In the Forex market, trades often remain open for more than one day and are therefore subject to overnight swaps.
A swap is essentially the interest charged based on the difference in interest rates between two currencies. According to Islamic jurisprudence, such interest is considered riba and is prohibited.
Muslim traders who adhere to Sharia principles cannot use accounts that include swaps. As a result, the Islamic account was designed to enable trading in the Forex market without paying or receiving swaps.
These accounts allow Muslims to participate in global financial markets without facing religious prohibitions.

What Is an Islamic Account?
An Islamic account in Forex is a type of trading account specifically designed in accordance with Islamic jurisprudence and does not involve overnight interest (Swap).
In standard Forex trading, if a position remains open overnight, the broker either credits or debits a swap fee based on the difference in interest rates between the two currencies. In Islam, this is considered riba.
The Islamic account eliminates this issue by completely removing swaps. In this account, the trader neither pays nor receives any interest. This is the key difference compared to standard accounts.
Some brokers may replace swaps with a fixed commission or alternative cost structure to keep the account commercially viable. However, the core principle of the Islamic account is the removal of riba, enabling halal trading in the Forex market.
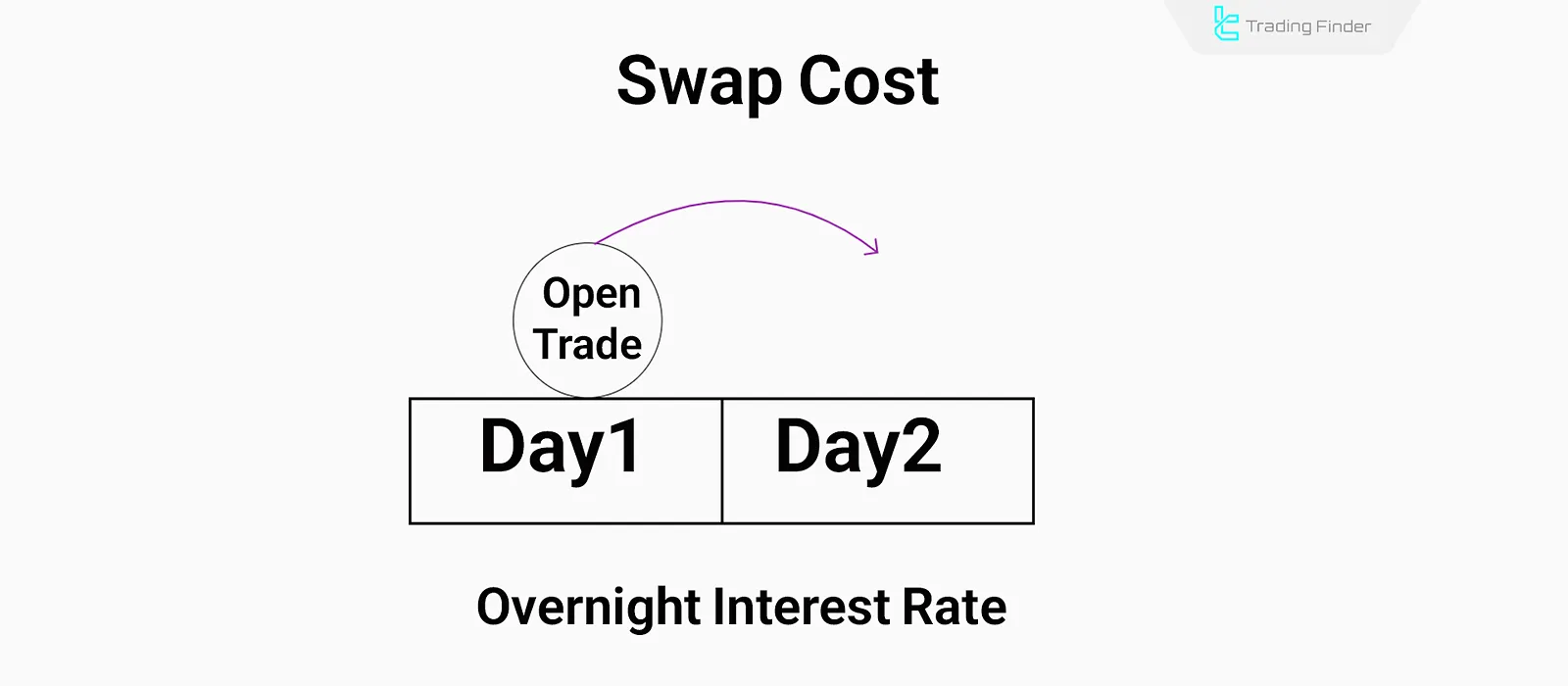
What Is Swap and What Role Does It Play in an Islamic Account?
