Money Management in Binary Options (Binary Option), as an important part of the trading process, determines the survival and growth of the trading account.
This concept is more important than choosing entry and exit points and provides a framework to control position size, distribute risk, and protect principal. In practice, Capital Management in Binary Options is what keeps a Profitable Trader in the Long Term.
What is capital management in binary options?
Capital management in binary options is a set of rules designed to control the size of each trade and limit risk.
In this market, due to the binary (win or total loss) structure, the importance of Binary Capital Management is multiplied, because even a few consecutive losing trades can quickly drain the account.
The main focus of capital management is on setting a specific percentage of equity for each position and preventing severe equity swings.
Educational video on risk management in binary options from the MARK TRADER YouTube channel:
Capital management indicator
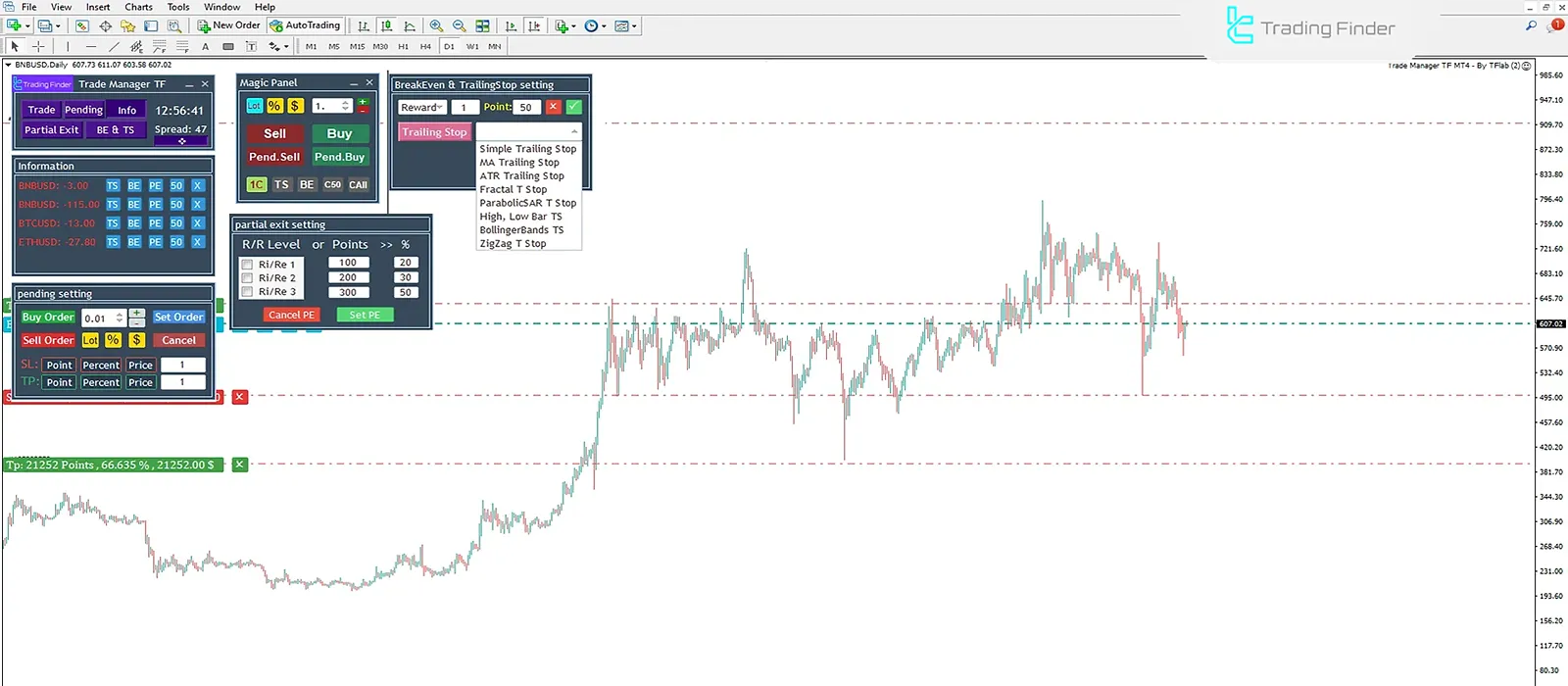
The Trade Manager TF trade management expert advisor is one of Trading Finder’s professional products designed for risk and capital management.
