A trading journal is a tool for recording Past trade review, analyzing performance, risk, and identifying mistakes. Trade date, symbol, direction, entry and exit price, trade volume, and risk-to-reward ratio are among the elements that must be recorded in a trading journal.
It is also advisable to add columns such as strategy type, trading timeframe, trading session (Asia, Europe, or America), and position holding duration to the trading journal in order to achieve a more comprehensive evaluation of the trading system’s efficiency.

What is a trading journal?
A trading journal is an important tool for recording all positions, their details, and reviewing the course of trades. In this log, all trades and related information such as date, trade volume, risk level, reason for entry, strategy review, and profit or loss are recorded.
It is even possible to log professional metrics such as risk-to-reward ratio (RR), R-Multiple, and MAE/MFE of each trade for more precise analysis. Visual guide to trading journal from Edgewonk YouTube channel:
Trading Journal Indicator
The TFlab Trading Journal indicator is a structured system for performance analysis that transforms raw trade data into practical and decision-making information. This tool extracts information directly from the trading account without the need for manual entry and organizes it into precise and processable reports. This automated process reduces human error and evaluates performance based on real and accurate data.
At its core, this indicator functions as a professional trading journal that combines statistical analysis with trading behavior assessment. Its analytical dashboard provides an integrated view of key metrics such as win rate, drawdown, profit factor, risk-to-reward ratio, and net profit.
The centralized display of these metrics helps the trader assess the health of their strategy in the shortest possible time and identify its strengths and weaknesses.
The trading calendar adds a time dimension to the analysis and separates daily and weekly performance. This feature makes it possible to identify behavioral patterns related to different sessions or specific market conditions.
In the trade list section, all details of each position including entry and exit points, volume, and final result are recorded, and with the use of advanced filters, deeper analyses can be conducted based on asset, timeframe, or setup type.
In addition to quantitative data, the ability to add tags and record notes introduces a qualitative dimension to the journal. Documenting entry reasons, market conditions, or execution errors turns each trade into a learning resource and strengthens trading discipline.
