A crypto wallet is a digital wallet within the blockchain space that, through encrypted processes, allows users to store digital assets both online and offline.
Therefore, depending on user needs, various wallets with different features and levels of security exist in the cryptocurrency world. Choosing between them depends on factors such as the user’s level of experience, intended usage, and more.

What Is Crypto Wallet?
A cryptocurrency wallet is a software or device used to store digital assets, including cryptocurrencies, NFTs, and other types of digital assets. Additionally, a crypto wallet is connected to the blockchain, allowing users to create transactions and transfer digital assets to various addresses.
There are different types of crypto wallets, each with its unique features and capabilities. However, most of them function similarly. Crypto wallets operate by using a public key and a private key, which together allow the user to view balances and initiate transactions on the blockchain.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of a Cryptocurrency Wallet?
Using a crypto wallet makes asset transfers easier, allows full personal control over assets, and eliminates the need for banks or third-party intermediaries. However, it also comes with disadvantages such as dependency on the internet, the risk of cyberattacks, and the risk of losing the private key. Advantages and disadvantages of a cryptocurrency wallet include:
Advantages | Disadvantages |
High security | Internet dependency |
No access for banks, governments, or institutions | Risk of losing the private key |
Easy portability | Requires user training and familiarity |
Ability to use fingerprint and facial recognition for security | Risk of technical problems with the wallet |
How Does a Cryptocurrency Wallet Work?
Cryptocurrency wallets enable various transactions on the blockchain by connecting to it and utilizing its capabilities. A crypto wallet uses the private key to grant access for transferring blockchain-based assets.
Contrary to popular belief, a crypto wallet does not store digital assets. Cryptocurrencies always remain on the blockchain. Thus, a crypto wallet generates a public key and a private key, allowing the wallet’s owner to access their digital assets.
What Are Public and Private Keys in a Crypto Wallet?
A public key is a code consisting of letters and numbers used as the wallet address. It functions like a bank account number and is shared to receive digital assets without compromising wallet security.
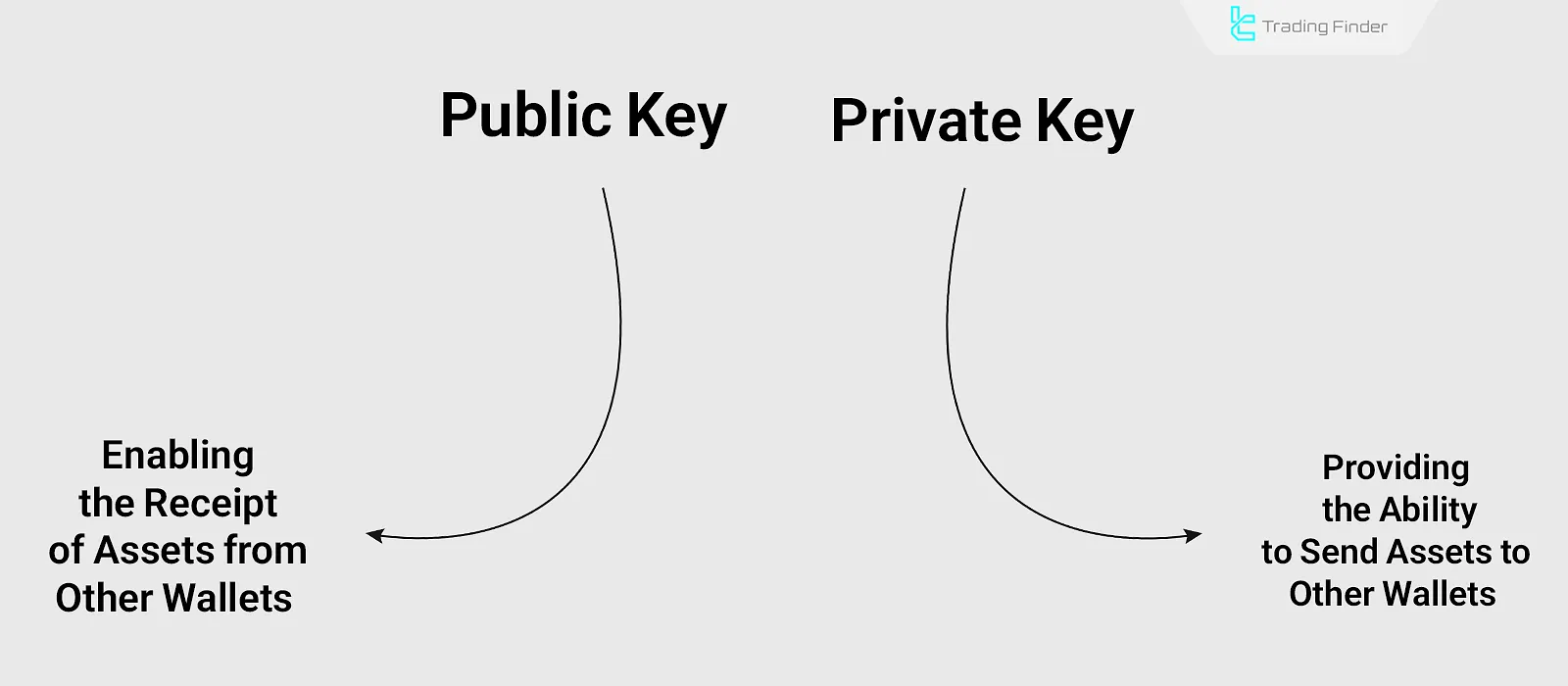
A private key is the access key to the assets inside the crypto wallet. Like the public key, it is an extended code. For easier storage and use, it is usually provided to the wallet owner as a 12- to 24-word phrase. Therefore, losing the private key means losing access to the wallet and all the assets it holds.
