Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA) is the financial regulator for Forex brokers in the United Arab Emirates, which is headquartered in Dubai. This authority is considered as a tier-2 regulator in the industry with a good reputation for stringent rules and supervision.
The list below contains some of the best brands with satisfactory trading conditions overall.
 | pepperstone | |||
 | triomarkets | |||
 | HFM | |||
| 4 |  | XM | ||
| 5 |  | HYCM | ||
| 6 |  | TICKMILL | ||
| 7 |  | xtb | ||
| 8 |  | IG |
Trustpilot Ratings in DFSA Brokers
The table below ranks the mentioned brokers based on the scores and reviews submitted on “Trustpilot”.
Broker Name | Trustpilot Rating | Number of Reviews |
HFM | 3,178 | |
Pepperstone | 3,188 | |
TrioMarkets | 69 | |
8,692 | ||
Tickmill | 1,064 | |
XM | 2,977 | |
HYCM | 137 | |
2,361 |
Trading Spreads in DFSA Brokerages
Some Forex brokers costs traders with a difference between buy and sell prices. The table here ranks the introduced brokerages based on the minimum spread.
Broker Name | Min. Spread |
0 Pips | |
0 Pips | |
TrioMarkets | 0 Pips |
Swissquote | 0 Pips |
XM | 0 Pips |
Axi | 0 Pips |
IG | 0.3 Pips |
XTB | 0.5 Pips |
Non-Trading Costs in DFSA Brokers
The table in this section mentions the deposit/withdrawal and inactivity fees for select DFSA brokers. The list is ranked based on total costs.
Broker Name | Deposit Fee | Withdrawal Fee | Inactivity Fee |
$0 | $0 | $10 Quarterly | |
Plus500 | $0 | $0 | $10 Monthly |
$0 | $0 for >$300 Transactions | $10 Monthly | |
XM | $0 | $0 for Credit/Debit Cards and E-wallets | $10 Monthly |
Swissquote | $0 for Wire Transfer | $0 | €15 Monthly |
IG | 0$ for Bank Transfers | $0 | $18 Monthly |
Axi | $0 for Under $50,000 per Month | $0 for Under $50,000 per Month | $10 Monthly |
TrioMarkets | $0 | From 1% on VISA/MasterCard, Wire Transfers, and SEA Solution | $30 Monthly |
Tradable Instruments in DFSA Brokers
This section of the article ranks top DFSA brokerages by the number of tradable assets and instruments offered.
Broker Name | Number of Instruments |
IG | 17,000+ |
CMC Markets | 12,000+ |
Plus500 | 2,800+ |
1,400+ | |
Tickmill | 600+ |
500+ | |
HYCM | 300+ |
Axi | 220+ |
Top 6 DFSA-Regulated Forex Brokers
Six of the top brokers among abovementioned ones are reviewed in summary around their trading costs, account types, and more parameters, in the following sections.
HFM
HFM, formerly known as Hot Forex Markets, is a multi-asset broker established in 2010 and serving over 2.5 million live accounts worldwide. The broker delivers Forex and CFD trading with floating spreads from 0.0 pips and commission-free pricing on most account types.

Operating under a strong multi-jurisdiction framework, HFM holds licenses from CySEC, FCA, FSCA, FSA, and the Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA). Its DFSA-regulated entity, HF Markets (DIFC) Ltd, enables compliant access for MENA-region traders under Dubai’s financial regulatory standards.
HFM offers four main account types, Cent, Zero, Pro, and Premium, supporting MT4, MT5, and mobile apps. Clients can trade Forex, indices, commodities, stocks, ETFs, bonds, and crypto CFDs, with features such as negative balance protection, segregated funds, and leverage up to 1:50 under DFSA.
Beyond trading conditions, HFM integrates value-added tools like Autochartist, VPS hosting, SMS market alerts, and copy trading via PAMM and Copy Trading services. The broker also supports crypto deposits, zero minimum deposit on select accounts, and multilingual customer support in 27+ languages.
Specifics and Parameters
Account Types | Cent, Zero, Pro, Premium |
Regulating Authorities | CySEC, DFSA, FCA, FSCA, FSA |
Minimum Deposit | From $0.00 |
Deposit Methods | Wire transfer, E-payments, Credit/Debit cards, Crypto |
Withdrawal Methods | Wire transfer, E-payments, Credit/Debit cards, Crypto |
Maximum Leverage | 1:2000 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MT4, MT5, Mobile App |
HFM Pros and Cons
HFM combines broad market access, flexible account structures, and DFSA oversight to appeal to traders seeking regulated exposure in the Middle East. Before HFM registration, here is a balanced snapshot of its main strengths and limitations before reviewing the detailed pros and cons.
