Forex market and Futures are two attractive financial markets that differ in nature, features, trading hours, liquidity, market depth, and applications in trading (speculation and hedging).
In futures trading, there is the possibility of price fixation in the future, making it a suitable tool for hedging (risk protection against fluctuations).
In contrast, with its high trading volume and 24-hour activity, Forex is a suitable market for speculation.

What is Forex?
Forex is a decentralized (OTC) market for trading currency pairs (speculation). In this market, traders speculate on the spot rates of currency pairs under CFD contracts, meaning traders do not own the underlying asset but can profit from price fluctuations through CFD agreements.
Note: In a CFD contract, the trader agrees to trade the price changes of a symbol without actually owning the underlying asset.
What is Futures?
In the futures market, futures contracts are traded. In futures contracts, traders agree to trade a specific asset at a specific price on a specific date.
Futures is a centralized market offered in official exchanges such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME), New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX), and others.
Futures contracts come in various types, as shown in the image below:
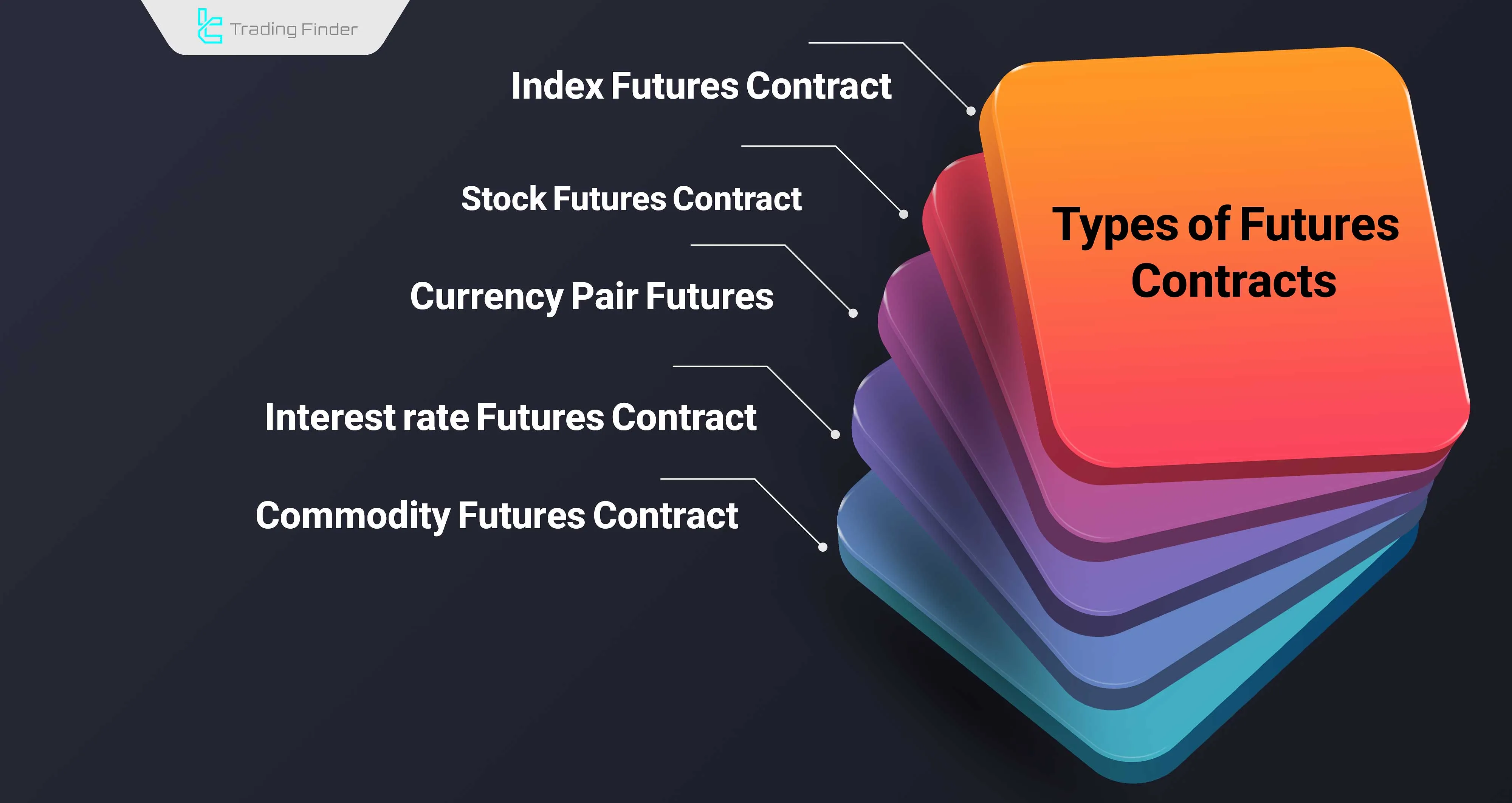
Comparison of the Forex and Futures Markets
The Forex and Futures markets have different natures and, therefore, different applications. Forex vs Future Table:
Feature | Forex | Futures |
Asset Type | Currency pairs | Currency pairs, commodities, cryptocurrencies, and bonds |
Market Structure | Decentralized | Centralized |
Trading Hours | 24/5 | Varies by broker and asset |
Costs | Spread, commission, swap | Spread, exchange fees |
Liquidity | Very high (5-7 trillion daily) | Lower than Forex |
Leverage | Very high (up to 1:500 or more) | More limited (usually up to 1:100) |