A swap is the cost or profit applied in Forex trading for holding a position overnight. It is calculated based on the interest rate differential between the two currencies in the trade.
If you buy a currency with a higher interest rate and sell one with a lower rate, you typically receive positive swap; in the opposite case, you pay negative swap.
For example, if you buy EUR/USD and the euro’s interest rate is higher than the dollar’s, the broker credits swap to your account at the end of the trading day. If the opposite is true, negative swap is deducted.
Why Is Swap Prohibited in Islam?
In Islamic jurisprudence, riba refers to the receipt or payment of interest for lending money or delaying payment.
Essentially, swap represents the same form of bank interest, calculated based on time and rate, which is classified as riba and therefore haram.
Traders receive or pay interest-based profit or loss without any actual work or production, conflicting with Sharia principles.
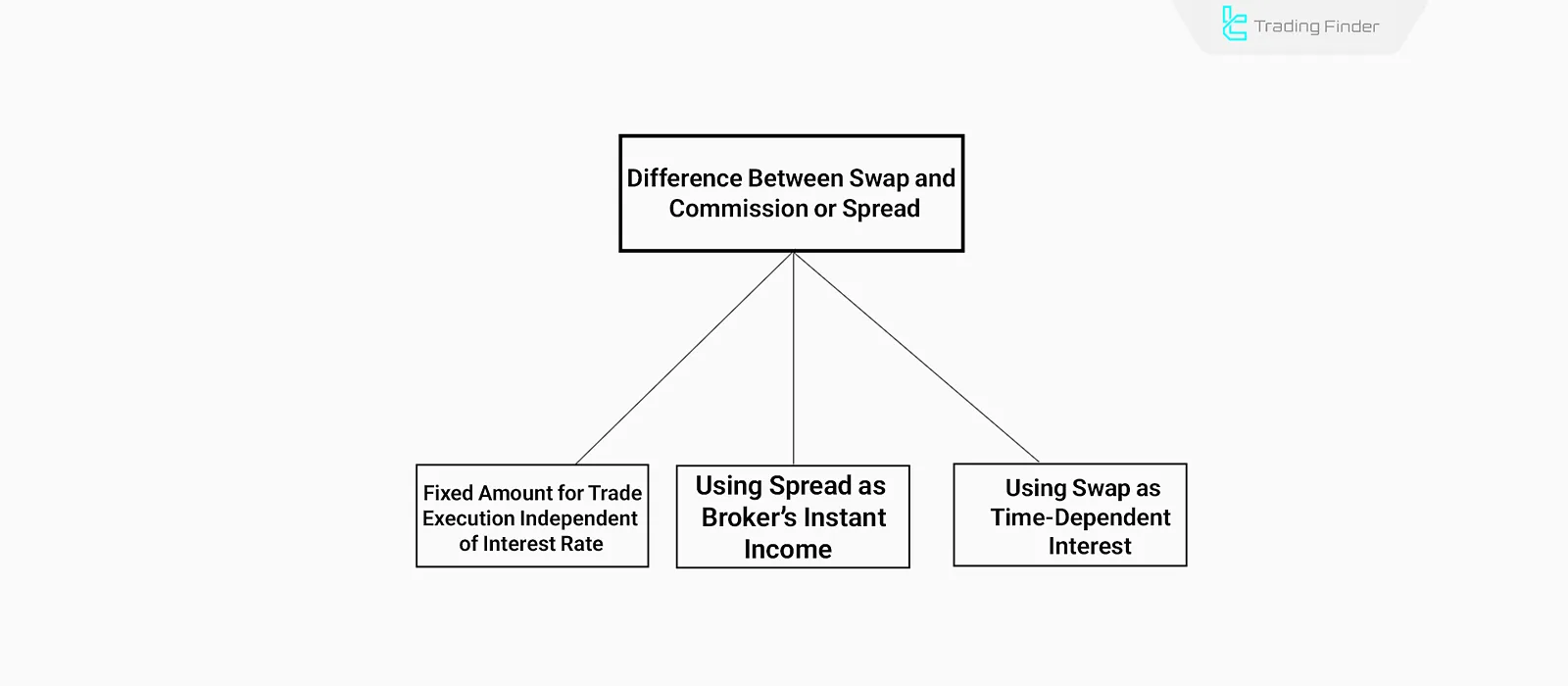
Difference Between Swap, Commission, and Spread
In Forex trading, costs such as spread, commission, and swap exist, each with distinct characteristics. To understand why swap is prohibited, it is essential to differentiate it from other trading costs:
- Commission is a fixed fee charged by the broker for trade execution; it is not tied to time or interest rates;
- Spread in Forex is the difference between the Ask (buy) price and Bid (sell) price, counted as the broker’s instant revenue;
- Swap is an interest-based cost tied to time, applied only when a position remains open overnight, and thus qualifies as riba.
