In technical analysis of financial markets, Fibonacci ratios and levels are recognized as one of the oldest tools for identifying price reversal points.
The main feature of these levels is their compatibility with the repetitive structure of the market, such that during both upward and downward waves, prices often react to these levels.
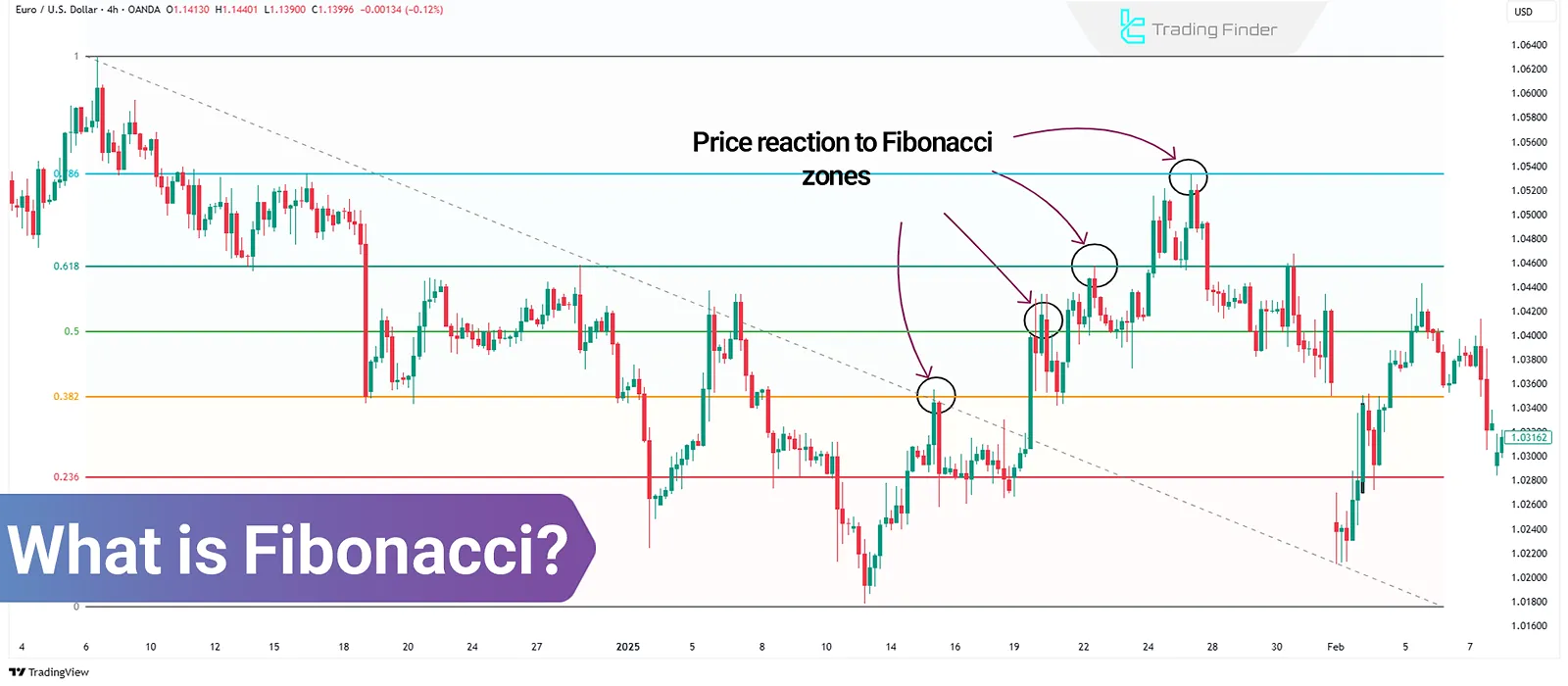
What is Fibonacci?
Fibonacci in financial markets is a set of mathematical ratios used to identify potential levels for price reversal or continuation. These ratios are derived from the famous Fibonacci sequence and are usually plotted as horizontal lines or various tools on the price chart.
Traders use Fibonacci to determine support and resistance areas and price targets during uptrends and downtrends. The main application of Fibonacci in technical analysis is to predict key points of price behavior change based on the market’s wave structure.
History of Fibonacci
The Fibonacci sequence was first introduced by Italian mathematician “Leonardo Fibonacci” in the 13th century, in his book "Liber Abaci".
In this sequence, each number equals the sum of the two preceding numbers; these sequences are found in nature, art, and technical analysis of financial markets.
The Use of Fibonacci in Technical Analysis
Fibonacci tools in technical analysis allow market behavior to be predicted based on recurring mathematical ratios.
These tools are not only used for identifying support and resistance levels but also to set price targets, identifying pullback points, detecting the end of main market moves, and risk management planning.
