Atrading plan is a set of rules that governs all activities of a trader. A properly written trading plan helps mitigate the impact of emotions in trading and enables the trader to make informed decisions during volatile market conditions.
Moreover, establishing clear rules for various aspects of risk management, such as position sizing andtrading plans for forex and other markets, facilitates better capital and risk management.
Also, a professionalplan, designed as a structured trading plan, helps the trader make their performance measurable and continuously evaluate their trading progress.
A trading plan establishes a framework for the trader's activities, resulting in more organized operations and facilitating long-term performance review.
What Is a Trading Plan?
A trading plan is a comprehensive roadmap for trading that encompasses various elements, including trading goals, account management (encompassing capital, risk, and emotional management), trading strategy, trading times, and more.
The rules in this program encompass all trading activities and structure the trader's operations in the market.
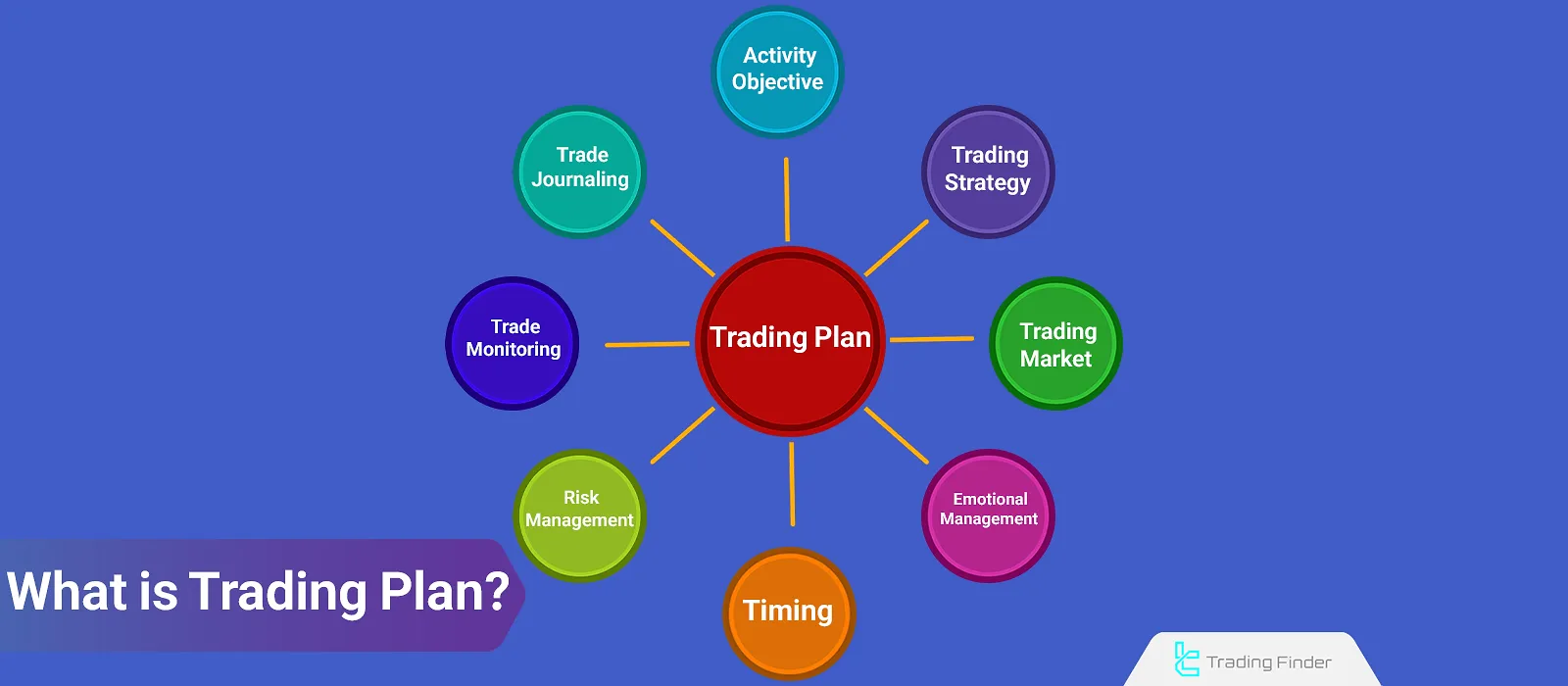
Components of a Trading Plan
A comprehensive trading plan encompasses all the activities of the trader. Each section includes rules that define the framework of the trader’s actions.
