Inflation is an economic concept introduced in the early 20th century by the German economist “Heinrich Von”. It refers to the uncontrollable increase in the general price level of goods and services. This price increase is analyzed and defined through various Fundamental analysis indices such as CPI, PPI, and PCE.

What is Inflation?
Economic inflation is the weighted average of price increases for a specific basket of goods and services over a certain period. The items in this basket (such as food, housing, clothing, etc.) are determined by each country's central bank.
Introduction to Inflation Indices
Inflation reports are published as inflation indices and used to predict monetary policy trends and financial markets. Types of inflation indices:
- Consumer Price Index (CPI)
- Core Consumer Price Index (Core CPI)
- Producer Price Index (PPI)
- Core Producer Price Index (Core PPI)
- Personal Consumption Expenditures Price Index (PCE)
- Core Personal Consumption Expenditures Price Index (Core PCE)
CPI (Consumer Price Index)
CPI, or “Consumer Price Index” reflects economic inflation. It is a weighted average of price changes for a specific basket of goods over a specific period. An important point about CPI inflation is the fixed nature of the basket of goods and their weighted impact.
The Consumer Price Index increases with the devaluation of currency and leads to a reduction in purchasing power.
Core CPI (Core Consumer Price Index)
The Core CPI or “Core Consumer Price Index” represents CPI inflation, excluding food and energy.
External factors such as geopolitical risks, supply chain disruptions, or supply shortages significantly impact the prices of food and energy [volatile items], making their control largely outside the government or central bank's reach.
Therefore, central banks use the Core CPI as the basis for evaluating economic inflation.
For example, when the ECB (European Central Bank) announces an inflation target of 2%, they aim for the Core CPI (core inflation) to reach 2%.
Note: In inflation indices, whenever the term Core is mentioned, it means the exclusion of food and energy from the calculations.
PPI (Producer Price Index)
The PPI or “Producer Price Index” reflects producer inflation. This index accounts for price changes in raw materials and service providers' costs.
An increase in oil and energy prices significantly impacts the PPI and leads to cost-push inflation.
A crucial point about PPI is its role as a leading indicator and a warning sign of consumer inflation before it rises. As production costs increase, their impact on consumer inflation becomes evident months later through increased final product prices.
Core PPI (Core Producer Price Index)
In the Core PPI or “Core Producer Price Index”, price changes in food, energy, and services are excluded.
The exclusion of the services sector is because wages constitute a major part of service companies' costs, and sharp fluctuations in wage growth cause significant changes in the PPI.
PCE Price Index (Personal Consumption Expenditures Price Index)
The PCE Price Index or “Personal Consumption Expenditures Price Index” is a comprehensive inflation measure reported only in the United States.
In addition to inflation and price increases, the PCE index provides complete data on income, monthly inputs per individual, and savings rates.
Core PCE Price Index (Core Personal Consumption Expenditures Price Index)
The Core PCE Price Index or “Core Personal Consumption Expenditures Price Index” is one of the most important economic indicators reviewed by the Federal Reserve (the U.S. central bank).
A crucial point about PCE and Core PCE is the seasonal changes [based on higher demand] in the basket of goods considered. Additionally, the weight of goods in the PCE calculation is variable.
This feature makes PCE a better indicator of economic inflation and consumer living costs than CPI. For this reason, since 2000, the Core PCE has replaced the Core CPI as the preferred index of the Federal Reserve for evaluating inflation.
Note: If Core PCE is released higher than expected, it usually strengthens the currency in Forex market.
How Does Economic inflation Occur?
Price increases in the long term are due to money supply and increased liquidity. However, this is not the only cause of inflation, and several factors contribute to its occurrence:

Demand-Pull Inflation (Monetary Inflation)
This type of Economic inflation arises from strong demand. In this situation, demand exceeds supply. Expansionary monetary policies such as lowering interest rates, central bank bond purchases, or increased government spending (e.g., increased government investment in production, wage hikes, or subsidies) contribute to this type of inflation.
Cost-Push Inflation
This type of inflation occurs when producers' costs increase, forcing them to raise final product prices. Increases in raw material prices or wages are the main causes of this inflation.
Inflationary Expectations
Inflationary expectations lead to the creation or continuation of inflation. When businesses or consumers expect inflation to rise, they rush to purchase, increasing demand and leading to inflationary pressure.
Inflationary expectations can be monitored through consumer sentiment indices available on Forex Factory.
Government Budget Deficit
Budget deficits and government borrowing from the central bank also cause inflation through increased monetary base and liquidity.
A budget deficit arises from an imbalance between government expenditures and revenues. In other words, a deficit occurs when government spending exceeds its income.
In such cases, if the government borrows money from the central bank to address the deficit, inflation occurs due to increased monetary base and liquidity.
External Factors
Sometimes, external factors such as geopolitical risks or supply chain disruptions lead to increased consumer costs by reducing the supply of goods, increasing transportation costs, or raising raw material prices.
Difference Between Monetary and Cost-Push Inflation
Monetary inflation is caused by increased liquidity.
In this type of inflation, if production does not grow alongside increased liquidity, inflation occurs.
In other words, the money supply increases, but the goods supply remains constant or grows slower than liquidity.