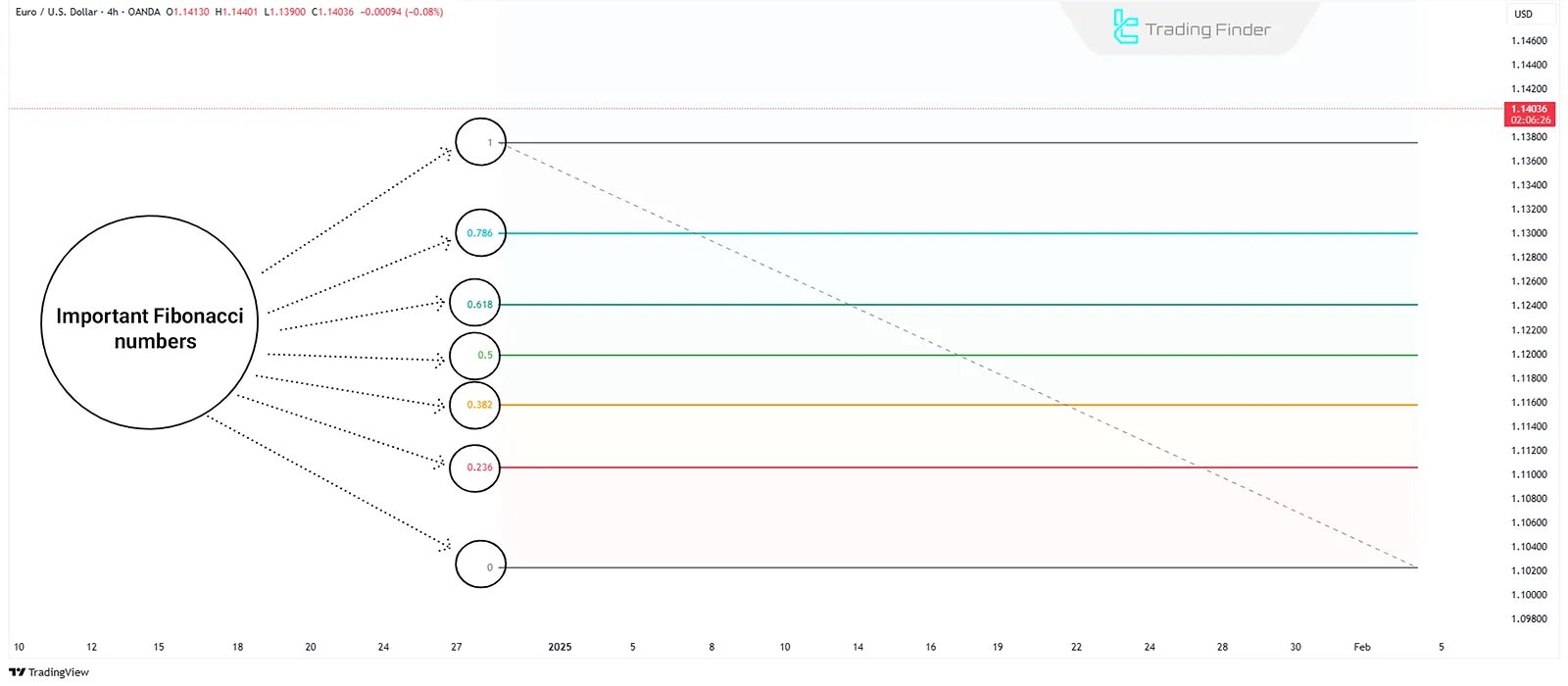
Fibonacci Numbers in Technical Analysis
The Fibonacci sequence is a series of numbers where each number is the sum of the two preceding ones (0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, ...). The most important use of this sequence is to extract ratios like 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 78.6%.
In technical analysis, these ratios are used to identify reversal points, support, resistance, and price targets.
The 61.8% ratio, or the golden ratio, holds the most significance in determining price reaction levels. Using these numbers and ratios, traders can analyze price movements with various Fibonacci tools on the chart and identify key market areas.
Why Does Price React to Fibonacci Levels?
Since a large number of traders follow these levels, the more attention they receive, the higher the probability of price reacting in these areas.
Of course, this reaction does not always occur, as other factors also influence price, but this collective attention often leads to noticeable reactions at these levels.
Types of Fibonacci Tools in Technical Analysis
