Forex brokers act as financial intermediaries, granting retail traders access to the global foreign exchange market.
These companies offer trading platforms, real-time currency pair quotes, analytical tools, and execution features, serving as a bridge between traders and the market.
Brokers, depending on their execution model (ECN, STP, or Market Maker), have different methods in order processing and risk management.
Selecting a reputable broker that matches trading needs determines the quality of trades, execution speed, capital security, and the trader’s returns in the forex market.
How Forex Brokers Work?
Forex brokers connect traders to the global currency market by receiving live quotes from liquidity providers or the interbank market and delivering them through trading platforms.
Order execution is handled either via direct models (STP/ECN), where trades are sent to the real market, or through market maker models, where the broker becomes the counterparty to the trade.
Forex brokers earn revenue through spread, commission, and swap fees, while also offering services such as diverse account types, analytical tools, and risk management.
Key criteria to evaluate how Forex brokers work include liquidity management, pricing transparency, and adherence to regulatory compliance.
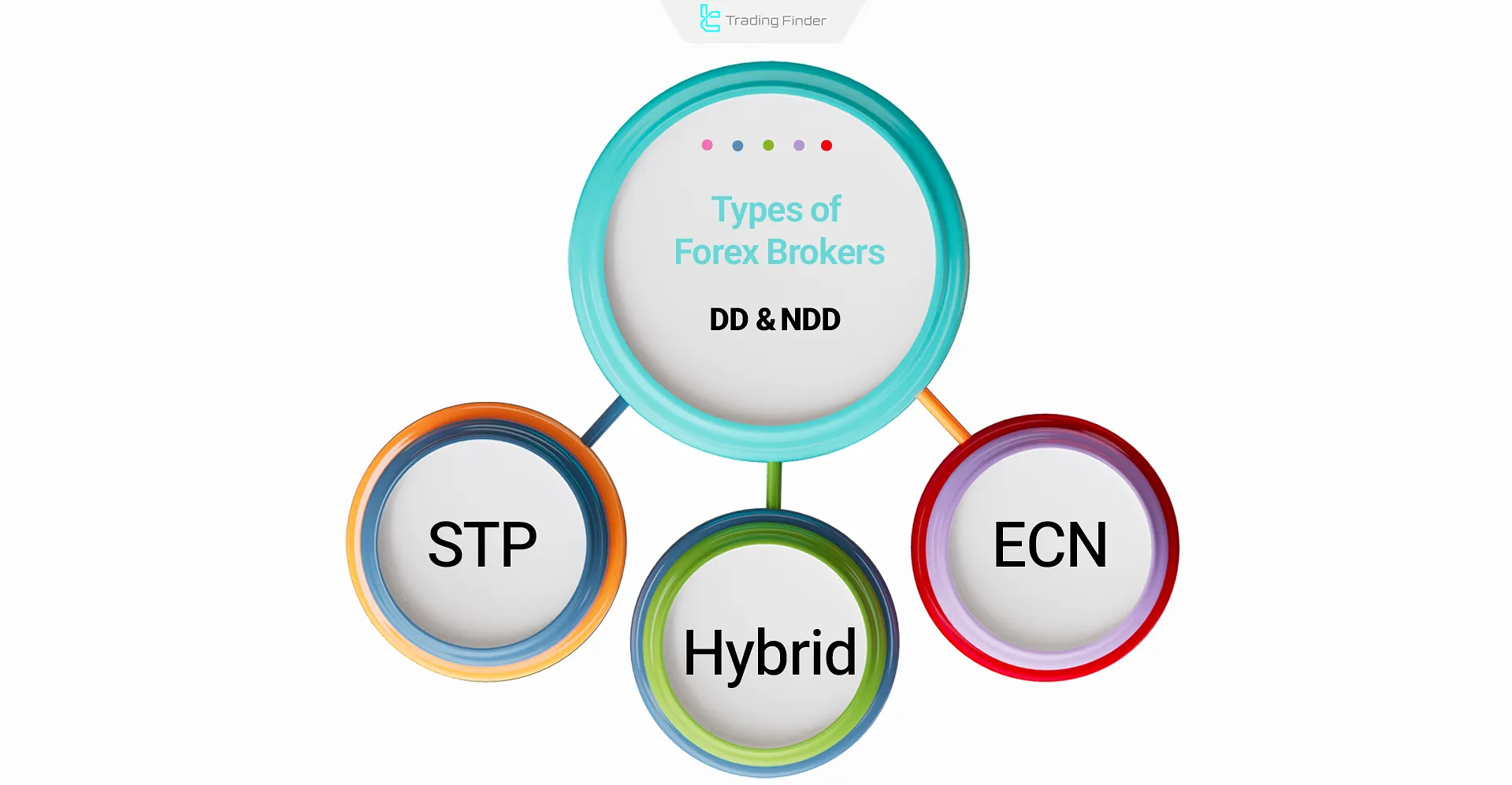
Types of Forex Brokers and Operating Models
The operational models of Forex brokers depend on how they manage client orders and connect to the market. Generally, there are three main models:
- Market Maker/Dealing Desk (DD)
- No Dealing Desk (NDD) including ECN (Electronic Communication Network) and STP (Straight Through Processing)
- Hybrid Broker
Market Makers/Dealing Desk (DD)
Market Maker brokers directly act as the counterparty to the trader’s order. In other words, when a trader buys a currency pair, the broker sells it, and vice versa. This model involves the following:
- Trades are not sent to the interbank market and are instead executed internally;
- Prices are aggregated from various sources and shown to the trader with either fixed or variable spreads;
- The broker’s profit comes from the spread or, in some cases, from the trader’s losses.
