A daily trading volume of around $7 trillion, a 24-hour decentralized market, high leverage, and an easy start witha demo account are some of the features that make Forex a suitable market for trading and speculation.
Forex market is international market that operates globally; Therefore, no specific organization or entity can manipulate its prices.
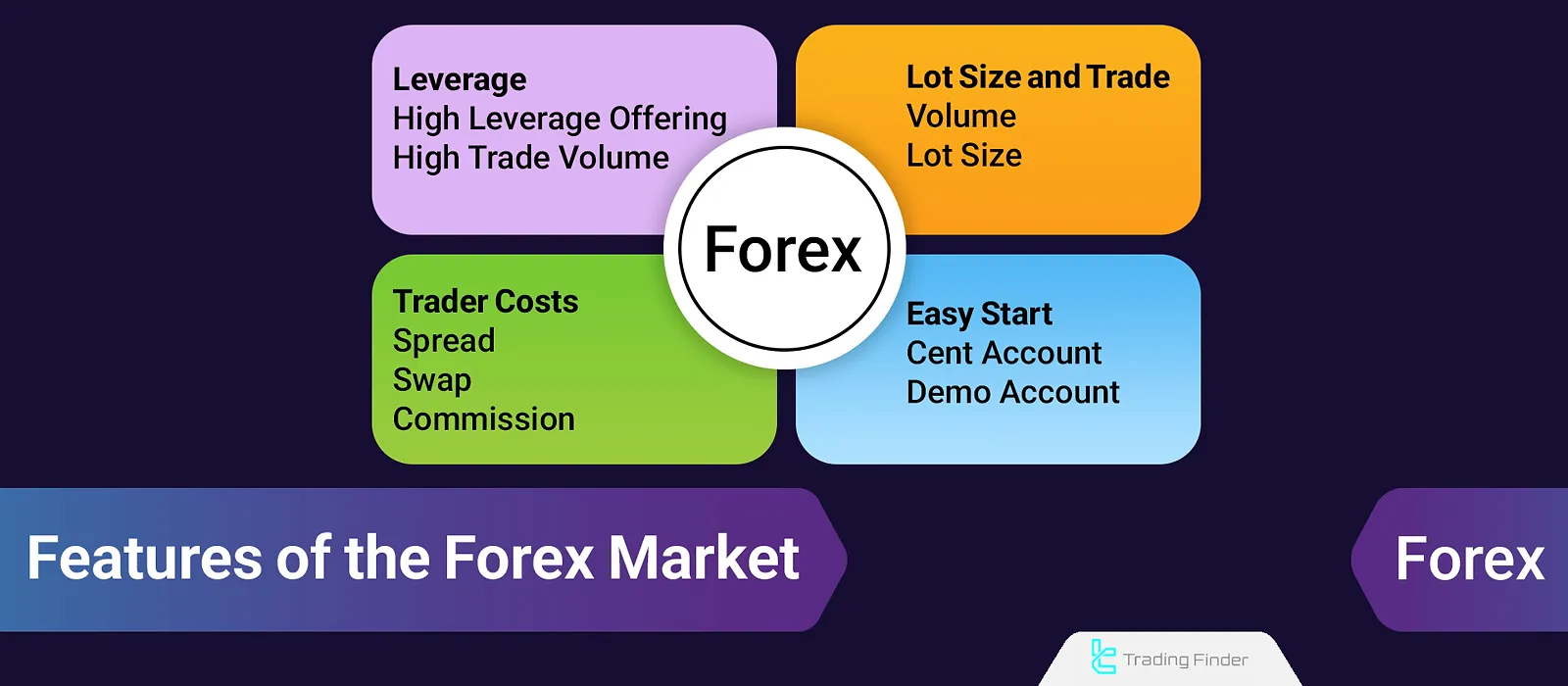
What are the Features of Forex?
The currency pair market is not dependent on any specific entity; in fact, decentralization, trading volume, liquidity, and the provision of high leverage are the key features of Forex.
The high speed of trade execution, easy access through online platforms, and the wide variety of currency pairs have also made this market highly attractive for traders with different styles and objectives.