On analytical platforms, various tools based on the Fibonacci sequence and ratios exist, each serving a specific purpose. The most important tools are:
- Fibonacci Retracement
- Fibonacci Extension
- Fibonacci Fan
- Fibonacci Arc
- Fibonacci Channel
- Fibonacci Time Zones
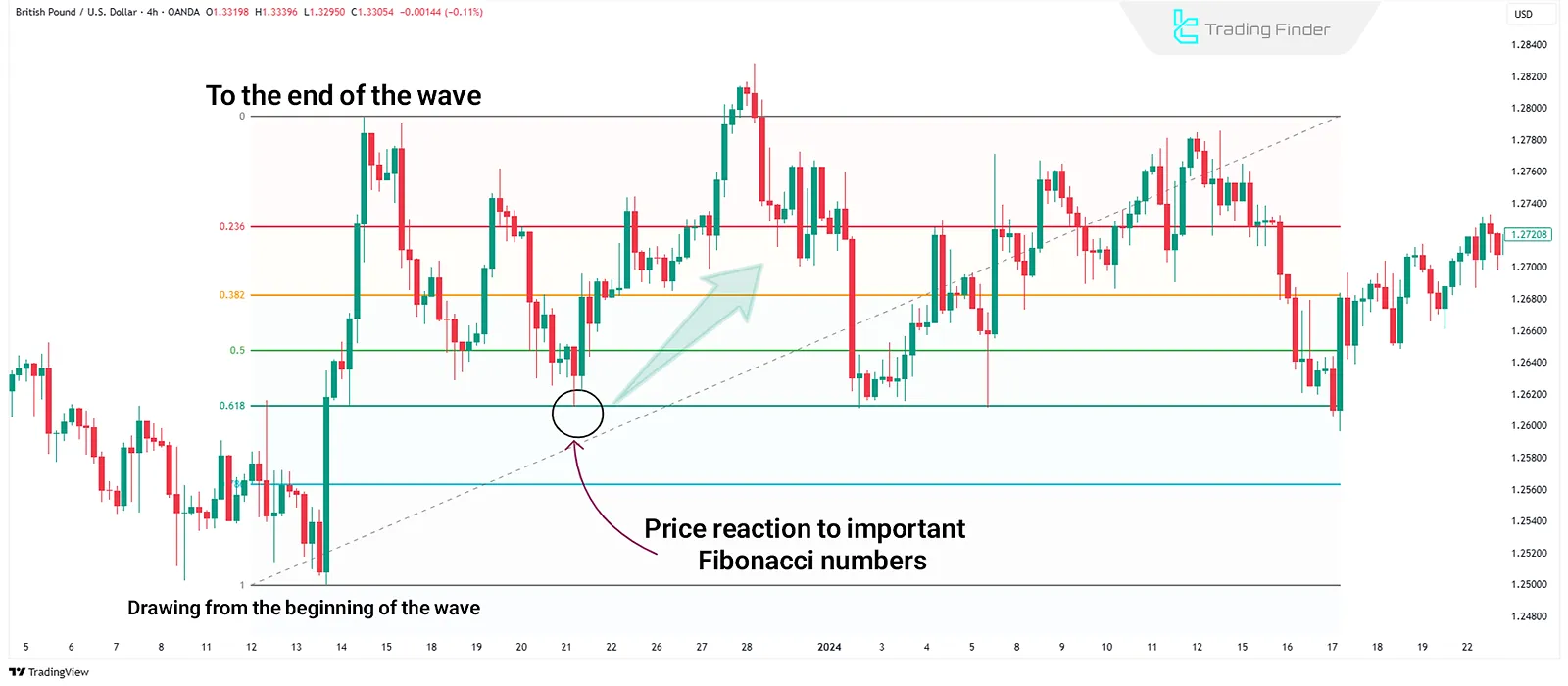
Fibonacci Retracement
The Fibonacci Retracement tool is used to identify levels where the price may halt or retrace after an upward or downward movement.
These lines show areas where the price has previously reacted or is likely to react. By combining these levels with other market data, traders can assess probable price behavior.
How to Draw Fibonacci Retracement?
To draw this tool, typically a main wave (low to high or high to low) is selected on the chart, and Fibonacci lines are drawn between these two points based on the 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 78.6% ratios.
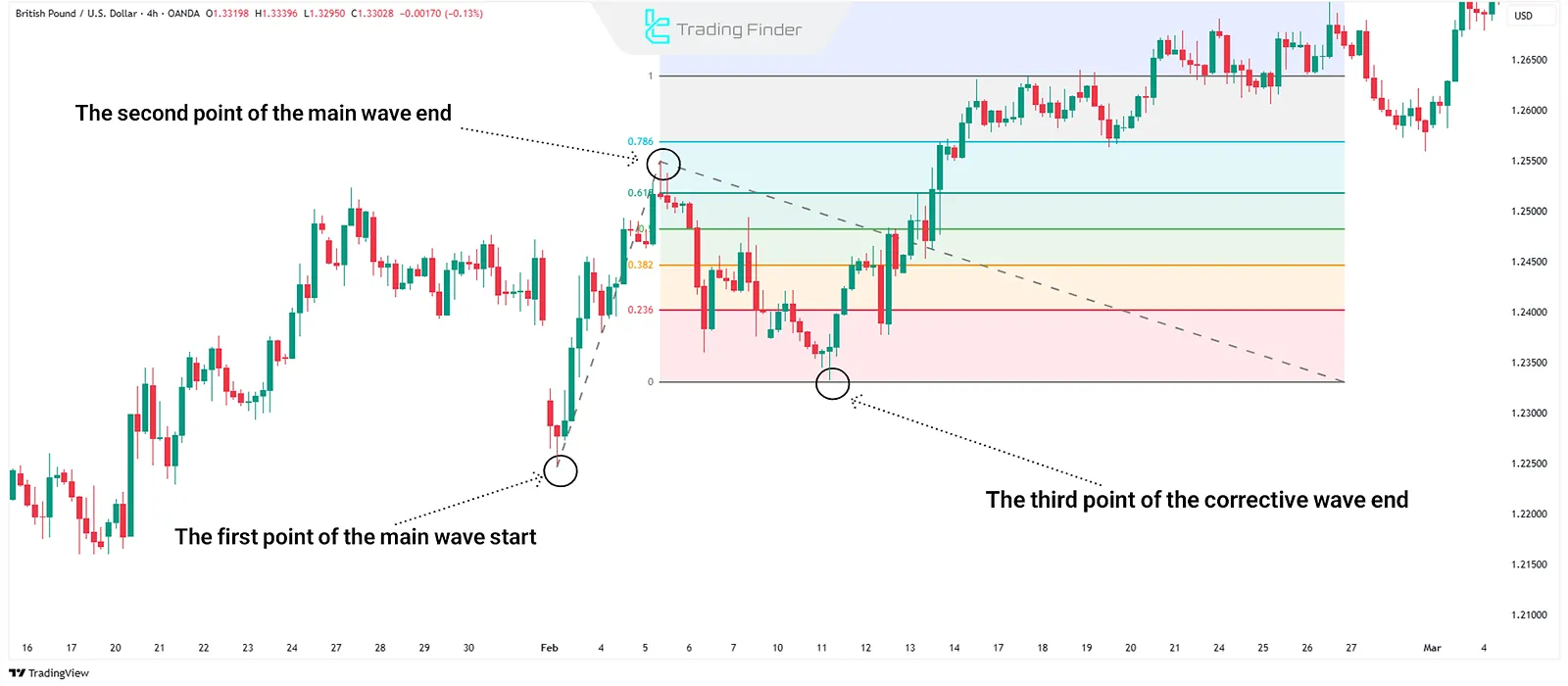
Fibonacci Extension
Fibonacci Extension is used to determine price targets following the continuation of a trend and is typically applied after a pullback or correction ends.