This model enables brokers with internal liquidity or large client volumes to execute orders swiftly; however, it may also create a conflict of interest, as the broker profits from client losses.
No Dealing Desk Brokers (NDD)
NDD brokers act as transparent intermediaries, transmitting orders directly to the market or liquidity providers without taking the opposite side of the trade.
This model is divided into two main subtypes:
STP (Straight Through Processing)
Orders are sent directly to a pool of liquidity providers such as banks and financial institutions:
- Broker revenue is earned via spreads or fixed commissions;
- There’s no manual intervention in execution, reducing the risk of slippage or delays.
Example of a Broker with the STP Model and No Dealing Desk
Suppose a buy order of 1 lot EUR/USD is placed in an STP broker. In this case, instead of being reviewed at the broker’s dealing desk (as in DD or Market Maker brokers), the order is directly sent to one of the liquidity providers connected to the broker, such as a bank or LP.
The STP broker acts solely as an intermediary and executes the order without human intervention and without altering the rate, at the best available price in the interbank market.
The broker’s source of income is obtained through commission or added spread (Markup), and it has no relation to the trader’s loss.
As a result, no conflict of interest arises between the trader and the broker, since the broker is not considered the counterparty to the trade.
ECN (Electronic Communication Network)
Traders are connected to an electronic network of banks, institutions, and other traders:
- Spreads are typically very tight or near zero;
- Brokers charge a separate commission per trade for this access;
- Full transparency, competitive pricing, and market depth are key benefits.
STP and ECN models are perfect for professional traders because they eliminate conflicts of interest, enable fast execution, and provide real market access.
Hybrid Brokers
In this structure, how Forex brokers work involves a combination of Market Maker and STP/ECN models.
Some orders are processed internally (B-Book) while others are passed to the real market or liquidity providers (A-Book). Most modern brokers operate under this hybrid model.
Comparison of Forex Brokers with Different Operating Models
In the table below, various types of brokers with different operating models are compared:
Broker Model | Nature of Order Execution | Pricing Source | Broker’s Income | Transparency / Conflict of Interest | Suitable For |
DD (Market Maker / Dealing Desk) | Counterparty to the client’s trade; internal settlement | Broker’s own price-making | Profit from client’s loss + fixed spread | Low transparency / high conflict of interest | Beginners and small accounts |
NDD (No Dealing Desk) | Direct order to the LP market | Liquidity providers | Variable spread + commission | High transparency / no conflict | More professional traders |
ECN (Electronic Communication Network) | Orders matched in the ECN network with real market depth | Real interbank rates (Level II) | Transparent commission + very low spread | Maximum transparency / no conflict | Scalpers, institutions, professionals |
STP (Straight Through Processing) | Direct transfer of orders to LPs | LP rates | Variable spread (sometimes + commission) | High transparency / no conflict | Retail and medium traders |
Hybrid Broker | Combination of DD and NDD depending on the client | Both internal price-making and real rates | Combination of the above models | Medium transparency / conflict in DD section | Large brokers and diverse clients |
Understanding A-Book, B-Book, and C-Book Models
The classification into A-Book and B-Book depends on how client orders are handled:
A-Book Broker (Agency Model)
Orders are transmitted directly to liquidity providers or the interbank market, with the broker acting merely as an intermediary. The broker's profit is independent of the trader’s gain or loss.
B-Book Broker (Dealing Desk Model)
Orders are processed internally and are not routed to the real market. The broker becomes the counterparty, meaning trader losses equal broker profits, and vice versa.
While riskier, this model can be highly profitable for brokers with proper risk management.