Pros | Cons |
DFSA regulation for MENA-region clients | No investor compensation scheme under DFSA |
Commission-free Forex trading on most accounts | Leverage lower than offshore entities |
Wide range of account types and markets | Platform choice limited to MT4/MT5 |
Supports crypto deposits and copy trading | Promotions restricted by regulation |
Pepperstone
Founded in 2010, Pepperstone is a high-volume global broker processing over $9.2 billion in daily trades for 400,000+ clients. The company supports 10 base currencies and flexible order sizes from 0.01 to 100 lots, making it suitable for both retail and active traders.
Pepperstone operates through a multi-entity structure and maintains a strong global footprint, with offices across major financial hubs. While headquartered in Australia, the broker serves international clients through regulated entities in Europe, the Middle East, Africa, and offshore jurisdictions, including Mauritius-linked structures used for global access.
A key strength of Pepperstone is its regulatory depth. The broker is supervised by multiple authorities, including ASIC, FCA, CySEC, BaFin, DFSA, CMA, and offshore regulators. Client funds are held in segregated accounts, and negative balance protection applies across entities, enhancing overall risk controls.
Also, a Pepperstone rebate program is available for discounts on costs.
From a trading-conditions perspective, Pepperstone offers leverage up to 1:500 (entity-dependent), spreads from 0.0 pips, and support for MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, cTrader, TradingView, and proprietary platforms. Traders can access Forex, commodities, indices, crypto CFDs, shares, and ETFs under a single account.
Does the account opening process look complicated? Check out our Pepperstone registration guide.
Table of Features and Details
Account Types | Standard, Razor |
Regulating Authorities | ASIC, SCB, FCA, DFSA, CMA, BaFin, CySEC |
Minimum Deposit | $1 |
Deposit Methods | Apple Pay, Google Pay, Visa, Mastercard, Bank transfer, PayPal, Neteller, Skrill, Union Pay, USDT, ZotaPay |
Withdrawal Methods | Apple Pay, Google Pay, Visa, Mastercard, Bank transfer, PayPal, Neteller, Skrill, Union Pay, USDT, ZotaPay |
Maximum Leverage | Up to 1:500 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | Proprietary Platform, cTrader, Trading View, MetaTrader 4&5 |
Pepperstone Pros & Cons
Pepperstone is positioned as an execution-focused broker rather than a promotion-driven one. Below is a clear snapshot of its main advantages and limitations, helping readers evaluate how it compares with other FSC (Mauritius) Forex brokers.
Pros | Cons |
Multi-jurisdiction regulation across top-tier authorities | No bonuses or promotional campaigns |
Tight spreads from 0.0 pips on Razor accounts | No PAMM or managed account structures |
Broad platform support (MT4, MT5, cTrader, TradingView) | Leverage limits apply under some entities |
No inactivity or account maintenance fees | Service availability varies by country |
TrioMarkets
TrioMarkets is a multi-asset Forex and CFD broker offering access to 500+ tradable instruments across Forex, shares, indices, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. Founded in 2019, the broker combines regulated market access with flexible trading conditions for both retail and advanced traders.

Operating under multiple regulatory frameworks, TrioMarkets is authorized by the Dubai Financial Services Authority, Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC), and the Financial Services Commission Mauritius (FSC). This structure allows it to serve both EU/EEA and international clients under different compliance regimes.
TrioMarkets provides four account types, Basic, Standard, Advanced, and Premium ECN, with a minimum deposit of $100. Depending on the regulatory entity, leverage can reach up to 1:500, while EU clients trade under stricter caps in line with ESMA-style protections.
On the technology side, traders can choose between MetaTrader 4 (MT4) and the proprietary TrioTrader platform.
We have a TrioMarkets dashboard review that could prove useful for those willing to learn about the broker’s interface.
The broker supports market execution, PAMM/MAM investment accounts, and trading tools such as VPS access, an economic calendar, and currency converters. Here’s a table of specifics.