Components of a Trading Plan:
- Market Activity Goals: Define trading goals and expected returns within specific time frames (daily, monthly, yearly, etc.);
- Trading Strategy: Select a strategy that aligns with your skills and goals;
- Choosing the Right Market: Analyze and choose the most suitable market for trading based on your strategy;
- Emotional Management: Control emotions and establish fixed rules to avoid emotional decisions in tense situations;
- Timing: Determine the optimal time to trade; for example, only during the overlap of the New York sessions and London sessions;
- Risk and Capital Management: Set the capital amount for trading and define the maximum allowable loss in each period (daily, weekly, monthly);
- Trade Monitoring: Due to the high pressure of trading, predefine the actions to take during the trade before entering the market;
- Journaling Method: Define the key components of a trade for journal writing.
Timing Rules and News Filter
Timing is one of the essential parts of any trading plan. Defining the allowed time windows for activity creates mental discipline and prevents emotional decision-making during unsuitable hours.
Trading during major news releases must also be prohibited in the plan to avoid irrational volatility.
- Trades should only be taken during active sessions such as London or the London–New York overlap;
- Entering the market must be avoided 15 minutes before and after major news events;
- In abnormal volatile conditions, a maximum of one trade per day should be executed.
Personalized Trading Plan Questionnaire
Writing a trading plan is effective only when it is tailored to personal characteristics, financial goals, and each trader’s risk tolerance. Before starting to write the plan, answering a few simple questions can create a clear mental pathway for decision-making.
This step forms the foundation for building a structured and personalized system.
- What is my purpose for trading and why am I active in the market?
- What level of loss or drawdown is acceptable for me?
- During which hours do I have the highest focus and efficiency?
Numerical Risk Management and Stop-Activity Rules
In every professional plan, defining numerical limits for risk and loss is essential. Without these rules, controlling emotions during losing periods becomes difficult and the account is exposed to danger. Limiting losses numerically creates discipline and ensures long-term survival in the market.
- The risk per trade should be a maximum of 1 percent of total capital;
- If three consecutive losses occur or a 2 percent drawdown happens, daily activity must stop;
- The risk-to-reward ratio must not be lower than 1 to 2.
Benefits of Using a Trading Plan
Market volatility often creates stress and anxiety for traders. However, having a specific trading plan ensures that the best trading decisions are made under various market conditions.
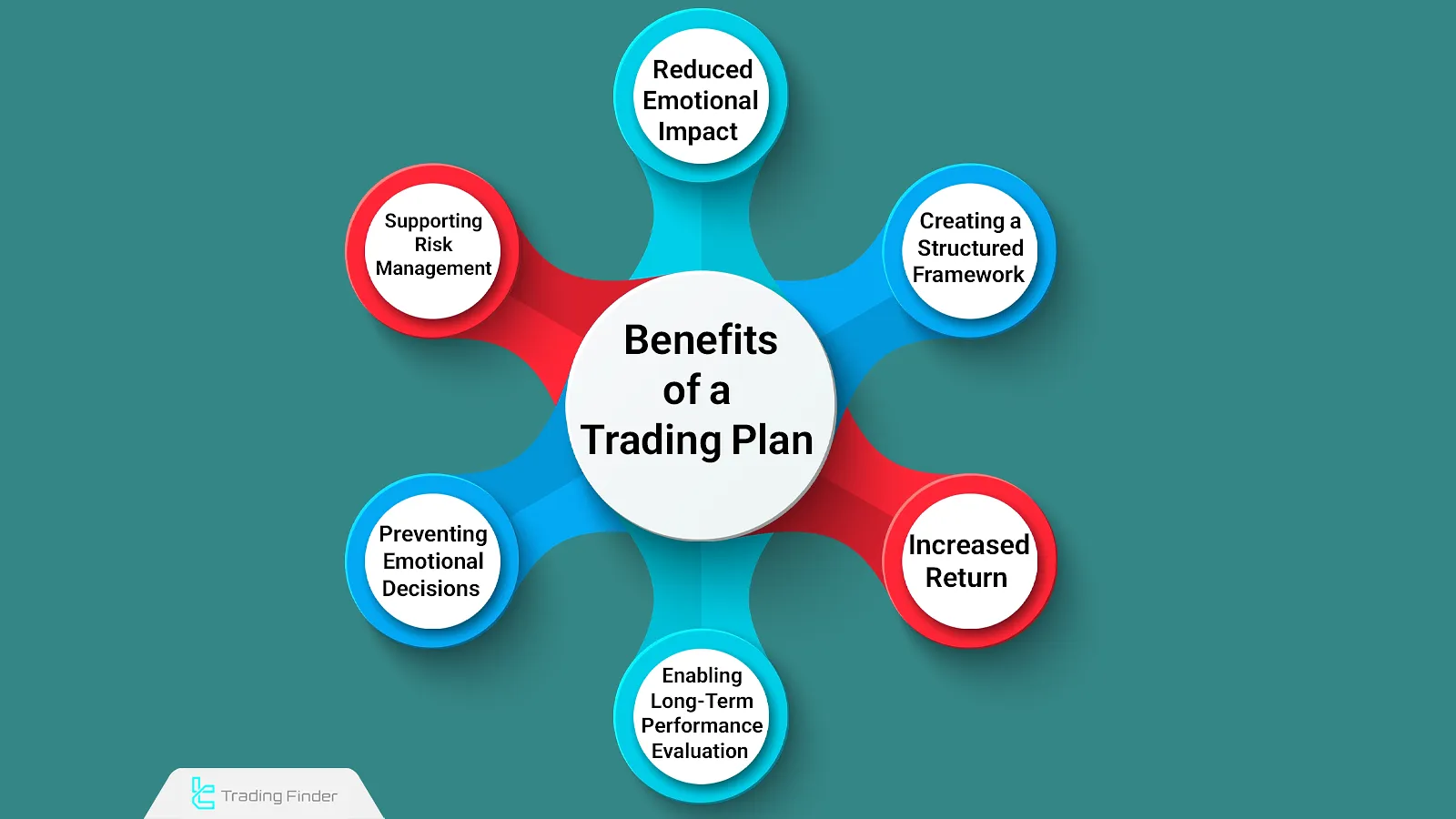
Benefits of a Trading Plan:
- Reduced Emotional Impact: A trading plan prepares you for various trading scenarios, reducing the influence of emotions on decision-making;