This tool provides a data-driven infrastructure for transforming trading experience into a sustainable statistical advantage; in such a way that decision making moves away from cognitive biases and emotional errors and becomes grounded in quantitative analysis, performance evaluation, and continuous strategy optimization.
Download links for the TFlab Trading Journal Indicator:
Advantages and disadvantages of journaling
By recording accurate data, journaling can be a method to review trading strategies; however, it requires time, high discipline, and entering details immediately after each trade. Advantages and disadvantages of trading journaling:
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Identifying strengths and weaknesses of the trading strategy | Time-consuming to record accurate information |
Controlling emotions and preventing impulsive trades | Possibility of forgetting to record trades regularly |
Providing enough data for statistical analysis (Win Rate, Expectancy, etc.) | Difficult for short-term trades and scalpers |
Allowing review and adjustment of strategies in different timeframes | Low analytical value if incomplete records are kept |
Increasing accountability and discipline in trading process | Dependency on tools (notebook, Excel, software) and possible human error in recording data |
Application of journaling in trading
The purpose and application of journaling in trading is to carefully review the process, identify strengths and weaknesses, and evaluate trading strategies. Applications of journaling:
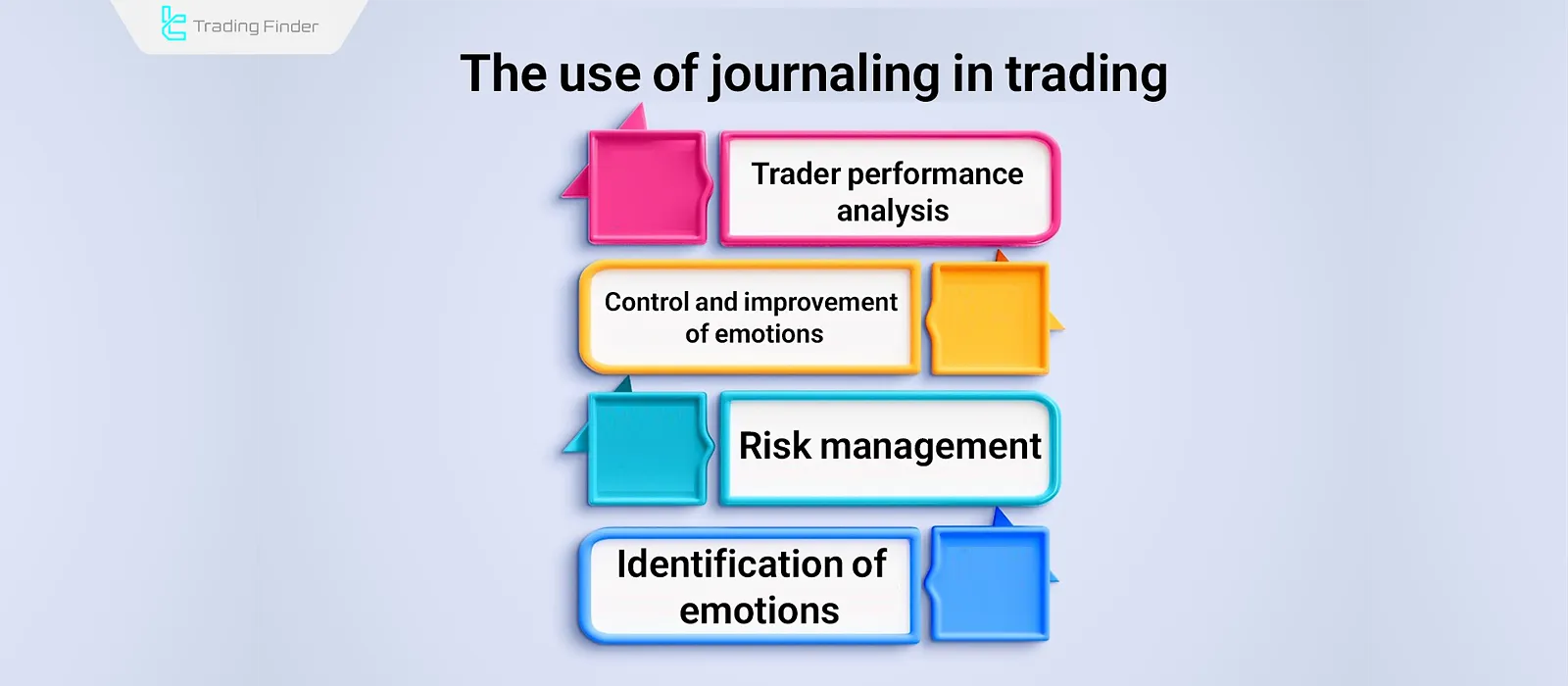
- Performance analysis: evaluating the success of strategies, developing and improving trading strategies;
- Emotional control: sometimes emotions such as fear or greed dominate traders; recording these helps improve emotional control;
- Risk management: controlling risk in trades according to capital Emotion management plans and protecting capital;
- Error identification: journaling allows traders to detect past mistakes and correct them.
How to identify past mistakes using a journal?
To detect mistakes, the journal should be reviewed regularly and at specific intervals.
For example, review the trading journal weekly to identify and note down mistakes; repeat this process the following week to spot recurring errors that lead to losses. In this way, after a few months, the number of mistakes will significantly decrease.
Managing emotions in a trading journal
One of the key sections of journaling is controlling and analyzing emotions during trading. Many losses occur not due to weak strategy but as a result of emotional reactions such as fear, greed, or revenge trading.
Regularly recording and analyzing these emotions in the journal helps traders identify their behavioral patterns and manage their trading mindset in the future.