How Are Transactions Performed?
When a wallet owner initiates a transaction, the crypto wallet signs the transaction using the private key. With this signature, ownership of the assets is confirmed, and the transaction is sent to the blockchain.
It is then verified by validators or miners and ultimately recorded on the blockchain.
Types of Crypto Wallets
In general, there are two types of crypto wallets:
- Cold Wallet
- Hot Wallet
Hot Wallet
Hot wallets are software wallets connected to the internet that store wallet keys online. They are available in various forms, including mobile apps, browser extensions, web platforms, and more.
Types of hot wallets include:
- Desktop Wallet
- Mobile Wallet
- Web Wallet
- Browser Extension Wallets
Cold Wallet
A cold wallet stores private keys offline and is not connected to the internet. Therefore, it offers a higher level of security compared to hot wallets. However, because it is not online, accessing and using digital assets is generally more difficult than with a hot wallet.
This type of wallet is usually offered as a USB storage device. Therefore, to use the assets stored in it, a connection to a computer and internet is required.
The Difference Between Custodial and Non-Custodial Wallets
Cryptocurrency wallets are categorized based on how they handle the private key, and fall into two groups:
- Custodial Wallets
- Non-Custodial Wallets
Custodial Wallet
In this type of wallet, the wallet provider platform is responsible for storing the private key, and assigns a username and password to the wallet owner for access. Thus, losing the password does not pose a risk, and the wallet and its assets can be recovered simply by verifying identity or requesting a password reset via email.
However, using a custodial wallet comes with risks such as:
- Account freeze by the platform
- Vulnerability to hacking and cyberattacks
- Bankruptcy of the wallet service provider
Non-Custodial Wallet
In this type of wallet, the private key is provided directly to the wallet owner, and no one else has access to it. Therefore, complete control over the assets rests with the wallet owner. Also, if the wallet owner loses the private key, there is no way to recover it, and the assets will be permanently locked in that wallet.
Using a non-custodial wallet ensures that no individual, government, or organization other than the wallet owner can access the stored assets. However, in this case, the full responsibility of safeguarding the assets lies solely with the wallet owner, which can be a significant burden.
Key Points for Storing the Recovery Phrase
The recovery phrase is essentially the private key of the wallet. If lost, there is no way to access the assets in the wallet. Therefore, it's crucial to follow best practices, such as using offline storage, making multiple copies, and storing them in secure environments.