- Improved Risk and Capital Management: With well-defined rules for managing the account and consistent application, account control improves;
- Increased Return Rate: A properly developed trading plan, when followed consistently, enhances the success rate of your strategy;
- Structured Trading Framework: Defining proper rules for market activity creates a disciplined and continuous trading process;
- Long-Term Performance Evaluation and Improvement: Following atrading plan allows for long-term review and correction of trading performance;
- Avoiding Confusion and Emotional Decisions: Having clear rules for special situations prevents confusion and emotional, loss-causing decisions.
The Importance of a Trading Plan in Trading
At times, prices in various markets experience sharp fluctuations due to different factors. In such conditions, traders often make emotional decisions and expose their trading accounts to irrational risks.
A sound trading plan includes pre-determined actions for each of these conditions to ensure minimal risk and maximum return.
Furthermore, a good trading plan clearly defines the trading objectives, which helps prevent overtrading.
Key Questions for Designing a Trader Plan Based on Personality
No two traders share the same mindset or behavioral pattern. An effective trader plan must align with each individual’s psychological and personal traits so it remains executable even under emotional pressure.
Answering a few key questions helps better understand this alignment and supports writing a trading plan that reflects real trading goals.
- What types of losses have the strongest emotional impact on me?
- When I am under stress or excitement, what is my typical reaction?
- How can I write my plan’s rules so they match my personal habits and stay consistent with my trading goals?
In the trading plan tutorial on Investopedia, this topic is taught in ten steps and guides traders through writing a trading plan tailored to their needs.
How to Create a Trading Plan?
Writing a proper trading plan involves evaluating multiple factors, such as price behavior in different markets, available capital, trading goals, and more.

Steps to Create a Trading Plan:
- Select a trading market
- Determine trading hours
- Set available capital
- Define trading goals
- Determine position size
- Define trade journaling factors
- Prepare a watchlist
- Choose a trading strategy
Example of a Real Trading Plan
Suppose you intend to trade with a $1,000 capital using the ICT strategy. You now need to write a trading plan suitable for this capital. Below is a simple trading plan for trading with $1,000:
Sections of the Trading Plan | Selected Factor |
Chosen Market | Forex Market |
Trading Time | Overlap of the London and New York Sessions |
Available Capital for Trading | $1,000 |
Trading Objective | 0.5% profit per trading week |
Journaling Factors | Reason for entering the trade, outcome, and emotions during the trade |
Watchlist | EUR/USD, USD/JPY, USD/GBP charts |
Position Size | 0.5% risk of total capital per trade |
Position Sizing Table
One of the most important components of risk control is determining the trade size based on account balance and stop loss distance.