Account Types | Basic, Standard, Advanced, Premium ECN |
Regulating Authorities | CySEC, DFSA, FSC |
Minimum Deposit | $100 |
Deposit Methods | Visa, MasterCard, Bank Wire, Neteller, Local Payment Solutions |
Withdrawal Methods | Visa, MasterCard, Bank Wire, Neteller, Local Payment Solutions |
Maximum Leverage | 1:500 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MetaTrader 4, TrioTrader |
Triomarkets Pros & Cons
This broker positions itself as a regulated broker with flexible leverage, multiple account tiers, and broad market coverage. Below is a concise overview of its key advantages and limitations, helping traders assess it before going through with TrioMarkets registration.
Pros | Cons |
Regulated by DFSA, CySEC, and FSC | High minimum deposits on upper-tier accounts |
500+ tradable instruments across multiple markets | Spreads on Basic accounts are relatively high |
MT4 support plus proprietary TrioTrader platform | Withdrawal and inactivity fees apply |
PAMM/MAM accounts and high leverage (entity-based) | No Islamic (swap-free) account option |
IG
Founded in 1974 in London, IG is one of the longest-established online brokers, serving over 381,000 traders worldwide. As a FTSE 250 constituent, IG combines public-company transparency with nearly five decades of brokerage expertise.
IG provides access to 17,000+ instruments, including Forex, indices, shares, commodities, bonds, ETFs, IPOs, and crypto CFDs. Features such as 24-hour index trading, extended US share hours, and advanced order types position IG as a multi-asset trading hub.
The broker operates under a strong multi-jurisdiction framework, including FCA, ASIC, MAS, and Dubai Financial Services Authority. For Middle East clients, IG’s DFSA-regulated entity ensures compliance with regional financial standards and institutional-grade governance.
IG supports a wide range of platforms, including MT4, TradingView, ProRealTime, L2 Dealer, and its proprietary web and mobile platforms, alongside algorithmic trading, APIs, and professional charting tools. This technology stack has earned IG 10+ global industry awards.
Note that for a full access to the broker’s features and capabilities, you should go through the IG verification process. Look at the table below for a summary of the broker’s specifications.
Account Types | CFD |
Regulating Authorities | ASIC, FCA, FSA, AMF, FMA, MAS, DFSA, FSCA |
Minimum Deposit | Unlimited |
Deposit Methods | Bank Transfer, Credit/Debit Cards |
Withdrawal Methods | Bank Transfer, Credit/Debit Cards |
Maximum Leverage | 1:200 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MT4, TradingView, L2 Dealer, ProRealTime, Proprietary Platform |
IG Pros & Cons
IG stands out for regulatory depth, market diversity, and professional-grade platforms. Below is a concise overview of the broker’s main strengths and limitations that are worthy of noting before IG registration.
Pros | Cons |
Regulated by DFSA and multiple tier-1 authorities | No Islamic (swap-free) account |
17,000+ tradable instruments across global markets | Limited crypto CFD selection |
Advanced platforms incl. MT4, TradingView, ProRealTime | Inactivity fee after long dormancy |
Long operating history and FTSE 250 listing | No PAMM or copy-trading system |
Tickmill
Tickmill is a global multi-asset Forex and CFD broker serving 785,000+ registered users across more than 180 countries. The broker delivers spreads from 0.0 pips, flexible execution, and leverage up to 1:300 under eligible entities, positioning itself toward cost-efficient and active trading styles.

Founded in 2014, Tickmill operates on a no-dealing-desk (NDD) model, routing orders directly to liquidity providers. This structure supports fast market execution and deep liquidity, contributing to the broker’s reported $129+ billion average monthly trading volume across Forex and CFD instruments.
Furthermore, there is a Tickmill rebate program provided for traders to reduce costs and spreads.
Tickmill follows a multi-jurisdiction regulatory framework, including oversight by the DFSA, alongside the FCA, CySEC, FSCA, LFSA, and FSA. Client protections include segregated funds, negative balance protection, and investor compensation schemes varying by entity.
Trading access is provided via MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, WebTrader, and mobile apps, covering Forex, indices, commodities, stocks, bonds, and crypto CFDs. With six base currencies and a $100 minimum deposit, Tickmill balances professional-grade pricing with accessible account entry.
Table of Features
Account Types | Classic, Raw |
Regulating Authorities | FSA, FCA, CySEC, LFSA, FSCA |
Minimum Deposit | $100 |
Deposit Methods | Crypto, Payment Systems, Credit/Debit Cards, Bank Transfers |
Withdrawal Methods | Crypto, Payment Systems, Credit/Debit Cards, Bank Transfers |
Maximum Leverage | 1:1000 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | Metatrader 4, Metatrader 5, Metatrader Web, Mobile App |
Tickmill Pros & Cons
Tickmill combines strong regulatory coverage, competitive spreads, and an execution-focused trading model. The following table highlights the broker’s main advantages and potential limitations to help assess its fit among DFSA-regulated Forex brokers.
