Arbitrage occurs when the same asset is simultaneously traded at different prices in two separate markets. If this price discrepancy is correctly identified, it can result in profit without requiring prediction of the market trend.
For example, if Bitcoin is priced at $93,800 on one exchange and $94,000 on another, it is possible to buy from the cheaper exchange and sell at the more expensive one.
This type of trading is common in markets like cryptocurrencies and the forex market, where liquidity is high and numerous platforms are available, and it does not rely on fundamental or technical analysis.
What Is Arbitrage Trading?
Arbitrage trading means taking advantage of price differences for the same asset across different markets.
This trading strategy doesnot require technical or fundamental analysis and is implemented when an asset is traded at different prices across two or more markets.
Arbitrage helps improve market efficiency by enabling traders to equalize asset prices between markets through their actions.
Successful arbitrage requires high execution speed, precision, and consideration of transaction costs. In the Learning arbitrage article on the Investopedia website, this type of trading is fully explained.
Law of One Price in Arbitrage
The Law of One Price, also known as define arbitrage, states that any identical asset should have a similar price across different markets. If a price difference occurs, it creates a profit opportunity known as an arbitrage opportunity, which professional traders take advantage of.
This concept forms the foundation of many arbitrage strategies in financial markets.
Whenever the price of an asset differs between two markets, a trader buys from the cheaper market and sells in the more expensive one, causing prices to return to equilibrium.
This cycle, known as the arbitrage process, explains why price discrepancies in a free market cannot persist for long.
How arbitrage works?
Executing arbitrage trades requires a combination of predefined rules, tools, and a deep understanding of the market.
Key factors in arbitrage include transfer costs,transaction confirmation time, and price volatility risk.
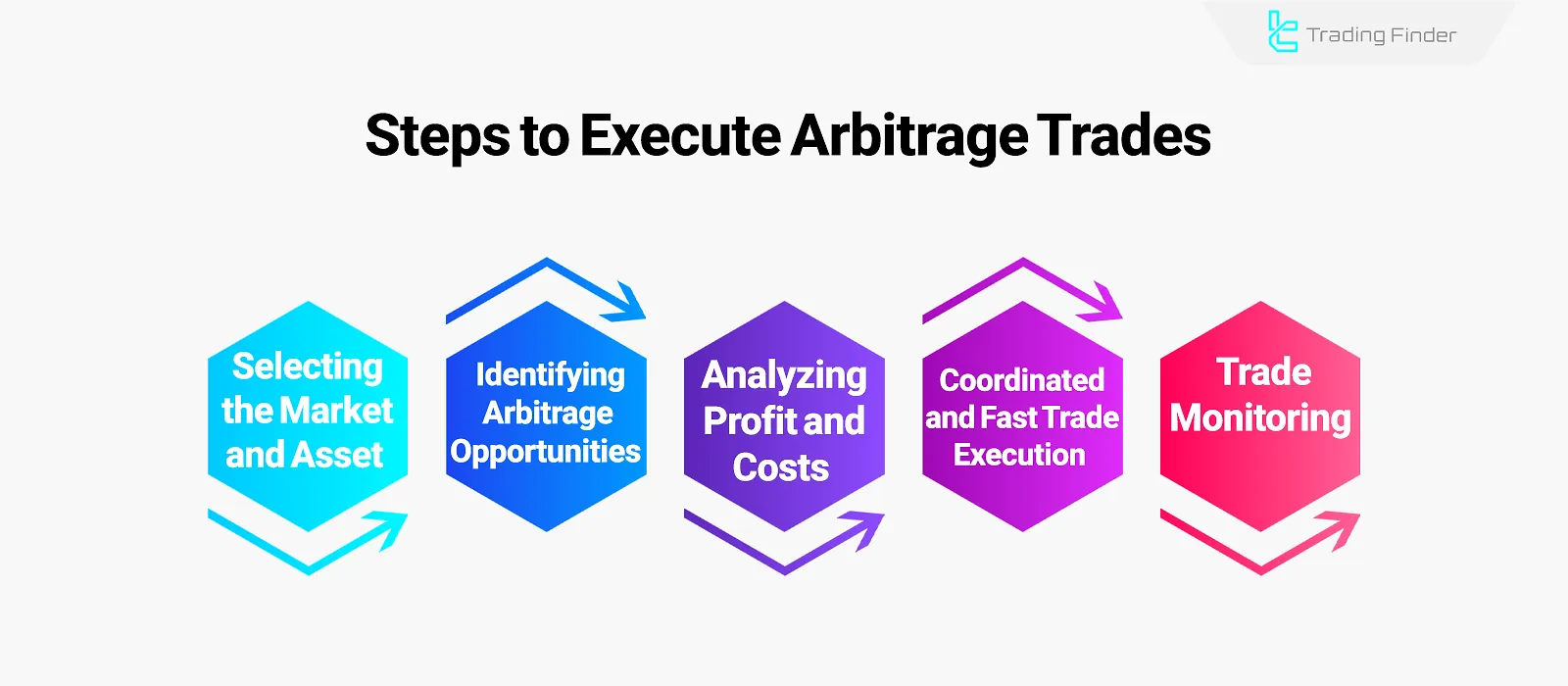
The steps to perform arbitrage are as follows:
#1 Selecting the Market and Asset
The chosen market must have high liquidity and frequent price discrepancies between platforms.
