Turtle Soup is a strategy from the ICT trading style that is most often used after the formation of price range movements, which constitute the majority of the market.
The Turtle Soup ICT trading strategy, in addition to identifying False Breakouts, enables the trader to take entries in the direction of the main market move by combining liquidity and market structure concepts.
This strategy is formed by combining several important concepts: Order Block, Market Structure Shift (MSS), Fair Value Gap (FVG), Fake Breakout, Stop Hunt, and Liquidity Sweep.
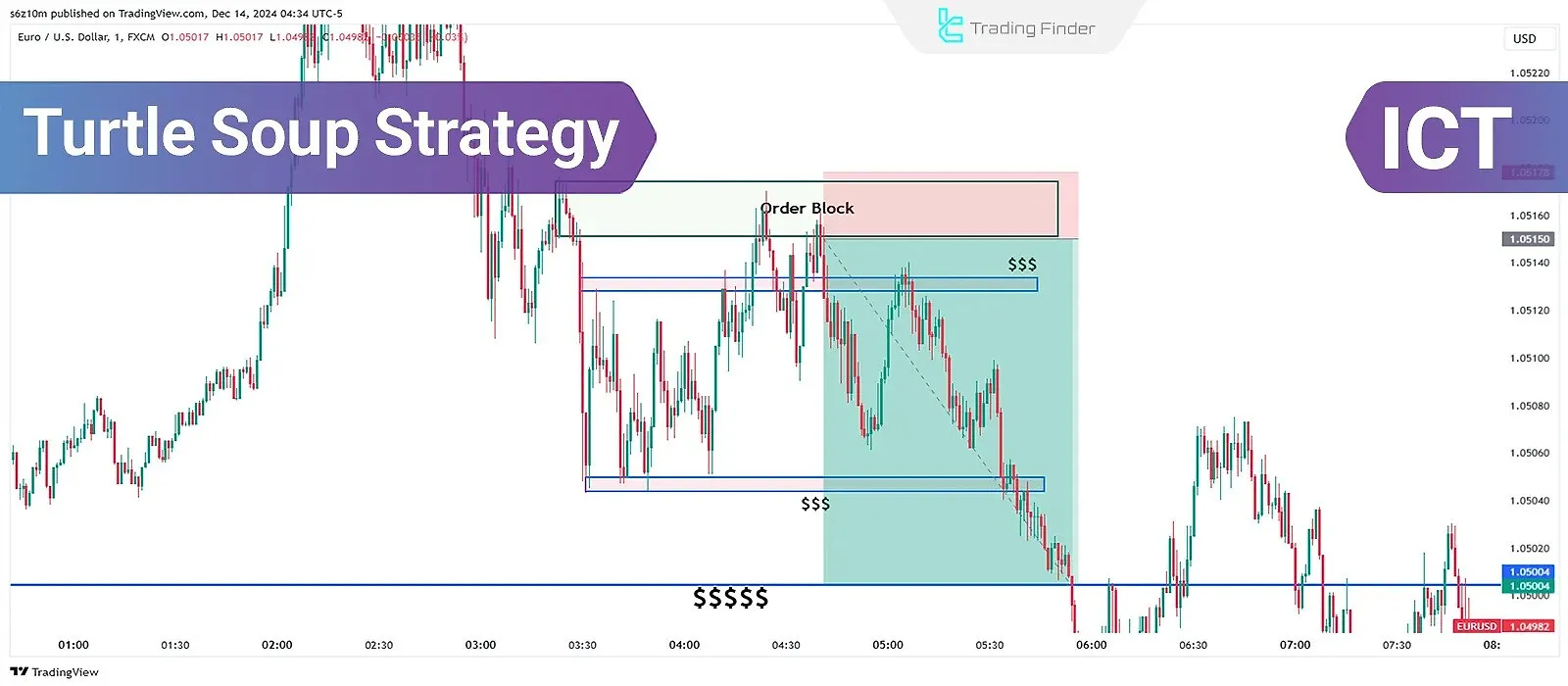
What Is the Turtle Soup Strategy?