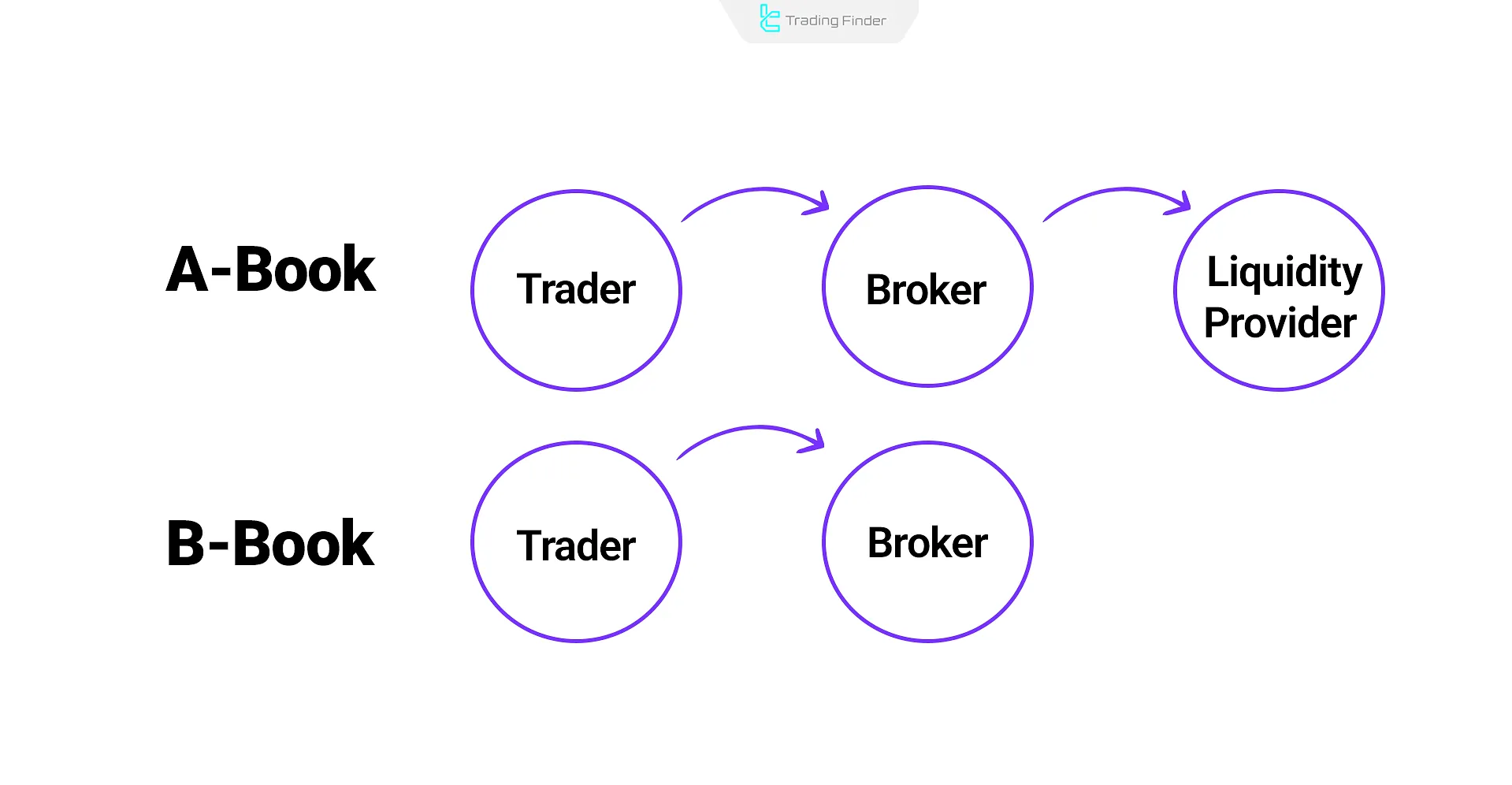
For more information and better understanding of A-Book and B-Book brokers, you can also refer to the educational video on Forex broker models available on the UKspreadbetting YouTube channel:
C-Book Broker (Client Book or Customized Book)
C-Book is not officially recognized in global Forex regulations but appears in some industry literature.
It typically refers to a broker’s internal management of a specific group of clients, where all trades are settled internally with no market exposure.
Regulatory bodies like the FCA or ASIC do not acknowledge the term C-Book in their frameworks.
Comparison of A-Book, B-Book, and C-Book Forex Brokers
In the table below, different types of brokers with A-Book, B-Book, and C-Book models are compared in terms of risk, source of income, transparency, and suitability for different traders:
Model | Nature of Execution | Broker’s Risk | Source of Income | Transparency / Conflict | Suitable For |
A-Book | Direct transfer of orders to LPs / interbank market | Near zero | Spread + commission | Transparent / no conflict | Professionals, scalpers |
B-Book | Broker is the counterparty to the trade (internal matching) | High (client’s profit = broker’s loss) | Client’s loss + spread | Low / severe conflict | Beginners, small accounts |
C-Book | Combination of A and B depending on client profile | Managed and segregated based on each client | Spread + commission + profit from some clients | Medium / limited conflict | Large brokers, diverse clients |
Review of Forex Brokers’ Sources of Income
The main sources of forex brokers’ income vary depending on the execution model:
- In the ECN model, the main source of income is commission and raw spread;
- In the STP model, a combination of markup on rates and spread;
- In the Market Maker model, in addition to the above, direct profit from client losses in the B-Book structure;
- Other sources include overnight swap and ancillary fees.