Markets such as cryptocurrencies are suitable for arbitrage due to their decentralized nature and diverse exchanges.
The selected asset directly impacts the stability, profitability, and success of the arbitrage.
#2 Identifying Arbitrage Opportunities
In this stage, the trader uses price comparison platforms and API tools to identify discrepancies in buy and sell prices across markets.
Latency and withdrawal limits on exchanges must be considered when identifying such opportunities.
#3 Analyzing Profit and Costs
Accurate evaluation of trading fees, withdrawal fees, and possible cross-chain transfer costs in Blockchain is necessary.
One must also consider spreads and real-time exchange rates in markets like Forex.
After all costs are deducted, arbitrage is meaningful only when the price difference leads to a positive net arbitrage profit.
#4 Coordinated and Fast Execution
Using trading bots or automated arbitrage algorithms enhances precision and speed in this stage.
Successful execution requires coordination between active accounts on two or more trading platforms.
#5 Risk Control and Continuous Monitoring
Arbitrage carries various risks, such as system failures or execution issues.
Exchange withdrawal suspensions, fast-changing prices, or human errors can result in losses.
Use real-time alert systems, demo account testing, and backtesting strategies to reduce such risks.
Arbitrage Operations Checklist
For successful arbitrage trading, both technical and financial infrastructure must be prepared in advance.
The trader should open accounts on several reputable exchanges and complete identity verification to be ready for action whenever an arbitrage condition arises.
Key steps for executing this type of trading include:
- Opening accounts on multiple exchanges and holding part of the capital in each to eliminate transfer delays;
- Using a VPS located close to exchange servers to reduce ping and increase execution speed;
- Setting a minimum acceptable price difference for entering a trade;
- Recording real-time transaction logs to control risk.
By following these principles, operational errors are minimized and the chance of losing arbitrage profit is reduced to the minimum.
Types of Arbitrage Strategies
Different arbitrage strategies depend on market structure, asset type, and available tools.
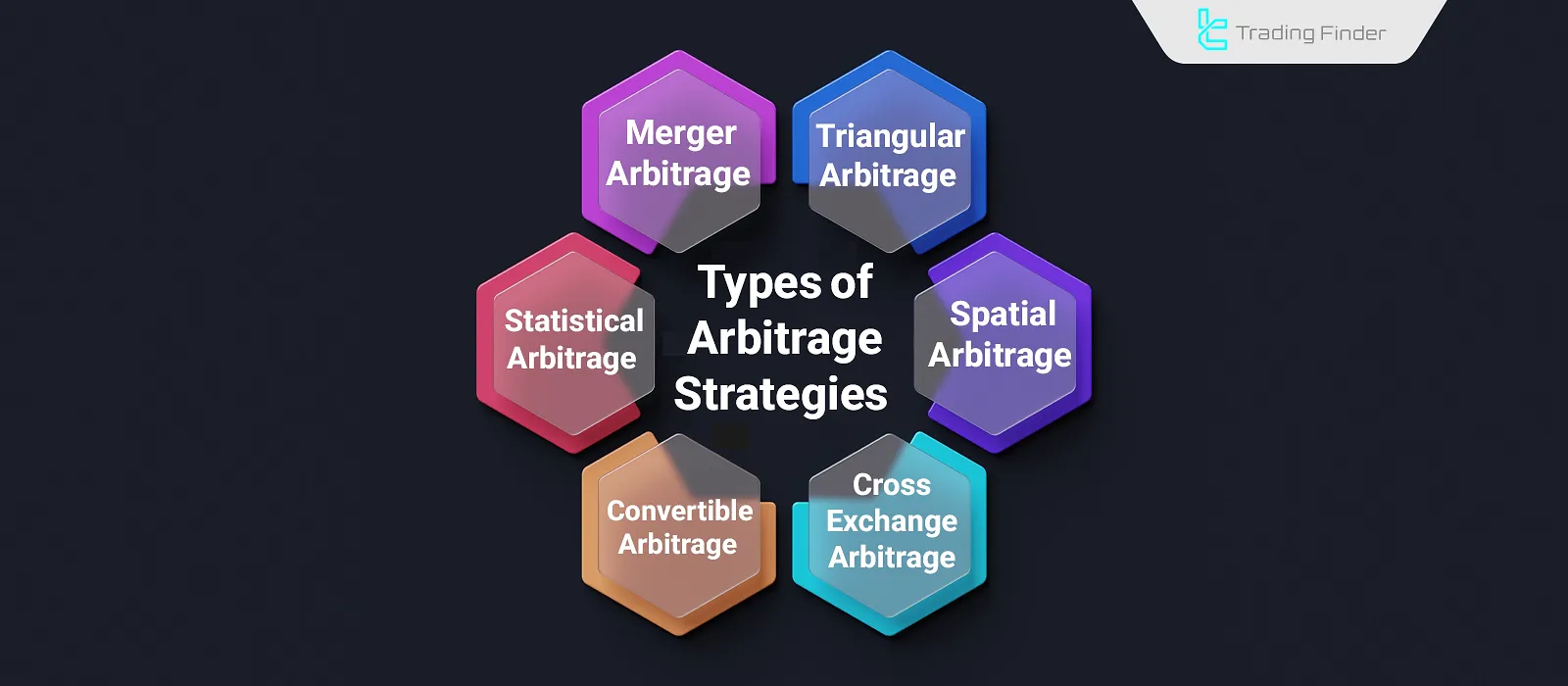
Cross-Exchange Arbitrage
In this strategy, a trader buys an asset from one exchange at a lower price and sells it on another exchange at a higher price.
This type of arbitrage is common in the cryptocurrency market due to high liquidity and frequent price differences between exchanges.
Spatial Arbitrage
This strategy exploits price differences for an asset in different geographic markets.
For instance, if a price gap exists, buying Bitcoin on an exchange based in the U.S. and selling it on one, based in Canada.
However, this may involve legal restrictions and international transfer costs.
Statistical Arbitrage