The founder of Turtle Soup Strategy, Michael, designed it as a trading method to hunt liquidity and perform market manipulation, taking advantage of reversal points.
This strategy is usually applied in situations where the price breaks out of a range or specific liquidity zones, seeking to attract more orders.
Turtle Soup Indicator
The Turtle Soup Indicator is one of the important tools in the Inner Circle Trader (ICT) trading style, with its main focus on identifying fake breakouts and liquidity hunt areas. This indicator generates reversal signals when the price passes through key levels but fails to continue its movement.
The essence of this tool is designed based on detecting deceptive market moves. Fake breakouts are categorized into two groups: Internal and External. This classification helps traders easily analyze market conditions and identify points where a reversal is likely to occur.
The indicator creates a structure by labeling new highs (HH) and new lows (LL) and connecting them with green lines, making it easier to identify liquidity flow and temporary trends. In addition, green arrows are used to show signals related to liquidity hunt zones or liquidity pools.
For further training about the Turtle Soup Indicator, you can watch the following videos:
In terms of classification, the Turtle Soup Indicator falls into the group of ICT indicators, liquidity, high-volatility, reversal, and signal-based tools. Therefore, it is considered one of the key instruments for strategies designed around fake breakouts and price reversals.
The settings section of this indicator is highly flexible and includes options for changing the theme, calculating minor and major trends using ZigZag, and enabling or disabling internal and external signals. These features help traders customize the indicator according to their analytical style.
Overall, the Turtle Soup Indicator is a specialized tool for detecting fake breakout patterns and liquidity zones, used by ICT traders to increase analysis accuracy and manage entries and exits.
- MetaTrader 4 version of the Turtle Soup Indicator
- MetaTrader 5 version of the Turtle Soup Indicator
- TradingView Indicator version of the Turtle Soup
Types of Turtle Soup Strategies
The Turtle Soup Strategy is not just a general pattern but includes two distinct setups with different entry conditions.
Understanding the difference between the short Trades version (TSS) and the long Trades version (TSL) helps traders act more precisely and purposefully in hunting market liquidity. Types of Turtle Soup Strategies:
- Turtle Soup Sell Setup (TSS): The focus of TSS is on hunting liquidity above previous highs and the subsequent reversal of price to the downside;
- Turtle Soup Buy Setup (TSL): The focus of TSL is on hunting liquidity below previous lows and the subsequent reversal of price to the upside.
This classification allows traders to know when the strategy is suitable for a sell position and when it is suitable for a buy position.
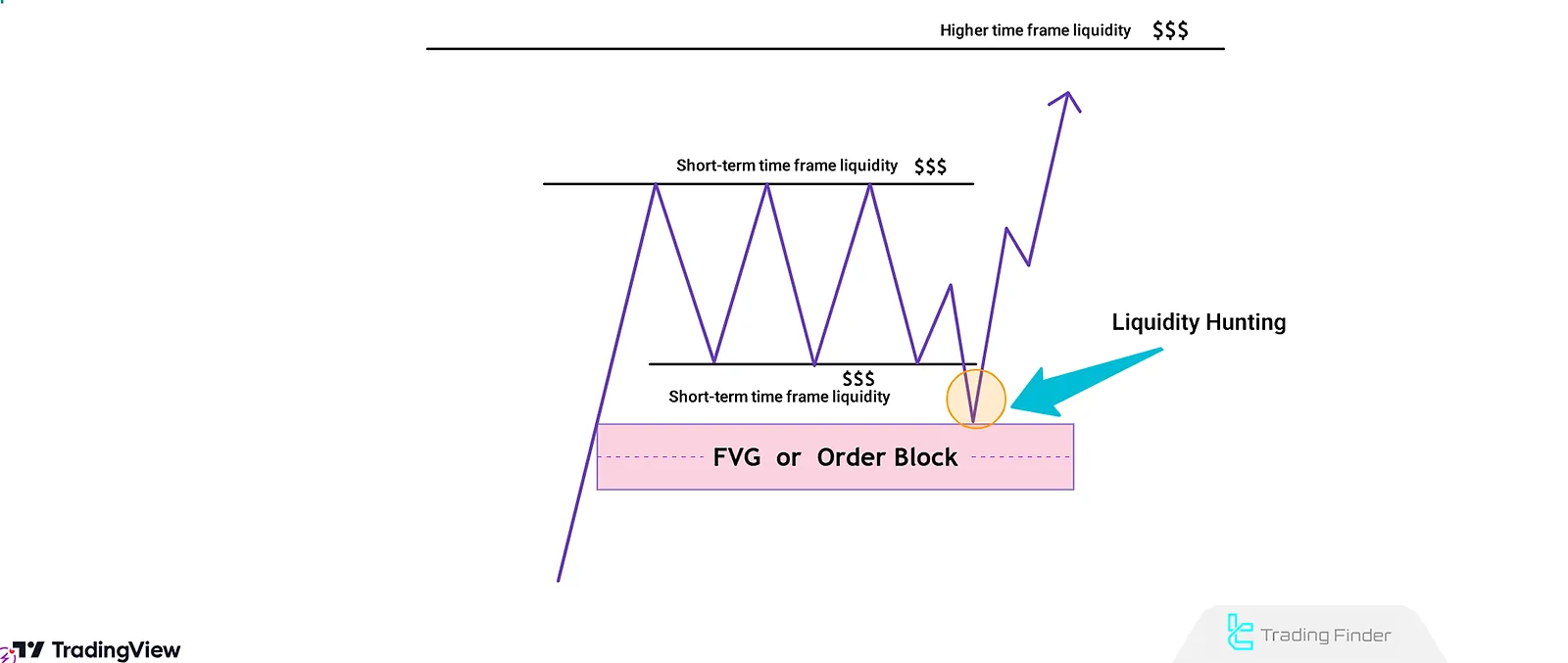
Why Does the Turtle Soup Strategy Focus on Liquidity?
