A stock market journal is a method for documenting, evaluating, and improving investment decisions in the stock market. Unlike financial reports or brokerage outputs that only present quantitative data, a stock market journal combines statistical data, behavioral analysis, and strategic notes.
In addition to recording trade history, the stock trade journal provides a structured framework for extracting successful patterns and identifying recurring mistakes.
This tool, especially in highly volatile stock environments, enables traders to examine the relationship between strategy, risk, and return based on real data.

What is a Stock Market Journal?
A stock market journal is a collection of personal data and analyses used to record and evaluate all activities related to stock trading strategy.
This journal includes details such as the time and volume of trades, reasons for entry or exit, analytical indicators used, and the trader’s psychological state at the time of decision-making.
The purpose of maintaining such a journal is to create a personal dataset for performance analysis, strategy optimization, and improving the quality of investment decisions. Learning reference on why traders use trading journals from Rocket Sheets:
Trading Journal Indicator
TFlab Trading Journal is an integrated analytical system for recording, processing, and evaluating trading performance that automatically extracts and structures real account data. This tool is designed with a focus on statistical accuracy, execution discipline, and risk management, providing a qualitative and measurable view of trades.
The journal structure includes an analytical dashboard, trading calendar, complete trade list, and a tags and notes section. In the dashboard, metrics such as win rate, drawdown, Profit Factor, average R:R, and net profit are displayed in aggregate form, enabling quick evaluation of strategy performance.
The trading calendar presents the time distribution of trades in daily and weekly reports and reveals behavioral patterns associated with different time periods. In the trade list section, detailed information for each position—including entry and exit time, prices, volume, and final result is recorded, and advanced filtering capabilities are available for deeper analysis.
The ability to add custom tags and analytical notes transforms the journal into a tool beyond a statistical report, creating a foundation for qualitative analysis of trading decisions.
Advanced modules such as the intelligent assistant, statistics based on machine learning algorithms, portfolio management, and mentoring system process data at a more structured level and extract recurring profitable or losing patterns.
This journal supports simultaneous analysis of multiple accounts and diverse markets, consolidating all trading activities within a unified framework.
Continuous use of TFlab leads to the development of a data-driven structure for performance evaluation, increased consistency of results, and improvement of trading standards.
Download links for the TFlab Trading Journal Indicator:
Using a Trading Journal in the Global Stock Markets (Stock Market Trading Journal)
In the global stock market, which operates as a dynamic structure with broad access to real-time data, a trading journal is one of the most important tools for maintaining discipline and consistency in profitability.
In a market where daily volatility can be affected by economic news, corporate earnings reports, Federal Reserve decisions, or geopolitical developments, keeping a trading journal enables the trader to record and analyze their behavior, trading patterns, successful strategies.
A trading journal in the stock market typically includes details such as the ticker symbol, entry and exit prices, position size, strategy type (Swing, Intraday, Position), timeframe, indicators used, and the dominant emotion during the trade.
Professional traders review this information to evaluate and optimize their performance over different periods (weekly, monthly, quarterly).
Many traders use intelligent journaling platforms such as TraderSync or Edgewonk, which import data directly from the broker account and generate precise statistical charts.
The Importance of a Stock Market Journal
A stock market journal is used to enhance the quality of decision-making and the consistency of investor performance in the stock market.
