Distinguishing between binary options and traditional options is not merely a comparison of two derivative instruments, it is an examination of two completely independent financial architectures, each built on its own analytical logic, risk structure, and trading mechanism.
The two instruments create distinct paths for analysis, execution, and management, and this is exactly what makes the difference between binary trades and binary options trades a more than superficial choice.
Each instrument has its own operational philosophy, a philosophy rooted in the way the trader perceives volatility, time value, risk structure, and pricing models.
What are Binary Options?
A binary option is a derivative instrument whose structure is built on binary decisions. This instrument makes sense when the trader evaluates the outcome of a price move in the form of a two state choice.
In this framework, the market becomes a decision driven space, a space in which there is only one correct path and any incorrect path destroys the trade capital. As a result, the binary nature of the product is formed around several core axes.
Derivative Instrument with Two Possible Outcomes Win or Loss
The binary structure is built on the logic that each trade, instead of generating a wide spectrum of outcomes, produces only two possible exits.
A correct outcome generates a fixed return, while an incorrect outcome eliminates the entire trade capital. This duality turns binary options into one of the most straight forward trading mechanisms.
Fixed and Predefined Payout in Binary Options
The nature of the fixed payout is one of the fundamental elements of binary options. Before entering the trade, the trader knows exactly how much will be received in the event of success.
This feature distances the valuation model from complex domains and enables faster mental planning.
Dependent on Up and Down Forecasts Within a Specific Time Window in Binary Options
Binary options are essentially a time based competitive mechanism. The trader only forecasts the direction of price within a defined time window.
The trade outcome is determined not by the magnitude of the price change, but by whether the direction was correct.
Structure Based on Strike Price and Expiry Time in Binary Options
Binary options have no meaning without the two key elements of strike price and expiry time.
These two components are the fixed points of the contract and the trader only needs to assess at what level the price will close relative to the strike price.
This structure turns binary options into a practical instrument for short term trading, yet the same simplicity can exponentially increase the risk.
What are Traditional Options?
A traditional option is a multi-layered derivative instrument designed to provide flexibility in risk management, structured speculation, and volatility hedging.
Unlike binary options, a traditional option is an open contract with diverse execution paths. In this instrument, the value of the contract is calculated based on pricing models and the trader can manage the trade path over time according to market behavior in the following ways
Derivative Instrument Based on the Right to Buy or Sell
The core axis of options trading is built on the concept of a right, a right that the contract holder can choose to exercise or not.
This structure creates a degree of freedom that does not exist in binary options and makes options a flexible instrument.
Complex Pricing with Premium
The value of an option is determined by its premium, and this premium is calculated as a function of volatility, time value, underlying asset price, and the Greek parameters. This very complexity turns options into a professional grade instrument.
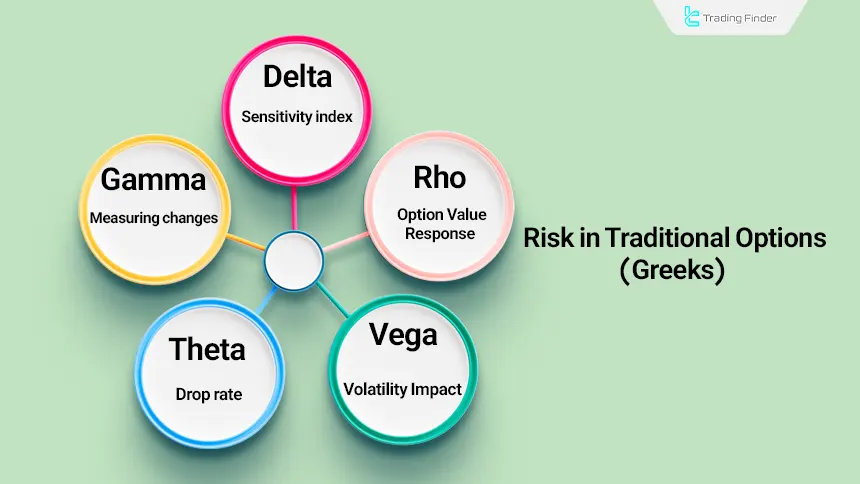
The Greek parameters in options trading are quantitative tools that measure the sensitivity of the premium to key variables:
- Delta: Measures how the option price changes relative to movements in the underlying asset
- Gamma: Monitors the stability of this change
- Vega: Shows the effect of volatility on the value of the contract
- Theta: Measures the rate of time value decay
- Rho: Indicates the sensitivity of the premium to interest rate changes
Types of Call and Put
Options are traded in the form of calls or puts. A call represents the right to buy and a put represents the right to sell.