This tool, by offering two separate floating panels, enables fast and precise trade control and allows the trader to manage stop loss, take profit, and position size with just a few clicks.
Its key features include Partial Exit, BreakEven, moving stop loss with Trailing Stop, and executing pending orders. Training video for the trade management expert advisor:
One of its strengths is support for 8 types of trailing stops (including MA, ATR, Parabolic SAR, and Bollinger Bands), which creates high flexibility in trade management.
In addition, features such as displaying the time remaining to candle close, the spread value, setting risk-to-reward, and managing multiple trades simultaneously in a single panel are also available.
This expert advisor is highly customizable and, with diverse options like setting lot, percent, or dollar for position size, caters to different trading styles.
Moreover, closing all trades quickly or partially (such as a 50% exit) is available to manage capital during price swings.
After connecting, the trader will be able to conduct analysis and manage binary options trades directly within MetaTrader and use features such as trailing stop or partial exit to optimize trades.
In short, Trade Manager TF is a powerful trading assistant that, by combining risk management, high flexibility, and the capability to connect to binary options. Download links for the capital management expert advisor:
Basic rules of capital management in binary options
Binary options, with their two-state structure, create a high-risk, high-volatility environment.
In such conditions, having only an analytical strategy is not enough; because without precise rules for capital management, even professional traders are exposed to a rapid drawdown of account equity.
Important rules that must be observed in Capital Management in Binary Options:
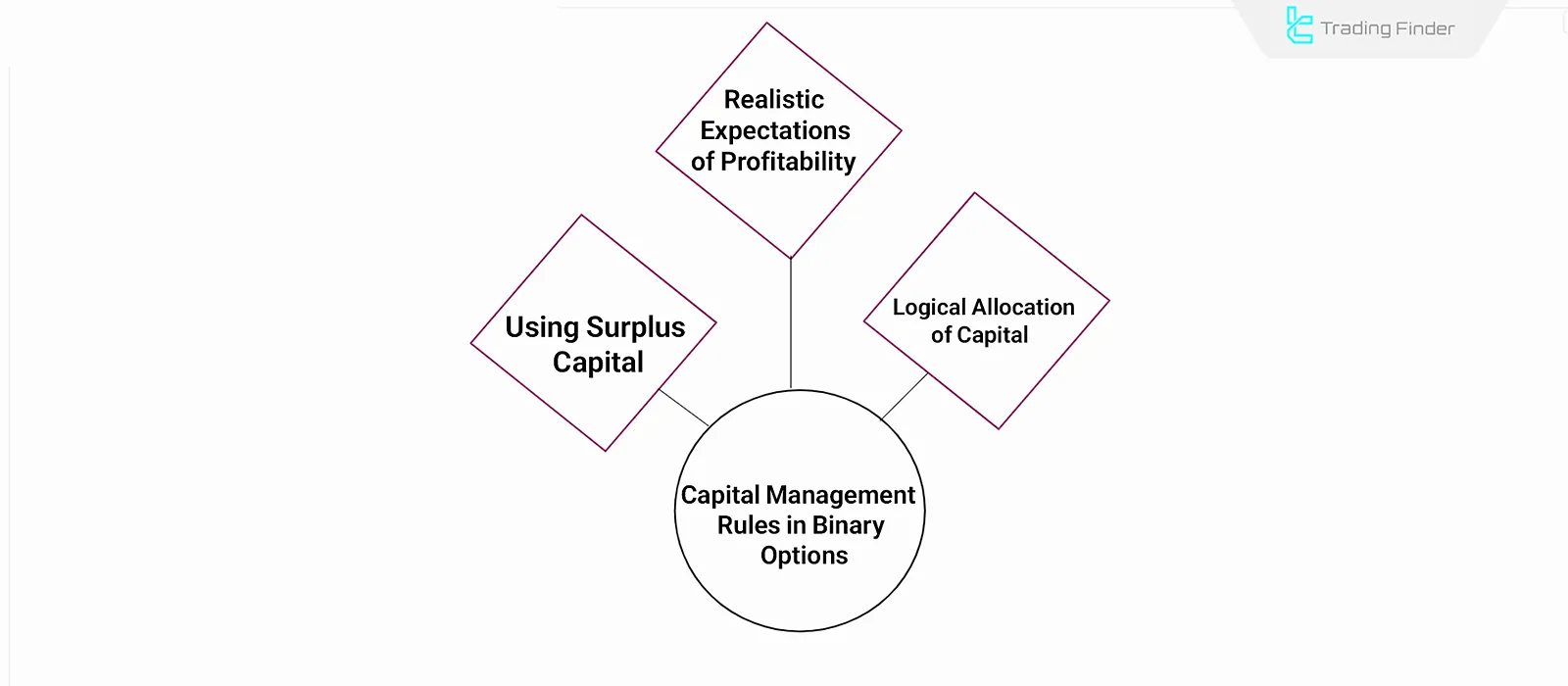
Using discretionary income
Entering binary options with essential day-to-day funds increases the risk of capital loss. The primary principle is that a trader should only commit a portion of non-essential income or savings.
Capital that you emotionally or practically depend on distorts rational decision-making and raises the probability of risky behaviors such as overtrading in Binary Options Trading.
Moderate allocation
The size of each trade should be a small percentage of the total account, usually recommended between 1% and 3%. Excessive risk makes returning to the previous capital level much harder; for example, a 10% loss requires an 11.1% gain to recover.