These levels indicate where the price might reach after a correction; they can be used as profit-taking targets or probable market reaction zones.
How to Draw Fibonacci Extension?
The trader selects three points (start, end of the main wave, and end of the correction) to draw the tool and display levels such as 127.2%, 161.8%, 261.8%, and 423.6% on the chart.
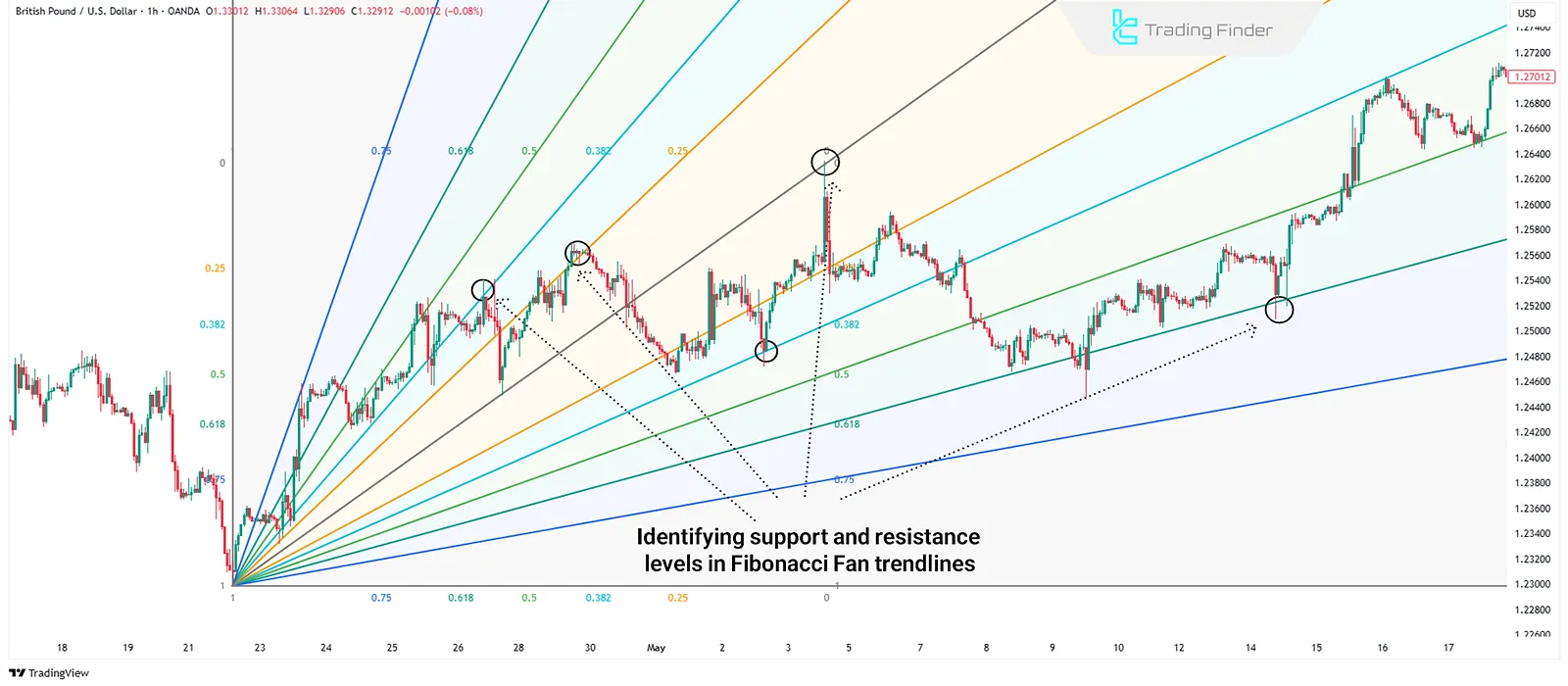
Fibonacci Fan
The Fibonacci Fan is a tool that draws diagonal lines based on Fibonacci ratios from a low or high point.
These lines are used to examine dynamic support and resistance levels over time, helping analysts evaluate the trend’s momentum and direction.
How to Draw Fibonacci Fan?
The analyst marks the low and high of a wave, then uses the fan tool to draw diagonal lines from low to high (or vice versa) based on Fibonacci ratios.
