The Displacement Move in the ICT methodology is fundamental in analyzing market structure, identifying the impact of liquidity flow and Smart Money entry. This movement happens when price braeks significant levels.
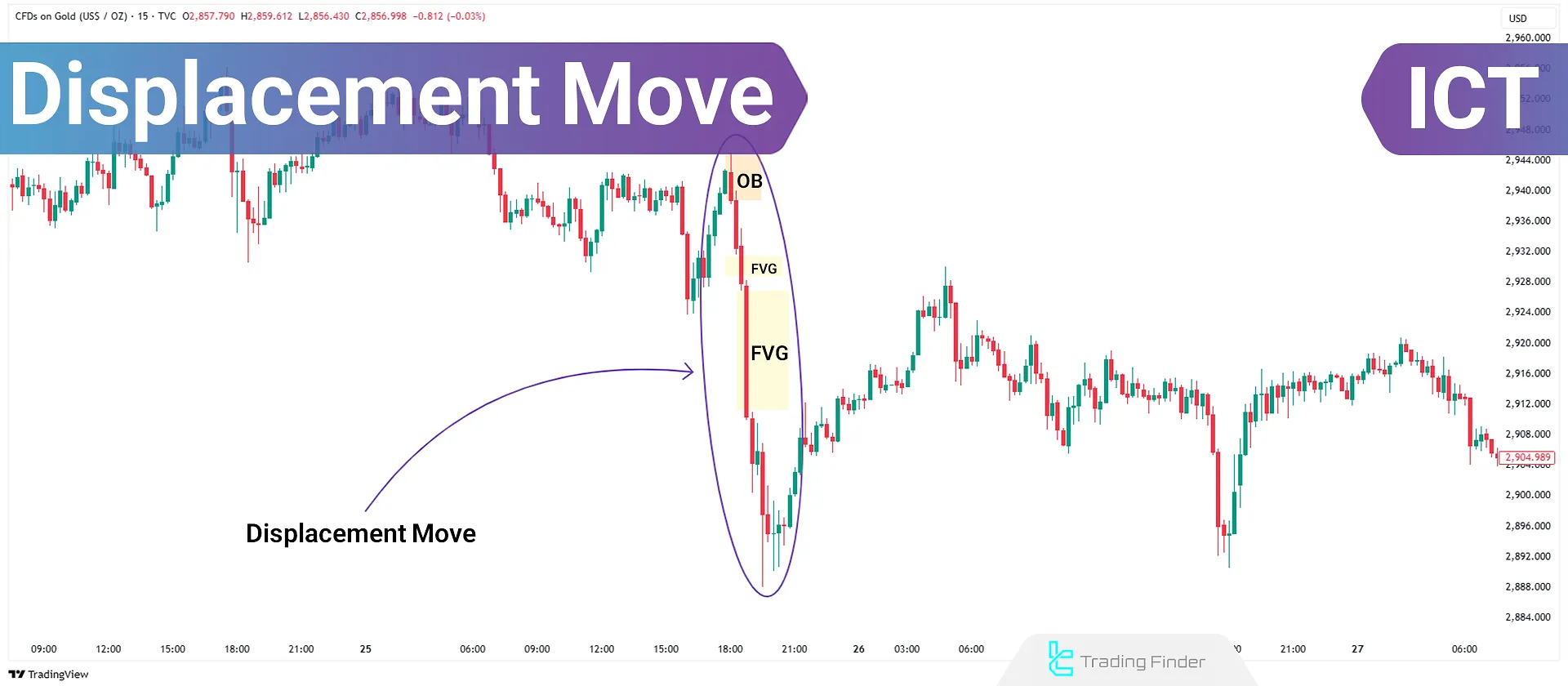
What is a Displacement Move?
A Displacement or Aggressive Move occurs when the price powerfully and rapidly breaks through a significant level, such as a short-term high or low.
For a displacement move to be valid, it must exhibit greater strength and momentum than previous movements. As a result, the price covers a larger distance in a shorter time.
When the price moves strongly in one direction, it indicates the entry of market makers into the market.
These movements can be used to identify daily bias, Breaks of Structure (BOS), and Changes of Character (CHOCH).
What Are the Characteristics of Displacement in ICT?
The displacement move has several key characteristics that distinguish it from other price movements:
Fast and Powerful Movement
Large candles with small or no wicks indicate complete dominance by buyers or sellers, and the market moves decisively in one direction.
Break of Key Levels
Displacement moves typically break support and resistance levels, previous highs and lows, and key market structures, which adds credibility to the move.
Liquidity Inducement
Before a displacement move occurs, the market may create traps for retail traders by Inducement liquidity and attracting liquidity to one side.
This often leads to retail traders entering in the wrong direction, while Smart Money uses this liquidity for its own entry.