Important Tips for Recovery Phrase Storage:
- Create multiple copies of the phrase: To mitigate risks such as floods, fires, etc., it is best to make several copies of the recovery phrase and store them in different locations;
- Store offline: Issues like hacking or mobile phone theft mean that online storage of the recovery phrase is not secure;
- Do not share it with others: No identity information is required to access a crypto wallet. Anyone with access to the private key can move the assets. Therefore, the private key must be stored confidentially and privately.
Crypto Wallet Security
The security of a crypto wallet is ensured through multiple factors such as private keys, fingerprint recognition, two-factor authentication, and more. Hence, the level of security varies from one wallet to another based on the services it offers in this regard.

Introduction to the Best Crypto Wallets
There are various wallets available on the market, both cold and hot, that provide services to users. Each of these wallets offers a different user interface and features and are used by participants in the crypto market based on their preferences. Below is an introduction and comparison of the best cryptocurrency wallets:
Wallet Name | Wallet Type | Number of Supported Blockchains | Number of Supported Tokens | Price | Security |
Trust Wallet | Software | More than 100 blockchains | More than 10 million tokens | Free | Fingerprint, facial recognition, two-factor authentication, password |
MetaMask | Software | 9 blockchains | More than 500,000 tokens | Free | Password and PIN |
Ledger | Hardware | Varies by model | More than 5,000 tokens | Varies by model ($90 to $455) | PIN |
Trezor | Hardware | More than 60 blockchains | More than 9,000 tokens | Varies by model ($49 to $169) | PIN |
Fantom | Software | 6 blockchains | Unlimited | Free | Password, PIN, fingerprint, facial recognition, two-factor authentication |
Rabby | Software | More than 100 blockchains | More than 10,000 tokens | Free | Secure address, password, fingerprint, facial recognition, two-factor auth |
SafePal | Hardware / Software | More than 100 blockchains | More than 30 tokens | Software: Free / Hardware: $49.99 to $89.99 | Secure address, password, fingerprint, facial recognition, two-factor auth |
Atomic | Software | More than 100 blockchains | More than 100 tokens | Free | Secure address, password, fingerprint, facial recognition, two-factor auth |