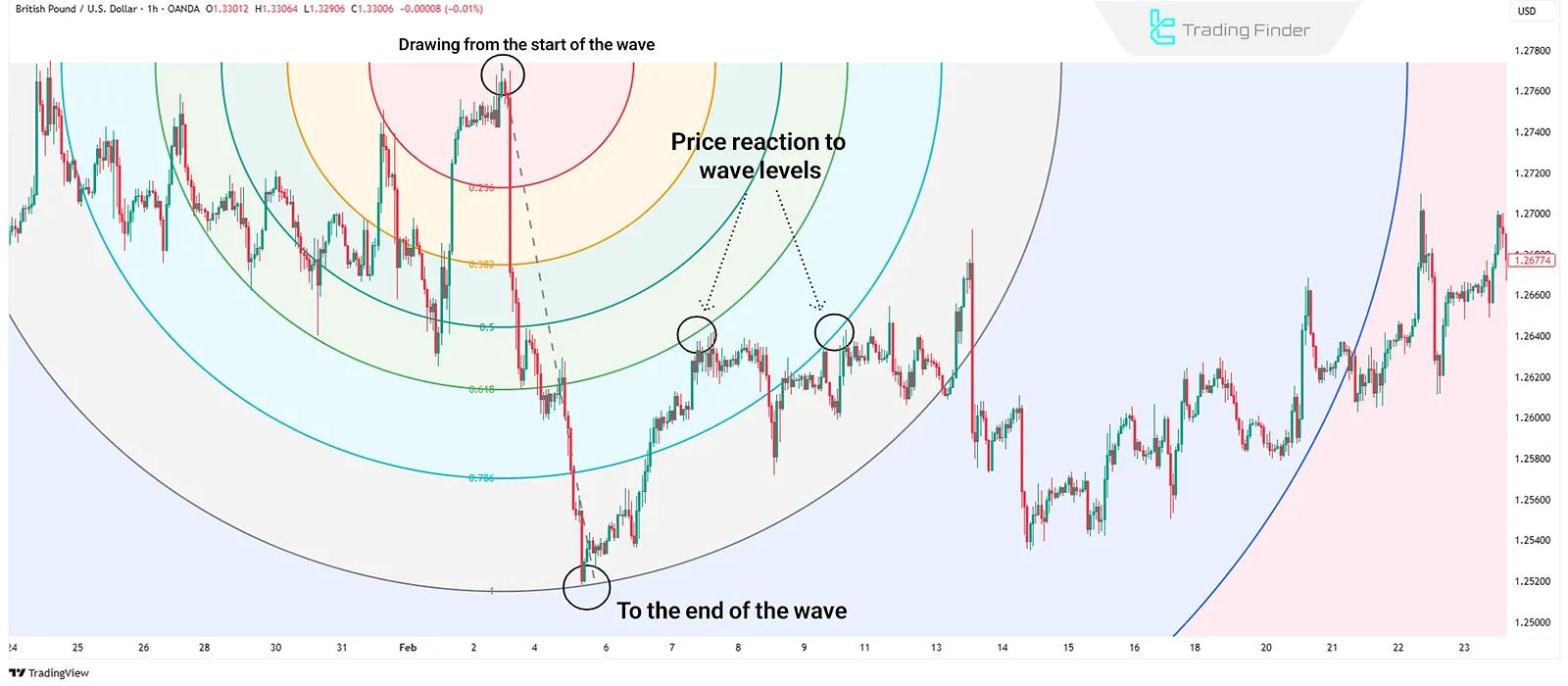
Fibonacci Arc
Fibonacci Arc creates arcs based on Fibonacci ratios from a primary price move. These arcs indicate areas where the price may react as it moves, often considered as combined support and resistance zones.
How to Draw Fibonacci Arc?
The analyst chooses a low and a high point, then applies the arc tool between these points so that arcs are drawn based on Fibonacci ratios.
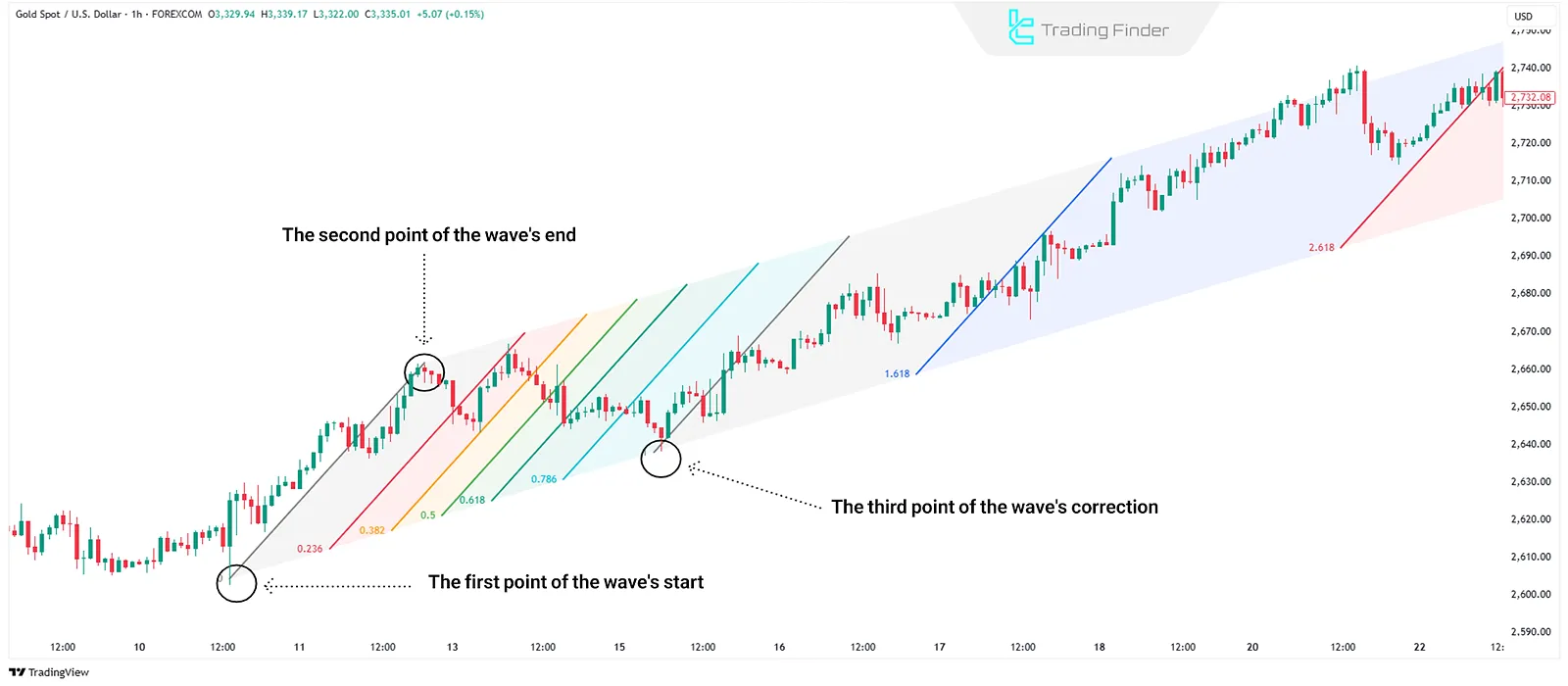
Fibonacci Channel
Fibonacci Channel draws parallel lines based on Fibonacci ratios along the main trend, outlining zones where support or resistance may occur.