These two structures allow the trader to make decisions based on directional price analysis and design various scenarios as follows

American and European Styles
The American style allows the contract to be exercised at any time up to expiry, while the European style only allows exercise at the moment of expiry.
This difference determines the level of flexibility and the premium of the contract. The presence of these four pillars turns traditional options into one of the main instruments in risk management and professional investing.
Structural Comparison of Binary Options and Traditional Options
A structural comparison of these two instruments shows that despite their similar names, they belong to two completely independent worlds.
Binary options are designed for simplicity and the trade path consists of only one entry point and one exit point. In this structure, after placing the trade, the trader has no discretion to manage the position.
Traditional options have a flexible and dynamic structure. The trader can exercise the contract, sell it, hedge it, or design a multi layered strategy such as a vertical spread or an iron condor.
This structural difference separates options from a purely speculative tool and turns them into an instrument in the realm of financial analysis.
Comparison Parameters | Binary Options | Traditional Options |
Structural complexity of trades | Simple, single stage structure | Multi layered, dynamic structure |
Management of trade points | Only one entry point and one exit point | Ability to create multiple entry, exit, and adjustment points |
Level of control over the position | No ability to manage, modify, or close early | Ability to exercise, sell, hedge, or adjust the trade structure |
Diversity of trading strategies | Limited to Up and Down decisions within a time window | Ability to use advanced strategies such as Vertical Spread, Iron Condor, and Strangle |
Flexibility in position management | No flexibility, limited to expiry outcome | High flexibility with the ability to adjust, shift, and rebuild positions |
Decision making logic | Conditional decision making based on final outcome | Decision making based on structural analysis and financial engineering |
Depth of risk management and position structuring | Lacks multi layered analytical architecture | A complete financial architecture with risk management and structured position building |
Regulatory Differences Between Options and Binary Options
Regulatory differences between the superiority of binary options or options are recognized as one of the most fundamental distinctions between these two instruments, because the legal framework of each instrument determines the trade execution path, the level of capital safety, and the manner of institutional supervision.
Binary options in many countries are subject to limited regulation, and this restriction stems from the structural similarity of this instrument to betting mechanisms and from its inherently high level of risk.
Extreme volatility, the possibility of total capital loss, and the activity of unlicensed brokers have led many financial authorities to classify binary options as a domain requiring restrictions.
In contrast, traditional options operate under the supervision of reputable institutions such as” SEC”, “FINRA”, and “CFTC”, and this regulatory structure creates precise reporting rules, transparent settlement standards, and a reliable financial architecture.
The history of fraud and misleading advertising in binary options has further emphasized the importance of supervision, and this legal disparity has made the choice between the two instruments not merely a financial decision, but a decision based on assessing legal risk and trust structure.
Comparison Parameters | Binary Options | Traditional Options |
Level of legal supervision | Limited oversight | Broad regulatory oversight |
Credibility of supervisory bodies | Often lacking reputable regulators in many countries | Supervised by SEC, FINRA, CFTC |
Legal and financial standing | Classified among quasi betting instruments | Part of the formal financial market |
Level of structural risk | High due to lack of unified standards | Lower due to well defined regulatory frameworks |
Operational transparency | Unlicensed brokers, misleading marketing, lack of transparency | Precise reporting, informational transparency, standard settlement |
Legal safety of capital | Extreme volatility, total capital loss, potential fraud | Strong legal framework with enforceable protections |
Instrument selection logic | Requires awareness of legal risks | Based on analytical models and formal frameworks |
Analysis of Return Structure in Binary Options and Traditional Options
Return behavior in derivative instruments is one of the key elements in selecting a trading style, because it shapes the nature of profitability and the risk model.
The difference between binary trades and options trades lies in the fact that although both are driven by price volatility, the path through which return is generated in each is fundamentally different.