Pros | Cons |
DFSA-regulated entity with multi-tier global oversight | Limited variety of account types |
Raw spreads from 0.0 pips with NDD execution | Narrower Forex pair selection than some competitors |
Support for MT4, MT5, WebTrader, and mobile apps | No PAMM account structure |
Segregated funds & negative balance protection | Educational resources less extensive than top peers |
XM
XM Group is a global forex and CFD broker founded in 2009, serving over 15 million clients worldwide. The broker reports nearly 14 million trades executed daily, offering access to 55+ forex pairs and more than 1,400 CFD instruments across multiple asset classes.
XM operates through a multi-entity structure with offices in Cyprus, Dubai, South Africa, and Belize, combining global reach with region-specific regulation. Its trading environment is built around MetaTrader 4 and MetaTrader 5, positioning XM as a MetaTrader-focused broker for both retail and advanced traders.
Also, there are passive income options such as XM copy trading in mentioned broker.
For Middle East clients, XM operates under DFSA supervision in Dubai via Trading Point MENA Limited (License F003484). This DFSA authorization places XM among regulated brokers in the DIFC, aligning its regional operations with recognized compliance and conduct standards.
XM stands out for its low $5 minimum deposit, flexible order sizing from 0.01 lots, and leverage up to 1:1000 under eligible entities. With features such as negative balance protection, Islamic accounts, and guaranteed execution for orders up to 50 lots, XM targets both accessibility and execution reliability. The table below summarizes the broker’s specifics.
Account Types | Standard, Ultra Low, Shares |
Regulating Authorities | FSC Belize, CySEC Cyprus, FSCA South Africa, DFSA Dubai, FSC Mauritius, FSA Seychelles |
Minimum Deposit | $5 |
Deposit Methods | Credit/Debit Cards, Bank Transfers, E-Wallet Payments |
Withdrawal Methods | Credit/Debit Cards, Bank Transfers, E-Wallet Payments |
Maximum Leverage | Up To 1:1000 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MT4, MT5, Mobile App |
XM Pros and Cons
Before making a decision and going through XM registration, take a look at this overview of the broker’s main strengths and limitations, helping traders assess how XM compares with other DFSA-regulated forex brokers.
Pros | Cons |
DFSA-regulated entity for Middle East clients | Inactivity fee charged on dormant accounts |
Very low minimum deposit ($5) | Not publicly traded and no banking license |
Access to 1,400+ CFDs including 55+ FX pairs | No PAMM or investment account options |
MetaTrader 4 & 5 with negative balance protection | Shares account requires high minimum deposit |
How Did We Choose Each Broker?
Selecting the Best DFSA-Regulated Forex Brokers requires more than surface-level comparisons. At TradingFinder, every broker featured in this article is evaluated using a 19-metric review methodology designed to reflect real trading conditions under the supervision of the Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA).
Regulation and licensing form the foundation of our assessment. We verify each broker’s DFSA authorization within the Dubai International Financial Centre, confirm legal entities, and analyze client-protection mechanisms such as fund segregation, capital adequacy, and compliance with AML and KYC standards.
Broker background data, including establishment year, headquarters, and global office presence, is also reviewed to assess long-term operational credibility.
Trading conditions are examined in depth. Our analysts compare account type diversity (Standard, ECN, Islamic, PAMM), leverage policies, margin rules, and the range of tradable instruments, from major forex pairs to CFDs on indices, commodities, stocks, and ETFs.
Costs are tested using real accounts where possible, covering spreads, commissions, deposit and withdrawal fees, and inactivity charges.