Who Should Use an Islamic Account?
An Islamic account is not only a religious requirement but also a clear solution for traders with specific needs and beliefs.
Besides complying with Sharia and avoiding interest, it provides a trading framework aligned with Islamic values.
Muslim Traders Committed to Sharia
For traders strictly adhering to Islamic principles, using a standard account involving interest is not permissible. An Islamic account is the only option that enables Forex trading without riba.
Traders Sensitive to Interest Rates
Some traders, even outside a religious context, prefer not to engage in interest-based systems. For them, Islamic accounts serve as an alternative to conventional finance.
Long-Term Forex Investors
Traders who hold positions overnight often face heavy swap charges. In an Islamic account, these charges are eliminated, making long-term position management possible without interest costs.
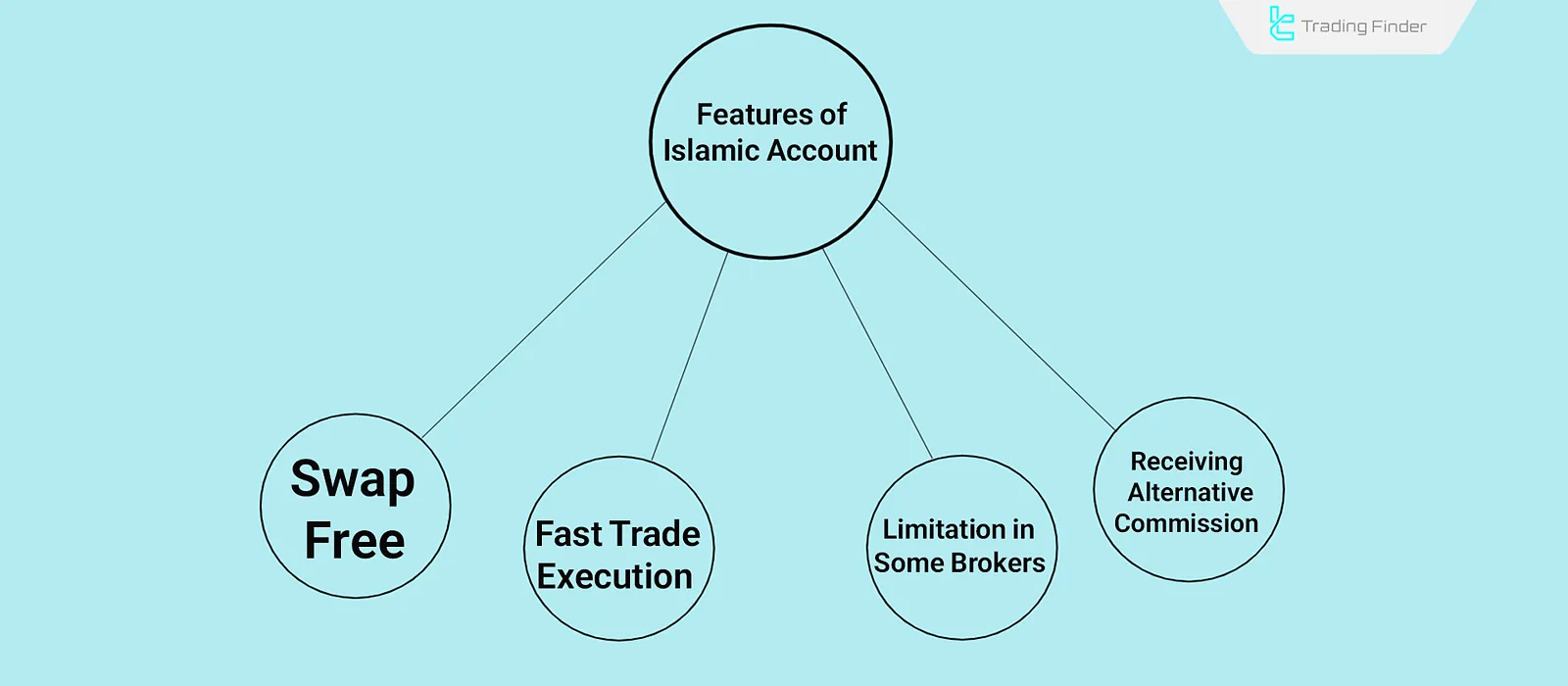
Features of Islamic Accounts
Islamic accounts have a distinct structure and key features that differentiate them from standard Forex accounts. Main features include:
- Swap-Free;
- Instant Execution;
- Limitations in some brokers;
- Alternative commission charges.
Swap-Free
The most important feature of an Islamic account is the complete elimination of overnight interest. Keeping a position open for multiple nights does not generate swap costs, ensuring compliance with Sharia.
Instant Execution
Many Islamic accounts are configured to execute trades instantly without delay. This avoids potential disputes about delayed execution and enhances transparency.
Limitations in Some Brokers
Certain brokers only offer Islamic accounts on specific currency pairs or restrict them to certain types of trading, such as excluding CFDs or commodities. Policies vary by broker.