Moreover, in binary options the risk to reward ratio is structurally set in favor of the contract issuer and the trader cannot optimize this ratio over the life of the trade.
In traditional options, returns can be designed in a nonlinear manner and depending on the type of strategy, profitability can be generated even in low volatility markets.
Return in Binary Options
The return structure in binary options is based on a completely fixed and predefined model, and the profit amount is determined at the moment the trade is placed.
The return percentage is usually between 70 and 85 percent and this amount does not change until expiry, even if the price experiences significant volatility along the way.
The absence of residual value at expiry means that the slightest prediction error completely wipes out the invested capital. This feature turns binary options into an instrument with absolute risk and ties profitability solely to the final outcome of the trade.
Return in Traditional Options
The return on traditional options has a floating structure, and the amount of profit or loss changes based on the magnitude of price moves, implied volatility, time value, and market behavior.
This instrument does not impose a fixed profit ceiling and the return can grow to multiple times the premium, although this same feature also increases the possibility of large losses.
The dependence of returns on pricing models such as Black Scholes and the Greek parameters creates a broad analytical space and enables the construction of complex trading strategies. This dynamic behavior has placed options in the category of engineered financial instruments with advanced profitability potential.
Structural Risk Differences in Binary Options and Traditional Options
Risk in derivative instruments is not just a quantitative variable, it is a core component of the decision making architecture and determines how the trade is structured.
Difference between binary options and Forex create different risk models and each instrument has its own behavioral logic and volatility range. Understanding this distinction enables traders to align their level of engagement, type of analysis, and strategy with the appropriate structure.
Risk in Binary Options Binary Options Risk
Risk in binary options is built on a fully absolute model and the trade outcome is recorded only as a win or loss. The profit and loss structure has no middle ground and a small error in forecasting the short term price path wipes out the entire invested amount.
Because this instrument depends entirely on a time based expiry outcome, it creates a level of psychological pressure and operational risk that cannot be changed or managed over the life of the trade.
The presence of unlicensed brokers and a history of fraud add another layer of risk and make the outcome resemble a final hit rather than a manageable process.
Those who wish to examine more closely the Difference between binary trades and options trading and options can use the educational video published on the "Trading IQ Option Wiki" YouTube channel as a complementary resource.
Risk in Traditional Options
Traditional options use a multidimensional analytical model and the trader can measure and adjust contract behavior according to different variables.
This model takes risk out of the absolute state and transforms it into an engineered structure as follows
- Delta: an index of the sensitivity of contract value to price movement
- Gamma: measurement of delta changes and the position reaction to new volatility
- Theta: presentation of the rate of time value decay and the direct effect of time
- Vega: determination of the level of impact of implied volatility on contract price
- Rho: measurement of the option value reaction to interest rate changes
This multi parameter structure enables risk control, forecasting, and management at a level that does not exist in binary options.
This property makes risk behavior in options act as a model based, measurable, and analyzable pattern.
Active Brokers in the Binary Options
Because of the absolute risk structure, the binary options market requires the selection of brokers that can offer transparent pricing, precise exit systems, and reliable support.
Binary options versus traditional options have a simpler structure and are based on forecasting price direction within a defined time window, as with the following brokers
- IQOption
- PocketOption
- Quotex
- OlympTrade
- Expert Option
These are among the active participants in this field and generally provide their services through online platforms. In this market, the outcome of each trade is defined as either successful or unsuccessful fixed profit or total loss.
Furthermore, the lack of a unified supervisory infrastructure in many countries has caused a significant portion of these brokers to operate under offshore regulations. As a result, broker assessment has become a critical step as follows
Transparency in Performance Reporting Among Binary Options Brokers
Platforms that transparently publish accurate reports on trade execution time, real order volumes, and return calculation methods also provide the possibility to analyze performance and risk control.
This transparency prevents decision making from being purely guess based and allows short term binary trades to be executed on the basis of data and logic.
Transparency is the most important trust indicator in a market where trade outcomes are determined in a matter of seconds.
Minimum Suitable Capital in Binary Options
Many binary brokers allow entry with low capital and the trader can begin exploring the instrument with a limited amount.