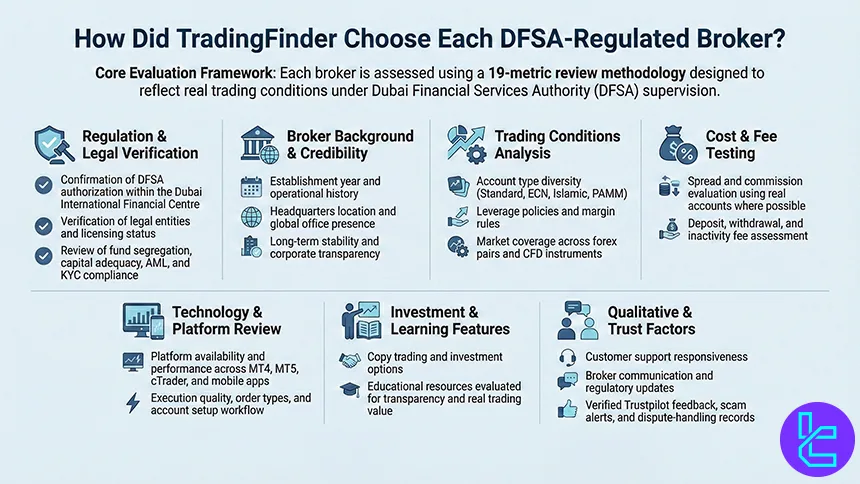
Technology and usability are key components of our methodology. We evaluate platform availability and performance across MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, cTrader, and mobile apps, alongside execution quality, order types, and the full account-opening and verification process.
Copy trading, investment features, and educational resources are assessed for transparency, depth, and practical value.
Finally, qualitative factors complete the review. Customer support responsiveness, broker communication quality, published infographics, regulatory updates, and verified user feedback from Trustpilot are all incorporated, along with scam alerts and dispute-handling records.
What is DFSA?
The Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA) is the independent financial regulator responsible for supervising financial services conducted in or from the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC). Established in 2004, the DFSA operates as an autonomous authority with its own legal and regulatory framework, separate from the wider UAE federal financial system.
The DFSA regulates a broad range of financial activities, including Forex and CFD brokers, banks, asset managers, investment firms, insurance-related entities, and market infrastructure providers operating within the DIFC.
Its regulatory framework is principles-based and closely aligned with international standards set by bodies such as IOSCO, Basel Committee, and FATF, ensuring global compatibility and institutional credibility.
For Forex brokers, DFSA authorization requires strict compliance with capital adequacy rules, client fund segregation, internal risk controls, transparency obligations, and ongoing supervisory audits.
Brokers must also meet robust AML and KYC requirements, maintain clear disclosure practices, and follow conduct-of-business rules designed to protect market integrity and professional investors.
Unlike offshore regulators, the DFSA emphasizes substance over form, requiring licensed firms to maintain a genuine operational presence in the DIFC, including local offices, compliance staff, and governance structures.
While DFSA regulation is often associated with professional or institutional-grade trading environments, it is widely regarded as a high-standard regional regulator, particularly for traders seeking a balance between regulatory oversight, global market access, and a sophisticated financial ecosystem.
Pros and Cons of DFSA Regulation
The DFSA provides a strong regulatory framework for financial firms operating within the Dubai International Financial Centre. Its regime emphasizes institutional-grade supervision, capital strength, and governance quality.
However, DFSA regulation is primarily designed for professional markets, which can limit retail-focused protections compared to some Western regulators.
Pros | Cons |
Independent regulator with a dedicated legal framework inside DIFC | No statutory investor compensation scheme |
Strong capital adequacy and governance requirements | Retail investor protections are more limited than FCA or EU regimes |
Mandatory client fund segregation and ongoing supervision | Fewer DFSA-licensed forex brokers compared to offshore jurisdictions |
Alignment with international standards (IOSCO, FATF, Basel) | Higher compliance costs may reduce promotional incentives |
Is Leverage Limited in DFSA Brokers?
Yes, leverage is regulated under the framework of the Dubai Financial Services Authority, but it is not capped by a single fixed ratio in the same way as EU or UK regulators. Instead, leverage limits at DFSA-regulated brokers are set through a risk-based and client-classification approach within the Dubai International Financial Centre.
DFSA rules require brokers to apply leverage levels that are appropriate to the client’s status, typically distinguishing between Retail Clients, Professional Clients, and Market Counterparties.
Retail clients are subject to more conservative leverage settings, reflecting suitability, risk disclosures, and margin-close-out requirements.
Professional clients, by contrast, may access significantly higher leverage, provided they meet experience, capital, and qualification thresholds defined by DFSA conduct-of-business rules.