Tonkeeper | Software | 2 blockchains | TON network tokens + USDT | Free | Password, fingerprint, facial recognition, two-factor authentication |
KeepKey | Hardware | 12 blockchains | More than 7,000 tokens | Varies by model ($78 to $98) | PIN |
Ellipal Titan | Hardware | More than 40 blockchains | More than 10,000 tokens | Varies by model ($39 to $199) | PIN |
Coinomi | Software | More than 125 blockchains | More than 350 tokens | Free | Secure address, password, fingerprint, facial recognition, two-factor auth |
Exodus | Software | More than 50 blockchains | All Ethereum tokens + 5 other coins | Free | Secure address, password, fingerprint, facial recognition, two-factor auth |
Criteria for Choosing a Reliable Crypto Wallet
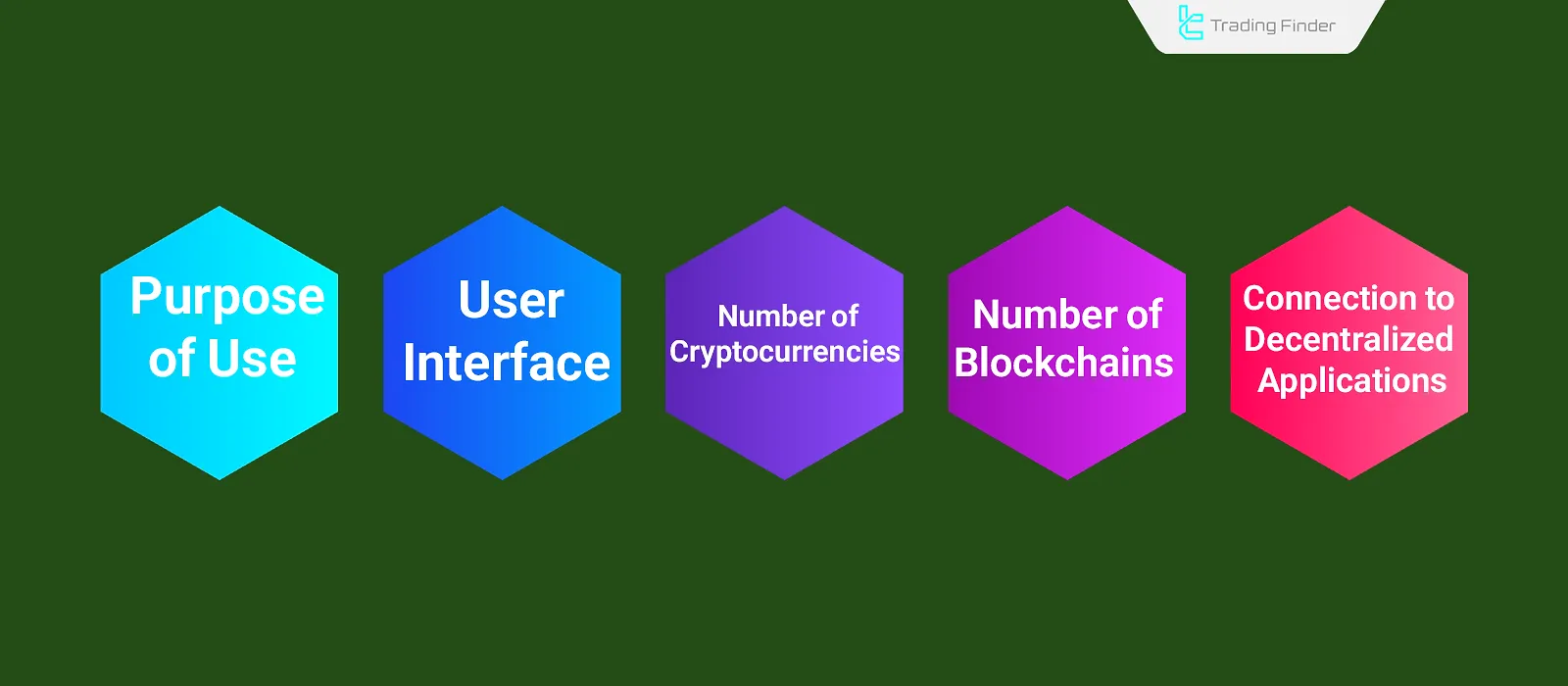
Choosing a cryptocurrency wallet depends on various criteria, such as security, user interface, the number of supported cryptocurrencies, intended use, and more.
Key selection criteria include:
- Purpose of use: There are different reasons for using a wallet—such as holding digital assets, Day Trading, etc.—and each may require a different wallet;
- User interface: Wallets vary in their complexity; selection should be based on how comfortable the user is with the interface;
- Number of supported cryptocurrencies: Based on the intended use, the number of tokens supported may influence the wallet choice;
- Number of supported blockchains: To transfer assets, ensure the wallet supports the desired blockchain;
- Security: Evaluate whether the wallet offers features like fingerprint recognition, facial recognition, and two-factor authentication;
- DApp compatibility: The ability to connect to decentralized applications (DApps) for activities such as staking, yield farming, and NFT marketplaces is a major benefit.
Important Tips for Using a Crypto Wallet
In general, cold wallets offer more security than hot wallets because they never expose the private key online. Even during transaction creation, the cold wallet only receives the transaction details, signs them offline, and then transmits the signed transaction online to be recorded on the blockchain.
Therefore, when using hot wallets, it’s essential to follow certain precautions such as avoiding unknown platforms, rotating wallets periodically, and more.