The low cost entry model is part of the appeal of binary options and the broker must offer this feature without hidden fees.
Speed of Execution in Binary Options Trades
Execution speed has vital importance in binary options because a delay of just a few milliseconds can change the trade outcome.
This time sensitivity means that the broker infrastructure is directly tied to trade accuracy, not merely to the recorded price.
A reputable broker must use fast execution engines so that the time gap between order submission and order fill is minimized. As a result, such infrastructure prevents unwanted price changes at the moment of execution.
Any weakness in the processing system leads to orders being filled under conditions different from those at the decision time and effectively makes execution quality part of the trading strategy itself in binary options.
Coverage of Diverse Assets in Binary Options
The ability to trade currency pairs, indices, commodities, and cryptocurrencies provides the variety needed to deploy different trading strategies. The broader the asset universe, the easier it is to align trades with market conditions.
Regulatory Status in Reputable Jurisdictions for Binary Options
Official oversight in the binary space is limited, but brokers that operate under reputable regulation present a more transparent model of performance and create a more trustworthy structure.
Reputable regulatory bodies, through defining standard reporting systems, strict financial requirements, and clear compliance frameworks, create an environment in which execution quality, capital safety, and transparency of order flow operate more reliably.
These criteria strengthen the trader’s decision making structure and transform the trading environment from a silent, high risk venue into a controlled setting.
Introducing a Binary Options Indicator for Entering Scalp Trades in Volatile Market Conditions
The fast binary options scalp signals indicator for M1 and M5 timeframes is a specialized tool in the MetaTrader platform developed for binary options, forex, and crypto traders so that they can structurally identify call and put trading opportunities in very short windows such as M1 and M5.
This tool is built on Smart Money Concepts logic and key structures such as order blocks, liquidity sweeps, and FVG formation. For traders who work with ICT concepts, it is therefore considered a fast and structurally reliable signal source.
The indicator logic is simple yet highly targeted. Whenever the market forms a valid order block and liquidity in the upper or lower range is collected, a gap called a fair value gap appears. The return of price to this zone is the area where the order flow of market makers reactivates.
The indicator analyzes this pullback as a potential entry point and generates a call or put signal.
This trading system falls into the category of trend, breakout, and entry exit indicators for MetaTrader 5 and is suitable for fast scalping and scalper styles. Since FVGs occur in all markets, this indicator is applicable to forex, cryptocurrencies, commodities, and indices.
The indicator plots all FVG zones on the chart and uses colored bullish and bearish arrows to display signals in a fully visible manner.
Ultimately, the fast binary options scalp signals indicator on M1 and M5 timeframes is a signal based tool that, with high processing speed and reliance on smart money structure, provides the ability to capture short term call and put opportunities with greater precision.
- Fast binary options scalp signals indicator on M1 and M5 TF for MT4
- Fast binary options scalp signals indicator on M1 and M5 TF for MT5
Brokers Active in the Options Space
The traditional options space operates as part of the formal market and includes brokers such as
- Interactive Brokers
- Charles Schwab
- TD Ameritrade
- E*TRADE
- Fidelity
- Saxo Bank
- IG Markets
- Tastytrade
These brokers must comply with more complex regulatory, operational, and financial standards. This requirement creates an extensive network of supervisory institutions, legal structures, and accounting frameworks that are all designed to preserve trading security as follows
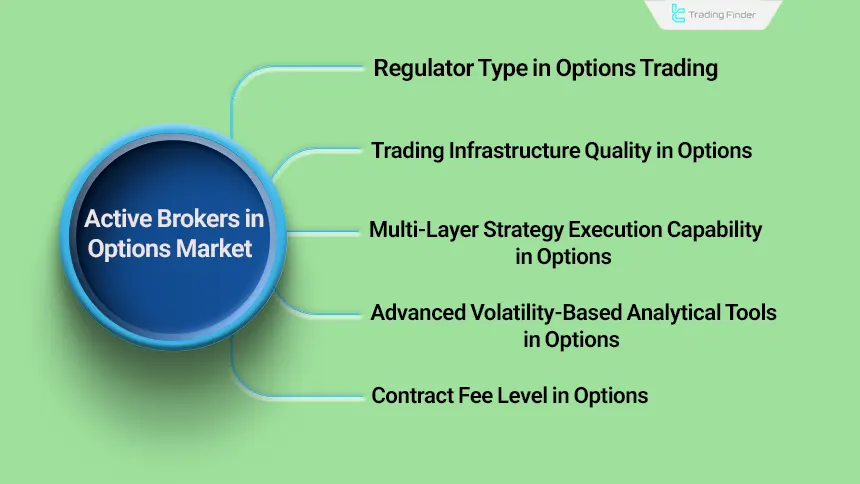
Type of Supervisory Regulator in Options Trading
The presence of organizations such as the “SEC”, “CFTC”, and “FINRA” creates a high standard of service provision.