According to this formula, if the money supply exceeds the goods supply, more money must be paid to purchase goods.
However, monetary inflation can be controlled through central bank monetary policies. The central bank can reduce liquidity in the economy by raising interest rates and curb price increases.
How Can Economic inflation Be Controlled?
Contractionary monetary policy and reducing government spending are ways to control inflation.
Additionally, policies supporting production strengthen goods supply and are effective in controlling inflation.
Some government-imposed policies, such as price controls or multiple exchange rates, are also used to control inflation. However, these policies [if not properly monitored] can lead to black markets and sometimes financial corruption.
Contractionary Monetary Policy
The most common method of controlling inflation is the contractionary monetary policy of the central bank. In this policy, the central bank aims to reduce liquidity in the economy by raising interest rates.
Raising interest rates reduces liquidity through two methods:
- Attracting liquidity to the banking system for higher returns;
- Reducing producers' demand for loans due to high interest rates.
Reducing Money Supply
The government attracts liquidity from the economy by increasing bond yields, as higher returns on bonds are seen as a low-risk investment.
Is Negative Inflation and Price Reduction Beneficial?
Deflation occurs when the average price level decreases over a specific period compared to the previous period.
Deflation is often caused by reduced demand, currency appreciation, or increased goods supply and is accompanied by reduced inflationary expectations and continued weak demand. Therefore, it is not considered economically beneficial, and central banks strive to prevent it.
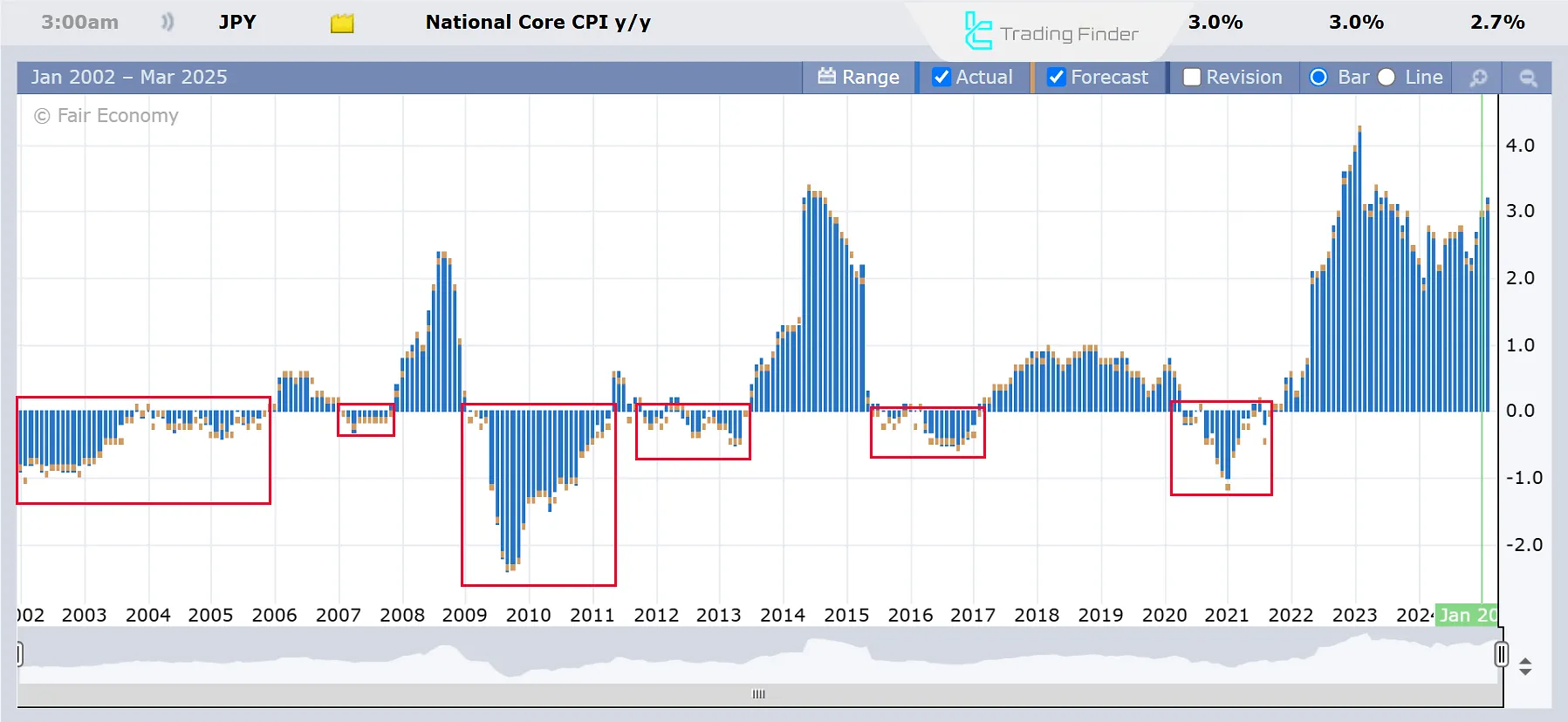
Deflation, if prolonged, leads to economic recession. To better understand this, the inflation and economic growth (GDP) trends of Japan are shown in the images below:
What Level of Inflation is Beneficial for the Economy?
A controlled level of inflation is beneficial for economic growth and labor market prosperity. For developed economies, 2% inflation is ideal, while 2-4% inflation is beneficial for developing economies.
However, if inflation exceeds this level, it leads to reduced purchasing power, labor market stagnation (increased unemployment), and ultimately reduced economic growth in the long term.
Conclusion
In most cases, inflation results from increased money supply and leads to higher living costs for consumers.
Price increases and inflation can be beneficial or harmful depending on their level, and one of the central banks' responsibilities is to control and stabilize it within the 2-4% range.













