Some currencies have positive or negative correlations with other assets due to their risk-on or risk-off nature. Currency correlation and its underlying reasons are vital for risk management, avoiding overexposure, swing trading, and other strategies.
Understanding this relationship allows traders to avoid unintended risk accumulation across multiple similar positions and, by relying on negative correlation, keep overall trade risk under control-especially in swing trading and capital management.
On the other hand, the intelligent use of negative correlation can serve a heding role within a trading portfolio and help maintain risk balance during volatile market conditions.

What Is Currency Correlation in Forex?
In the Forex market, currencies like AUD and NZD share similar characteristics and often move together. Thus, currency pairs may exhibit similar or opposite price movements. This synchronization or divergence is called correlation.
Example of Currency Correlation in Forex
For instance, when AUD/USD is bullish, NZD/USD is also likely to rise, as the drivers of AUD and NZD are highly similar.
This positive correlation between AUD/USD and NZD/USD mainly stems from the similar economic structures of Australia and New Zealand, both currencies’ reliance on commodity markets, and their high sensitivity to global risk sentiment.
As a result, changes in commodity prices, Chinese economic data, or the overall financial market environment often affect both currency pairs simultaneously, causing their price movements to align across many time periods.
Understanding Currency Nature to Grasp Pair Correlation
Currencies with similar natures tend to move alike, and trading them simultaneously in the same direction is high-risk. ForexCurrency Characteristics:
Risk-On Currencies | Risk-Off Currencies | Neutral Currencies |
AUD | JPY | EUR |
NZD | USD | GBP |
CAD | CHF | – |
From this table, during risk-off market conditions (strengthening of safe-haven currencies), the CAD/CHF pair may correct while USD/CAD trends upward.
These pairs often have a negative correlation coefficient and move in opposite directions.
Volatility in Correlated Currency Pairs
In the above example, If SNB turns dovish Stance while the Fed stays hawkish (assuming strong U.S. GDP rate growth), USD/CAD's rise could outweigh CAD/CHF's fall.
In such conditions, differences in monetary policy orientation disrupt the balance of volatility between correlated currency pairs, causing one pair to react more strongly.
As a result, the intensity of price movement increases in currency pairs whose base or quote currency is directly affected by the stronger monetary policy. This can lead to volatility asymmetry and increased hidden risk when trading correlated pairs simultaneously.
An educational video on the Trader Nick YouTube channel explores correlations on price charts across different instruments and explains how to apply them within trading strategies, offering strong value for multi-market analysis.
What Is the Correlation Coefficient?
The correlation coefficient between two instruments is expressed numerically as a value between 1 and −1; in fact, the correlation coefficient determines both the strength and the direction of positive or negative correlation between currency pairs.
- Correlation coefficient +1: Perfect positive correlation - the assets move identically;
- Correlation coefficient 0: No correlation - the assets have no linear relationship;
- Correlation coefficient −1: Perfect negative correlation - the assets move inversely.