Following this principle prevents irreversible losses and helps maintain capital stability. The table below shows a simple example of calculating position size based on fixed risk:
Account Balance ($) | Risk Percent | Stop Loss Distance (Pips) | Pip Value ($) | Allowed Position Size (Lots) |
1000 | 1% | 20 | 1 | 0.05 |
1000 | 0.5% | 40 | 1 | 0.012 |
When determining trade size, calculation should always be done by dividing the dollar risk by the stop loss distance. This table can be replaced with each trader’s personal data so that it perfectly matches their account conditions and individual plan.
Sample ICT Daily Plan
In the ICT style, the daily plan is built around daily bias, liquidity zones, and Kill Zones. The main focus is finding a low risk entry zone along with an appropriate risk to reward ratio. Such a plan provides a clear framework for daily performance and prevents random entries. This structure helps traders understand how to make a trading plan based on market sessions and liquidity alignment.
- Checking the Daily Bias on the higher timeframe;
- Looking for the setup in the London or New York Kill Zone;
- Entry only when structure, liquidity, and volume confirmation align.
ICT KillZones Hunt Indicator
The ICT KillZones Hunt indicator is one of the advanced tools in the ICT trading methodology designed for precise analysis of time based zones and market liquidity.
This indicator is available on the TradingView platform and accurately displays the main trading sessions including Asia, London, and New York on the chart so the trader can analyze price behavior based on reactions to key zones such as Order Block and Fair Value Gap (FVG).
The main goal of the ICT KillZones Hunt indicator is to identify high probability trading zones. In an uptrend, after detecting the London session time range, the tool plots the session high and low and then marks order blocks and fair value gaps.
When price touches the session low, the support area becomes active and if the London high breaks, continuation of the move is confirmed. In a downtrend, the same logic applies in reverse. For example, after forming bearish FVGs in pairs like USD/JPY, breaking the London low confirms trend continuation.
In the settings section, various customization options are available, including setting the Pivot Period for order block detection, the Mitigation level, FVG validity duration, and configuring alerts for touching session highs and lows.
It also allows displaying different colors for each session and activating alerts related to diminishing supply and demand zones.
his indicator belongs to the Intraday and multi timeframe tool category and is applicable to Forex, cryptocurrency, and stock markets. Scalpers can use it on timeframes below 5 minutes to capture fast market movements.
Overall, ICT KillZones Hunt is a powerful tool for ICT style analysts that combines time, liquidity, and market structure to help identify precise entry and exit zones while significantly improving accuracy in major sessions. It is especially useful for traders who are creating a trading plan based on time cycles, session volatility, and liquidity sweeps.
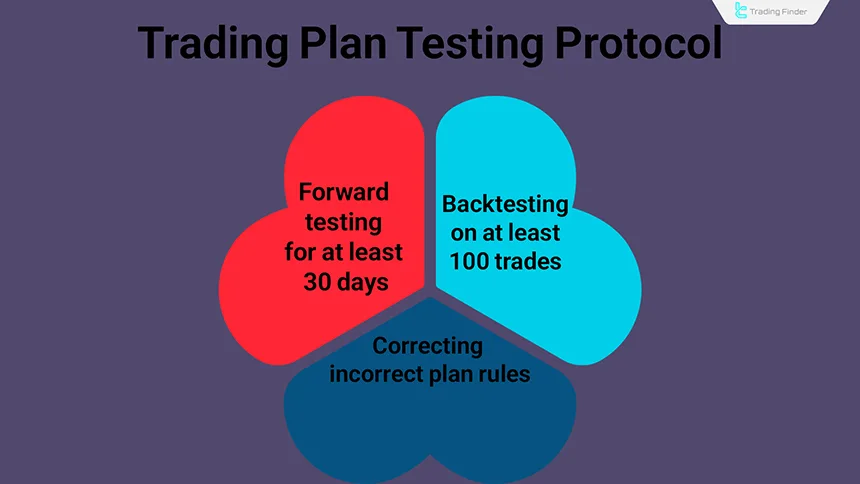
Trading Plan Testing Protocol (Backtest and Forward Test)
Before implementing a plan in a real account, its effectiveness must be tested in different market conditions. Backtesting on historical data and forward testing in a demo account help the trader fix strategy weaknesses before entering the real market.