Hedging | Suitable for short-term currency pairs | Suitable for long-term hedging on all assets |
Note: When comparing Forex vs Futures, Forex traders often benefit from lower transaction costs and no expiration dates, while Futures traders can hedge against price fluctuations in commodities, indices, and currencies.
One of the most important differences between currency pairs and futures markets is the method of hedging and risk management.
Hedging
Hedging and risk management are significant advantages in Futures, which are more limited in Forex.
Hedging in Futures is done because futures allow for the fixing of prices, meaning commodities can be purchased at a specific price.
How is Risk Hedging Done in Futures Market?
For example, an airline company that needs oil is concerned about price increases in the future. This company can use oil futures contracts to purchase this product at a specific price (e.g., $75) in the future. The price is determined based on market supply and demand.
Hedging in Forex
Hedging in Forex is done differently, aiming to protect against short-term currency fluctuations.
For example, a European company exporting goods to Switzerland is concerned about the depreciation of the Swiss Franc against the Euro (if the Franc weakens, the company will incur losses).
In this case, the company hedges the risk of Franc depreciation by purchasing EUR/CHF.
Hedging is not exclusive to market makers; individual traders may also engage in hedging based on the fundamental analysis of the market.
Comparison of Hedging in Forex and Futures:
Parameter | Forex | Futures |
Time | Suitable for short-term hedging | Suitable for longer-term hedging |
Swap | Yes | No |
Price Fixation | No | Yes |
Difference Between Forex and Futures in Trading Hours
Trading hours in the futures and currency pair markets differ. Due to the global nature of Forex, trading hours are fixed, while in Futures, trading hours are determined by the market.