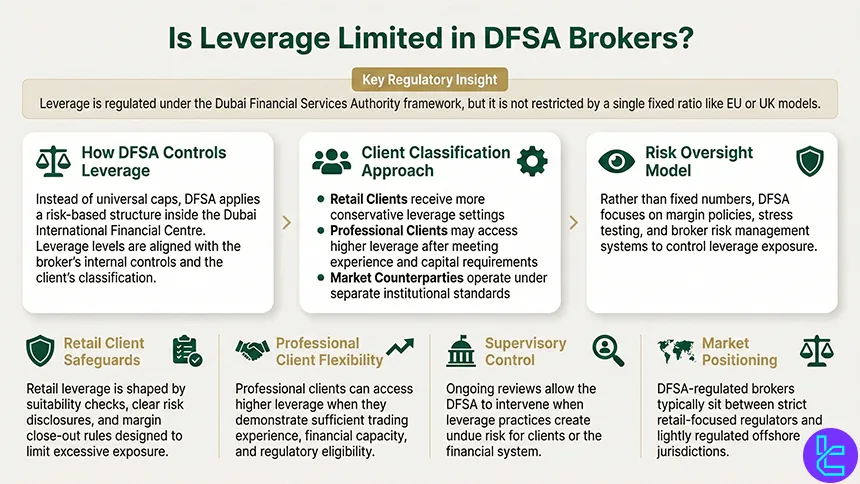
Rather than imposing a universal leverage ceiling, the DFSA focuses on prudential controls, including margining policies, stress testing, and internal risk management systems. Brokers must demonstrate that their leverage offerings do not expose clients or the firm to excessive systemic risk.
Ongoing supervisory reviews allow the DFSA to intervene if leverage practices are deemed inappropriate.
As a result, DFSA-regulated brokers often sit between strict retail regimes (like FCA or ESMA) and offshore jurisdictions.
What Are DFSA Rules for Forex Brokers?
Forex brokers regulated by the Dubai Financial Services Authority must comply with a comprehensive regulatory framework governing financial services within the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC).
These rules are designed to ensure market integrity, financial stability, and appropriate client protection through ongoing supervision and risk-based regulation. Key DFSA rules and obligations for Forex brokers include:
- Authorization and Licensing: Brokers must obtain DFSA authorization for specific financial services and operate strictly within the scope of their approved license;
- Capital Adequacy Requirements: Firms are required to maintain minimum regulatory capital levels proportionate to their business model, risk exposure, and client liabilities;
- Client Fund Segregation: Client funds must be held in segregated accounts, separate from the broker’s own operating capital, to reduce insolvency risk;
- Client Classification and Suitability: Brokers must classify clients as Retail or Professional and apply leverage, risk disclosures, and suitability standards accordingly;
- Conduct of Business Rules: Clear pricing, fair execution policies, conflict-of-interest management, and transparent disclosures are mandatory;
- Risk Management and Internal Controls: Brokers must implement robust governance structures, compliance functions, stress testing, and ongoing risk monitoring;
- AML and KYC Compliance: Strict anti-money laundering and customer verification procedures are enforced in line with international standards;
- Ongoing Reporting and Supervision: Licensed firms are subject to regular reporting, audits, and supervisory reviews, with the DFSA retaining enforcement and sanctioning powers.
These requirements position DFSA-regulated Forex brokers as operating within a high-standard, institution-focused regulatory environment, rather than a lightly supervised or offshore regime.
How Can I Check if a Broker is Regulated by DFSA?
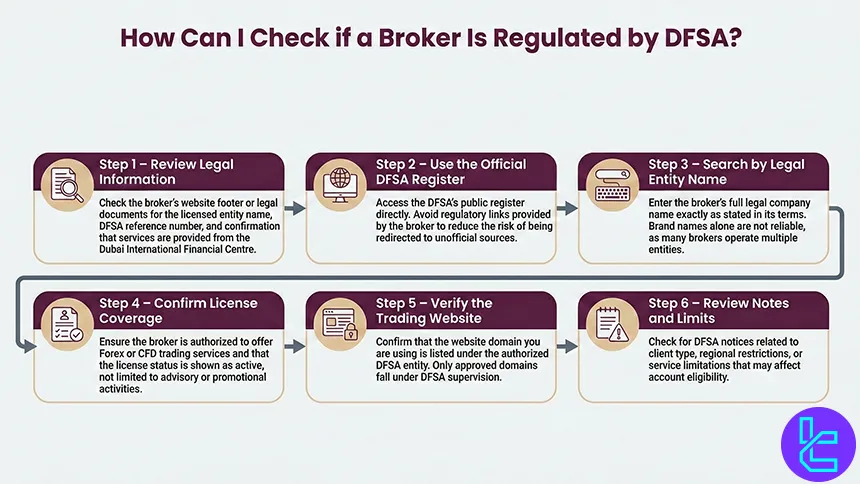
Verifying whether a broker is genuinely regulated by the Dubai Financial Services Authority is an essential step before opening a trading account. The process is straightforward, but it must be done carefully to avoid misleading or cloned regulatory claims.