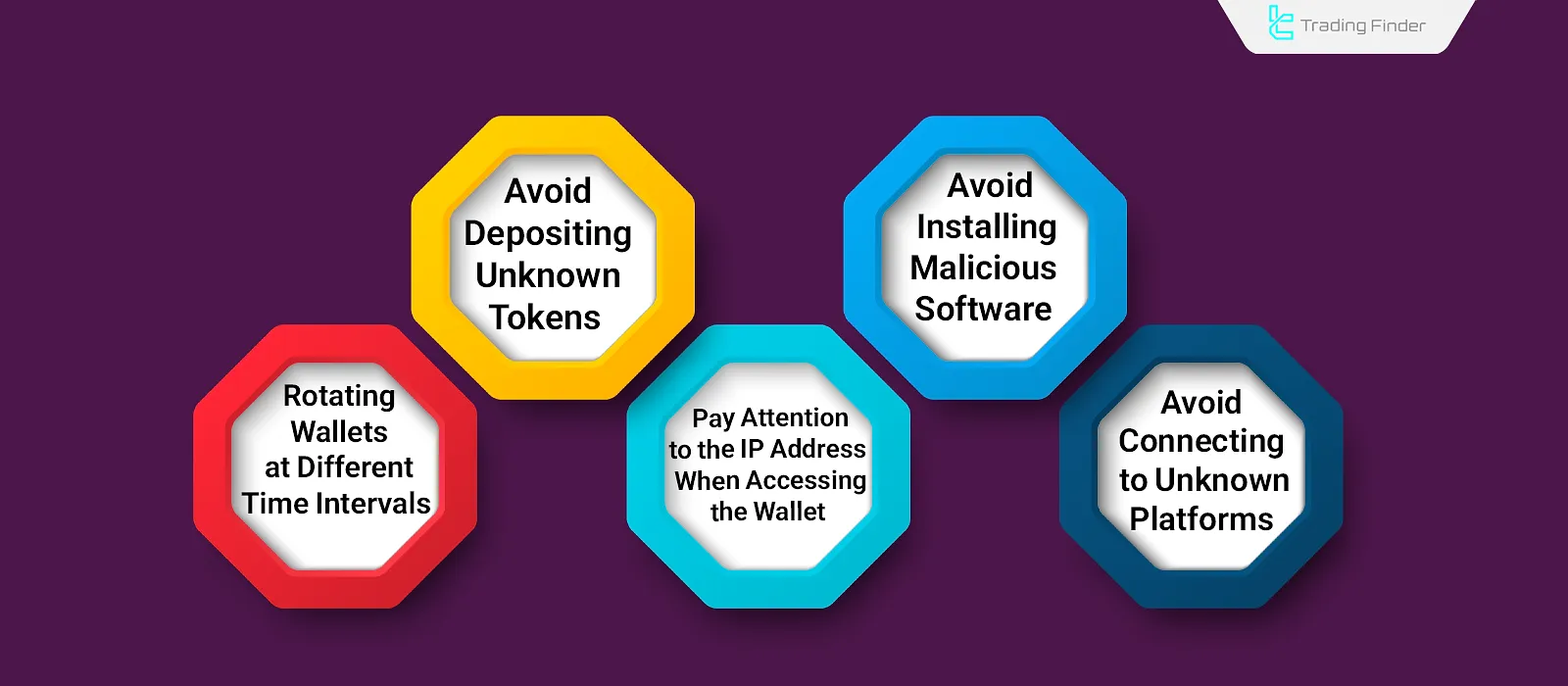
Important Tips for Using Hot Wallets:
- Avoid connecting to unknown platforms: Many platforms embed smart contracts that allow them access to connected wallets. Thus, it's crucial to verify the credibility of any platform before connecting your wallet;
- Rotate wallets periodically: Some smart contracts activate ongoing access to the wallet after initial transactions. Therefore, transferring your assets to a new wallet after a few uses enhances security;
- Avoid receiving unknown tokens: Some suspicious tokens are promoted with deceptive advertising and may act like malware, jeopardizing wallet security;
- Check your IP when logging in: Repeated and suspicious changes in IP addresses may trigger the wallet to be locked or the assets frozen;
- Do not install malware on the device hosting the wallet: Many malware programs are designed to grant the attacker access to the wallet as soon as they are installed. Hence, using only trusted software is essential.
Conclusion
A crypto wallet is a device or software that uses encryption to generate a private and public key pair, which allows the storage, sending, and receiving of digital assets on the blockchain.
It is not possible to withdraw digital assets from the blockchain. In reality, the crypto wallet creates a private key that gives the wallet owner access to their digital assets on the blockchain.
Crypto wallets are categorized into cold and hot wallets, with the main difference being how the private key is stored: cold wallets keep it offline, while hot wallets store it online.
The private key is a cryptographic string that provides access to the wallet’s assets. For ease of storage, it is usually presented to the user in the form of 12 to 24 words. Losing this phrase means the wallet and its contents are lost forever, and the recovery of the private key is not possible under any circumstance.