Traders use this tool to analyze price behavior within channel trends and identify suitable entry or exit points.
How to Draw Fibonacci Channel?
The analyst selects three points (two highs and one low, or vice versa) to draw parallel lines based on Fibonacci ratios in the direction of the main trend.
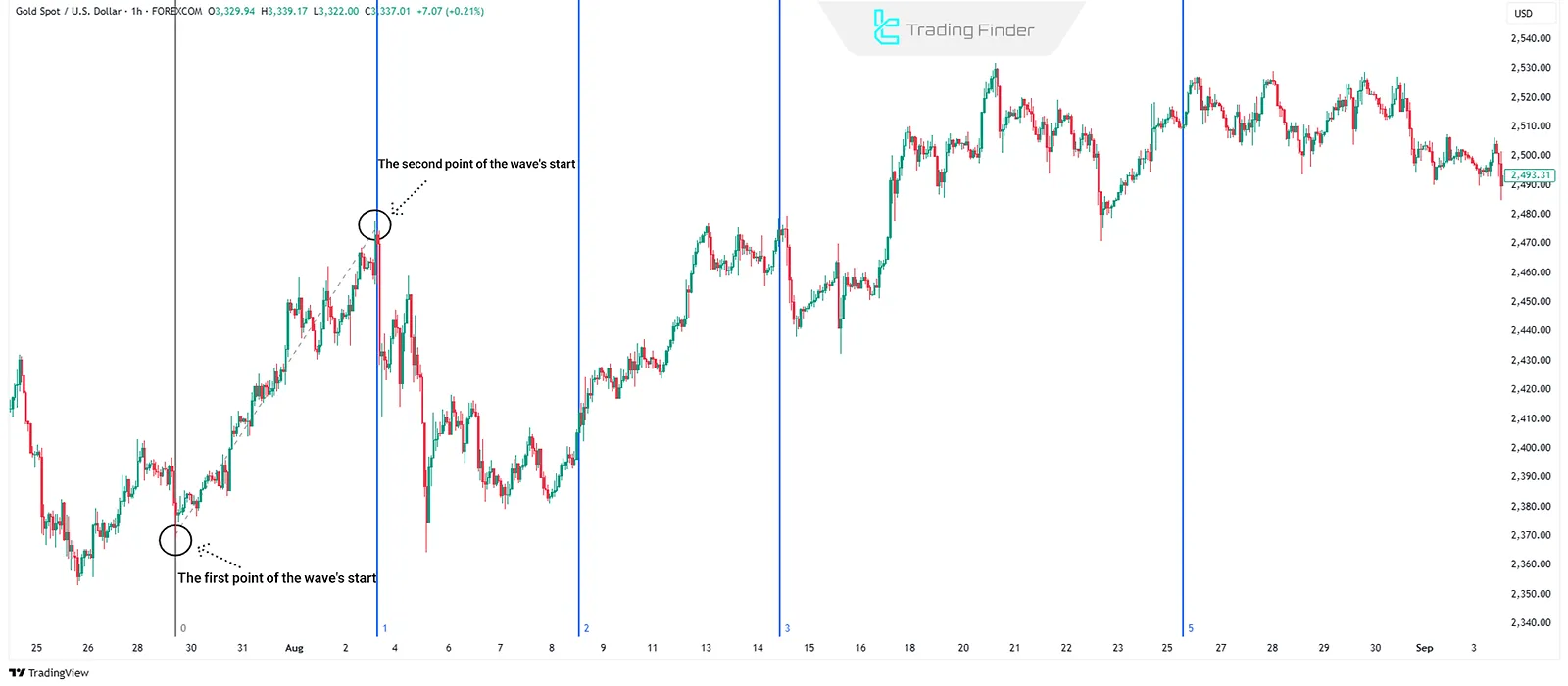
Fibonacci Time Zones
Fibonacci Time Zones are vertical lines drawn using the Fibonacci sequence from a significant price point into the future.
