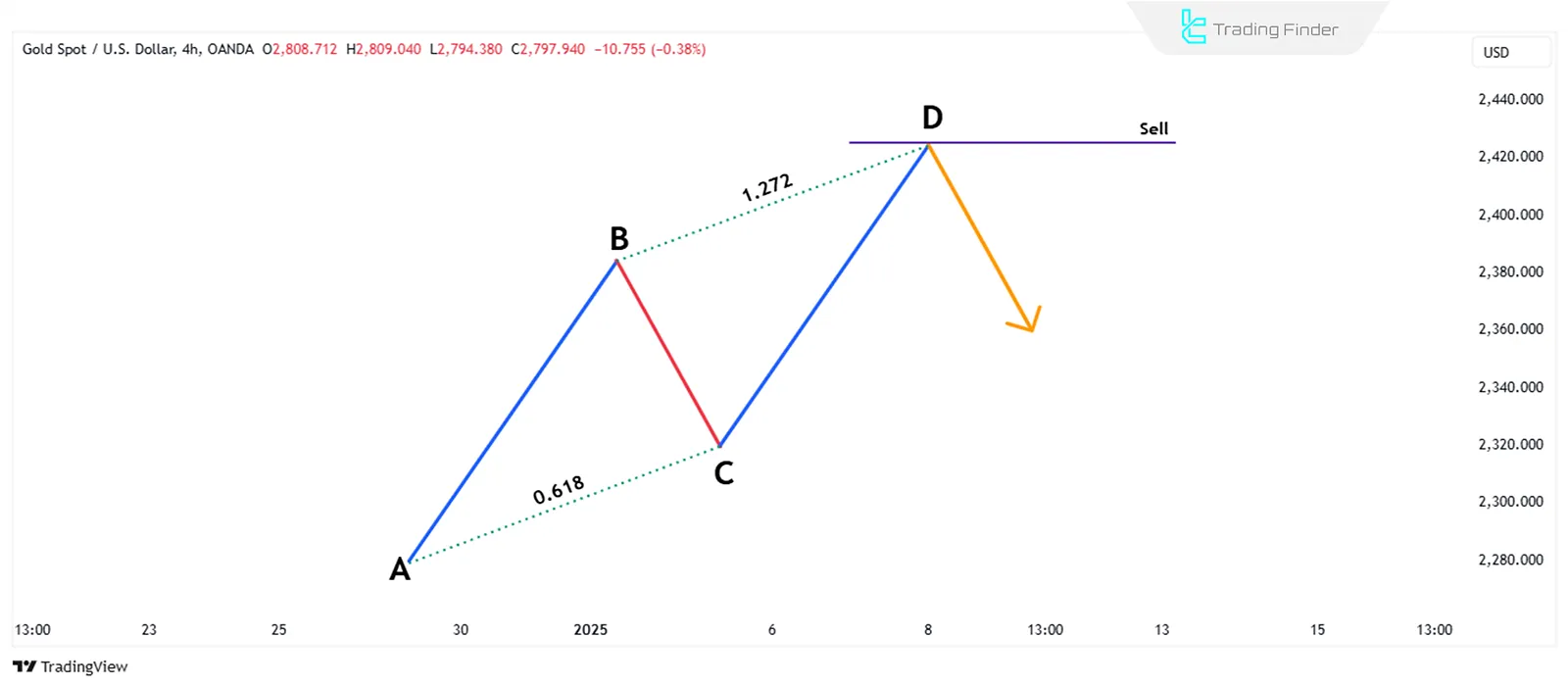
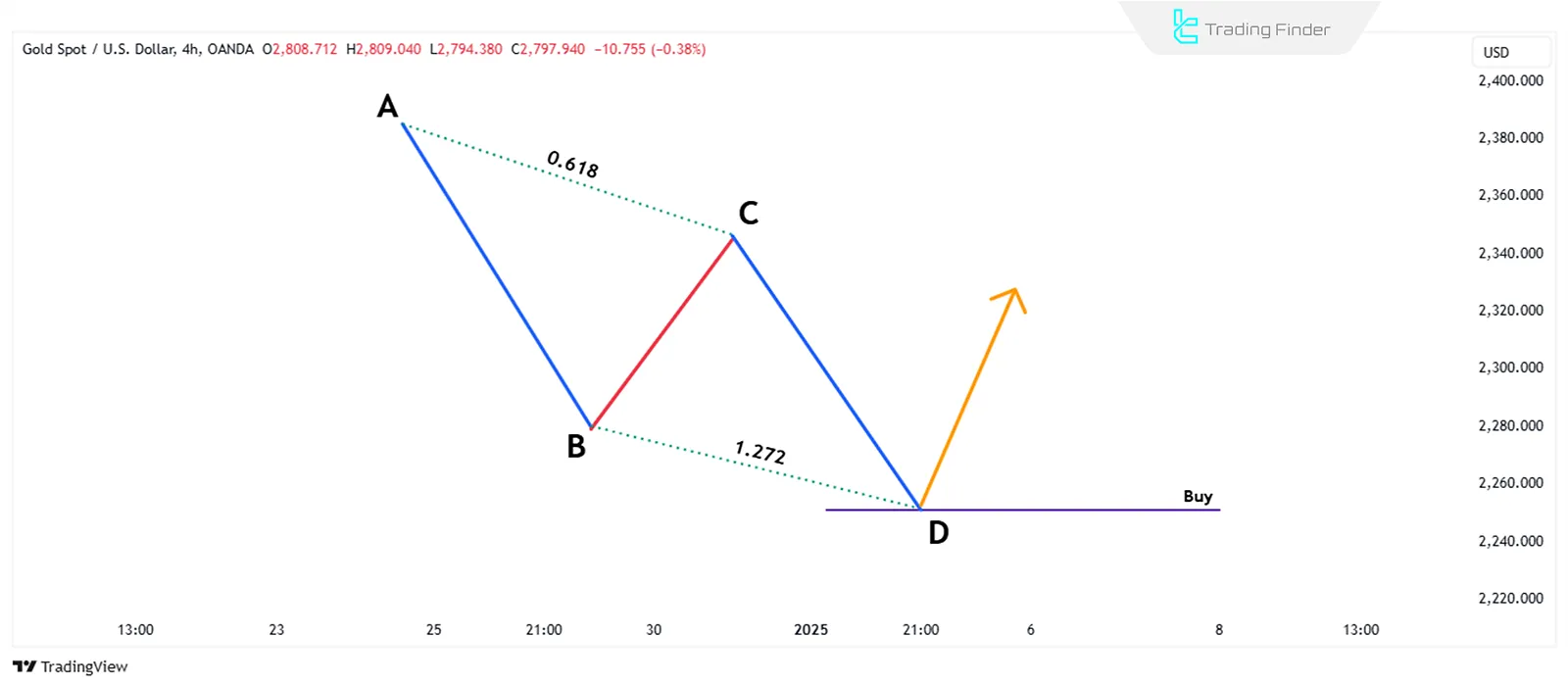
Using Fibonacci tools is essential to detect this pattern. In this pattern, the BC correction should extend to the 0.618 level of the AB wave, and the CD wave should continue to the 1.272 Fibonacci extension of the BC correction.
You can use Trading Finder's indicators to make working with the ABCD pattern easier:
When does the ABCD pattern form?
The ABCD Harmonic pattern is valid when the following conditions are met:
- The length of the AB wave should be equal to the length of the CD wave;
- The time taken for price movement from A to B should be equal to the time taken for price movement from C to D;
- The entry point into the trade is determined after the pattern is completed and the price reaches point D.
