Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the main measure of economic growth, showing whether the economy is in a boom or a recession. Central banks use this concept to set monetary policies.
Moreover, traders can use GDP and its calculation method to assess and identify whether the economy is experiencing a boom or recession.
This concept is also applied in economic inflation analysis, labor markets, monetary policies, and financial markets.

What is GDP?
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the total value of all final goods and services produced in a countrythin a specific time frame.
GDP is one of the most important production indicators and a key measure of economic growth.
Key Points in Calculating GDP
Certain goods (including housework, charitable services, and illegal goods) are not included in GDP calculations. Only the value of final goods is considered in GDP.
Calculation of Final Goods Value
To prevent double-counting, only the value of final goods is included in GDP calculations.
For example, if the price of flour is counted separately in GDP when making bread, and then the price of the bread (the final product) is included again, the value of flour is counted twice.
This repetition leads to a decrease in the accuracy of the statistics.
Importance of Borders in GDP
Borders matter in GDP; only goods produced within the country are included. For instance, consider Apple, an American company.
If Apple produces a product in China, the value of the product produced will be counted in China's GDP!
Exclusion of Certain Productions in GDP
Goods produced and traded illegally (such as drugs), second-hand goods, securities, and housework or charitable activities are not included in GDP.
What is GNP and How Does it Differ from GDP?
Gross National Product (GNP) includes the total value of goods produced by companies owned by the citizens of a country.
For example, if Nike produces goods in China, the final value of the products will be included in the U.S. GNP.
Similarly, investments made by citizens outside the country will be included in the GNP. The formula for calculating GNP is shown below:

Difference in Concept
The primary difference between GDP and GNP lies in the goods included in their calculations. In GDP, borders matter, and only goods produced within the country are considered, regardless of nationality.
However, nationality is important in GNP, and all national goods, regardless of where they are produced, are considered.
Difference in Function
GDP is mainly used to assess economic activity (whether in a recession or a boom), while GNP indicates the degree of dependence and profit a country gains from foreign resources.
Thus, if a country focuses more on foreign investment, it will likely to have a higher GNP than GDP. However, if the country is dependent on foreign investment, its GDP will likely be higher than its GNP.
How is GDP Calculated?
Since GDP only accounts for the value of final goods and services (excluding intermediate goods), there are three methods for calculating GDP:
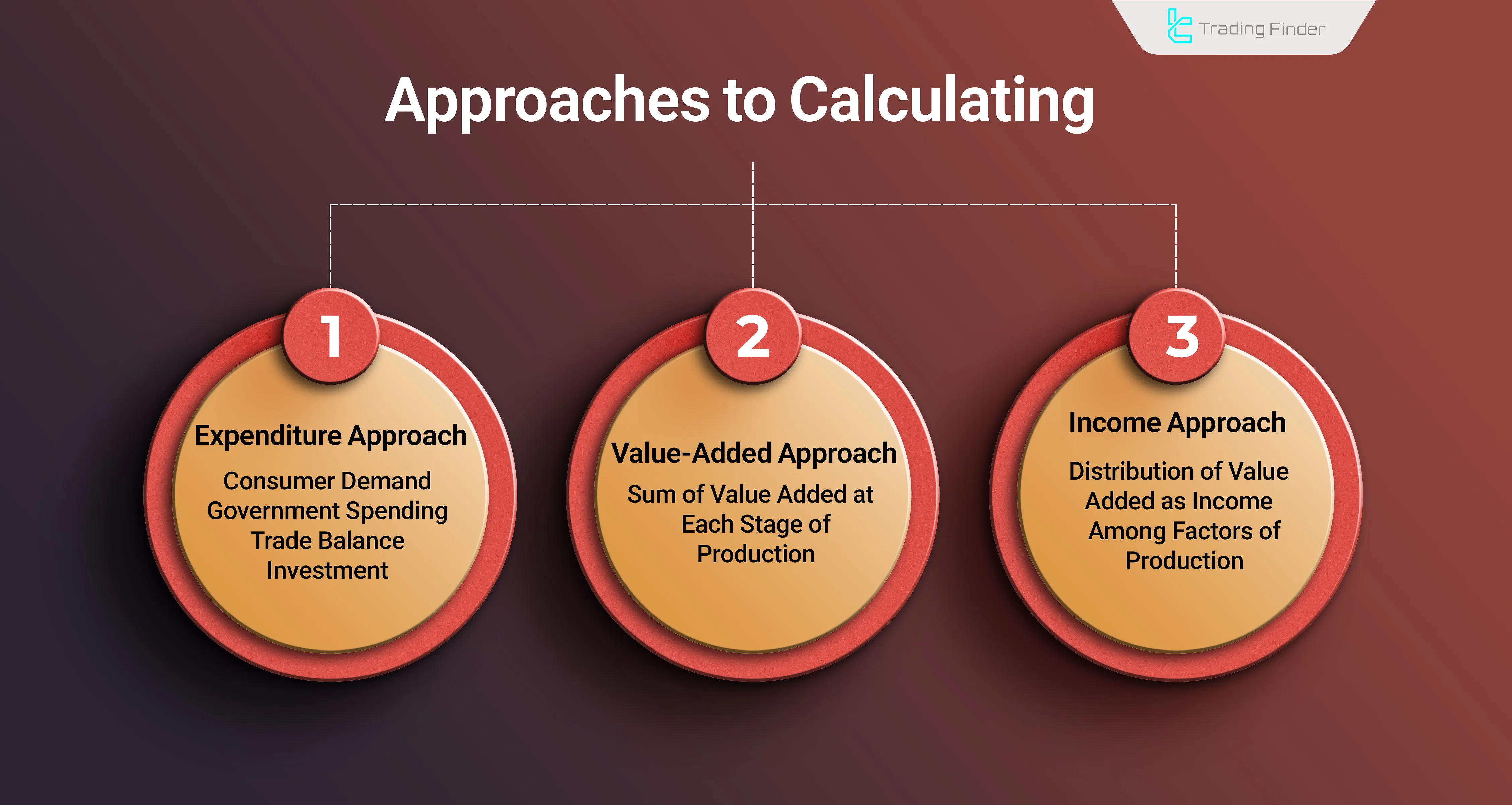
Expenditure Approach
Four components in the expenditure approach influence GDP. This method is the most common and widely used for calculating GDP.
This formula is based on classical economic theory, which assumes that all goods produced in the economy are consumed.
Therefore, according to this theory, the value of produced goods can be derived from the total expenditure by consumers, the government, and investments.
In other words, four factors are considered in the GDP calculation formula:

- Consumer Expenditures: The amount households spend on goods and services;
- Government Expenditures: The amount the government spends on public services and benefits;
- Investment in Production: The costs spent on capital goods and investments in production;
- Trade Balance: The net value of imports and exports.
Value-Added Approach
In this approach, the value added at each production stage is summed up. In this method, the full value of goods produced without intermediates is considered in GDP.
Finally, by summing up the value added at each production stage, the price of the final product is determined.
Income Approach
The added value of production is distributed as income among production factors. Therefore, the total income can be used to calculate the added value or the total value of goods produced.
Gross Domestic Income (GDI) reports can be used to track income distribution flow, identifying the sectors of the economy with the largest share of production.
What is Negative Economic Growth?
If GDP is lower in the current period compared to the previous period, the economy is experiencing negative economic growth.
The formula for calculating the economic growth rate is:
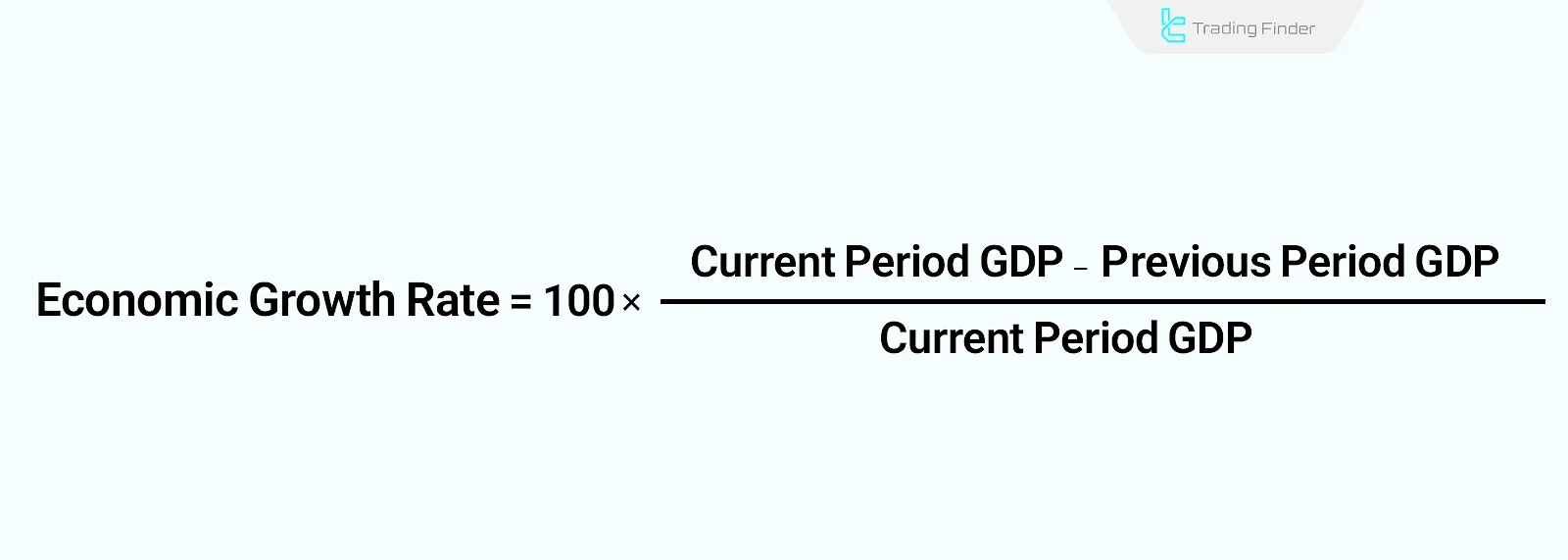
According to this formula, if the GDP of the current period is less than the previous period, the economic growth rate will be negative.
Negative economic growth means that the total value of domestic production in the current period is lower than it was in the previous period.
Key points on negative economic growth:
- A decrease in economic growth is different from negative economic growth;
- According to the definition, if two consecutive quarters show negative economic growth, the economy is in a recession;
- During negative economic growth, market sentiment in financial markets shifts towards risk aversion.
Importance of Real GDP
GDP calculates the total value (price) of all produced goods. Therefore, if goods become more expensive due to inflation, GDP will also increase, but this does not necessarily mean economic growth.
Central banks use Real GDP in their calculations to eliminate the effects of inflation in measuring economic growth.
Conclusion
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the primary measure of economic growth and the health of production, and central banks use it for decisions related to monetary policy.
In fundamental analysis, Real GDP is used to compare the countries' economic growth, as Real GDP eliminates the inflationary effects from the total value of goods produced.