As a result, formal supervision places broker behavior within a predictable framework and allows the trader to monitor order execution with greater precision.
Quality of Trading Infrastructure in Options
Options trading requires infrastructures capable of transmitting real time data, implied volatility, expiry volumes, and multi layered pricing without delay.
This level of technological demand distinguishes options brokers from binary brokers and highlights the need for robust software architecture.
Ability to Execute Multi Layered Strategies in Options
The options structure allows traders to use combinations of call and put contracts to create strategies such as spreads, straddles, or iron condors. A reputable broker must also provide the ability to build, adjust, or close these structures.
Advanced Volatility Based Analytical Tools in Options
Options have no meaning without the analysis of volatility and Greek parameters. Graphical tools, volatility charts, internal pricing models, and risk measurement tools are among the advantages of professional brokers.
Level of Contract Fees in Options
The fee structure in options is one of the key elements of profitability. Each option contract has its own transaction cost and a professional broker must offer a transparent, stable, and comparable fee schedule.
These components complete the analytical side of broker selection and provide a realistic picture of the trading environment for option based instruments.
For a more detailed study of binary options versus traditional options, the educational content published about training and examining the differences between binary options and traditional options on pocketoption.com serves as a suitable reference and provides a deeper view of how these trades are executed.

Comparing Market Behavior Under Volatile Conditions
The volatility segment of the market is where the technical comparison of binary options vs options trading reaches its peak.
The reaction of each instrument to sudden price changes transforms its profitability structure and underscores the need for careful analysis of this area.
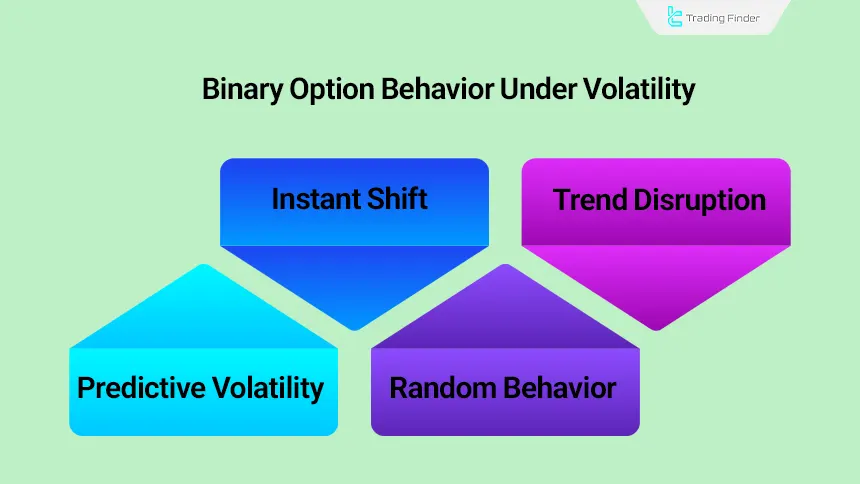
Binary Options Behavior Under Volatility
Within the binary structure, sharp price swings are a double edged sword. Price may move away from the desired level in a matter of seconds and change the trade outcome. Since the outcome is recorded only at expiry,
extreme volatility makes the decision making space unpredictable, and as a result, binary options in highly volatile environments typically display riskier behavior as follows
- Rapid structural changes and instantaneous outcome shifts
- Sudden candle moves that disrupt the identification of a stable trend
- Extreme volatility and reduced accuracy in forecasting Up and Down
- A shift in the trading environment from analyzable conditions to random behavior
This structure has led binary options in high volatility markets to lean more toward simulated, high excitement behavioral patterns.
