Monetary policy shapes the cycles of economic expansion and recession. Therefore, understanding monetary policy, its tools such as interest rates, bonds, discount rates, reserve requirements, and the central bank’s approach in adopting these policies helps to choose the best market for investment in any economic phase.
What is Monetary Policy?
Monetary policy refers to the actions taken by a central bank to control Economic inflation and regulate the unemployment rate at an optimal level.
Central banks of different countries implement their own monetary policies using various tools, and these policy differences directly impact volatility in the forex market.
Forex traders use differences in monetary policies to capitalize on market fluctuations based on central bank actions. Differences in monetary policy refer to the divergence in approaches between central banks.
For example, the ECB (European Central Bank) may start cutting interest rates and adopt an expansionary policy, while the Federal Reserve (U.S. central bank) continues with a contractionary policy. This creates a monetary policy divergence, which may strengthen the U.S. dollar.
Monetary Policy Tools
Central banks have multiple tools to implement monetary policy, which affects liquidity levels by either increasing or decreasing them.
For example, central banks use monetary policy tools like interest rates and open market operations (OMO) to control inflation.
Key Monetary Policy Tools:
- Interest Rates: Changes in interest rates influence deposit levels and loan demand, thereby increasing or decreasing liquidity;
- Open Market Operations (OMO): The central bank’s buying and selling of government bonds. Buying bonds increases liquidity, while selling bonds reduces it;
- Credit Ceiling: The central bank sets credit limits to control bank lending;
- Reserve Requirement Ratio: The percentage of deposits banks must hold in reserve at the central bank. Increasing it reduces liquidity, while decreasing it boosts liquidity;
- Discount Rate: The interest rate banks pay when borrowing from the central bank. Raising it reduces liquidity, while lowering it increases liquidity;
- Inflation Targeting: Central banks use hawkish or dovish stances, inflation targets, policy statements, and even the tone of speeches to influence inflation expectations. These are modern monetary policy tools that affect market sentiment;
- Currency Intervention: Central banks directly intervene in forex market to control exchange rates in emergencies.
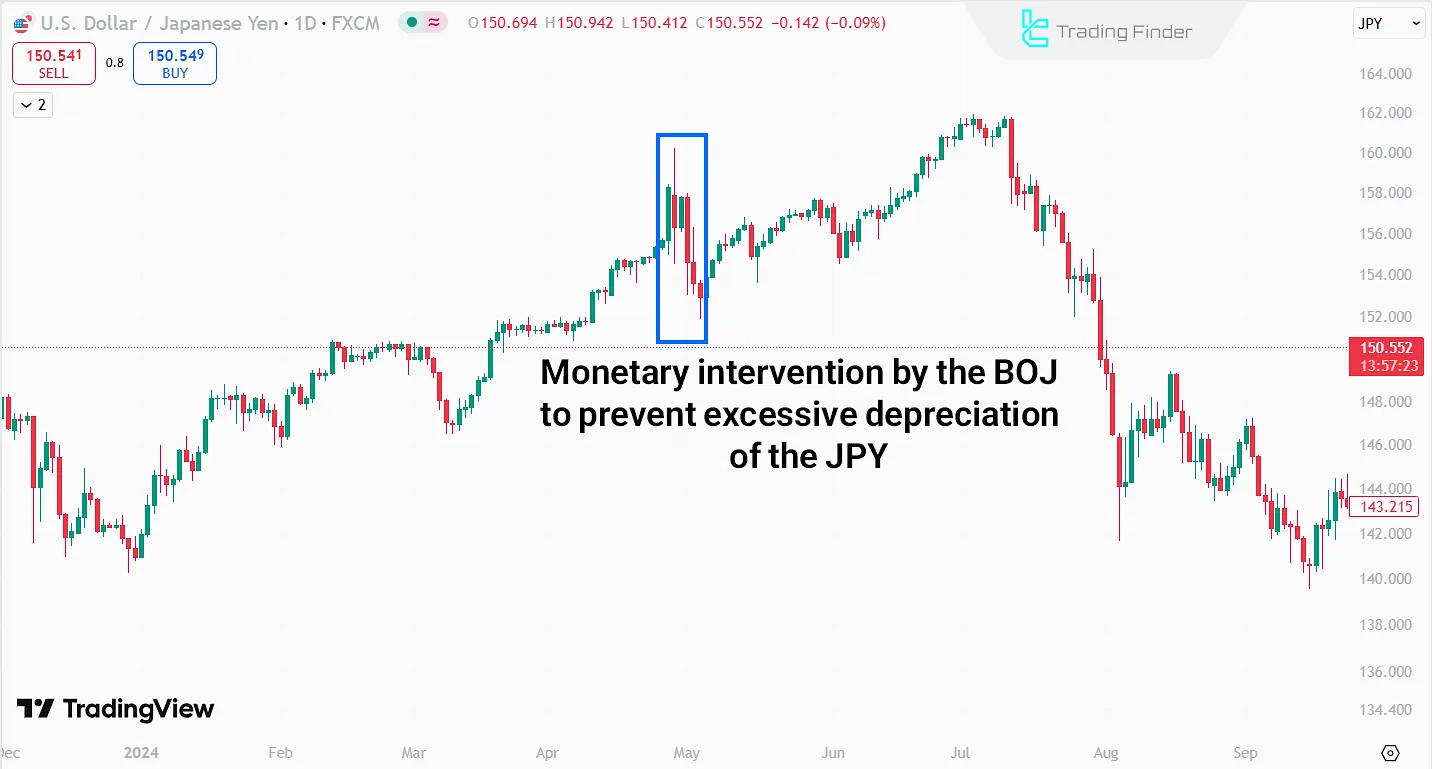
The image above shows the BOJ’s monetary intervention in forex when the yen hit historic lows against the dollar. Notably, the BOJ spent ¥9.8 trillion (≈$62.7 billion) on this intervention.