In general, a broker either earns from trading volume turnover or by taking the opposite side of clients’ trades.
For more information and a better understanding of how forex brokers work and how do forex brokers make money, you can also refer to the educational article and learn how do forex brokers work available at investopedia.com.
Order Execution Methods by Forex Brokers
Order execution in forex brokers depends on their operational model, and the quality of execution is influenced by factors such as speed, slippage, and the likelihood of order rejection.
Types of Order Execution Models in Brokers:
- Dealing Desk/Market Maker: Orders are processed internally with the broker as counterparty. Pricing is broker-defined and may involve a conflict of interest;
- No Dealing Desk - STP/ECN: Orders are routed directly to the market or liquidity providers. In STP, the broker selects from the best available prices. In ECN, orders are matched within a network of market participants.
Risks and Potential Drawbacks of Brokers in Order Execution
Just as brokers provide diverse services, traders must also be aware of certain risks and drawbacks. Recognizing these issues makes it possible to choose a transparent and reliable broker:
- Conflict of interest in Market Maker brokers and the possibility of trading against the client;
- Risk of negative slippage and order execution delays during high market volatility;
- Danger of operating with illegal brokers or those lacking valid regulation;
- Non-transparent withdrawal conditions in some weak brokers.
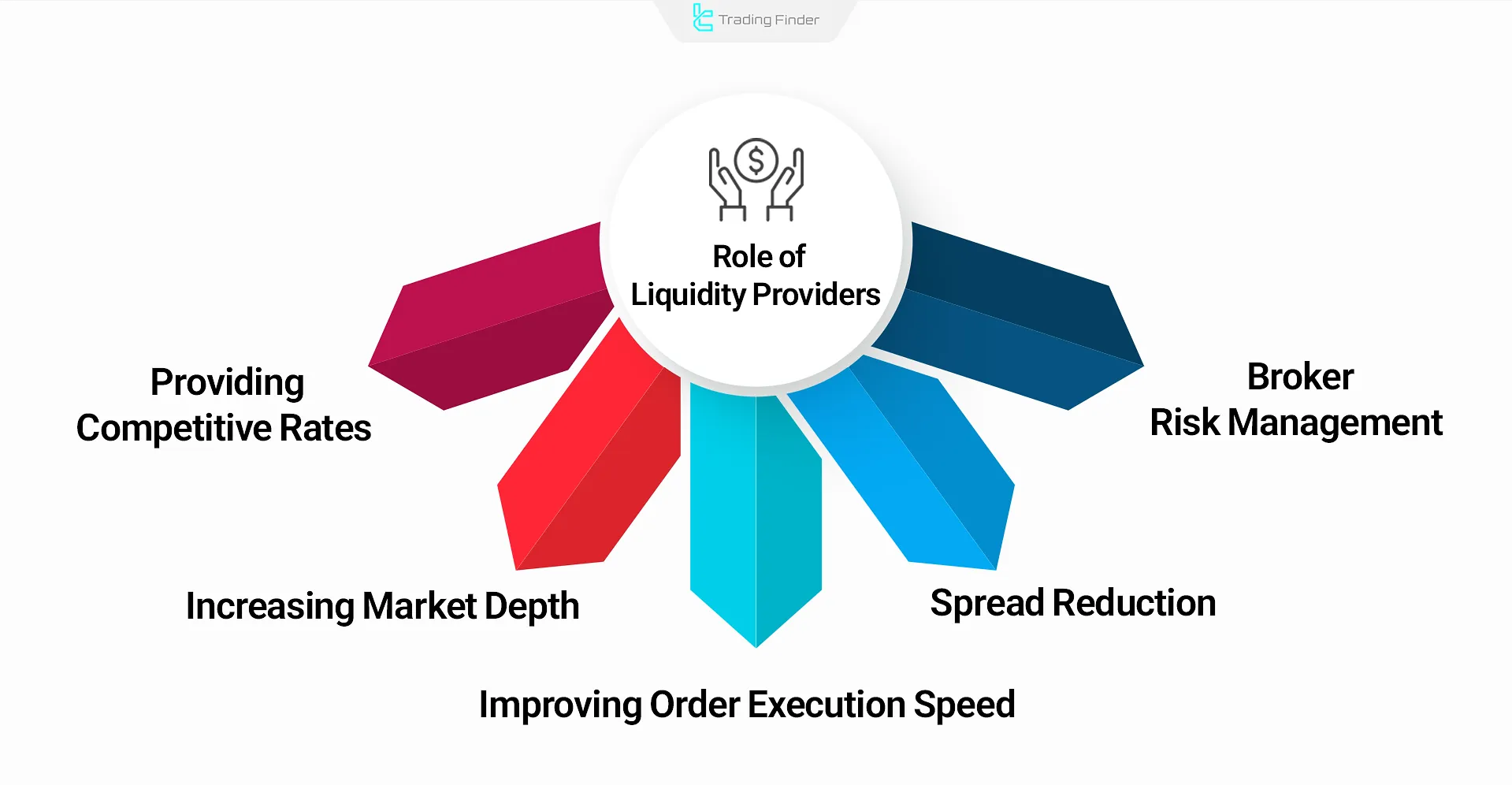
Role of Liquidity Providers in How Forex Brokers Work
Liquidity providers (LPs) are institutions that offer bid and ask prices for currency pairs and enhance the performance of forex brokers by executing orders instantly.