- Check the Broker’s Legal Disclosure: Review the broker’s website footer or legal documents for the licensed entity name, DFSA reference number, and confirmation that the services are provided from the (DIFC);
- Visit the Official DFSA Register: Go directly to the DFSA’s public register of authorized firms. Avoid clicking regulatory links provided by the broker itself to reduce the risk of redirection to unofficial pages.;
- Search by Legal Entity Name: Enter the broker’s full legal name exactly as displayed in its terms and conditions. Brand names alone are often insufficient, as many groups operate multiple entities;
- Confirm Authorization Scope: Check that the firm is authorized to provide Forex or CFD trading services, not just advisory or promotional activities, and that the license status is shown as active;
- Match the Trading Domain: Ensure the website domain you are using is listed under the authorized DFSA entity. Only approved domains fall under DFSA supervision;
- Review Regulatory Notes and Restrictions: Examine any DFSA notices regarding client classification, geographic limitations, or service restrictions that may affect your eligibility.
Completing these steps helps ensure that a broker’s DFSA regulation is legitimate and that your trading activity falls under the DIFC’s regulatory protections.
Are DFSA-Regulated Brokers Allowed to Offer Crypto Services?
DFSA-regulated brokers are allowed to offer crypto-related services, but only within a clearly defined and tightly regulated framework set by the Dubai Financial Services Authority inside the Dubai International Financial Centre.
The DFSA does not treat cryptocurrencies as legal tender, but it recognizes “Crypto Tokens” and regulates them as financial products when specific conditions are met.
Brokers and financial firms must obtain explicit DFSA authorization to engage in any crypto-related activity; a standard Forex or CFD license alone is not sufficient.
Under DFSA rules, licensed firms may offer:
- Crypto token trading services, including brokerage and dealing;
- Crypto-related derivatives, subject to product approval and risk controls;
- Custody and wallet services, provided enhanced safeguarding and operational standards are met.
All crypto services must comply with strict AML and KYC requirements, enhanced market surveillance, capital adequacy rules, and disclosure obligations due to the higher risk profile of digital assets.
The DFSA also imposes client classification requirements, meaning access to certain crypto products may be limited to professional or institutional clients.
Importantly, DFSA regulation of crypto services is far more restrictive than offshore regimes and focuses on market integrity rather than broad retail access.
As a result, DFSA-authorized crypto offerings tend to prioritize regulated infrastructure, transparency, and institutional-grade controls, making them suitable for traders seeking regulatory clarity rather than high-risk speculation.
Does DFSA Offer Any Investor Protections?
The Dubai Financial Services Authority offers investor protections, but its approach is preventive and supervisory, rather than compensation-based. Within the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC), the DFSA focuses on reducing investor risk through strict regulatory controls, ongoing supervision, and firm-level resilience.
DFSA-regulated brokers are required to segregate client funds from their own operating capital, which helps protect client assets if a firm faces financial difficulty.
In addition, firms must meet capital adequacy requirements that reflect the scale and risk profile of their activities, ensuring they are financially capable of withstanding market volatility and operational stress.
Investor protection under the DFSA also relies heavily on conduct-of-business rules. Brokers must classify clients appropriately, apply suitability standards, provide clear risk disclosures, and maintain fair execution and conflict-of-interest policies.
These obligations are designed to ensure that clients understand the risks involved and that products are offered in a responsible and transparent manner.
Ongoing supervision is a core element of DFSA protection. The regulator conducts regular reporting reviews, compliance assessments, and inspections, and it has the authority to impose fines, restrict activities, or revoke licenses when breaches occur.
However, it is important to note that the DFSA does not operate a statutory investor compensation scheme. As a result, DFSA regulation prioritizes strong oversight and risk prevention over post-insolvency compensation, making it most suitable for informed and risk-aware traders.
How Is DFSA Different from Offshore Brokers?
The Dubai Financial Services Authority differs from offshore regulatory regimes in both regulatory depth and legal accountability. DFSA-regulated brokers operate within the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC), which has its own independent legal system based on common law, dedicated courts, and enforceable regulatory oversight.
This structure creates a level of transparency and accountability that is typically absent in offshore jurisdictions.
DFSA regulation requires firms to maintain a real physical and operational presence in the DIFC, including local offices, compliance staff, and governance structures.