To simplify the use of the Three Drives pattern, you can use the indicators provided by the Trading Finder collection:
Three Drives Indicator for TradingView
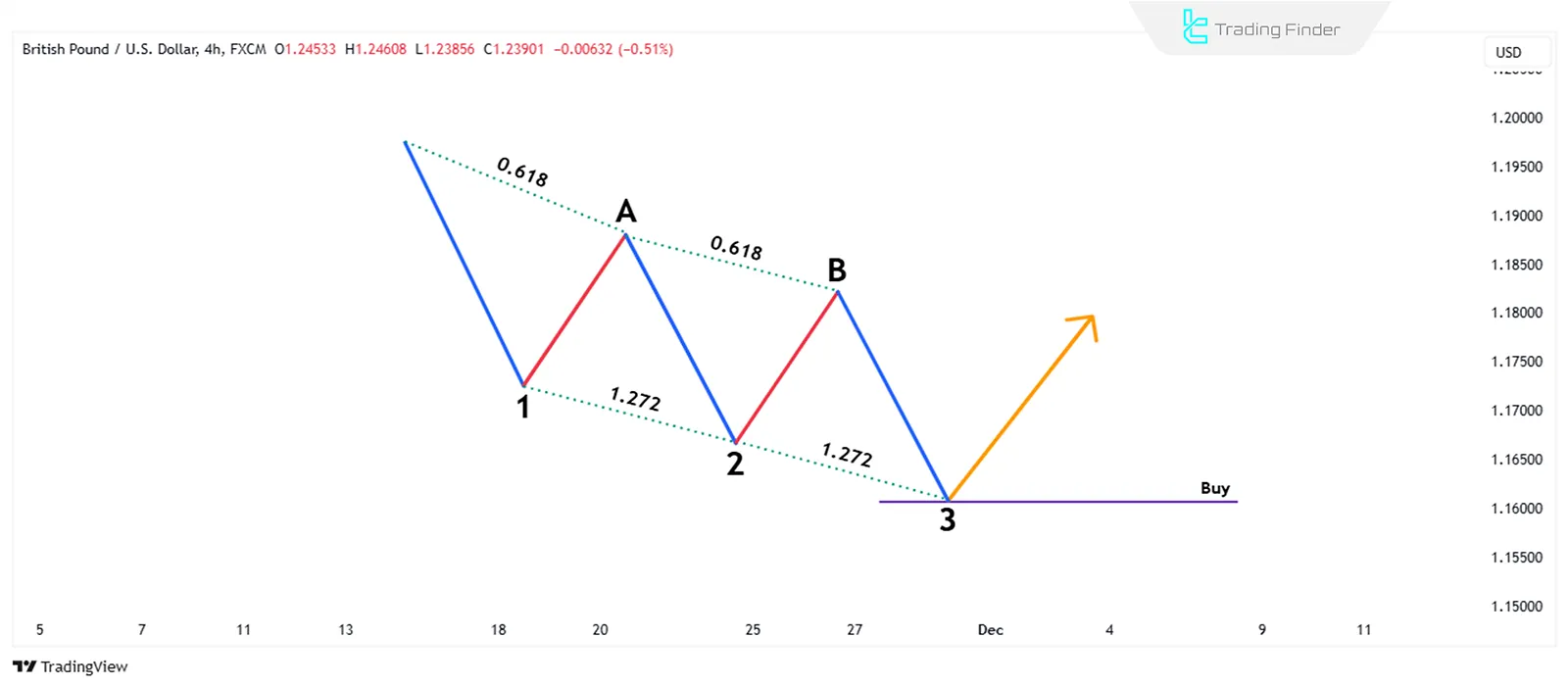
What is the Three-Drive Pattern?