What Are the Types of Monetary Policy?
Monetary policy has different types, each affecting the economy differently. Central banks choose policies based on their objectives.
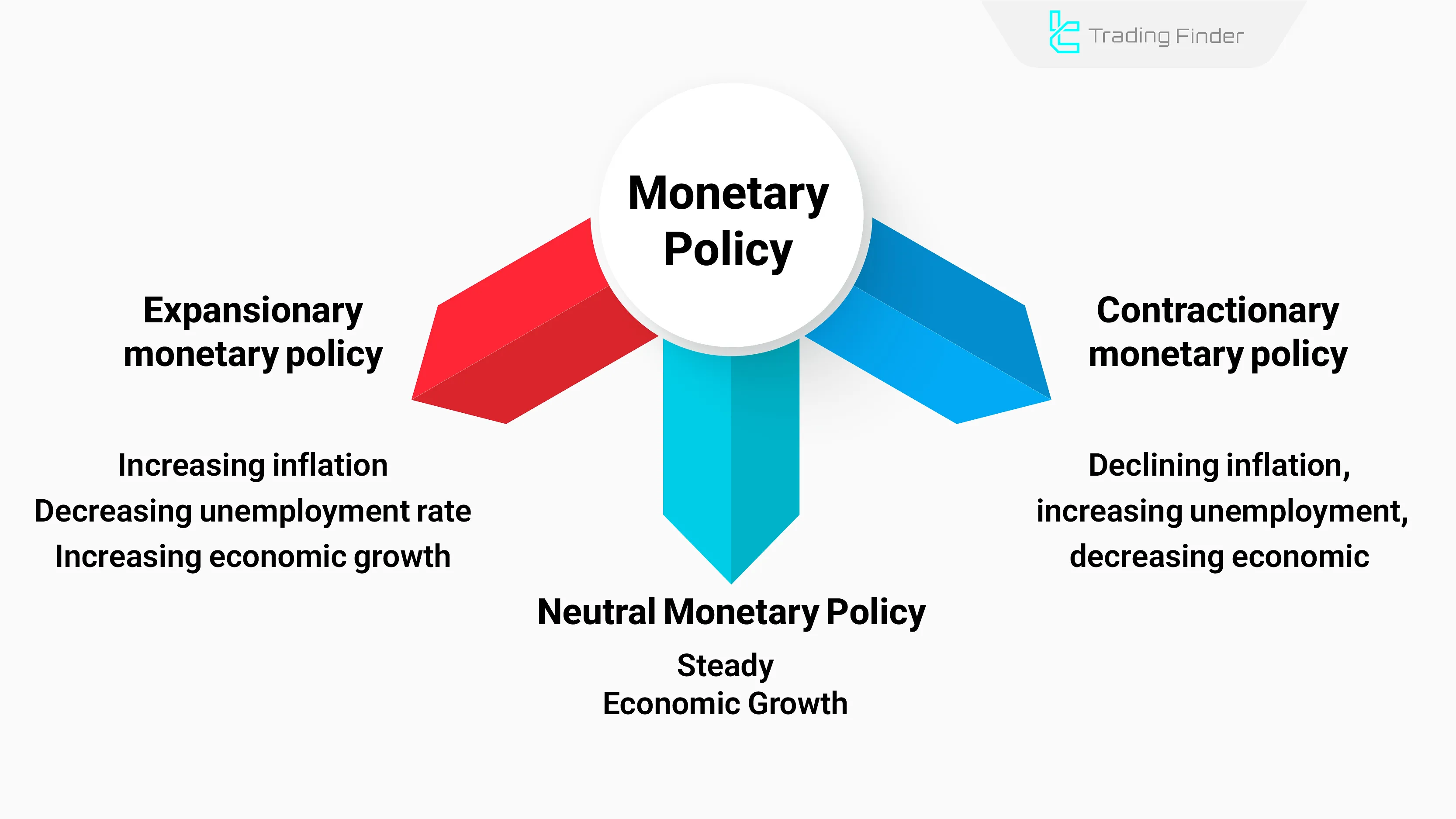
Expansionary Monetary Policy
Expansionary monetary policy is typically implemented via interest rate cuts or bond purchases, increasing liquidity.