Proper allocation reduces psychological pressure and increases trading stability as a form of Risk Reduction.
Realistic growth expectations
Binary options returns, contrary to common belief, are not instantly spectacular. The payout structure in this market imposes an inherent limit on rapid growth.
Accepting that sustainable profitability is time-consuming prevents unreasonable increases in trade volume and irreversible risks. By focusing on gradual, consistent growth, the trader will build a more stable equity curve in Binary Investment.
Capital Management Example
A binary options trader with an initial balance of $1000, based on capital management principles, decides to risk only 3% of capital per day. Thus, the daily loss cap will be $30.
Why these matters in the binary options market?
- Binary Investment either closes fully in profit (usually with a 70% to 90% return) or fully in loss;
- Without capital management, just a few losing trades can wipe out the whole account.
In this example, even if the trader loses for 10 consecutive days, $700 of the original capital will still remain in the account.
Common capital management strategies in binary options
Capital Management in Binary Options, in addition to following basic rules, requires specific strategies to control floating risk and grow the account. Comparison table of capital management methods in binary options:
Method of Capital Management | How to calculate position size | Risk level | Main advantage | Main disadvantage |
Fixed % Rule | Allocate 1% to 5% of total capital to each trade | Low to medium | Risk control and prevention of rapid capital wipeout | Slow account growth in case of consecutive wins |
Martingale | Double the position size after each loss | Very high | Quick recovery of previous losses | Possibility of account call during several consecutive losses |
Anti-Martingale | Increase position size after each win | Medium | Use of winning streaks to grow capital | Loss of a large portion of profits in case of a sudden loss |
Fibonacci | Determine position size based on the Fibonacci sequence | Medium to high | Balance between risk and return | Complexity in calculation and need for high discipline in execution |
Kelly Criterion | Calculate optimal position size with a mathematical formula based on win probability | Medium | Maximize long-term capital growth | Difficulty of accurately estimating win probability in the real market |
Methods such as the Percent Rule, Martingale, Fibonacci, or the Kelly Criterion each have different logic and structure adapted to Binary Options Trading.