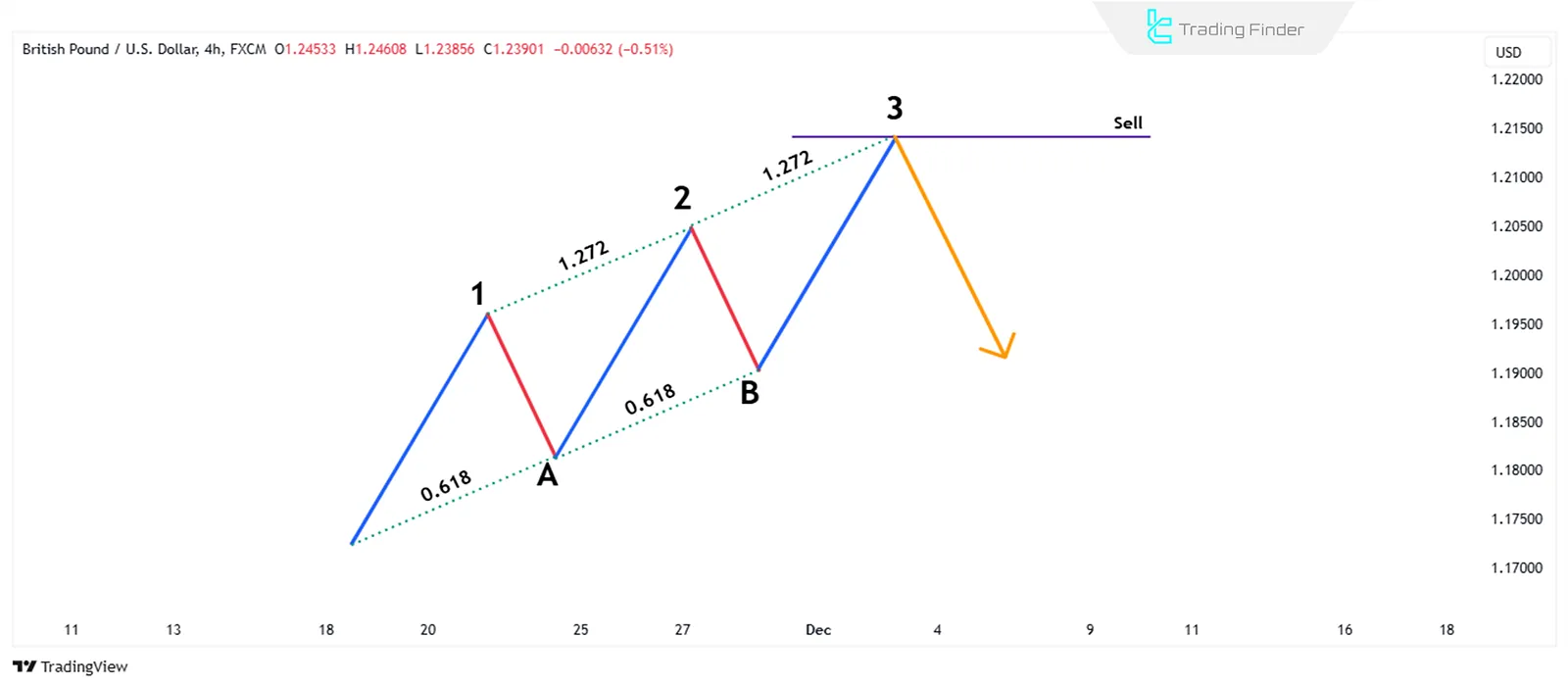
Although the Three-Drive pattern shares many similarities with the ABCD pattern, it has three price movements (Drive 1, Drive 2, and Drive 3) in alignment, with two corrective waves, A and B, formed between them.
This pattern resembles the Elliott Wave's five-wave structure and can predict future price movements.
In this pattern, point A must be at the 0.618 corrective level of the first wave, and point B should be at the 0.618 corrective level of the second wave.
The second wave must extend to the 127.2% Fibonacci extension of the A correctio; The third wave should extend to the 127.2% Fibonacci extension of the B correction.
When does the Three-Drive pattern form?
The Three-Drive Harmonic pattern will be valid when the following conditions are met:
- The time required to complete the second wave must equal the time required to complete the third wave;
- The time for the A correction should be equal to the time for the B correction;
- The entry into the trade occurs after the pattern is completed and the price reaches the final point of Drive 3.
Conclusion
The ABCD and Three-Drive harmonic patterns are some of the most important harmonic patterns in technical analysis. They help identify potential price reversal points using Fibonacci ratios.
Following the necessary conditions to validate these patterns and using tools like Fibonacci levels correctly enhances their accuracy.