Trading Hours in Forex
Forex operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, and is closed on Saturdays and Sundays. In the currency pair market, trading hours are divided into four sessions:
- Sydney
- Tokyo
- London
- New York
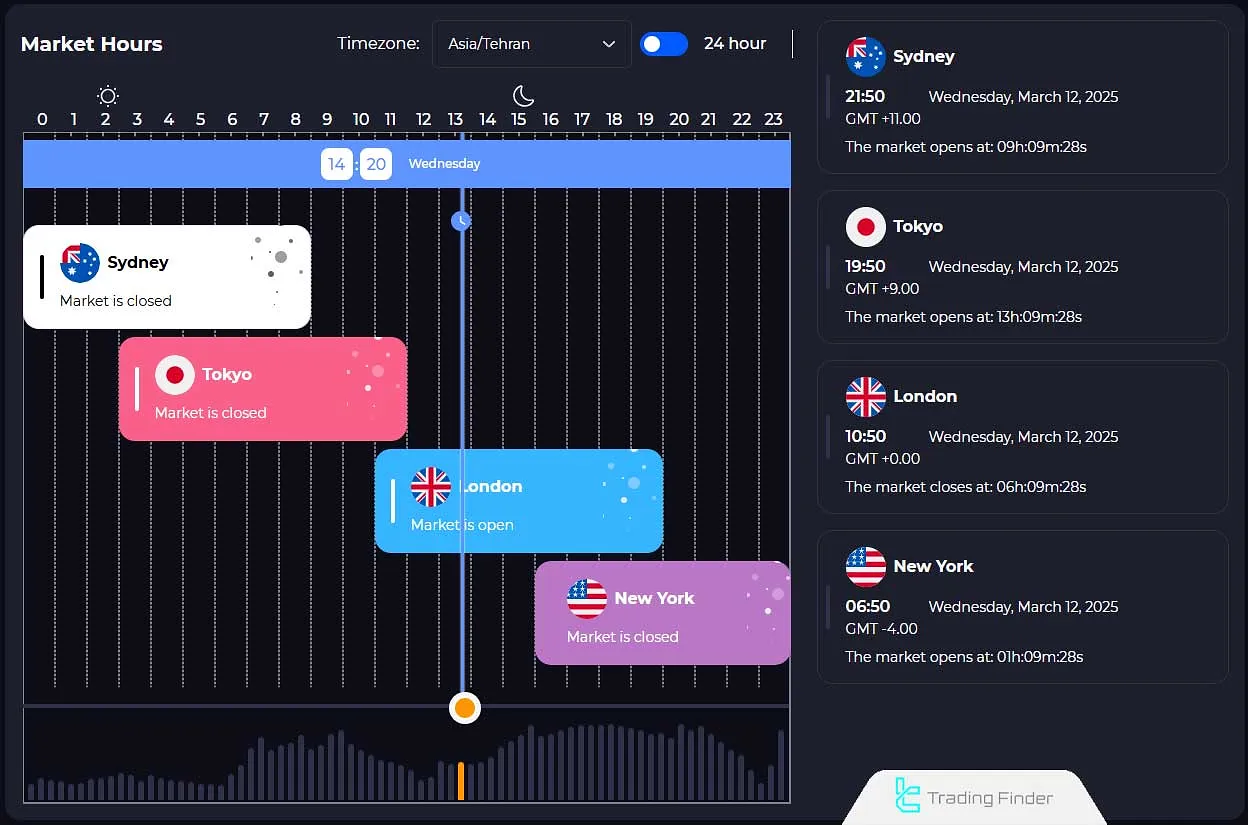
To view Forex market sessions, you can use the Trading Sessions Tool from Trading Finder.
Trading Hours in Futures
The futures market has specific trading hours depending on the asset (e.g., oil, gold, indices, currencies) and the broker offering the service.
The image below shows the trading hours of important assets in the futures market:
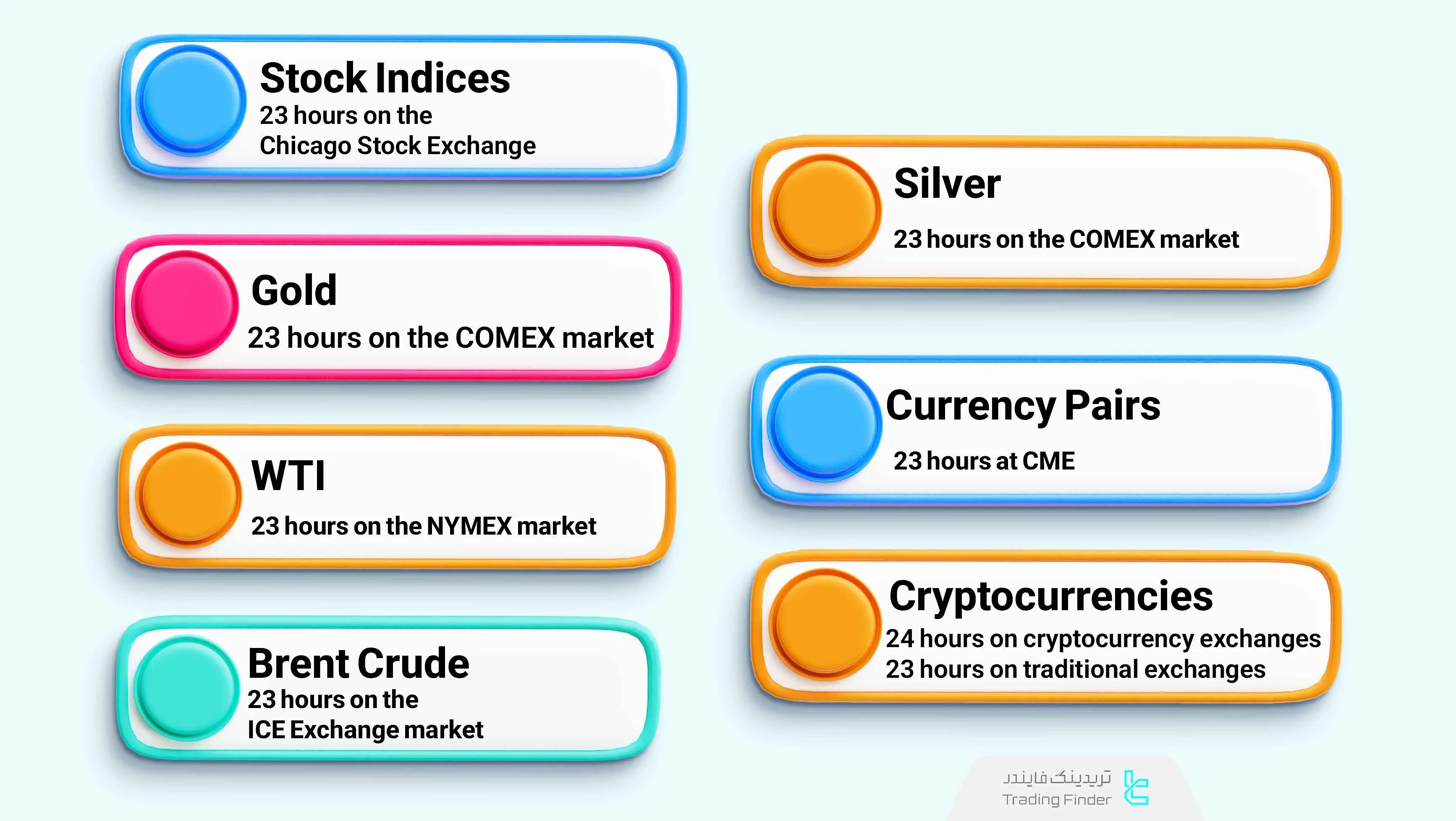
Note: Some exchanges are closed on holidays, but crypto futures markets like Binance Futures operate 24/7.
While Forex operates 24/5 with two days off, futures markets have a 1-hour break for liquidity management and are closed on specific holidays.
Forex vs Futures in Leverage and Trading Volume
The Forex market, with a daily trading volume of approximately 5-7 trillion Dollars, is the largest financial market in terms of trading volume and liquidity.
In contrast, in Futures, trading volume varies by asset; some assets, like S&P500, gold, and oil, also have high volumes in futures.
A key difference in Forex vs Futures is that Forex trading allows for greater leverage, but Futures trading offers more transparency and regulation due to its centralized exchange structure.
Feature | Forex | Futures |
Daily Trading Volume | 5-7 trillion dollars | Around 30-40 billion dollars |
Liquidity | Largest financial market (varies by currency pair, higher for major pairs) | Varies by asset, generally lower |
Slippage | Lower | Higher for low-volume assets |
Conclusion
Due to the difference in nature between the Forex and Futures markets, there are differences in their applications and trading styles.
Futures, with the ability to fix prices at a specific future date, is a suitable tool for hedging price fluctuations for commercial companies and individual traders.
On the other hand, with its high trading volume and liquidity, Forex is suitable for speculators and speculating on currency pairs.