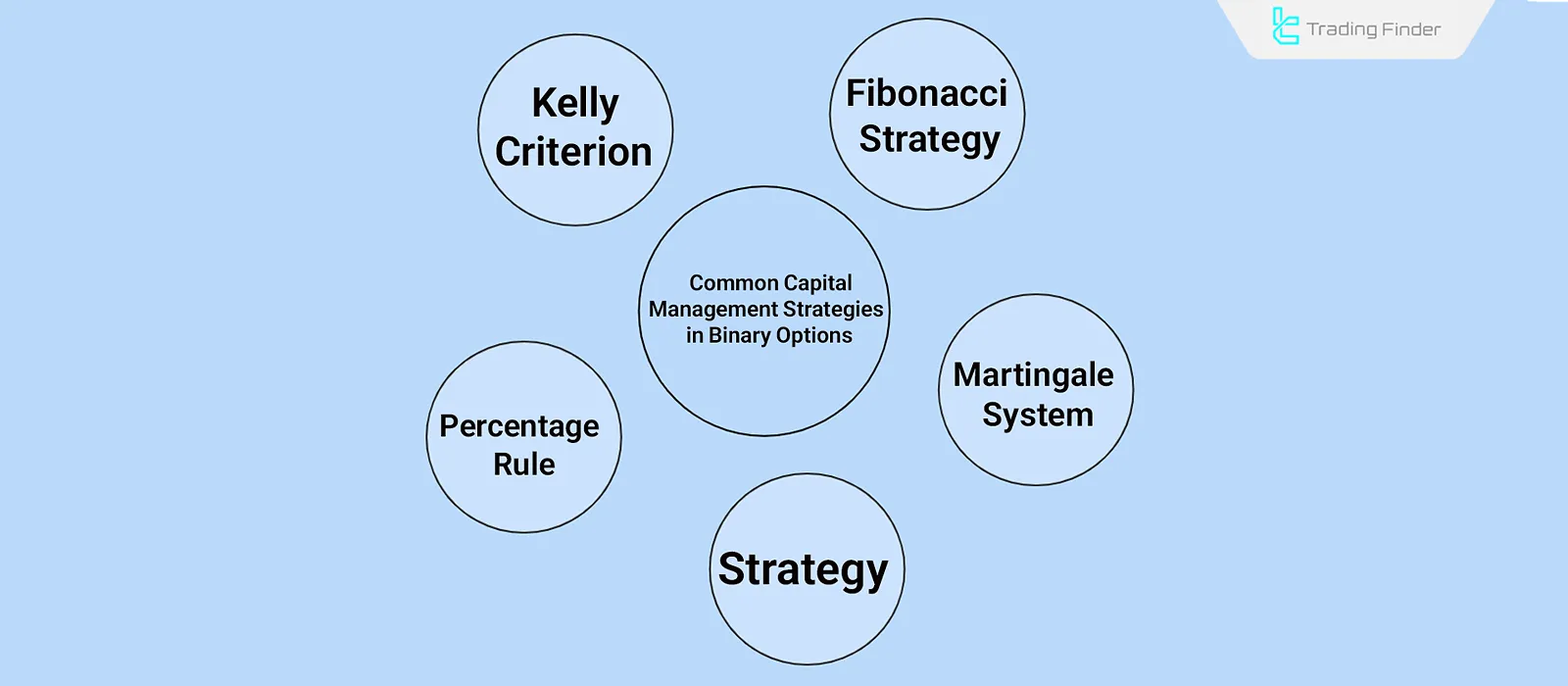
The Percent Rule
The Percent Rule operates by allocating a fixed percentage of total capital to each trade, most commonly between 1% and 3%. For example, a trader with $1000 allocates only $10 to $30 per position.