The Role of Liquidity Providers (LPs) in Brokers:
- Competitive pricing
- Increased market depth
- Faster execution
- Tighter spreads
- Risk management for brokers
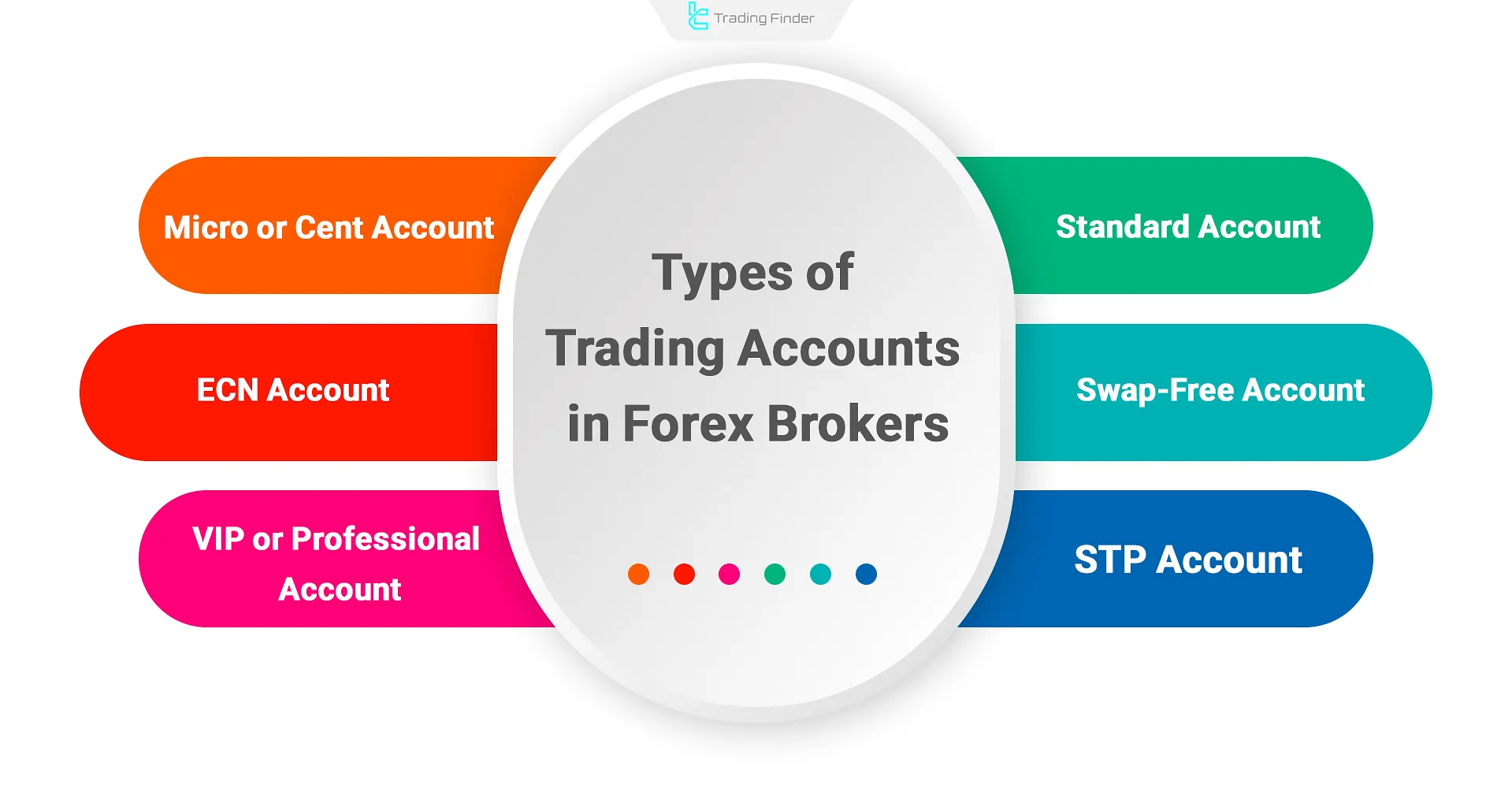
Types of Trading Accounts Offered by Forex Brokers
Forex brokers offer multiple account types to cater to various trader profiles:
- Standard Account: Common account with fixed or variable spreads, suited for intermediate to professional traders;
- ECN Account: Direct access to interbank markets, tight spreads, and per-trade commission;
- STP Account: Direct order routing to liquidity providers, often with variable spreads and no commission;
- Micro/Cent Account: Smaller lot sizes for risk control or practice with limited capital;
- Islamic (Swap-Free) Account: Interest-free accounts aligned with Islamic laws;
- VIP/Professional Account: Lower spreads, minimal commissions, and premium services for high-volume traders.