Emotion labeling method
To manage emotions effectively in a trading journal, it is better to use fixed and repeatable labels. These labels allow you to more quickly detect behavioral patterns when reviewing past trades. Types of emotion labeling:
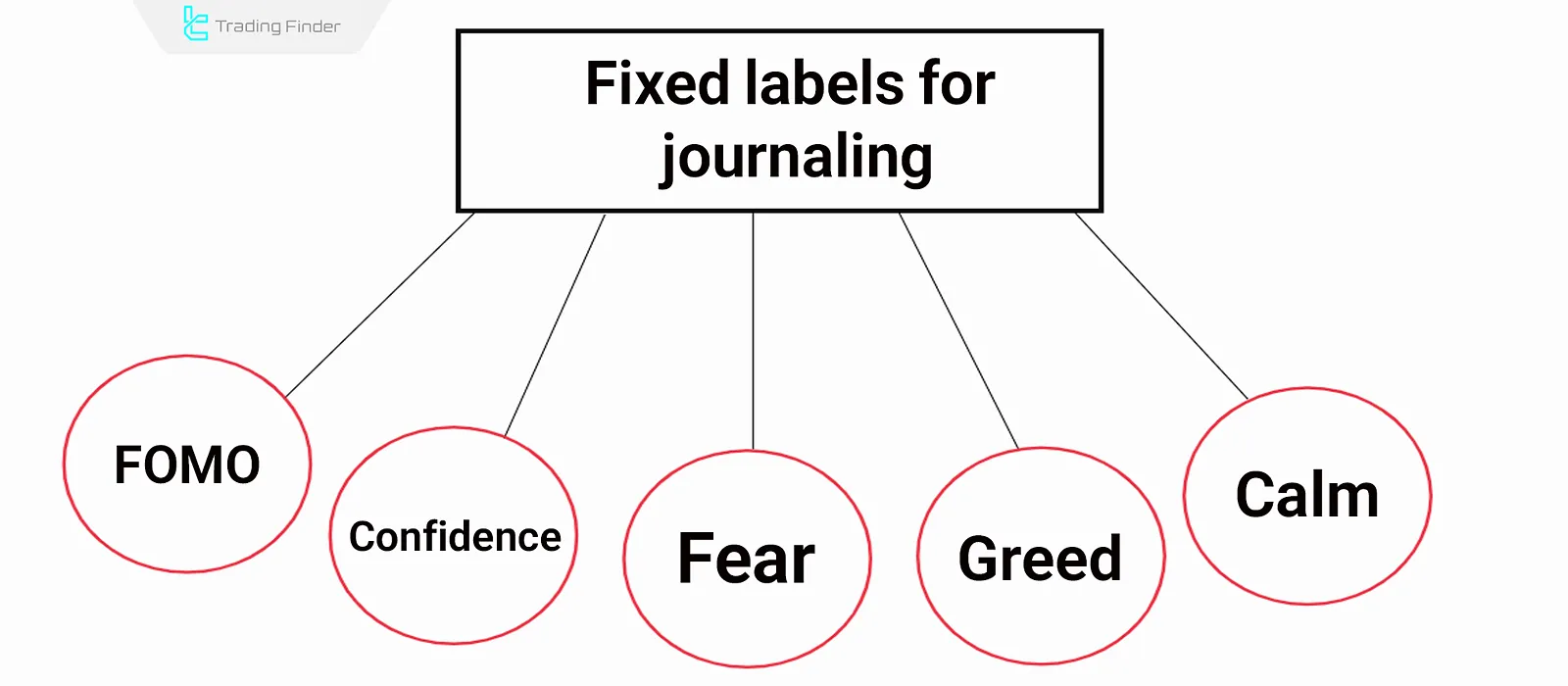
Note your dominant emotion when entering or exiting a trade;
For better standardization, you can use fixed labels such as:
- FOMO (Fear of Missing Out)
- Confidence
- Fear
- Greed
- Calm
What should be recorded in a trading journal?
A trading journal must include all information related to a trade. Recordable items:
- Date: entry and exit date of the trade
- Symbol: traded asset symbol
- Trade direction: buy or sell
- Entry and exit price: entry price, targets, and exit point
- Trade volume: volume, lot size, and value of the trade
- Risk level: risk taken in positions
- Reason for entry: could be technical setup, fundamental or sentiment analysis, or a combination
- Trade result: profit or loss in percentage and monetary value
- Emotions: recording emotions (fear, greed, anxiety, etc.) during the trade
- Key notes and improvement suggestions: any additional notes that may help your trading process
Importing trade history from MT4/MT5 into the journal
One of the best ways to complete a trading journal is to directly transfer trade history from MetaTrader 4 or 5 into Excel or Google Sheets.