Markets naturally gravitate toward areas with concentrated liquidity. In the Turtle Soup Strategy, two types of liquidity are emphasized:
- Internal Liquidity: Found within short-term range areas, consisting of Fair Value Gaps or short-term highs/lows;
- External Liquidity: Found outside the short-term range, including stop-losses or other imbalance zones.
First of all, price absorbs internal liquidity before moving to target external liquidity, aligning with the overall higher timeframe Order Flow trend.
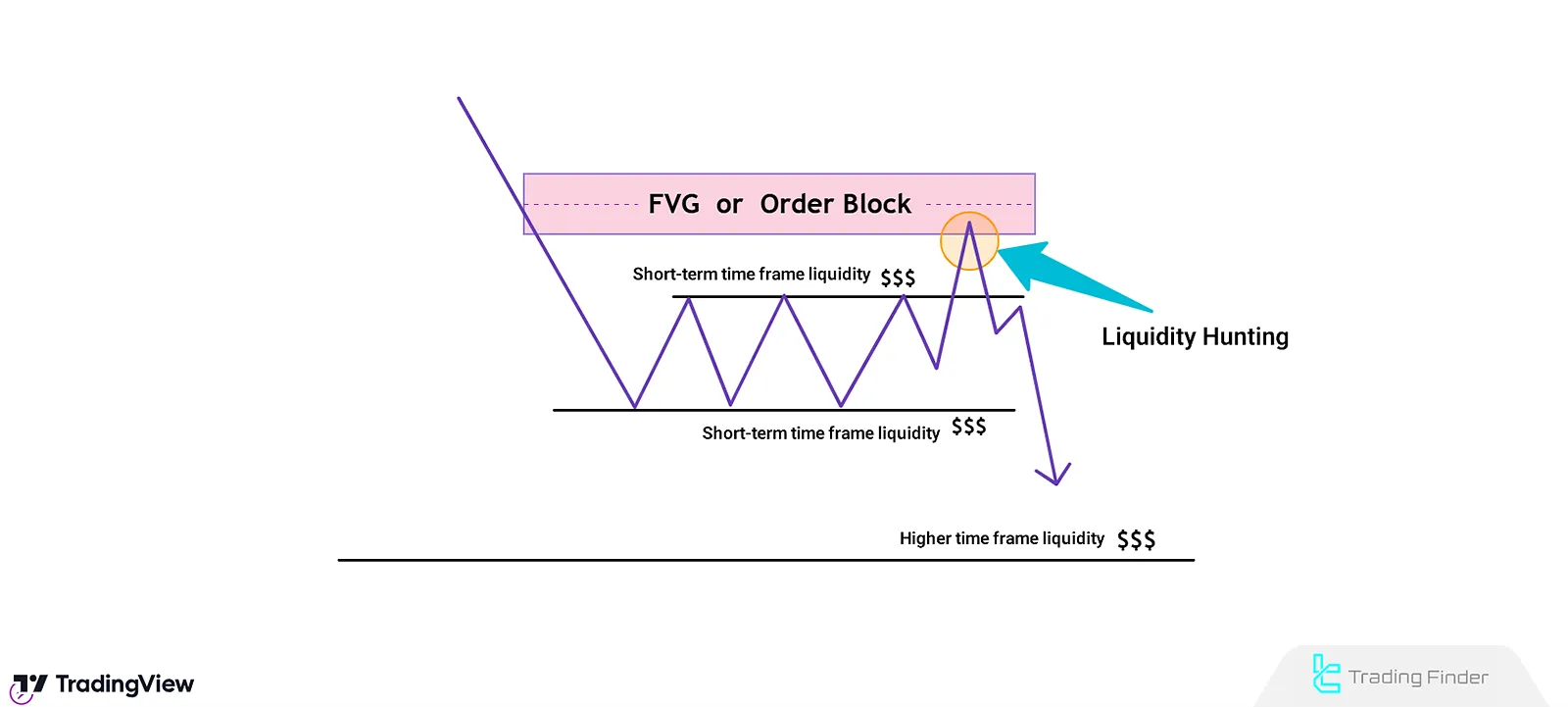
How Does the Turtle Soup Strategy Work?
To apply this strategy, follow these prioritized steps:
#1 Identify the Range
The range is defined between a specific high and low on the chart, where older highs and lows act as zones of significant liquidity.
#2 Identify Entry Points
One of the key principles in the Turtle Soup Strategy is how price interacts with liquidity in bullish Setup and bearish trends, which determines the next market direction. Identifying entry points in Turtle Soup:
- Uptrend: the price must absorb the lower liquidity (Swing Lows) and then, after a retest, move upward;
- Downtrend: Price hunts higher liquidity (Swing Highs) before moving downward.
#3 Align with the Higher Timeframe
Analyzing the market direction in higher timeframes (daily and hourly) is necessary to ensure alignment; in the lower timeframe, wait for the price to return to key areas such as order blocks and liquidity zones.
Then, after the pullback in the lower timeframe, with confirmation, a trade entry can be made.