For example, the correlation coefficient between NZD/USD and AUD/USD in February 2025 was +0.94, indicating a strong positive correlation.
To analyze forex pair correlations, use TradingFinder’s Forex Correlation Tool. In the currency correlation table below, the relationships between major currencies are examined:
First currency pair | Second currency pair | Correlation type | Approximate correlation coefficient | Analytical explanation |
EUR/USD | GBP/USD | Strong positive | +0.75 to +0.90 | These two currency pairs often move in the same direction due to their high dependence on the U.S. dollar and the close economic conditions of Europe. |
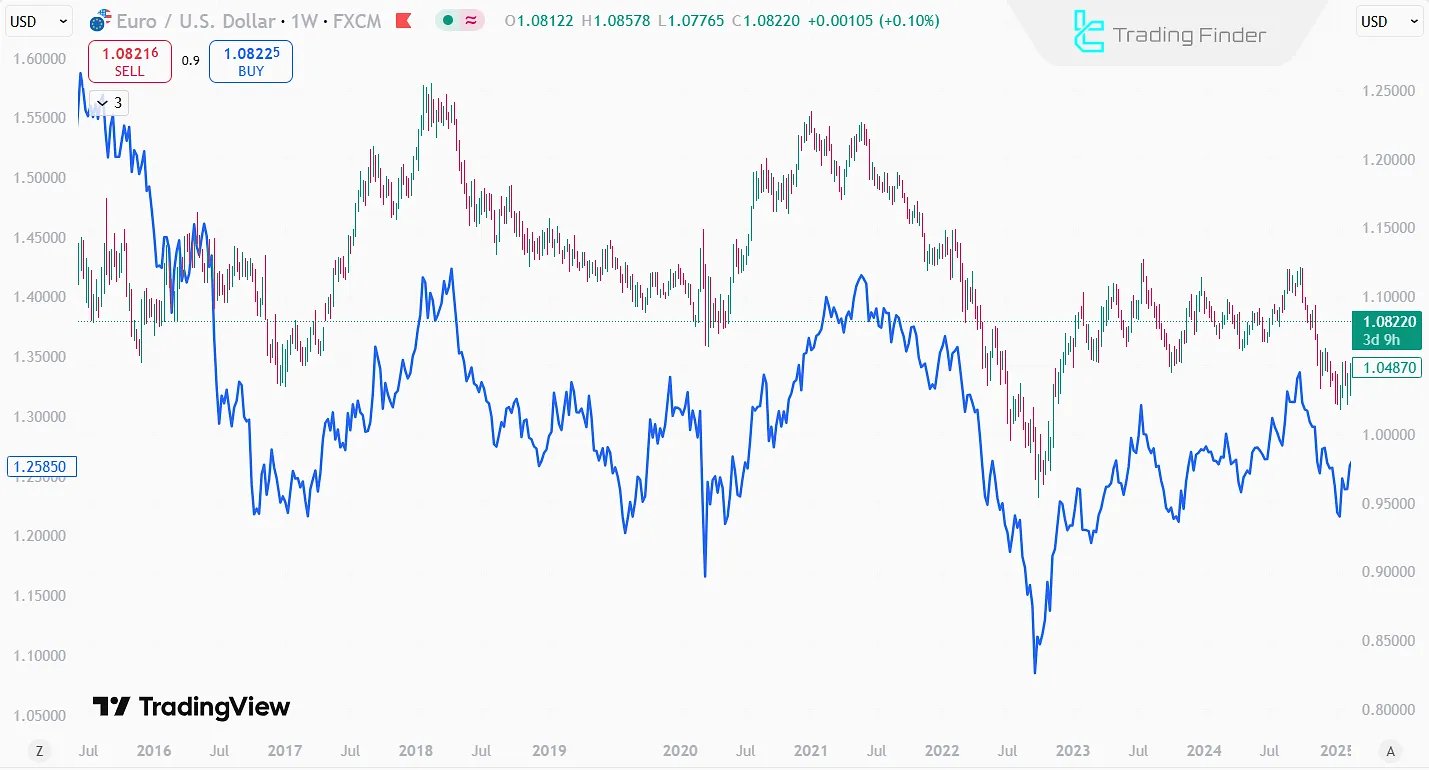
EUR/USD | USD/CHF | Strong negative | −0.80 to −0.95 | Since the Swiss franc usually acts as a safe-haven asset, its movement is often opposite to that of the euro. |
GBP/USD | USD/CHF | Medium to strong negative | −0.65 to −0.85 | These pairs are both influenced by the U.S. dollar, but differing reactions of the pound and the franc create negative correlation. |
AUD/USD | NZD/USD | Very strong positive | +0.85 to +0.95 | Similar economic structures, commodity dependence, and geographic proximity cause these two pairs to move almost in the same direction. |
AUD/USD | USD/CAD | Medium negative | −0.50 to −0.70 | Differences in the types of commodities influencing the Australian and Canadian economies lead to relatively inverse behavior between these pairs. |
EUR/USD | AUD/USD | Weak to medium positive | +0.30 to +0.55 | Although both pairs are traded against the U.S. dollar, differences in fundamental drivers reduce the strength of correlation. |
USD/JPY | EUR/USD | Weak to medium negative | −0.30 to −0.55 | Differences in monetary policy and the role of the yen as a safe-haven asset cause these two pairs to often fluctuate in opposite directions. |
GBP/USD | AUD/USD | Weak positive | +0.20 to +0.45 | Shared influence of the U.S. dollar creates some correlation, but the independence of base economies prevents strong correlation. |
Correlation of Currencies with Gold, Oil, and the Dollar Index
Correlation in the forex market extends beyond currency pairs, and major currencies maintain structural links with commodities and financial indices.
Understanding these connections clarifies capital flow paths and enables multi-layered analysis in active trading.
- S. dollar (USD): Usually has an inverse relationship with gold; dollar strength often leads to gold decline, while dollar weakness supports gold growth;
- Canadian dollar (CAD): Directly correlated with crude oil; rising oil prices often strengthen CAD and exert downward pressure on USD/CAD;
- S. dollar index (DXY): Provides an overall view of dollar strength or weakness and determines the dominant direction of dollar-based currency pairs.
For a deeper understanding of correlation structures, studying the specialized article on currency pair correlation training on the investopedia.com website is recommended as a reliable educational reference.
The Role of Currency Correlation in Risk Management
If the nature of and relationships between currency pairs are not properly understood, a trader may be exposed to higher risk.
Ignoring currency correlations can cause a trader to unknowingly open multiple positions with similar risk, effectively underestimating the true risk exposure of the account.
Understanding currency behavior and pair correlations helps structure trades to reduce risk concentration and manage portfolio volatility across market conditions.