These lines indicate times when trend changes or new moves may occur, mainly used to assess the time aspect of market moves, especially in larger trends.
How to Draw Fibonacci Time Zones?
The analyst identifies a starting and ending point for a trend, then uses the tool to draw vertical lines based on the Fibonacci sequence from the starting point into the future.
Additional Tips for Using Fibonacci Tools
For effective use of Fibonacci tools in trading, consider the following:
- It is better to use Fibonacci only on clear moves and strong trends;
- Fibonacci levels can be combined with other technical tools such as price action, candlestick patterns, indicators, and trading volume for more reliable signals;
- Always look for Fibonacci clusters (areas where multiple Fibonacci levels overlap); Points where multiple Fibonacci levels from different tools or timeframes converge are often especially important;
- Fibonacci should not be the sole decision-making tool; pay attention to market psychology and capital management as well.
Combining Fibonacci with the RSI Indicator
Combining Fibonacci levels with the RSI indicator increases the accuracy of trading signals.
When the price reaches a key Fibonacci level and, at the same time, the RSI enters the overbought or oversold zone, this confluence increases the probability of a price reaction or reversal.
Traders use this combination to better identify entry and exit points and reduce trading risk.
Example of Combining RSI with Fibonacci
On the 15-minute EUR/USD chart, after a bearish correction in an uptrend, the price reaches the key 0.618 Fibonacci level. At the same time, the RSI indicator shows that the price has entered the oversold area, so in such situations, traders may enter a buy position.
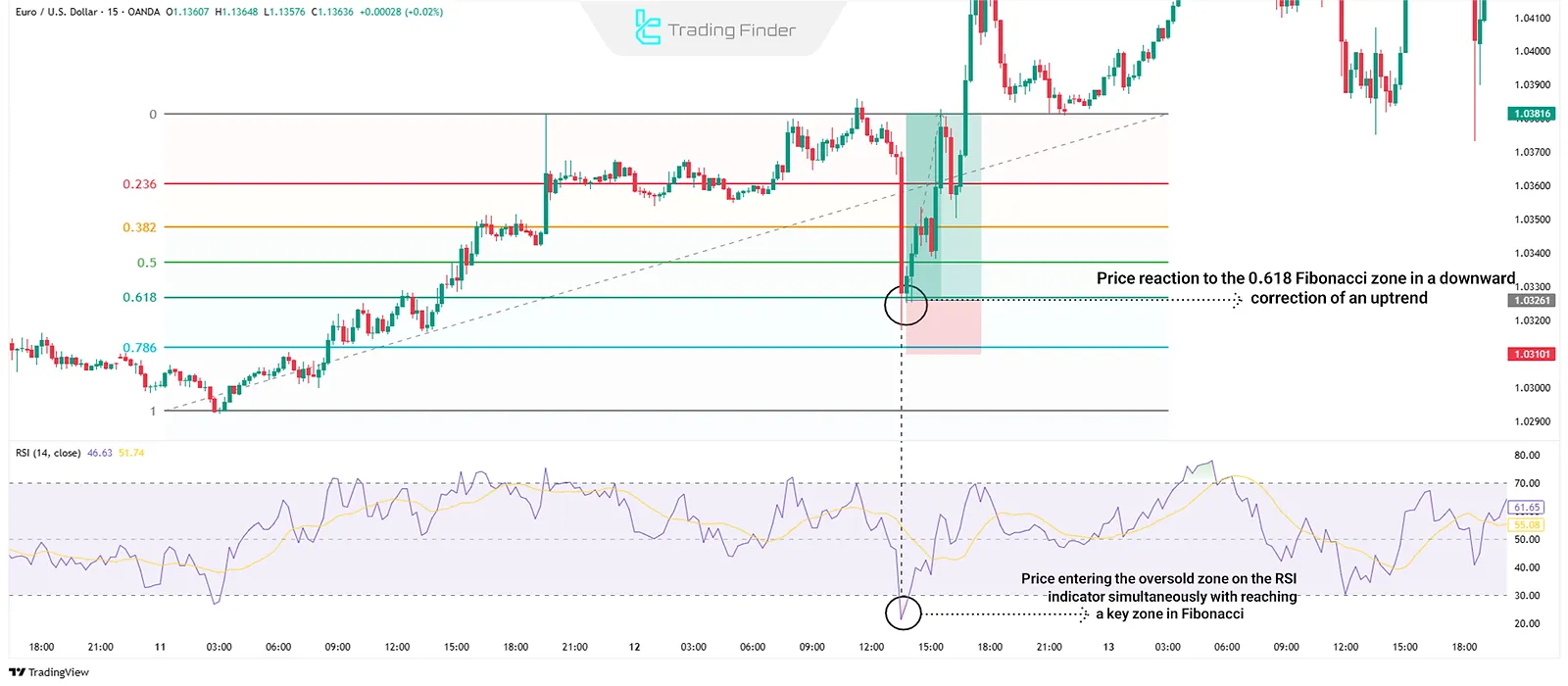
Combining Fibonacci with Price Action
In this combination, the trader first draws important Fibonacci levels and then observes price behavior, support/resistance, and candlestick patterns near these levels.