This ensures all details of each position are systematically available without needing to manually record everything. Guide for creating Excel trading journal on axi.com:
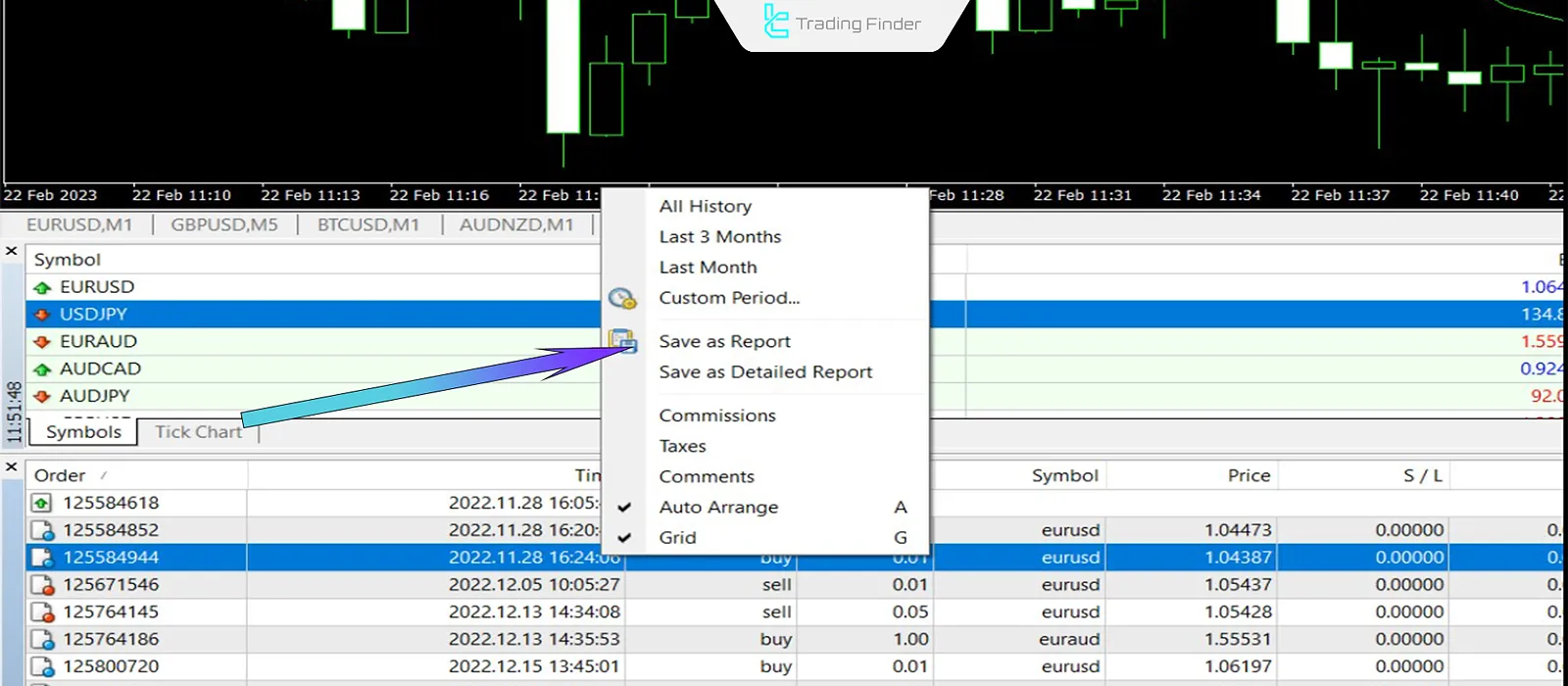
Steps to extract history in MetaTrader 4 (MT4)
To ensure the trading journal includes actual trade data in addition to manual notes, account history can be directly exported from MetaTrader 4. Steps to export trade history from MT4:
- Go to the Account History tab;
- Right-click on an empty area and select Save as Detailed Report or Save as Report;
- The output file will be saved in HTML format;
- To convert to Excel:
- In Excel, go to Data From Web and import the HTML file;
- Or right-click the HTML file, open it in a browser, and copy the data.