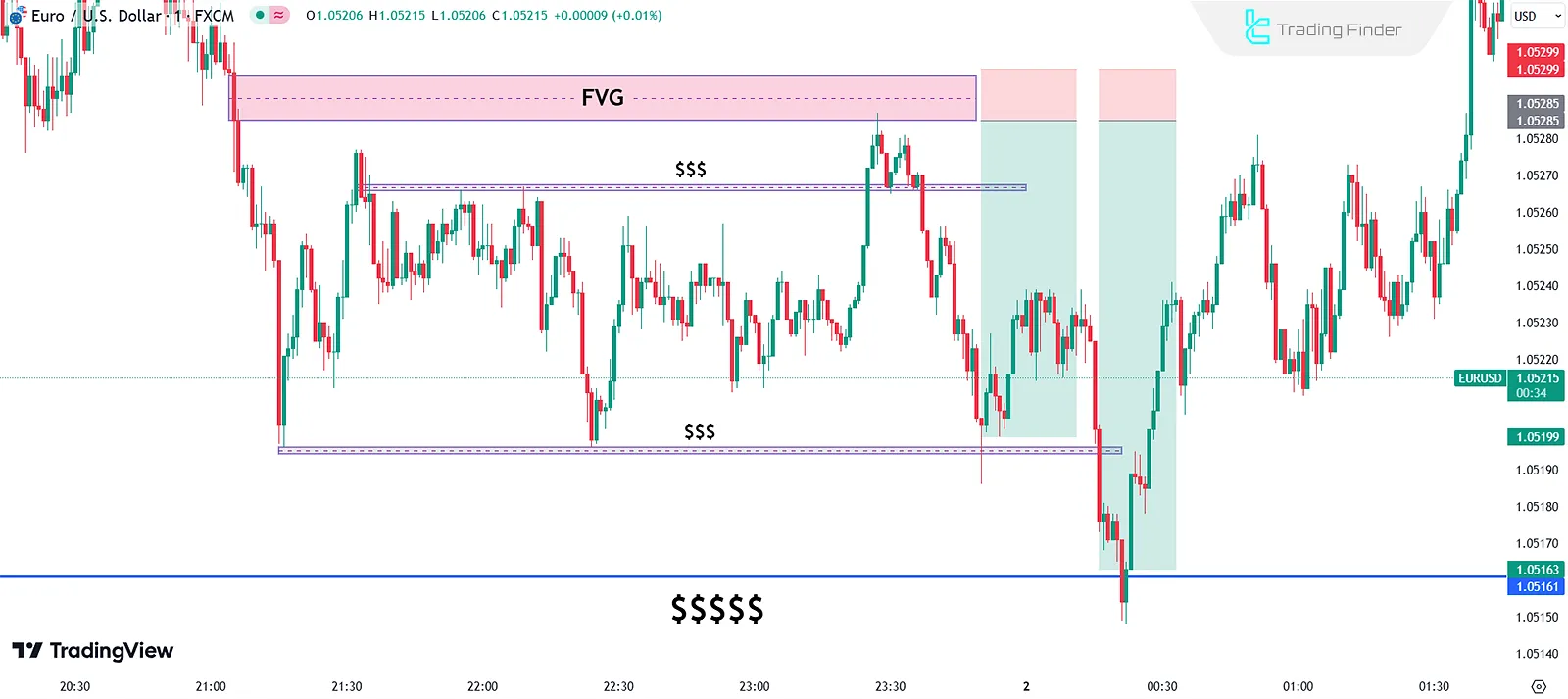
Bearish example of the turtle soup tutorial Strategy on Flux Charts:
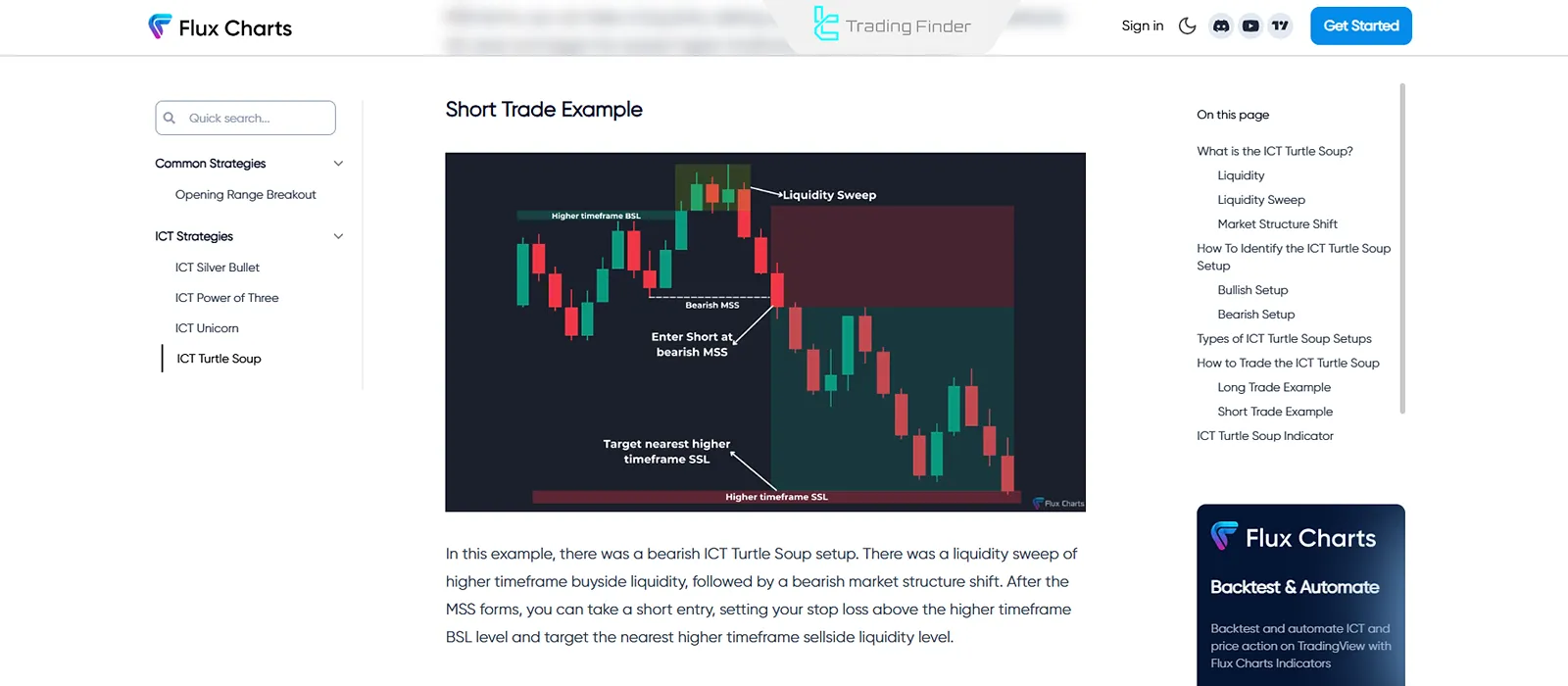
Pros and Cons of the Turtle Soup Strategy
Like any trading strategy, Turtle Soup has its specific advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Clear identification of liquidity points | Requires patience for price to reach key zones |
Usable across different timeframes | Demands understanding of liquidity and market behavior |
Higher-timeframe analysis ensures alignment | Risk of misidentifying all components |
In the image below, you can see the performance of the Turtle Soup Strategy in an uptrend:

Also, for a visual tutorial of the Turtle Soup Strategy, you can use the educational video from the Mullham Trading channel:
Key Points in Using the Turtle Soup Strategy
The execution of the Turtle Soup Strategy is only successful if the trader pays attention to its details and key principles.
To reduce trade risk and manage positions, the trader must follow the important points of this strategy. Table Key Points in Using the Turtle Soup Setup:
Point | Importance / Explanation |
Application after range movements | High probability of fake breakouts and liquidity hunts |
Occurrence of stop hunts at key levels | Increases the validity of the setup by breaking significant highs and lows |
Checking higher timeframe | Helps with entries in the main market direction |
Combining with Order Block or FVG | Enhances accuracy and quality of trading signals |
Risk management | Prevents losses caused by sharp volatility and invalid breakouts |
Practical Steps for Using the Strategy
The execution of the Turtle Soup Strategy requires following systematic and precise steps to ensure everything is done correctly, from identifying liquidity to the final trade entry. Steps for Executing Turtle Soup:
- Analyze the Higher Timeframe: Identify external liquidity points and mark them clearly on the chart;
- Define the Range: Mark highs and lows within a price range to distinguish internal and external liquidity;
- Wait for Internal Liquidity to Be Hunted: Once internal liquidity is absorbed, look for moves toward external liquidity.
- Enter the Position: After observing the confirmation of a reversal signal in key zones, proceed to enter the position.