Central banks use expansionary monetary policy tools during recessions to stimulate GDP and reduce unemployment.
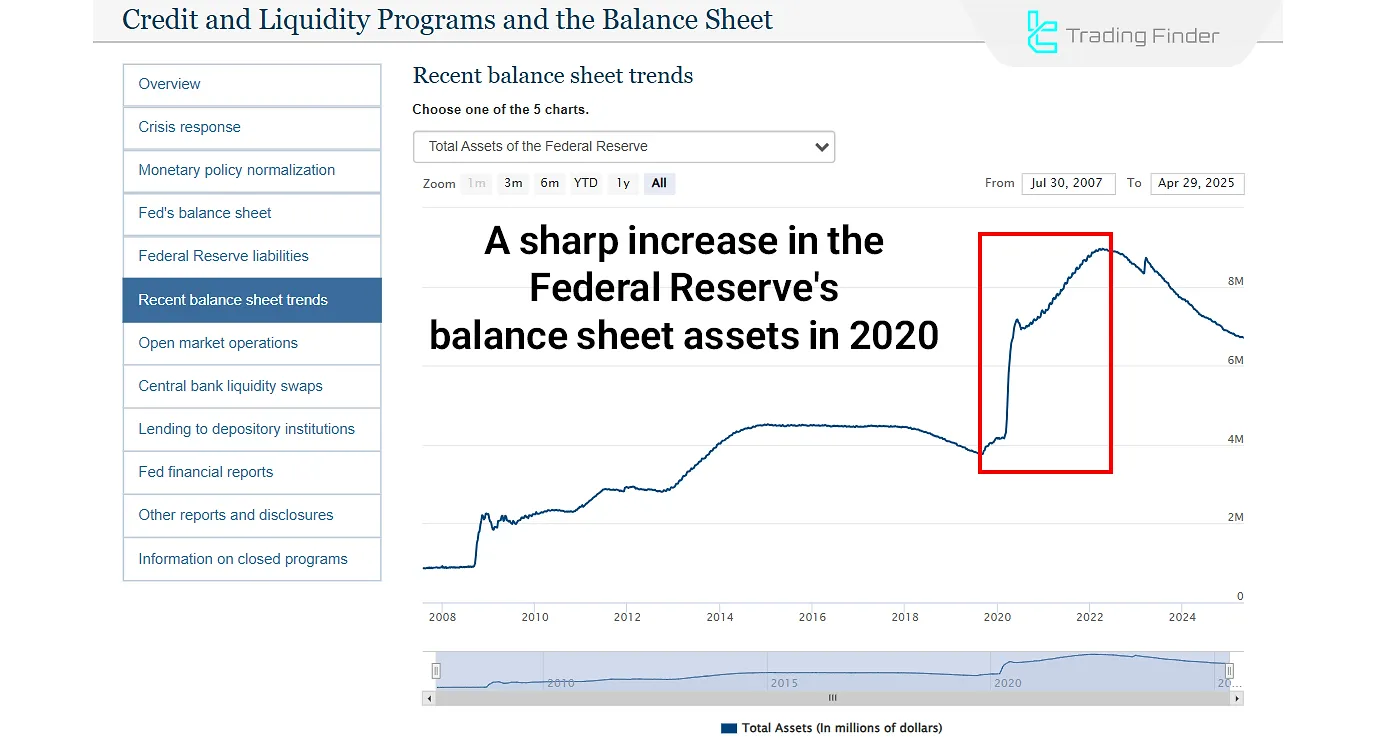
The image above shows the Federal Reserve’s balance sheet expansion in early 2020 (Source: federalreserve.gov). This was due to bond purchases, an expansionary monetary policy combined with interest rate cuts, leading to economic growth, lower unemployment, and higher inflation.
Impact of Expansionary Monetary Policy:
- Unemployment Rate: Stimulates economic growth and demand, reducing unemployment;
- Economic Growth: Boosts demand, liquidity, and easier credit access, enhancing growth.
Contractionary Monetary Policy
Contractionary monetary policy is usually implemented via interest rate hikes, reducing liquidity and weakening demand, which slows economic growth.
This policy is used to control inflation or prevent overheating.
Impact of Contractionary Monetary Policy:
- Unemployment Rate: Reduces consumer demand and pressures producers, increasing unemployment;
- Economic Growth: Lowers liquidity and suppresses demand, slowing growth. Prolonged contractionary policies may lead to recession.
Neutral Monetary Policy
Neutral monetary policy maintains interest rates at a level that neither stimulates nor restricts growth. The economy grows at a steady rate.
Note: Central banks estimate the neutral interest rate and is not precisely defined.
Conclusion
Central banks implement monetary policies to stimulate growth, improve labor markets, or control inflation. Tools include interest rates, bond purchases/sales, reserve requirements, discount rates, and credit ceilings.
Central bank policy stances significantly impact forex, bonds, stocks, Cryptocurrency, and commodities. Understanding monetary policy cycles helps traders and investors identify optimal opportunities.