Trading Costs and Broker Income
Forex traders must consider the costs of commission, swap, and spread when trading with brokers:
- Spread: The difference between an asset's buy (Ask) and sell (Bid) price. The Ask is the most attractive (lowest) price among sellers, and the Bid is the highest price among buyers;
- Swap or Overnight Interest: The cost incurred for holding a position overnight. The swap is calculated based on the interest rate difference between the bought and sold currencies;
- Commission: The fee charged by the broker for executing trades.
These are the income sources for brokers; however, brokers offer accounts with different features (such as swap-free accounts, low spreads, or no commission) for different users.
To learn about different brokers’ commissions and costs, read the TradingFinder Forex broker reviews.
Trading Volume in Forex
Forex traders trade on currency pair fluctuations under CFD contracts. In CFD trading, the trader does not own the asset and only trades or speculates on the price changes of a currency pair; CFD contracts are one of the Forex Features.
Trading volume in Forex is measured based on the number of contracts in lots, where 1 lot is equivalent to 100,000 units of a CFD contract.
For example, when you buy the EUR/USD currency pair with a volume of "1 lot" (long trade), the trading volume is 100,000 CFD contracts, which is equivalent to 100,000 euros.
To determine the appropriate trade size (lot size) based on your account balance and risk management, you can use the TradingFinder Position Size Calculator Tool.
The educational video on trading volume in forex from the YouTube channel The Moving Average has provided more comprehensive information for understanding position volume structure, risk calculation, and selecting the appropriate forex trade size.
Pip Value and Profit/Loss in Forex
Profit and loss in Forex trading vary based on the lot size (trading volume). In currency pairs involving the US dollar, with a trade size of 1 lot, each 1-pip movement equals a profit or loss of $10. In this case, the pip value (Pip Value) is $10.
Note: A pip is the smallest unit of price change in most currency pairs; measuring price fluctuations in pips is a characteristic of Forex market. The formula for calculating Pip Value is:

Practical Example for Calculating Pip Value
Assume you open a 1 standard lot trade on the EUR/USD currency pair:
- Each 1 pip price change equals a profit or loss of 10 dollars;
- A trade size of 0.1 lot equals a pip value of 1 dollar;
- A trade size of 0.01 lot equals a pip value of 0.1 dollar.
These calculations make it possible to accurately estimate trade risk before entry and strengthen capital control within the framework of risk management.
Position Size or Contract Size
Contract Size indicates how many contracts are included in one lot for a specific asset. The contract size for all currency pairs in 1 lot is 100,000. However, the contract size for other assets such as oil, silver, gold, etc., varies across different brokers.
Forex Market Trading Hours (forex trading sessions and the forex market time cycle)
The Forex market is open 24 hours a day, five days a week (excluding Saturdays and Sundays). The 24-hour day is divided into four sessions:
- Sydney Session: The market is less active during the Australian session, and the Australian and New Zealand dollars are mostly traded;
- Tokyo Session: During the Tokyo session, Asian markets become active but remain less volatile, and currencies such as AUD and JPY are in focus;
- London Session: With the start of the London session, liquidity increases, and the impact of European and global news is observed;
- New York Session: With the start of the American session, liquidity and volatility peak, and U.S. news influences the market.
When the London and New York sessions overlap, the market experiences high liquidity and intense volatility.
To view the market session during trading hours, you can use the TradingFinder Forex Sessions & Market Hours tool.
The educational article on forex market hours on the forex.com website has provided additional explanations regarding forex trading hours, which interested readers can also use.
Decentralized and High Liquidity
The Forex market, with a daily trading volume of approximately $7 trillion, is the largest financial market in the world. Reasons for the high trading volume in Forex:
- 24-Hour Market: This feature, along with market stability and reasonable volatility, attracts traders from around the world to Forex;
- Decentralized: Unlike stock exchanges that operate within specific organizations, Forex trading is conducted decentralized through OTC platforms and is accessible in all countries;
- High Leverage: Forex offers high leverage (up to 1:2000), which not only adds to the appeal but also increases trading volume;
- Participation of Banks and Financial Institutions: Most Forex market volume comes from banks, governments, and international financial institutions.