Creation of Imbalances and Fair Value Gaps (FVGs)
Displacement moves often result in price delivery imbalances, leading to Fair Value Gaps (FVGs), as shown on the chart. These gaps typically act as potential corrective zones or re-entry points into the trend.
Importance of Higher Timeframe Market Structure
In ICT, every displacement move must align with the market structure on higher timeframes (HTF). This helps identify the primary market direction and prevents entering invalid trades.
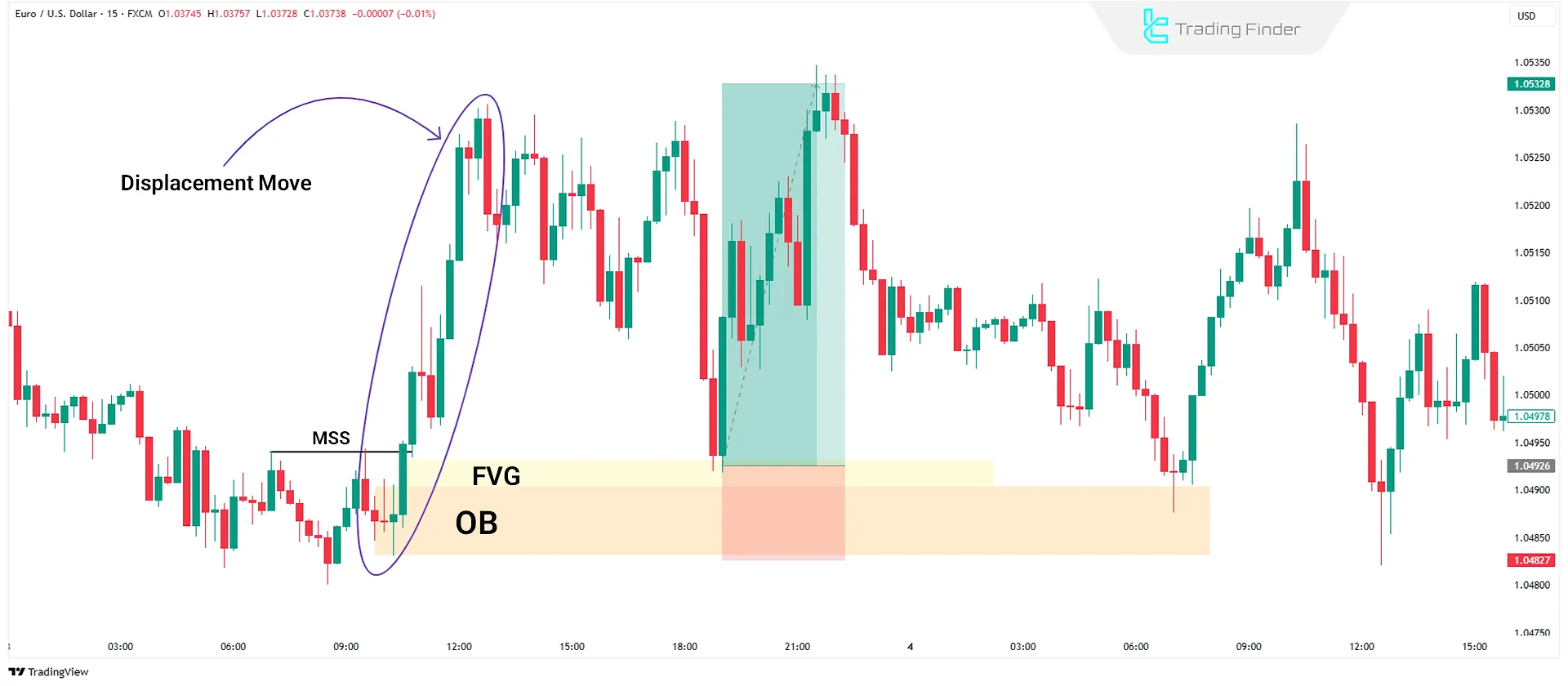
Bullish Displacement Move
A Bullish Displacement Move occurs when the price moves strongly upward, indicating institutional buying and market-maker activity. Key features of this move include:
- At least three consecutive bullish candles with large bodies and small or no wicks;
- A Fair Value Gap (FVG) between candles indicates efficient price delivery;
- Absence of corrections or irregular movements during the move, confirming the strength and clarity of the trend.
How to Trade Based on a Bullish Displacement Move?
In the EUR/USD chart, after analyzing the market structure on higher timeframes and confirming the bullish trend, identify thePremium and Discount Zones to find the best entry point. After a strong bullish displacement move, wait for a price correction to the FVG or Order Block.
Then, with confirmation of a Market Structure Shift (MSS) or Break of Structure (BOS), enter a buy trade and target liquidity at higher levels.