This method identifies arbitrage opportunities using mathematical and statistical models.
Traders use algorithms and data-driven analysis to detect unusual price disparities and profit from them.
Cash-and-Carry Arbitrage
In types of arbitrage trading, one of the classic models is cash-and-carry arbitrage, in which an asset is purchased in the spot market and simultaneously sold in the futures market.
The goal of this method is for prices to converge by the expiration date, generating profit from the initial difference.
For example, if the spot price of Bitcoin is 40,000 dollars and its three-month futures price is 41,000 dollars, the trader can take advantage of this gap.
This method is an example of arbitrage in trading that creates a guaranteed profit regardless of market direction.
Merger Arbitrage
In this strategy, a trader buys shares of a target company involved in a merger or acquisition, anticipating that the stock price will rise after the announcement.
This form of arbitrage carries risks such as failed mergers or changing deal terms.
Convertible Arbitrage
Here, a trader buys convertible bonds and simultaneously sells the related stock. The aim is to profit from the bond and stock price difference.
Successful execution requires detailed market analysis and effective risk management.
Triangular Arbitrage
One of the most well-known types of arbitrage in the cryptocurrency and forex markets is triangular arbitrage, which takes advantage of the exchange rate differences among three currency pairs.
In this method, a trader may convert dollars to euros, euros to pounds, and then pounds back to dollars to profit from rate discrepancies.
This structure is known as triangular arbitrage and is also explained in educational materials related to cross currency arbitrage.
In some cases, this concept is combined with triangular merger in corporate finance to identify profitable merger opportunities.
This concept is taught in a video on the YouTube channel Ryan O'Connell, CFA, FRM:
Triangular Arbitrage
This involves trading between three different currency pairs within a single exchange.
For example, converting USD to EUR, then EUR to GBP, and finally GBP back to USD, if exchange rates create a profitable cycle.
In Different Markets how arbitrage works
Arbitrage execution varies across markets due to differences in transaction costs, liquidity levels, execution speed, and price spreads.
Cryptocurrency MarketArbitrage
Due to the decentralized structure and the high number of exchanges, the cryptocurrency market provides a suitable environment for cross-exchange arbitrage.
Price discrepancies in this market stem from differences in liquidity,trade volume, and exchange fee policies.
To perform arbitrage in this space, factors such as transfer fees, transaction confirmation times, and withdrawal limits must be carefully evaluated.
Atomic Arbitrage in DeFi
In the DeFi ecosystem, there is a type of different types of arbitrage called atomic arbitrage.