Additional Services of Forex Brokers
In addition to trade execution, reputable brokers also provide a set of other supplementary services:
- Facilitation of financial operations including fast and secure deposits and withdrawals;
- Access to daily market news along with fundamental analysis and technical analysis;
- Provision of educational content for both beginner and professional traders;
- 24-hour support via chat, phone, or email.
These services play a decisive role in choosing the right broker, especially for novice traders who require reliable educational resources and dependable support.
Forex Broker Regulatory Oversight
Licensing by top-tier regulators like FCA, ASIC, or BaFin indicates transparency, fund safety, and international compliance.
Next, we will examine the regulation of brokers. The table below outlines the regulatory bodies and their key features:
Regulator | Country | Key Feature |
FCA (Financial Conduct Authority) | UK | Strict capital protection rules |
ASIC | Australia | Transparent reporting and leverage restrictions |
CySEC | Cyprus | Trader protection and licensing rules |
NFA & CFTC | USA | Rigorous compliance for brokers and investment banks |
BaFin | Germany | Strong legal frameworks |
FINMA | Switzerland | Strong supervision for global markets |
FSCA | South Africa | High-level regulations in emerging markets |
Differences Between Regulated and Unregulated Brokers
Whether a broker is regulated or not reflects its level of transparency, security, and reliability. These two categories of brokers differ significantly in several key areas.
Differences Between Regulated and Unregulated Brokers:
Regulated Broker | Unregulated Broker |
Segregated client funds | Weak or no supervision |
Mandatory transparent reporting | No guarantee of fund safety |
Legal complaint mechanisms | No legal protection for traders |
Standardized trading conditions | Arbitrary changes to trading terms |
Regulated brokers offer greater fund security and legal protection compared to unregulated brokers, where traders may face elevated risks.
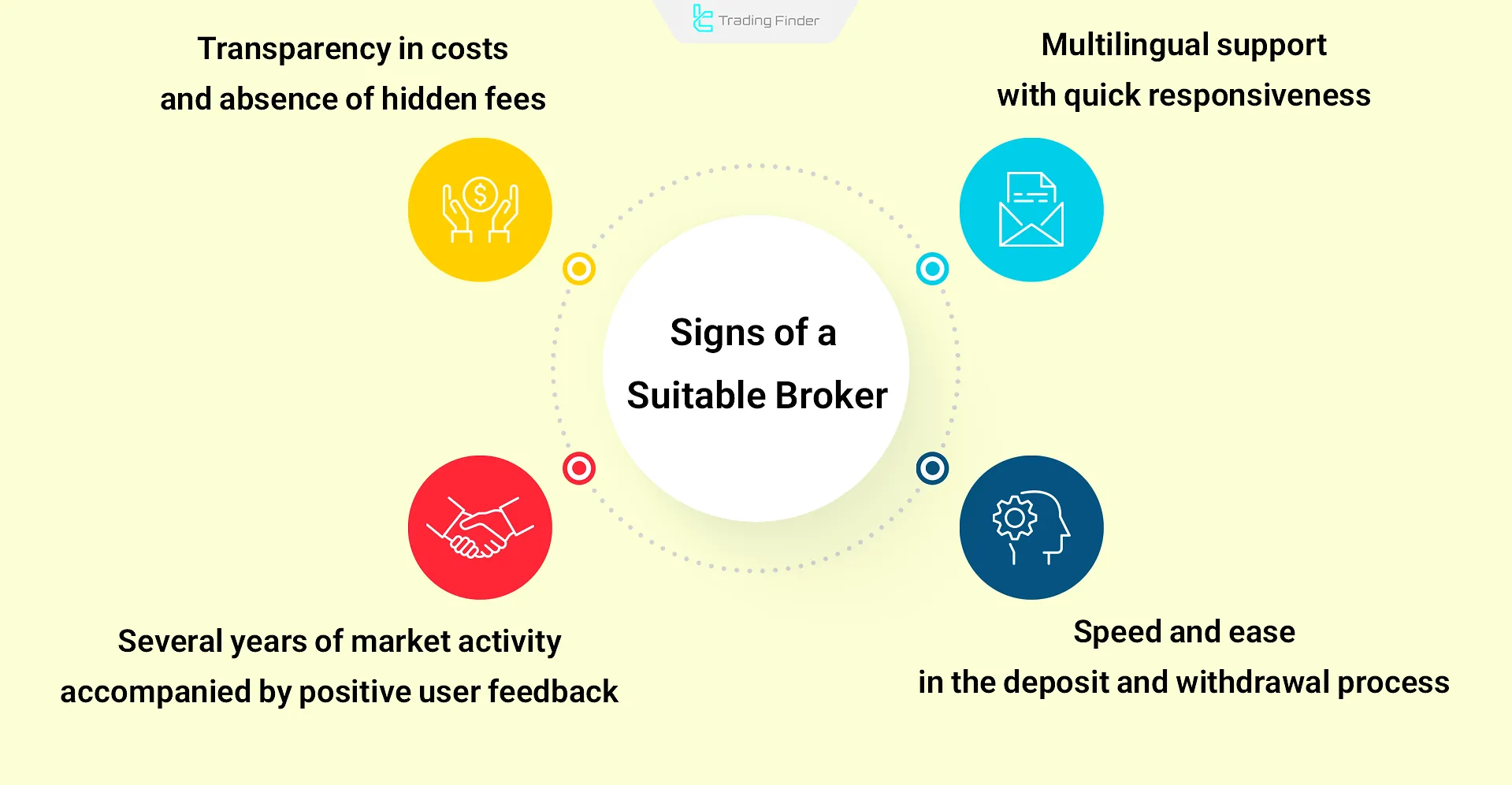
How to choose the best forex broker?
Having a regulatory license alone is not sufficient to evaluate a broker, and traders must also examine its credibility and track record. The signs of a reliable broker include:
- Transparency in costs and absence of hidden fees;
- Speed and ease in the deposit and withdrawal process;
- Several years of market activity accompanied by positive user feedback;
- Multilingual support with quick responsiveness.
The combination of these factors creates a comprehensive criterion for assessing a broker’s trustworthiness and making an informed choice.
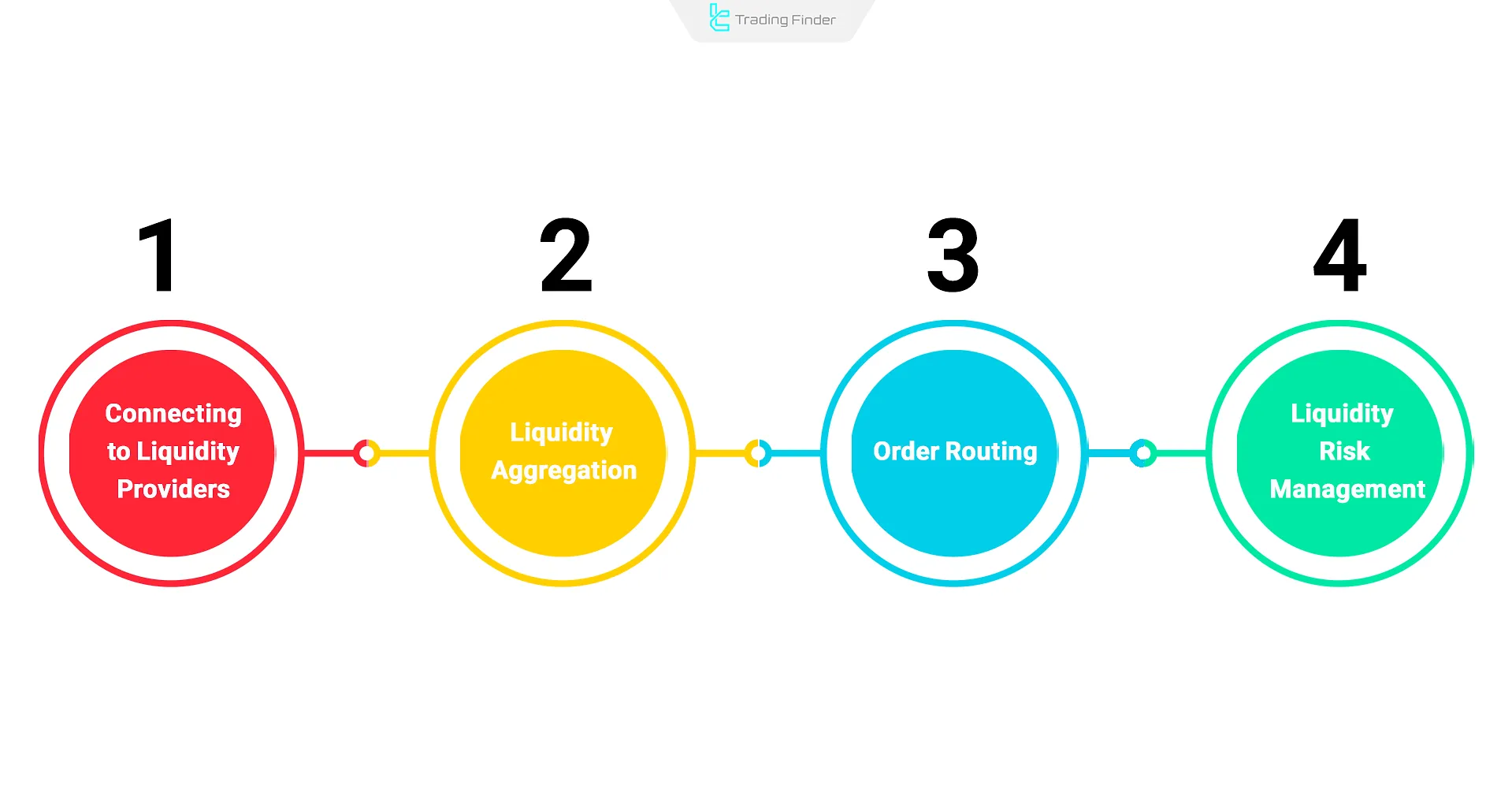
Liquidity Management by Forex Brokers
Forex brokers ensure efficient execution by sourcing liquidity from Tier-1 banks and financial institutions.