If a price action reversal signal is seen alongside a Fibonacci level, that signal is considered more valid.
Example of Combining Fibonacci with Price Action
On the GBP/USD chart, the price reaches the key 0.618 Fibonacci level. At the same time, the price hits a 5-minute trendline, and a bullish engulfing candlestick pattern form. These conditions are considered a suitable signal to enter a trade.
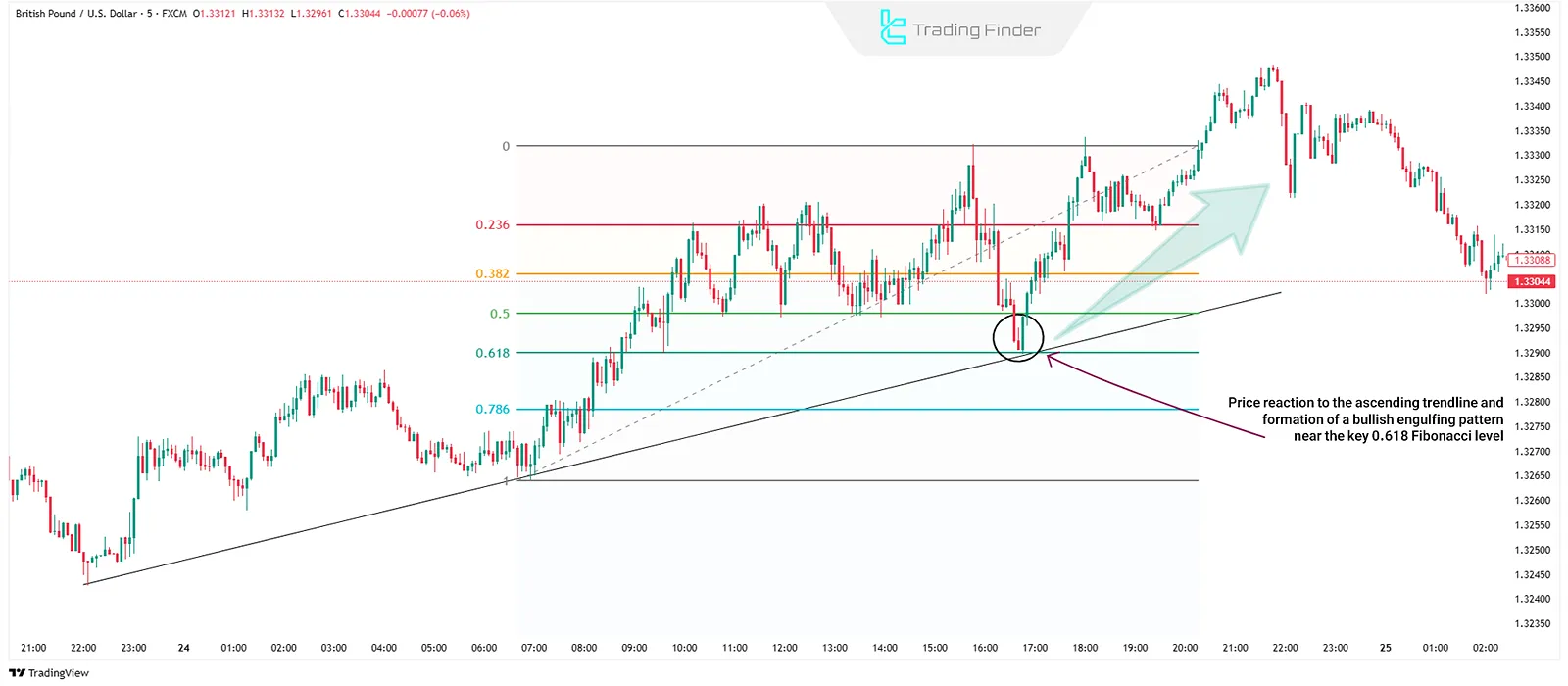
Common Mistakes in Using Fibonacci
Common mistakes of using Fibonacci in technical analysis include:
- Drawing Fibonacci levels in unclear trends;
- Incorrectly choosing swing highs and swing lows;
- Over-reliance on Fibonacci and ignoring other tools;
- Disregarding trade confirmations;
- Ignoring market psychology and news.
Using Fibonacci in Multi-Timeframe Analysis
Multi-timeframe analysis is one of the effective methods for increasing the accuracy of Fibonacci levels.
In this approach, the trader first draws Fibonacci levels on higher timeframes (e.g., daily or weekly) to identify major support and resistance areas. Then, the same is done on lower timeframes (e.g., 4-hour or hourly).
When Fibonacci levels from multiple timeframes overlap in a price zone, the probability of a price reaction in that area increases.
Conclusion
Fibonacci tools, due to their simplicity and ability to combine with other analytical methods, are an essential part of technical analysis and are used for identifying reversal points, setting price targets, and managing risk.
Their highest effectiveness is observed when evaluated alongside trading volume, trend type, price action, and confirmation from indicators or candlesticks. Analyzing Fibonacci in multiple timeframes also increases the reliability of the levels.