In this method, all stages of buying and selling are executed within a single transaction, and if any stage fails, the entire transaction is canceled.
This type of spatial arbitrage is usually carried out on decentralized networks such as Ethereum and requires advanced technical knowledge of smart contracts.
However, gas fees and network congestion can reduce arbitrage profit.
Funding Rate Arbitrage in Perpetual Contracts
In the crypto derivatives market, when the funding rate differs between exchanges, an opportunity arises for arbitrage forex or arbitrage in finance.
For example, if the funding rate on Exchange A is positive and on Exchange B is negative, a trader can open a long position on one and a short position on the other to profit from the difference.
This model is one of the best arbitrage methods for professional traders, as it allows for periodic profits without exposure to market direction risk.
Forex Market Arbitrage
In the Forex market, arbitrage occurs through exchange rate differences between liquidity providers or trading accounts.
This type of arbitrage investment relies on price update delays across platforms and requires infrastructure such as low-latency VPS connections to brokers’ data centers.
However, brokers may restrict arbitrage through slippage or order rejections.
Stock MarketArbitrage
In stock trading, arbitrage can happen through price differences for the same stock listed on multiple exchanges or between a stock and its futures contracts.
For example, traders can profit from the gap if a company’s stock trades at different prices on the NYSE and LSE.
This strategy requires a precise understanding of market structure, transaction costs, and timing.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Arbitrage Trading
Although arbitrage trades are generally categorized as relatively low-risk, their execution requires close attention to technical infrastructure, fast order execution, and awareness of legal constraints.
The table below outlines the most important pros and cons of this strategy:
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Profiting from momentary price differences without needing to predict market trends | Requires fast execution to take advantage of fleeting opportunities |
Ability to use automated trading bots for precise execution | Increased risk due to transfer delays or order rejections |
Independent from technical or fundamental analysis | High impact of transfer and trading fees on net profit |
Enhances market efficiency by eliminating price disparities | Legal restrictions in some countries or platforms |
Can be applied in various markets such as crypto, forex, stocks | Requires simultaneous access to multiple accounts or exchanges and real-time asset management |
Example of Calculating Net Arbitrage Profit
To better understand arbitrage profit, suppose the price of Ethereum on Exchange A is 1,950 dollars and on Exchange B is 1,970 dollars. If each trade has a 0.1 percent fee, the trader must calculate the buying cost (1,950 × 1.001 = 1,951.95) and the selling revenue (1,970 × 0.999 = 1,968.03).
The net profit equals 1,968.03 − 1,951.95 = 16.08 dollars.
This is an arbitrage example in practice, showing that even small differences can be profitable.
Hidden Risks in Arbitrage
In addition to fees and slow transfer speeds, arbitrage can involve hidden risks, including:
- Withdrawal freezes on the destination exchange during high volatility;
- Changes in network fees during transfers;
- Severe slippage at the time of order execution;
- Exchange rate differences during currency conversion.
Furthermore, in global financial markets, differing national regulations can create a form of regulatory arbitrage, where traders use regulatory gaps to increase profits. This topic is widely discussed in arbitrage in finance.
What Are Arbitrage Bots?
Arbitrage bots are automated programs that use advanced algorithms as part of an arbitrage strategy to identify price discrepancies of an asset across different markets or exchanges and execute buy and sell orders instantly.
These bots connect to exchanges via APIs, receive real-time price data, and execute trades based on predefined strategies.

Types of Arbitrage Bots
Due to the importance of speed in arbitrage trades, trading bots capable of quickly detecting price gaps are essential.
Cross-Exchange Arbitrage Bots
These bots detect price differences between one or more exchanges and simultaneously buy the asset from the cheaper one and sell it on the pricier one.
Statistical Arbitrage Bots
These bots use statistical models and historical data analysis to identify price patterns and execute arbitrage strategies accordingly.
AI-Powered Arbitrage Bots
Using artificial intelligence, these bots can process massive amounts of price data in real-time, identify arbitrage opportunities, and execute trades instantly.
Top Arbitrage Bots Across Different Financial Markets
Due to differences in structure, technology, and volatility in various financial markets, arbitrage bots' performance may vary across them.
Below are the top arbitrage bots categorized by market:
Forex Market
Due to the high liquidity and variety of currency pairs in the forex market, arbitrage bots must be able to analyze real-time rates and execute fast trades.
Recommended arbitrage bots for forex:
- HaasOnline
- Trality
- 3Commas
- AlgosOne
Cryptocurrency Market
Due to the decentralized nature of crypto exchanges and high price volatility, crypto arbitrage bots must be capable of connecting to many APIs and managing automated trades across platforms.