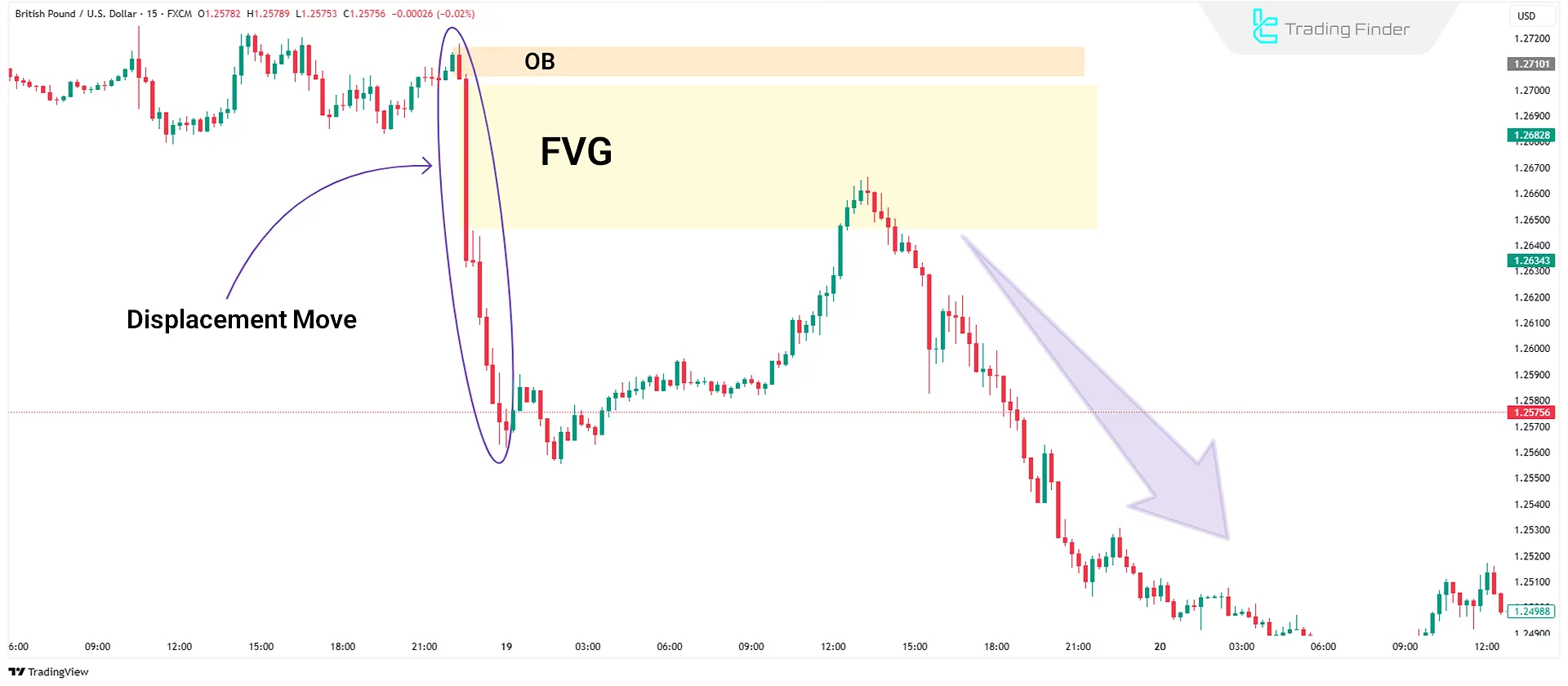
Bearish Displacement Move
A Bearish Displacement Move indicates widespread selling and institutional exit from the market. Key features of this move include:
- At least three consecutive bearish candles with large bodies and small or no wicks;
- Formation of an FVG in the downward direction, indicating efficient price movement;
- Absence of strong corrections during the move, confirming strong selling pressure.
How to Trade Based on a Bearish Displacement Move?
In the GBP/USD chart, after analyzing the market structure on higher timeframes and confirming the bearish trend, identify the Premium and Discount Zones to find the best entry point.
After a strong bearish displacement move, wait for a price correction to the FVG or Order Block.
Then, with confirmation of a Market Structure Shift (MSS) or Break of Structure (BOS), enter a sell trade and target liquidity at higher levels.
Risk Management in Displacement Move Trades
Displacement moves can create great trading opportunities, but they also come with risks, such as:
- Unexpected market volatility and sudden reversals;
- Misinterpretation of market structure, leading to incorrect entries;
- Late entry into trades, resulting in missed risk-to-reward opportunities.
Using Stop-Loss orders and proper capital management is essential to mitigate risks. Additionally, traders should analyze displacement moves within the context of higher timeframe trends.
Conclusion
The Displacement Move in ICT is a concept that aims to understand price dynamics and the objectives of large market makers.
These moves are characterized by strong candles, breaks of key levels, and the formation of FVGs.
By combining market structure analysis, higher timeframe analysis, and risk management, traders can use these moves to enter and exit trades effectively.