The advantage of this method is reducing the chance of a total wipeout during losing streaks and creating stability in account growth. Its main drawback is slower balance growth compared to higher-risk methods within Binary Options Trading.
Doubling Up strategy
In some brokers, a trader can, a few minutes before expiry, double the size of a currently profitable position. This increases potential profit, but if the market reverses, loss will also double.
Proper use of the Doubling Up strategy is recommended only when the trading signal has high confidence and the account has sufficient backing to absorb the added risk as part of Binary Capital Management.
Martingale system
In this method, after each loss, the next trade size is doubled so that the first win recovers all previous losses. For example, if the trader loses $10, the next trade is $20, then $40, and so on.
The main problem is the continuous growth of losses in a prolonged negative streak. The adjusted version, or Anti-Martingale, does the opposite; position size decreases after a loss and increases after a win to maintain more Fixed Risk relative to Floating Risk.
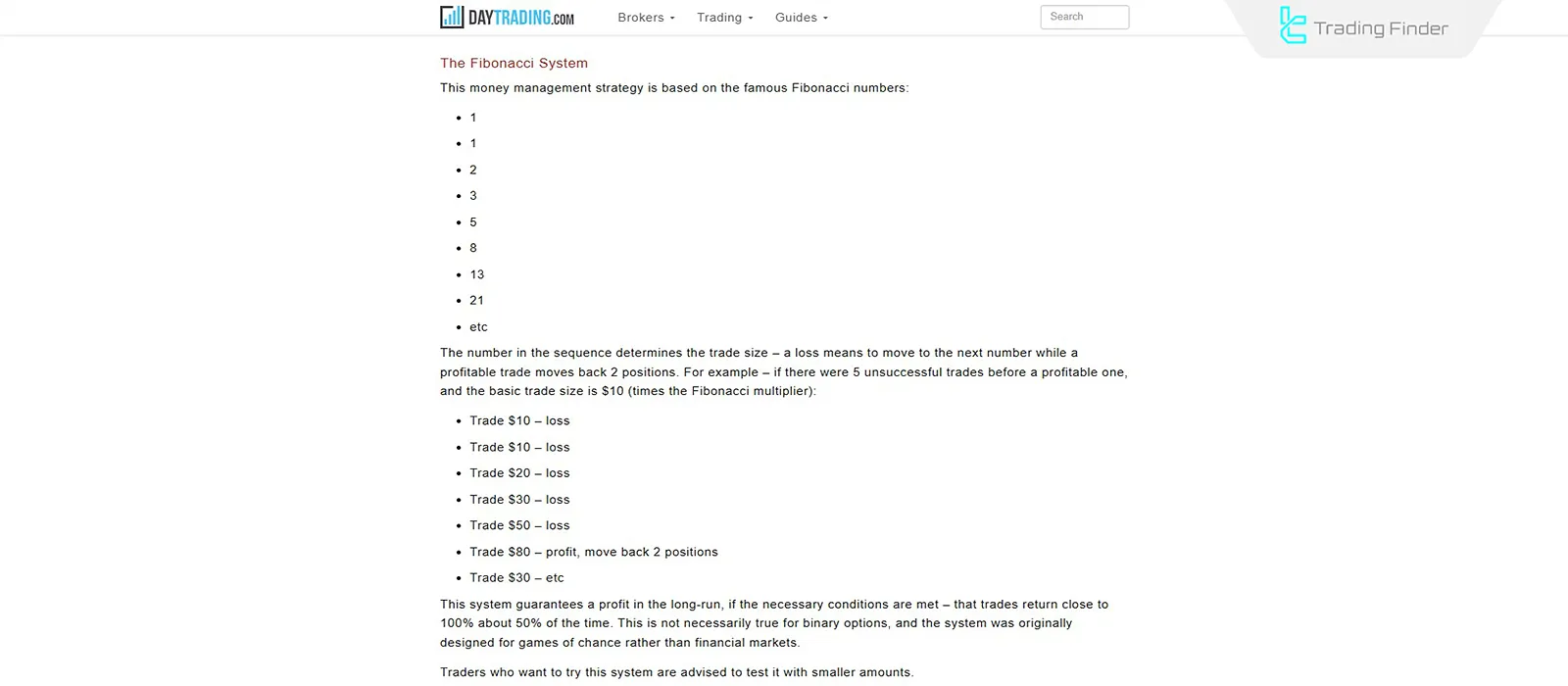
Fibonacci strategy
This strategy is based on the Fibonacci sequence (1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13 …). After each loss, the trade size moves to the right along the sequence (increasing position size), and after each win, it moves to the left (decreasing position size).