Leverage
High leverage in Forex is an advantage compared to other markets; however, this also increases the risk of trading. Comparison of leverage in different financial markets:
Market | Leverage (Typically) |
Stocks | 1:2 to 1:10 |
Forex | 1:50 to 1:2000 |
Crypto | 1:2 to 1:1000+ |
Futures | 1:10 to 1:100 |
Commodities | 1:10 to 1:20 |
Bonds | 1:2 to 1:5 |
Commodity Exchange | 1:2 to 1:4 |
Forex; a Decentralized Market!
The activity of the forex market does not rely on any specific organization or institution and is carried out in a decentralized (OTC) manner through online platforms.
OTC transactions, or Over The Counter, are not conducted within a specific centralized organization; rather, they take place directly through agreement between the buyer and the seller and via online platforms.
Easy Start Without Initial Capital
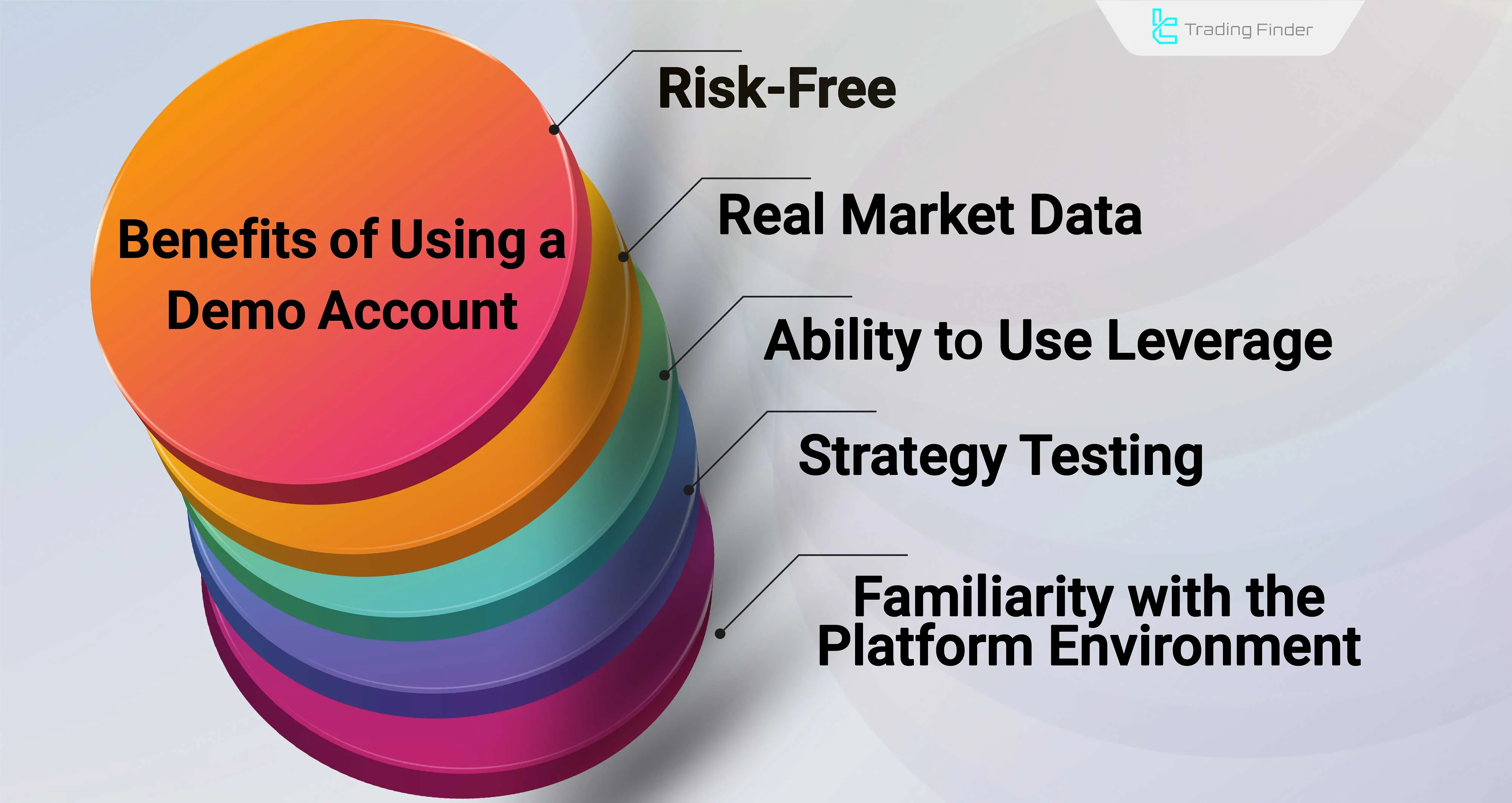
In Forex, it is possible to start trading with a demo account and trade without real money, which is ideal for beginner traders.