Recommended crypto arbitrage bots:
- Cryptohopper
- Bitsgap
- WunderTrading
- Pionex Arbitrage Bot
- Arbismart
- Coinrule
Stock Market
In the stock market, arbitrage opportunities typically arise from price differences between exchanges or derivatives and their underlying assets.
Bots suited for this market must offer structured analysis tools and access to accurate market data.
Some of the forex bots listed above are also suitable for the stock market.
What Are the Regulations for Arbitrage?
Although arbitrage is a legal trading strategy, it is subject to specific regulations depending on the market and jurisdiction.
Arbitrage Regulations in the Crypto Market
In many countries, arbitrage in crypto is legal and considered a legitimate way to earn profits.
However, the following factors must be reviewed:
Arbitrage Regulations in the Forex Market
In forex trading, arbitrage is also legal, but various regulations monitor it:
- Regulatory Oversight: In the U.S., it's regulated by the CFTC; in Europe, by organizations like ESMA;
- Leverage Limits: Restrictions on leverage may impact arbitrage strategies;
- Broker Policies: Some brokers limit arbitrage trading or offer specialized accounts.
Arbitrage Regulations in the Stock Market
In stocks, arbitrage occurs between exchanges or between derivatives and underlying assets.
Why Do Prices Differ Across Platforms?
These differences are due not only to market volatility but also to several other structural and regulatory factors.

Liquidity and Trading Volume Differences
Each platform has different levels of liquidity and trade volume.
Higher volume platforms tend to have more stable prices, while low-volume platforms may show greater volatility, leading to price differences.
Regional Demand and User Behavior
Trading platforms operate in different geographic areas, serving users with varied preferences.
This variation in demand can affect the price of an asset across platforms.
Market Volatility and Price Update Delays
In highly volatile markets, asset prices change rapidly. If platforms update prices with a delay, it may cause price mismatches for the same asset.
Fees and Transaction Costs
Each platform has its own fee structure. These fees can influence the final purchase or sale price, creating discrepancies between platforms.
Legal and Regulatory Constraints
National regulations can impact pricing across platforms. For instance, trading or tax restrictions may cause price differences on a given exchange.
Key Points for Arbitrage Traders
Ultimately, successful arbitrage execution requires three main factors:
- Execution speed: even a one-second delay can eliminate potential profit;
- Low fees: in small-margin trades, transaction costs play a decisive role;
- Capital management: holding funds across multiple exchanges must be done with strict risk and wallet security control.
By combining these three principles, a trader can make the most of temporary market opportunities without being exposed to major price risks.
Buy Sell Volume Indicator for Market Analysis Before Starting Arbitrage Trades
The Buy Sell Volume indicator is one of the powerful tools it designed to analyze liquidity flow and detect the level of buying and selling pressure in each candlestick.
This indicator allows traders to evaluate two key factors in arbitrage trading: trading volume and execution speed.
By calculating and separating buy and sell volumes, it shows which side of the market has more control at any given moment.
The results are displayed as a colored histogram around the zero line, where yellow bars represent buyer strength and pink bars indicate seller dominance.
When the histogram moves into positive areas, buying pressure increases and price growth becomes more likely.
Conversely, when the bars enter negative zones, selling pressure dominates and prices may decline. This makes the Buy Sell Volume indicator a practical tool for identifying both short-term and long-term trends.
This indicator belongs to the category of volume-based and reversal oscillators and can be used in forex, stocks, cryptocurrencies, indices, and commodities markets.
Traders can choose their preferred timeframe and make decisions based on volume behavior in that period.
In the settings section, parameters such as smoothing period, calculation method (SMA, EMA, etc.), volume type (Tick or Real Volume), and alert options (sound, text, or email) are available.
These features allow users to customize the indicator according to their trading style.
Overall, Buy Sell Volume is an analytical tool for measuring the balance between supply and demand in the market. Using it helps traders visually identify buyer and seller strength, leading to more accurate and informed trading decisions.
- Download Buy Sell Volume Indicator for MetaTrader 5
- Download Buy Sell Volume Indicator for MetaTrader 4
Conclusion
Arbitrage is a trading strategy based on taking advantage of temporary price differences across markets. To execute this strategy effectively, trader must understand market structures, transaction costs, regulatory limitations, and automation tools.
Arbitrage can be applied in crypto, forex, and stock markets, each with its execution methods. It requires an accurate analysis of opportunities and the usage of specialized trading bots.
Success in arbitrage depends on trader's ability to manage risk and adapt to technical and regulatory changes.