Using Liquidity Aggregation Systems, brokers consolidate pricing from multiple sources to offer optimal market prices. Order routing then determines the execution path.
During volatility or liquidity shortages, brokers use liquidity risk management strategies such as volume limits, spread adjustments, or provider switches.
Steps in broker liquidity management:
- Connecting to LPs for deeper markets and better pricing
- Liquidity aggregation from multiple providers
- Order routing based on order volume, market speed, and internal policies
- Liquidity risk management using volume caps or spread changes
Modern Technology Used by Forex Brokers
Modern brokers use advanced technologies for better speed, security, and performance:
- ECN Connectivity for direct, intermediary-free trading
- Liquidity Aggregation Systems to offer the best bid/ask prices
- VPS (Virtual Private Servers) for ultra-fast, uninterrupted execution
- FIX API for fast execution and bot connectivity
- AI and Machine Learning for data analysis, pattern detection, and forecasting
- Advanced platforms like MetaTrader 5 and cTrader
- Cybersecurity tools such as SSL encryption and IDS/IPS systems
Forex Trade Manager Expert Advisor for MetaTrader
The Forex Trade Manager Expert Advisor, from the specialized Trading Finder toolkit, is specifically designed for risk and capital management within the MetaTrader environment.
This intelligent system structures the trading process and provides customizable frameworks, enabling traders to follow their trading plan in an organized and controlled manner without being distracted by repetitive details or behavioral errors.
- Download Forex Trade Manager Expert Advisor for MetaTrader 5
- Download Forex Trade Manager Expert Advisor for MetaTrader 4
This advanced expert advisor offers a collection of essential features for professional trade management:
- Setting multiple levels of Take Profit (TP) and Stop Loss (SL);
- Partial Close execution;
- Break Even activation to shift risk to the breakeven point;
- Graphical management of positions on the chart;
- Account Protector – a tool with 7 tabs for risk control, trade limitation, and volatile news filtering.
The advantages of this powerful tool for traders include:
- Prop Firm Users: Compliance with strict requirements such as daily or percentage loss limits and prevention of account failure during challenge phases;
- Forex Traders: Full support for instant and pending trades, volume management based on capital or risk percentage, and precise execution of strategies across different timeframes;
- Strategy-Oriented Traders: Compatible with widely used styles such as ICT, Smart Money, Price Action, and Scalping for flawless trading plan execution.
Unlike many expert advisors that automatically enter trades, this tool does not make trading decisions on behalf of the trader; instead, it acts as a management framework, allowing full focus on technical and fundamental analysis.
In addition, the automatic calculation of trade volume based on account balance and selected risk level prevents high-risk or unplanned entries.
The Forex Trade Manager Expert Advisor is a comprehensive and professional solution for maintaining discipline, controlling risk, and structuring the trading process.
With its extensive features and full customization, this tool is not only an ideal choice for prop account traders and forex market participants but also for crypto traders, as it ensures sustainable capital management and precise execution of the trading plan.
Conclusion
Forex brokers act as intermediaries between traders and the global currency market using models such as Market Maker, STP, and ECN.
Key evaluation points include order handling, liquidity sourcing, applied technologies, and regulatory structure.
To understand how Forex brokers work, one must explore:
- The A-Book vs. B-Book models
- Regulated vs. unregulated brokers
- Trading account types
- Role of liquidity providers
Ultimately, modern brokers leverage advanced technology and strict compliance to deliver a fast, safe, and transparent trading environment.