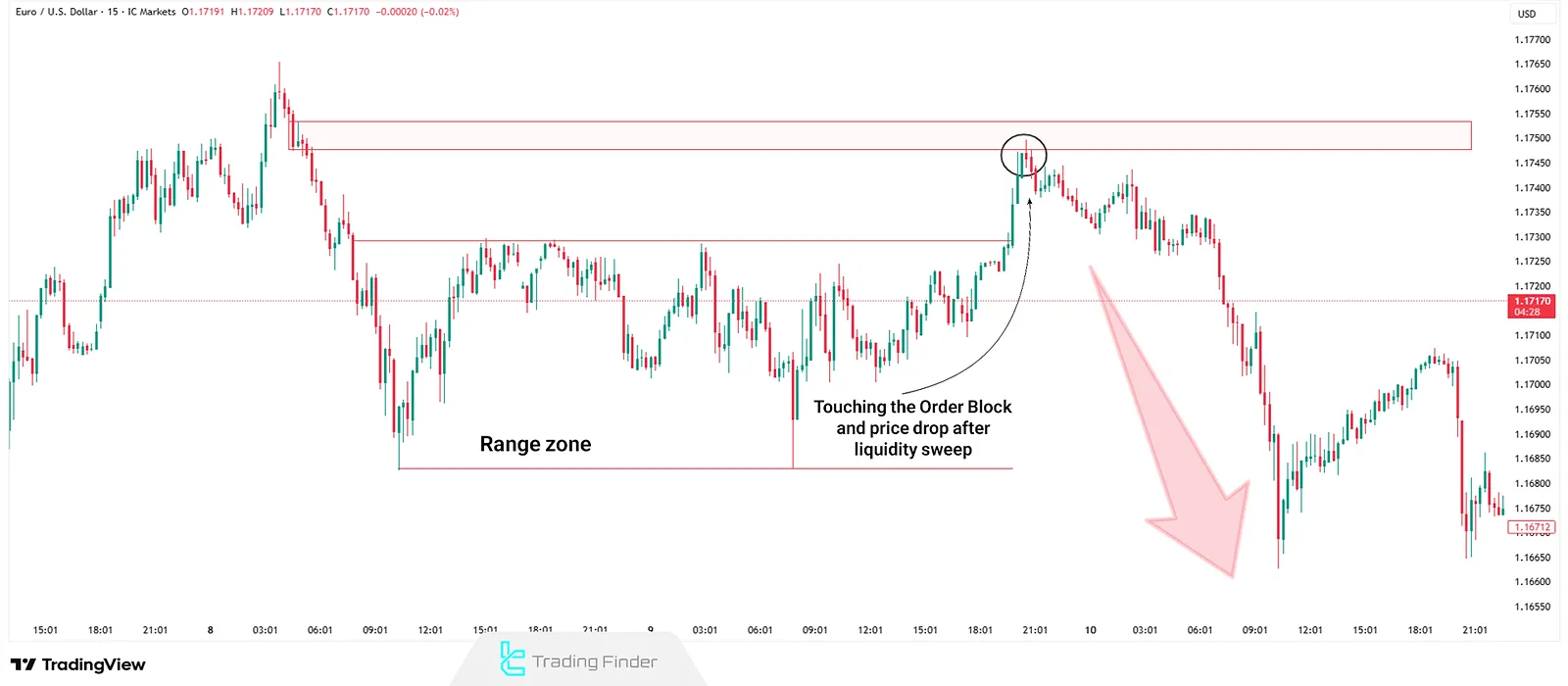
Example of a Trade with the Turtle Soup Strategy
In the EUR/USD 15-minute chart, the price enters a range phase within a downtrend. In this situation, one should wait for the breakout of the range; after the breakout, the price moves toward a previously formed bearish order block, and upon reaching it, the market drop can be observed according to the Turtle Soup Strategy.