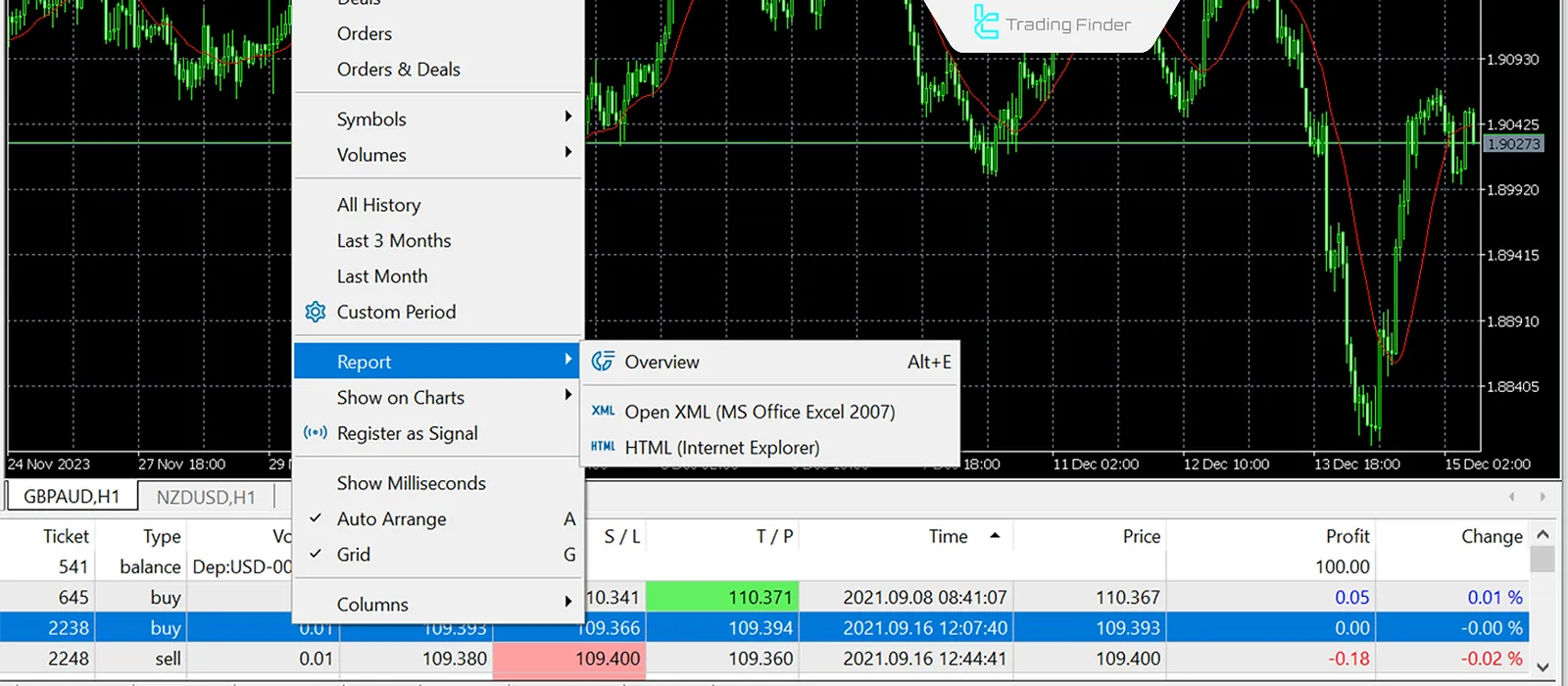
Steps to extract history in MetaTrader 5 (MT5)
In MetaTrader 5, the trade report export process is simpler than in MT4, often allowing direct export as CSV. This feature enables opening trade data in Excel or Google Sheets without extra conversion. Steps to export trade history from MT5:
- In the History section, right-click on an empty area;
- Select Report or Save as Report;
- The output file will be saved as HTML or, in some versions, CSV;
- If CSV, simply open it directly in Excel or Google Sheets.
Trading journal example
This example shows how details of a position such as date, symbol, entry and exit price, volume, risk level, reason for entry, final result, and additional notes can be systematically recorded in the journal.
These records can then be used for both statistical and psychological trading analysis. Example of a trading journal entry:
Date | Symbol | Trade direction | Entry price | Exit price | Volume | Risk | |||
25/01/29 | EUR/USD | Short | 1.0437 | 1.0213 | 0.01 | 0.25 | |||
Reason for entry | Result | Emotions | Notes | ||||||
Monetary policy divergence | 224 pips / $22.4 profit | I felt anxious | Trading with fundamental data was a new experience! | ||||||
Conclusion
Discipline in trading is the primary application of a journal; by using a trading journal, one can increase profits and minimize losses.
In trading journaling, all trade information including profit and loss, reason for entry, risk level, and emotional state is recorded. Thus, it can be used to identify mistakes and flaws in a strategy.