Alternative Commission Charges
In some cases, brokers charge a fixed commission per trade instead of swaps. This fee is not interest-based but rather a service charge, though it may increase overall trading costs.
Therefore, traders should carefully review fee structures before selecting an Islamic account.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Islamic Accounts
Islamic accounts, while offering a solution for eliminating riba in Forex trading, may still come with certain limitations imposed by brokers or within their cost structures.
Table of advantages and disadvantages of Islamic accounts:
Advantages | Disadvantages |
No swaps (overnight interest) | Limited availability with some brokers |
Sharia compliance | Replacement with fixed commissions |
Suitable for long-term trading | Restrictions on some trading instruments |
No payment or receipt of interest | Broker approval required for activation |
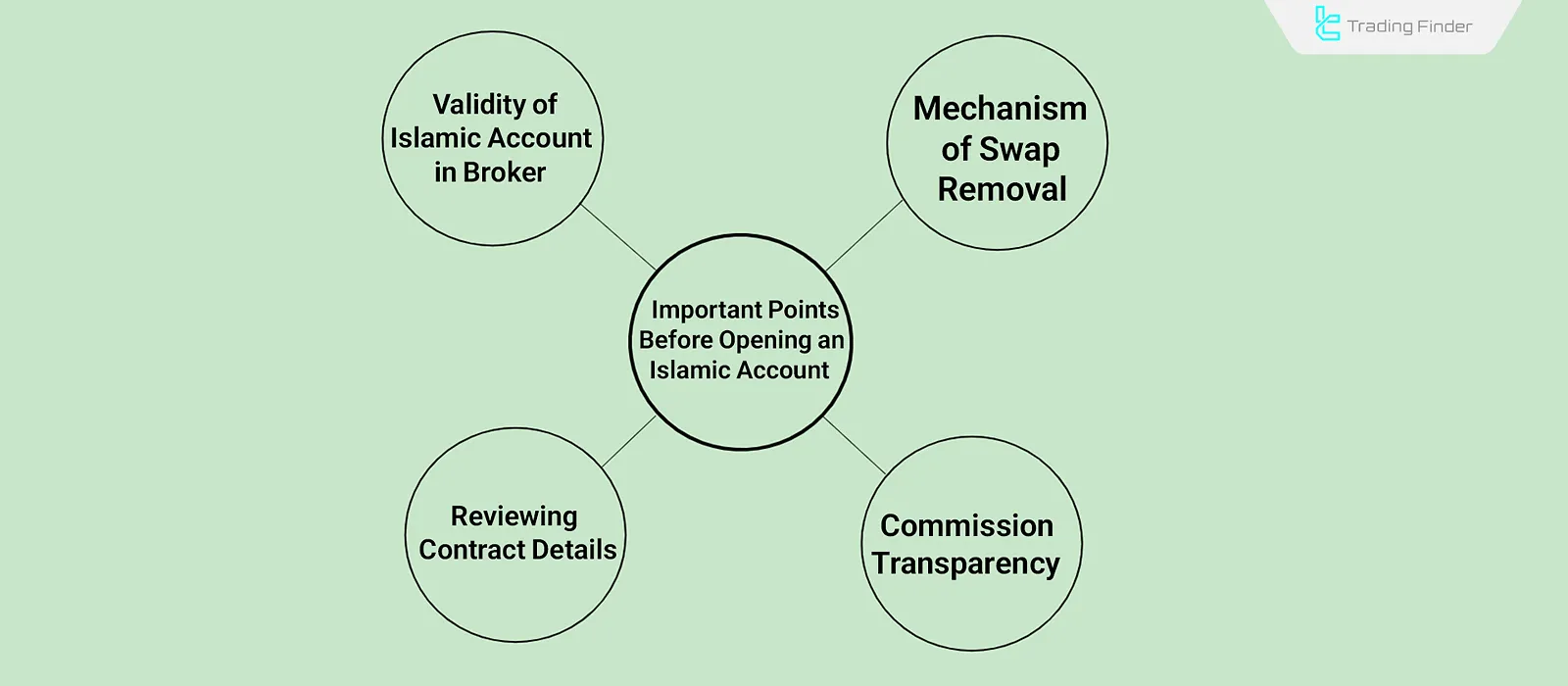
Key Points Before Opening an Islamic Account
Before opening an Islamic Forex account, it is essential to thoroughly review the account conditions. Many brokers advertise “Islamic Account” without genuine Sharia compliance. Points to check include:
- Credibility of the broker’s Islamic account: Ensure swaps are truly removed and not replaced with hidden costs;
- Contract details: Review the specific Terms & Conditions for Islamic accounts, as brokers may apply restrictions such as limited holding periods or specific trading instruments;
- Swap removal mechanism: Verify whether all symbols are permanently swap-free or if the benefit applies only for a limited period or to selected pairs;