A demo account makes it possible for traders to become familiar with the platform environment, order placement methods, and market fluctuations, and to test different strategies without financial risk.
This type of account is highly useful for hands-on learning, increasing confidence, and reducing common mistakes at the beginning of the trading journey.
Advantages of a forex demo account:
- No financial risk
- Real market data
- Ability to use leverage
- Strategy testing
- Familiarity with the platform environment
Option to Use a Cent Account
In a cent account, the balance is displayed in cents. For example, if you deposit $10, your balance will be 1000 cents. This account is suitable for individuals with little trading experience or those who want to trade with small capital.
In addition, a cent account creates conditions that allow traders to practice risk management, stop-loss placement, and the execution of trading strategies in a real market environment without the psychological pressure associated with large capital.
Using very small trade sizes in this type of account enables trial and error and the development of trading skills, while at the same time keeping the impact of potential losses on the main capital limited.
Advantages and Limitations of the Forex Market
Understanding the advantages and limitations of the forex market helps traders make a more informed decision when entering and operating in forex. In the table below, we examine the advantages and limitations of forex:
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Very high liquidity; order execution with low slippage | High leverage risk; possibility of significant losses |
24-hour trading, 5 days a week; suitable for time constraints | High sensitivity to news; rapid volatility |
Low trading costs; competitive spreads and no fixed commissions | Lack of a centralized market; price dependency on the broker |
Diversity of instruments; ability to trade currencies, commodities, indices, and metals | - |
Who are the Main Participants in the Forex Market?
Forex is an international market in which various economic participants take part. Understanding the structure of these participants can help in understanding price behavior:
- Central banks: Through monetary policies and interest rates, they have the greatest impact on currency values;
- Commercial and investment banks: The largest volume of forex transactions is conducted by banks;
- Financial institutions and hedge funds: They are active in the market for risk management, arbitrage, and speculation;
- Multinational companies: They trade to carry out currency transactions related to imports and exports;
- Retail investors and traders: A growing segment of the market that enters CFD trading through brokers.
Understanding the role of these participants enables traders to analyze price behavior more logically and better understand the impact of economic news.
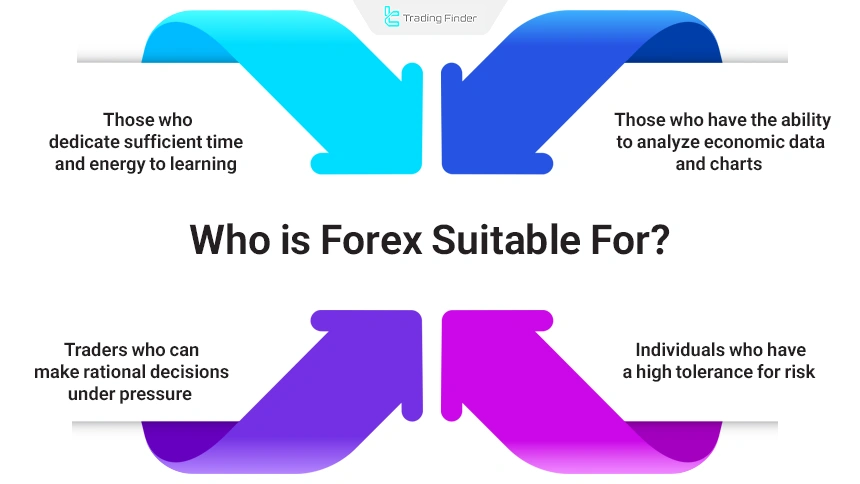
Is Forex Suitable for Everyone?