Offshore regulators, by contrast, often allow brokers to operate with minimal on-the-ground substance, lighter supervision, and limited ongoing audits.
As a result, DFSA oversight is continuous and risk-based, rather than largely reactive.
From a client-protection perspective, DFSA-regulated brokers must comply with strict rules on client fund segregation, capital adequacy, internal controls, and conduct of business.
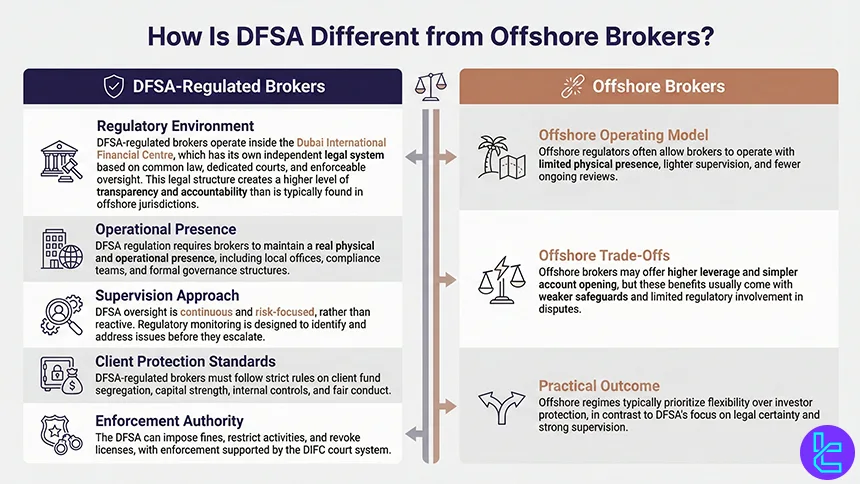
Offshore brokers may offer higher leverage and fewer onboarding requirements, but these advantages usually come with weaker safeguards, limited transparency, and reduced regulatory intervention if disputes arise.
Another key distinction is enforcement power. The DFSA has the authority to impose meaningful fines, restrict activities, and revoke licenses, with enforcement actions supported by the DIFC court system.
Offshore regulators often lack comparable enforcement reach or judicial backing. In practice, DFSA regulation prioritizes institutional-grade supervision and legal certainty, while offshore regimes tend to prioritize flexibility at the expense of investor protection.
DFSA Compared Against Other Regulatory Authorities
The Dubai Financial Services Authority is often positioned between strict Tier-1 regulators and offshore frameworks. Operating within the DIFC’s independent common-law system, DFSA combines strong legal accountability with moderate trading flexibility.
When compared to regulators such as JFSA, ASIC, and FSC (Mauritius), the main differences appear in capital thresholds, leverage limits, investor protection depth, and enforcement intensity.
The table below highlights how DFSA oversight structurally compares with these well-known regulatory regimes, helping traders understand the practical trade-offs between protection and flexibility.
Parameter | DFSA (Dubai) | JFSA (Japan) | ASIC (Australia) | FSC (Mauritius) |
Regulatory Tier | Tier-2 | Tier-1 | Tier-1 | Mid-tier / Offshore |
Minimum Capital Requirement | High, risk-based (varies by license class) | Based on net capital & exposure | ~AUD 500,000–1,000,000 | From ~USD 250,000 (license-type dependent) |
Client Fund Segregation | Required | Required | Required | Required (principle-based) |
Investor Compensation Scheme | No statutory compensation fund | Japan Investor Protection Fund | No statutory fund (AFCA dispute resolution) | No statutory compensation fund |
Leverage Limits (Retail) | Moderate, risk-based (often ~1:30) | Strict cap ~1:25 | ~1:30 | Flexible, often up to 1:500+ |
Negative Balance Protection | Required | Required | Required | Not mandatory (broker-dependent) |
Regulatory Enforcement | Strong, court-backed within DIFC | Very strict, conservative | Strong, active enforcement | Limited compared to Tier-1 |
Reporting & Audits | Ongoing, risk-based supervision | Frequent reporting & monitoring | Regular compliance reporting | Periodic reporting & audits |
Conclusion
DFSA is introduced as an independent tier-2 regulatory authority headquartered in Dubai, regulating UAE Forex brokers. Supervising financial services conducted in DIFC, it regulated several brokers, but the best choices for average trader are HFM, Pepperstone, TrioMarkets, and IG.
To learn about the parameters and factors considered in reviewing and choosing mentioned brokerages, visit our Forex methodology page.













