Leverage in the Forex market allows traders to open larger positions using a small portion of their own capital, thereby increasing their potential profit margin. However, using leverage also introduces significant risks.
In essence, leverage refers to a type of borrowed credit that traders can use to increase their purchasing power and Profit from small market fluctuations.
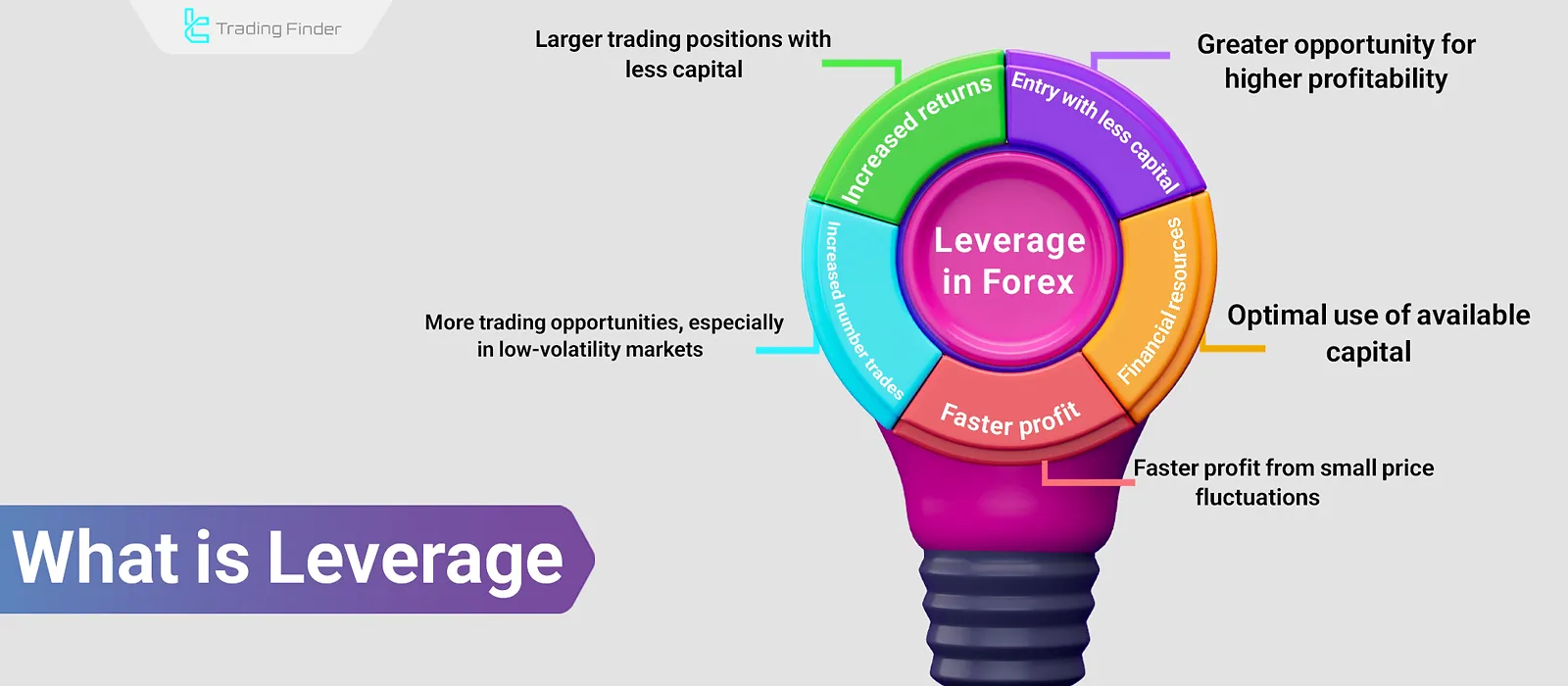
What Is Leverage?
Leverage means using borrowed funds to place trades larger than the trader’s actual capital. In other words, the trader borrows multiple times their capital from a broker, prop firm, or exchange to open positions beyond their own financial capacity.
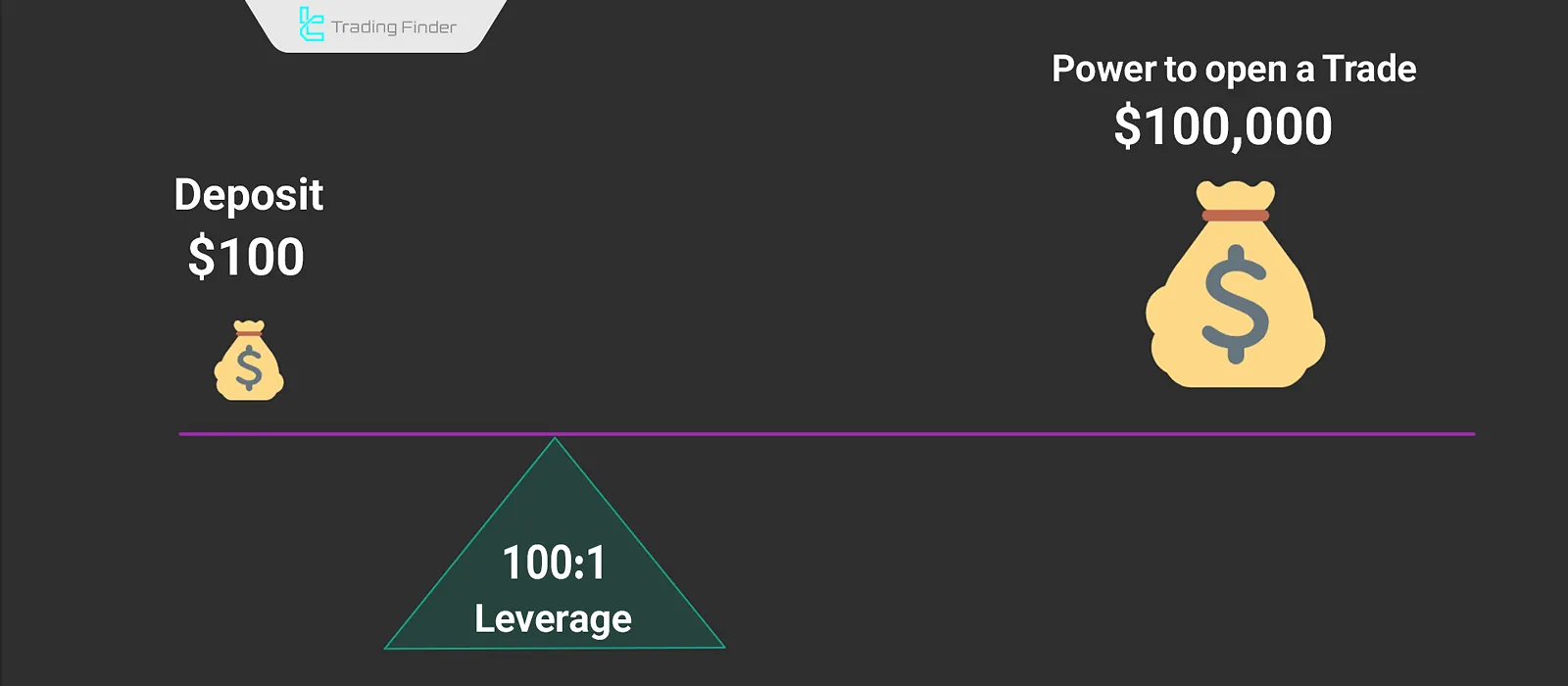
Leverage is represented as a ratio. For example, a leverage of 100:1 means that for every $1 of actual capital, the trader can open a $100 position. While leverage can lead to high returns in the short term, it also carries substantial risk.
How Leverage Works in Forex
In Forex, traders can use leverage to open positions significantly larger than their available balance. For instance, with a $1,000 account and 100:1 leverage, a trader can open a $100,000 trade.

How to Calculate Leverage
To calculate leverage, you must consider the ratio between the trade volume and your real capital (account balance). The trade volume is the amount of money used in a position, while the real capital is the actual funds deposited.
Leverage Formula:
- Leverage × Real Capital = Trade Volume
Leverage Calculation Example
If a trader uses 100:1 leverage and has $3,000 in their account, the trade volume would be:
- 100 × 3,000 = $300,000
Advantages and Disadvantages of Leverage
Leverage in the Forex market offers various advantages and disadvantages, especially for short-term traders:
Advantages of Leverage
- Increased Trade Size: Ability to make larger trades with less capital;
- Higher Profit Potential: Earn more Profit from smaller investments;
- More Opportunities: Enter more trades due to greater buying power;
- Capital Efficiency: Cover more positions with limited funds;
- Faster gains: Accelerate profits with the right market analysis.
Disadvantages of Leverage
- Increased Risk: Losses can be magnified if the market moves against you;
- Margin Call Risk: The broker may automatically close positions to prevent further losses;
- High Volatility: Natural market swings are amplified with leverage;
- Total Loss: Misusing leverage can lead to losing the entire account balance;
- Complex Risk Management: Makes managing risk more difficult and dangerous.
How to Use Leverage Effectively
To use leverage effectively in the forex market, traders should follow several important guidelines:
- Use Appropriate Leverage: Use high leverage (e.g. 100:1) only if you're experienced; lower leverage (10:1–20:1) is safer for beginners;
- Risk Management: Always set a clear Stop Loss and Take Profit for each trade. This helps limit losses and avoids emotional decisions;
- Market Analysis and Volatility: Effective leverage use demands strong knowledge from market conditions, as it magnifies losses—so strict strategy adherence is essential;
- Practice in a Demo Account: Before using real leverage, it’s best to practice with a demo account. This allows you to experiment with different tools and strategies without risking real money.
Leverage in Forex Trading Strategies
In many forex trading strategies, leverage plays a key role in boosting returns. Here are some strategies where leverage is commonly used:
Scalping Strategies
In scalping, traders aim to profit from small price movements. Leverage helps increase the profitability of these quick trades.
Swing Trading
In swing trading, traders hold positions from a few days to several weeks. Leverage allows them to control larger positions with a portion of their own funds, thus amplifying mid-term gains.
Trend Following
In trend trading, traders profit from the long-term direction of the market. Leverage enables them to enter larger trades, increasing their profit potential from sustained price moves.
Top Forex Brokers Offering High Leverage
The leverage range offered by forex brokers varies based on factors like broker type, region, account type, and regulatory policies. Some well-known high-leverage brokers available to traders include:
Leverage in Islamic Accounts
Islamic accounts in Forex, also known as swap-free accounts, are designed to comply with Islamic finance principles.
One of the key concerns is interest (Riba), which typically appears in the form of overnight swap fees. Islamic accounts eliminate these fees to ensure compliance with Sharia law.
However, leverage is still offered in Islamic accounts, allowing traders to open larger positions with limited capital.
What Is a Suitable Leverage in Forex?
Choosing the right leverage depends on your strategy, capital, experience, and risk tolerance. In general:
- Low Leverage (1:10 to 1:50) is more suitable for beginners and Long-term traders;
- Higher Leverage (1:50 to 1:500) is better suited for experienced traders and scalpers.
Conclusion
Leverage in the forex market is a powerful tool that defines the risk-to-reward ratio. It allows traders to trade larger volumes than their actual capital. While leverage can significantly increase profits, it can also amplify losses.