Example of Unintended Risk Exposure
EUR/USD and GBP/USD are highly positively correlated. If a trader opens simultaneous sell positions on both, they face amplified risk because a fundamental factor (e.g., a strong U.S. economic report) could weaken both pairs.
In essence, buying 1 lot of EUR/USD and 1 lot of GBP/USD is similar to buying 2 lots of EUR/USD
Currency Correlation and Hedging
Traders can mitigate risk by leveraging currency correlations and market sentiment.
For example, during geopolitical tension (risk-off), a trader might long gold and CHF while opening a position in a risk-on asset to balance exposure.
When Should Correlation not be Trusted?
Despite the wide application of correlation, this concept is not reliable under all conditions, and in certain situations, disregarding it is a more logical decision. Ignoring these limitations can lead analysis off the correct path.
In low-volume and low-volatility markets, price movements are often random in nature, and the correlation structure loses its coherence. In such environments, relying on past relationships does not provide an accurate picture of market behavior.
During unexpected political or economic shocks, previous correlation patterns also lose their validity, as capital flows shift suddenly and market reactions deviate from normal logic.
If correlation is used as a substitute for technical or fundamental analysis, the likelihood of entering low-quality trades increases. Correlation should always be used alongside the main strategy and serve a complementary role.
Differences in Currency Correlation Across Different Timeframes
One common mistake among traders is viewing currency correlation as static, whereas this relationship is dynamic and changes with different trading timeframes.
On short-term timeframes such as 5-minute and 15-minute charts, sudden news events and emotional market reactions weaken or even eliminate correlation structures. In this environment, scalpers should not base decisions on long-term correlations.
On higher timeframes such as 4-hour and daily charts, correlations are more stable and are shaped by fundamental factors and capital flows. These conditions allow swing traders and position traders to rely more accurately on these relationships when analyzing and executing trades.
Common Mistakes in Using Correlation
Despite the importance of correlation in forex market analysis, misinterpreting this concept increases risk and distorts trading decisions.
Many traders enter trades without a proper understanding of the nature and limitations of correlation and ultimately experience a decline in trading performance. The most common mistakes in using correlation include the following:
- Opening multiple same-direction trades on currency pairs with strong positive correlation, assuming risk is diversified, while in reality overall risk exposure increases;
- Relying on outdated correlation data and coefficients, even though relationships between currencies change as market structure evolves;
- Using correlation as the primary entry signal, whereas its correct role is as a confirmation tool alongside technical and fundamental analysis.

Currency Pairs Correlation Indicator for MetaTrader
One of the practical analytical tools on the MetaTrader platform is the Currency Pairs Correlation Indicator, which is designed to analyze behavioral relationships between assets and guide traders toward more informed decision-making in financial markets.
Instead of focusing on issuing buy or sell signals, this indicator emphasizes market structure analysis and risk management, which is highly important for many professional traders.
The operating mechanism of the correlation indicator compares the currency pairs defined in the settings with the active chart symbol and displays their correlation levels across two key timeframes: the one-hour (H1) and daily periods.
This multi-timeframe approach allows traders to gain both short-term and medium-term perspectives on asset behavior.
One of the key features of this tool is the Correlation Limit parameter, which is set to 70 by default. When the correlation value exceeds this level, the indicator highlights it in red, signaling strong directional alignment between assets.
Lower values are shown in green, indicating weaker or more independent correlation. This color distinction warns traders that opening simultaneous positions on highly correlated assets can result in compounded risk.
In the settings section, full customization is available. Traders can define up to three different currency pair lists (PairList1, PairList2, and PairList3), adjust the number of candles used in correlation calculations (Length_Calculation), and set the interval between recalculations (Calculation_Interval) according to their strategy.
This flexibility makes the indicator suitable for various trading styles, including scalping, day trading, and swing trading.
The currency pairs correlation indicator is applicable across multiple markets such as forex, cryptocurrency, stocks, commodities, and indices, and it is also understandable and usable for beginner traders.
Alongside this tool, traders can also use the online currency pair correlation display tool available on the Trading Finder website to gain a more comprehensive view of relationships between assets.
Conclusion
Understanding currency correlation is key for hedging, risk control, and strategies like swing trading. Currency pairs with positive correlations tend to move in the same direction, so opening positions on both simultaneously increases risk exposure.
In medium- and long-term trading strategies, currency correlation is considered a key variable in designing risk structures and hedging frameworks.
High positive correlation between currency pairs creates “hidden cumulative risk” meaning that several seemingly independent positions are, in practice, tied to a single underlying risk factor.
Therefore, correlation analysis plays a decisive role not only in selecting appropriate currency pairs, but also in position sizing, building a balanced trading portfolio, and executing effective hedging. It enables traders to manage account volatility in a structured and controllable manner.