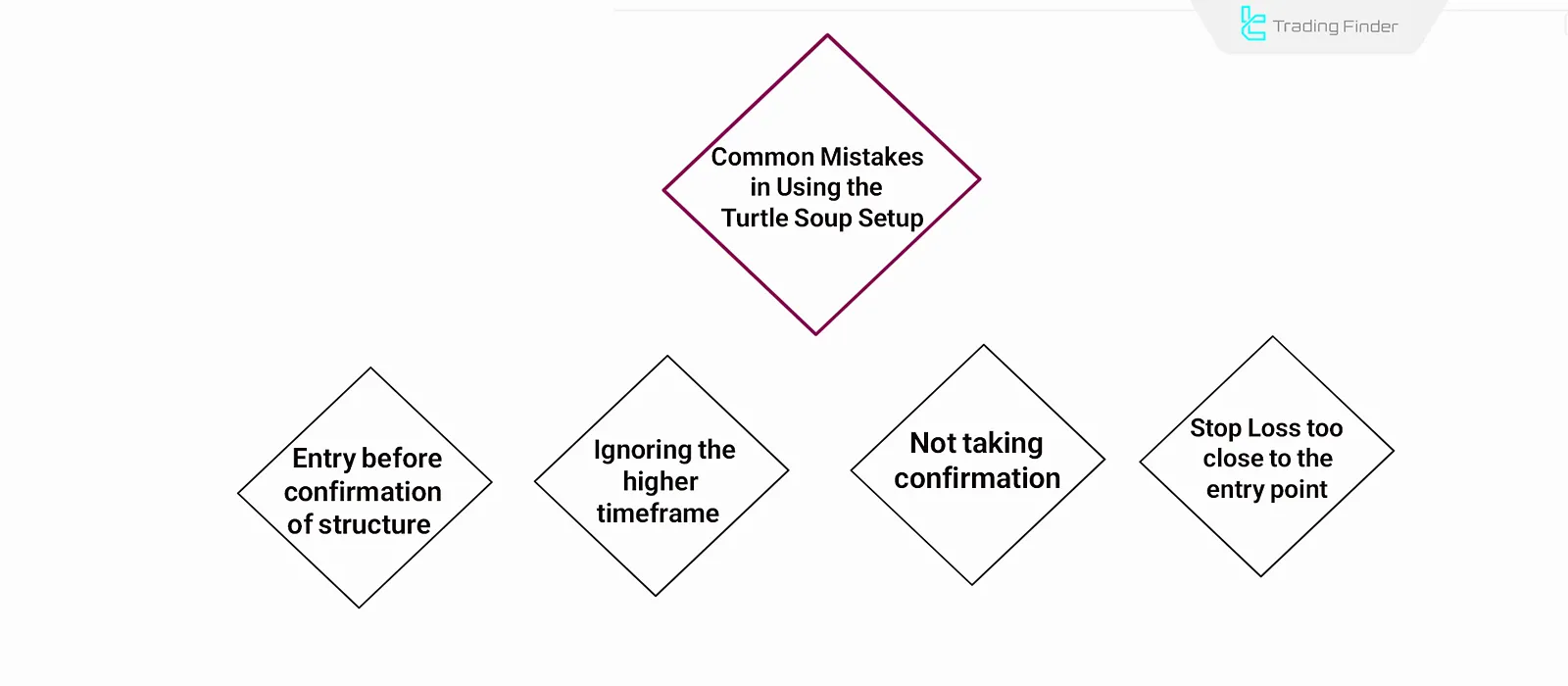
Common Mistakes in Using the Turtle Soup Trading Setup
Many traders make mistakes when applying the ICT Turtle Soup Strategy due to rushing or ignoring details.
Identifying and avoiding these mistakes is essential for executing the Turtle Soup Strategy correctly. Common Mistakes in the Powerful Turtle Soup Setup:
- Entering too early before confirming the change in market structure;
- Ignoring the overall trend in the higher timeframe;
- Not using complementary confirmations (such as Order Block or FVG);
- Placing the Stop Loss too close to the entry point.
Conclusion
The Turtle Soup Strategy is a tool for liquidity hunting and utilizing confirmed directional moves in higher timeframes.
This strategy is particularly suitable for traders seeking clear market movements. Mastery in liquidity concepts and synchronization across timeframes is essential for success in this method.