- Transparency of commissions: Confirm whether the broker substitutes swaps with clear, non-interest-based commissions. Lack of transparency may raise Sharia concerns.
Conditions for Registering an Islamic Account with Brokers
Registering for an Islamic account with brokers is usually straightforward and similar to opening other accounts, except for the selection of the Islamic account option.
Some brokers require an additional request to activate it, while others may ask for further documents or proof. Steps include:
Initial Registration and Account Selection
During account opening on the broker’s website, traders must choose “Islamic Account” or “Swap-Free”. Some platforms provide this option directly; others require manual selection or support team confirmation.
Submitting Identification Documents (KYC)
Verification requires providing documents such as a passport, ID card, or proof of residence. This is mandatory for all real accounts, including Islamic accounts.
Submitting an Activation Request (with some brokers)
Some brokers do not automatically activate Islamic accounts. In such cases, traders must submit a ticket or fill in a dedicated Islamic Account form.
Rarely, brokers may ask for proof of religion or nationality, though this is uncommon.
Conclusion
The Islamic Forex account is a swap-free trading structure designed to eliminate riba from transactions. It is tailored for traders who follow Islamic principles or wish to avoid interest-based systems.
Key features include removal of overnight interest, instant order execution, and in some cases, replacement commissions.
While offering advantages such as Sharia compliance and suitability for long-term trading, limitations exist, including fewer reliable brokers, restricted instruments, and varying broker fee models.