This method allows the trader to recover losses gradually, but if the negative streak is prolonged, it creates high financial and psychological pressure, especially under Price Volatility of the Underlying Asset.
The image below shows an example of gradually reducing losses using Fibonacci on DAYTRADING.com:
Kelly Criterion
The Kelly Criterion is a mathematical formula that calculates an appropriate risk percentage based on the probability of winning and the payout rate of the binary options trade. The Kelly formula in capital management:
f: percentage of capital for each trade
p: probability of winning
b: trade payout ratio
Lesser-known capital management strategies in binary options
In addition to classic methods, some complementary strategies are also used in binary options capital management.
These strategies are mostly employed by professional traders to improve returns in specific market conditions, such as high volatility or reduced trading frequency. Lesser-known strategies in binary options management:
- Capital Efficiency Strategy: focus on optimizing capital usage to reduce incidental costs and improve overall returns;
- Liquidity Management Strategy: by holding a portion of capital as a buffer, the trader can have sufficient funds during adverse conditions or when unexpected market opportunities arise to continue operating despite the Number of Trades fluctuating.
Common mistakes in capital management in binary options
Capital management in binary options is effective when the trader avoids behavioral and computational errors.
Many heavy losses, in addition to the lack of an analytical strategy, stem from mistakes such as excessive risk-taking, emotional decision-making, and using non-discretionary funds.
Common mistakes by traders in binary options capital management:

Excessive risk per trade
One common error is allocating a high percentage of account balance to a single position.
This raises the probability of a rapid wipeout across a few losing trades. In a market like binary options with only two possible outcomes, maintaining balance in position size is critical for Binary Options Trading.
Sudden increase in position size after a win or loss
Many traders, after a winning streak, develop false confidence and multiply their position size. Conversely, after consecutive losses, they increase size to recover.
Both scenarios lead to emotional decisions and usually put account equity at serious risk due to weakened Emotional Control.
What is diversification in binary options?
One important capital management technique is diversification. In binary options, as in the stock market, limiting capital to a single Underlying Asset can increase overall risk.
The trader can allocate capital among different assets such as currencies, stocks, commodities, or indices so that losses in one area can be offset by gains in others as part of Binary Capital Management.
Advantages and disadvantages of capital management in binary options
Before selecting a capital management model in binary options, it should be examined how each method applies in volatile or ranging market conditions.
Table of advantages and disadvantages of capital management in binary options:
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Creating financial discipline | Limitation of potential short-term profit |
Reducing the probability of losing all capital in a few unsuccessful trades | Need for constant adherence and emotional control |
Increasing capital efficiency in the long term | Complexity in combining different methods to find the best personal model |
Conclusion
Capital Management in Binary Options is the factor behind survival and sustainable profitability. Basic rules such as using discretionary capital, moderate allocation, and having realistic expectations form the foundation of financial discipline in Binary Options Trading.
Strategies such as the Percent Rule, Martingale, Fibonacci, and the Kelly Criterion are practical tools in this approach, but they will only be effective by understanding their limitations and avoiding common mistakes such as excessive risk.