Entering the forex market requires specific behavioral traits and skills. This market is more suitable for the following individuals:
- Those who have the ability to analyze economic data and charts;
- Individuals with a high tolerance for risk;
- Traders who can make rational decisions under pressure;
- Those who invest sufficient time and energy in learning.
However, forex may not be an appropriate choice for impatient, emotional individuals or those without risk management. Recognizing this helps you make a more informed decision before getting started.
Types of Trading Orders in Forex
Knowing different types of orders leads to more accurate and better-controlled trading. To enter or exit a trade in the forex market, you can use various types of trading orders:
- Market order: Immediate execution of a trade at the current market price;
- Limit order: Entry or exit at a better price than the current price;
- Stop order: Activation of a trade at a point the market passes through; often used for breakouts;
- Stop-loss and take-profit: Risk management tools for setting loss and profit limits.
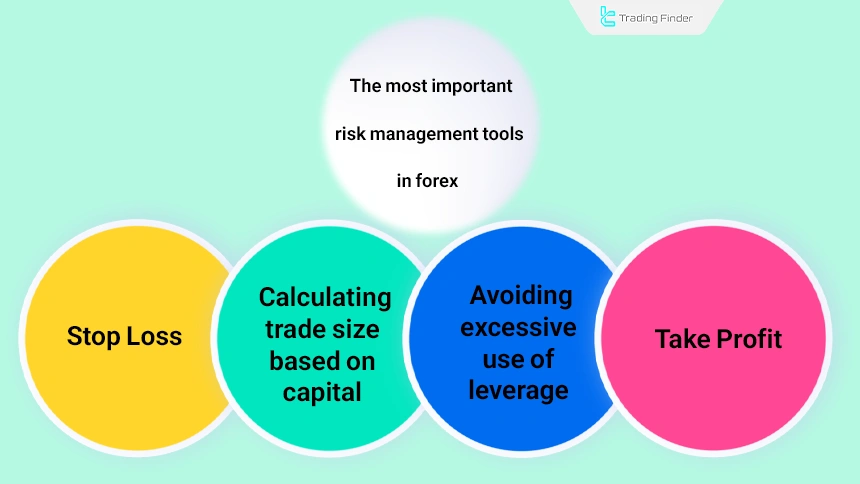
Risk Management in Forex
The forex market offers many profit opportunities, but without risk management, the probability of loss increases significantly. The most important risk management tools include:
- Stop loss: The most essential tool for controlling losses;
- Take profit: Exiting a trade at target levels;
- Calculating trade size based on capital: Determining standard position size using a risk-based formula;
- Avoiding excessive use of leverage: The suitability of high leverage for professional traders and the role of risk management in profitability even with an average trading system.
Risk to Reward Ratio Indicator with Lines (RRR with lines) in MetaTrader for Risk Management
The risk to reward ratio indicator with lines (RRR with lines) is one of the practical tools in MetaTrader in the field of capital management and risk management, which guides traders before entering a trade to accurately evaluate the ratio of potential profit to possible loss.
This tool is especially valuable for traders who have a structured and logical decision-making approach. The indicator functions by drawing three adjustable horizontal lines on the price chart.
These lines represent the entry point (Entry), stop loss (Stop Loss), and take profit (Take Profit).
- Risk to reward ratio indicator with lines for MT5 (RRR with lines)
- Risk to reward ratio indicator with lines for MT4 (RRR with lines)
After defining these levels, the indicator automatically calculates the risk-to-reward ratio and displays the result in the form of an information box next to the chart.
This feature enables quick identification of a trade’s justification from a risk management perspective and structures decision-making before entry.
In an uptrend, the take profit is placed above the entry point and the stop loss below it. For example, on a currency pair chart, the indicator may display a ratio of 1 to 2.71, indicating the superiority of expected profit over risk.