- Backtest should be performed on at least 100 trades in three different market conditions;
- Forward test should be conducted for at least 30 days with real size volume;
- Changes to plan rules are allowed only after completing the testing phase.
Difference Between Trading Plan and Trading Strategy
A trading plan encompasses all aspects of a trader’s activity, from capital to analysis systems. In contrast, a trading strategy establishes rules for trade entry andexit, thereby improving the trade success rate.
Here is a comparison between the trading plan and trading strategy:
Trading Strategy | Trading Plan |
Focuses on position size for each individual trade | Focuses on managing overall capital and account risk |
Can be adjusted after each trade | Can be adjusted after long-term use |
Only includes entry and exit conditions | Covers the full trading process, including timing and market selection |
Aims for profit on individual trades | Aims for consistent long-term activity |
Includes entry point, take profit, stop loss, etc | Includes trading time, capital, market, asset selection, and other relevant factors |
Pre trade checklist
The pre trade checklist acts as a safety filter to prevent impulsive decisions. Before entering a position, the trader must review several key factors to ensure the conditions match their plan. Following these principles prevents random entries and improves trade quality.
- The main trend and market direction must be identified
- The trading time and session must align with the daily plan
- No major news events should be present during the trade window
Weekly Review and Journal Protocol
No trading system can remain consistent without regular review. Recording trades, emotions, and outcomes in a journal helps identify behavioral patterns and recurring mistakes. At the end of each week, analyzing real data provides a way to evaluate progress or identify the need for plan adjustments.
- Record the average weekly profit and loss
- Note emotional factors in specific trades
- Analyze points where deviation from the plan occurred
Trading Performance KPI Dashboard
To measure the success of a plan, performance metrics must be evaluated numerically. These metrics include win rate, average risk to reward, percentage of plan rule compliance, and drawdown. Having a dashboard of this information ensures decisions are made based on data rather than emotion.
- Calculate win rate and average profit to loss weekly
- Record the percentage of plan rule compliance
- Measure drawdown and performance changes over a one month period
Key Points for Using a Trading Plan
To use a trading plan effectively and achieve desirable returns, it's essential to follow certain principles, such as adhering to rules, regularly updating the plan, and reviewing its performance.
Key Points for Using a Trading Plan:
- Updating the Trading Plan: Financial markets are constantly changing; adjustments to your trading plan should be made periodically;
- Fixing Plan Errors: After some time, any flaws in the trading plan should be reviewed and corrected;
- Commitment to Plan Rules: All updates or changes should be made when not actively trading, and all rules must be followed during live trades;
- Market Compatibility: Every market has unique characteristics; the trading plan must be tailored to the specific market being traded.
Inside the ANTHONYSWORLD YouTube channel, the process of creating a trading plan is taught in a video, step by step:
Common Mistakes in Designing a Trading Plan
Mistakes in various aspects of trading plan creation such as goal-setting or market selection can reduce trading success and yield opposite results.

Common Mistakes in Designing a Trading Plan:
- Unrealistic Goals: Setting goals that are detached from reality or incompatible with capital can lead to discouragement and trading discontinuity;
- Irrational Risk Management: Taking excessive risk in each trade shortens the lifespan of a trading career;
- Ignoring Component Relationships: Failing to align various plan components results in ineffective performance and reduced success rate.
Role of Indicators in the Trading Plan
In a trading plan, indicators must have a clear and specific role. Using too many technical tools creates confusion and leads to conflicting decisions. Each indicator should be included in the plan based on a defined analytical purpose so that its data becomes interpretable and practical.
- Moving Average for identifying the direction of the main market trend;
- RSI for measuring overbought or oversold conditions;
- Trading volume for confirming the strength of price movement.
Conclusion
A trading plan is a set of rules encompassing all trader activities in the financial market. It defines trading goals, market selection, trading strategy, trading time, and more, each with pre-defined decisions to be executed under specific conditions.
Having a sound trading plan reduces emotional influence in trading and streamlines capital and risk management. It also creates an organized structure that enhances the success rate of trading activities.
Strict adherence to rules, correction of plan flaws, and periodic updates are essential for boosting trade productivity. Conversely, poor goal-setting, irrational risk-taking, and lack of coherence among plan components decrease the likelihood of success.