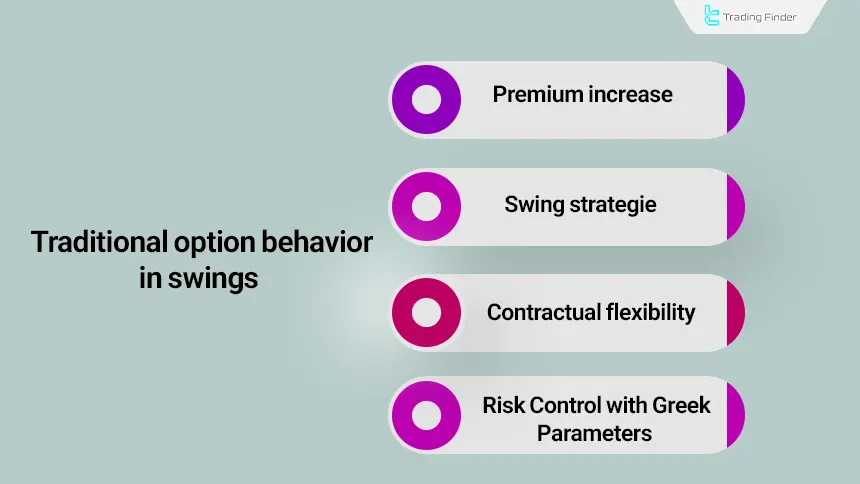
Traditional Options Behavior Under Volatility
In options, volatility has a direct role in valuation. When volatility rises, time value and implied volatility increase and this increase supports the contract premium.
In volatile conditions, the options structure provides traders with the following tools
- Increased value of call and put premium
- Ability to use volatility-based strategies such as straddles
- Flexibility in closing, hedging, or adjusting contracts
- Risk control using the Greek parameters
This pattern of reaction has made traditional options create a more analyzable and flexible structure in volatile markets.
Live Market Example and How Binary Options and Traditional Options Behave
The release of the “NFP” economic report is usually one of the riskiest events in the market. Under these conditions, the binary structure turns into a highly unstable arena.
Heavy candles and violent price shifts make direction forecasting difficult and many trades randomly move away from the desired level.
The time restriction and total capital loss in the event of incorrect forecasting both increase the trader’s psychological pressure.
In traditional options, however, the intense volatility triggered by NFP creates a new element called increased time value. The trader can use combinations of call and put contracts to build a structure such as a straddle.
This strategy is designed to profit from sharp price moves. Even if the direction is uncertain, rising volatility often increases contract value. This feature shows that in high volatility events, options are generally the more appropriate instrument.
Timing in Binary Options
In binary options, the decision making window is very narrow. The trader must forecast the price path at a single point in time and compress all analysis into a short time frame.
This limitation causes many decisions to be emotion driven and keeps the trader’s mental space under constant pressure.
Timing in Options
Options have a time based structure. Use of time value, contract management, position adjustment, or hedge execution during the trade path is possible. This feature transforms time from a threatening factor into aneffective tool for controlling and containing risk.
Differences in Valuation Models of Options and Binary Options
Binary valuation is simple and is based on a fixed return. The trader only sees the profit percentage and there is no direct linkage between the premium, market conditions, or the supply and demand structure. This simple model eliminates complex analysis.
On the other hand, options have one of the most complex valuation structures in financial markets.
The following factors play a direct role in determining the premium:
- Current price of the underlying asset
- Implied volatility
- Time value
- Greek structure
- Interest rate
- Distance between price and strike price
This model gives the trader multiple options for risk management.
Conclusion
From an analytical standpoint, the superiority of Binary options vs traditional options reflects two incompatible architectures of risk, return, and position management, and each demonstrates a completely different financial behavior.
Binary options, with their fixed structure, binary outcomes, and lack of residual value, create a high risk and non-manageable environment.
Traditional options, through time value and the ability to construct multi layered strategies, offer an engineered model of risk control.
Differences in regulatory levels, flexibility, and profitability models require traders to select their trading instrument according to their analytical skill and investment capacity.