Conversely, in a downtrend of another currency pair, the stop loss is placed above the entry point, and ratios such as 1 to 3.98 may be displayed, which still indicates a logical trade.
The RRR indicator is compatible with all timeframes and is applicable in various styles, including scalping, day trading, and swing trading. It can also be used in markets such as forex, cryptocurrency, stocks, commodities, and indices.
Full customization of the information box in terms of color, font, size, and display position also allows this tool to easily align with each trader’s trading environment.
Overall, RRR with lines, by providing a clear picture of the profit-to-loss ratio, helps traders select only positions with a logical risk-to-reward ratio and avoid entering high-risk and unprofessional trades.
Tradable Assets in the Forex Market
Although the core of forex consists of currency pair trading, brokers also offer a wide range of CFD instruments:
- Major, cross, and exotic currency pairs
- Precious metals such as gold and silver
- Energies including Brent oil and WTI
- Global stock indices such as Nasdaq, S&P500, and DAX
- Shares of international companies in the form of CFDs
This diversity allows traders to optimize their trading strategies across different assets and take advantage of opportunities in the global market.
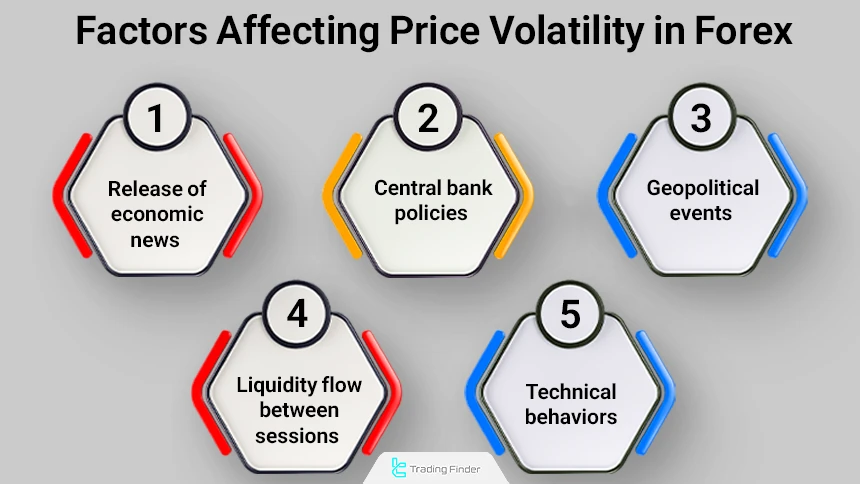
Factors Affecting Price Volatility
Volatility is one of the characteristics of the forex market, and a significant portion of trading opportunities and risks originates from this feature.
Price movements are shaped by a combination of fundamental and technical factors, which determine market direction. Below are the main factors affecting price volatility in forex:
- Release of economic news: Such as interest rates, NFP, inflation, and GDP
- Central bank policies: Changes in interest rates can alter currency values
- Geopolitical events: Wars, sanctions, or political crises
- Liquidity flow between sessions: Trading volume in the London and New York sessions has the greatest impact
- Technical behaviors: Breakouts, support/resistance, and price patterns lead to rapid movements
Forex Regulatory Bodies (The Role of Regulation in Trader Security)
Due to its decentralized structure, the forex market is not managed by a single authority; however, in different countries, regulatory organizations are responsible for supervising brokers’ operations.
By establishing transparent rules regarding client fund protection, account segregation, and reporting standards, these bodies reduce the risk of misconduct or broker bankruptcy.
The most important and reputable forex regulators include:
- FCA - United Kingdom
- ASIC - Australia
- CySEC - Cyprus
- NFA/CFTC - United States
Brokers operating under these organizations offer higher financial transparency and are required to provide periodic reports. Therefore, reviewing a broker’s regulation is one of the most important selection criteria for traders.
Conclusion
The deep market and high liquidity make Forex a manipulation-resistant market with relatively reasonable volatility.
Forex offers attractive features such as high leverage, 24-hour trading, and decentralized (OTC) transactions, which encourage traders to participate.