It serves as an analytical feedback system that records a trader’s behavior, logic, and financial results in the form of measurable data. Reasons for the importance of a stock market journal:
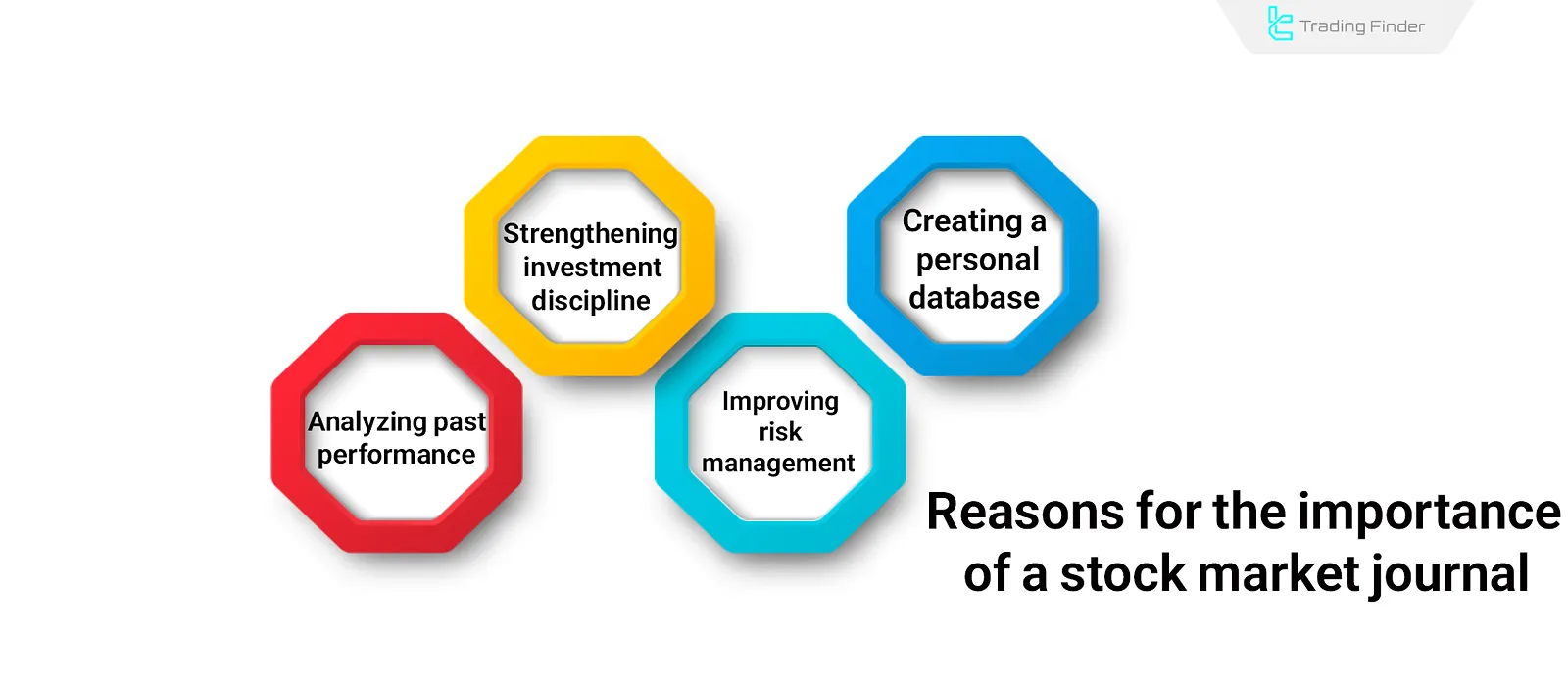
Analyzing Past Performance and Identifying Recurring Mistakes
Continuous recording of market data analysis (price, time, volume, and market conditions) allows for comparison of past decisions and assessment of each strategy’s success rate.
By reviewing the journal, an investor can identify and correct structural errors in analysis or trade timing.
This process also enables the trader to identify their hidden behavioral patterns, such as rushing into entries, the fear of missing out (FOMO), or exiting positions emotionally.
Strengthening Investment Discipline and Eliminating Emotional Behavior
A journal requires the trader to make documented and logical decisions. Recording reasons for entering and exiting a stock deters impulsive reactions and reduces emotional trades in volatile market conditions.
This process ensures that during highly volatile market conditions, the trader relies on their trading plan instead of emotional reactions, allowing the quality of their decision-making to improve consistently over time.
Improving Risk Management and Controlling the Profit-to-Loss Ratio
By recording trade details, patterns of loss or weaknesses in strategy can be analyzed quantitatively. These data help investors optimize the risk-to-reward ratio and achieve a more balanced capital allocation.
Moreover, systematic trade analysis allows the impact of external factors such as sharp volatility, unexpected news events, or execution errors to be evaluated effectively.
Creating a Personal Database for Future Decision-Making
By turning trading experiences into analytical data, the stock market journal becomes a kind of “performance memory”. This memory serves as a foundation for refining strategies, designing new investment models, and enabling data-driven decision-making in the future.
Moreover, consistently recording mistakes and success factors over time reveals patterns that are not recognizable in the moment. Such patterns help the trader identify their behavioral and technical weaknesses more clearly.
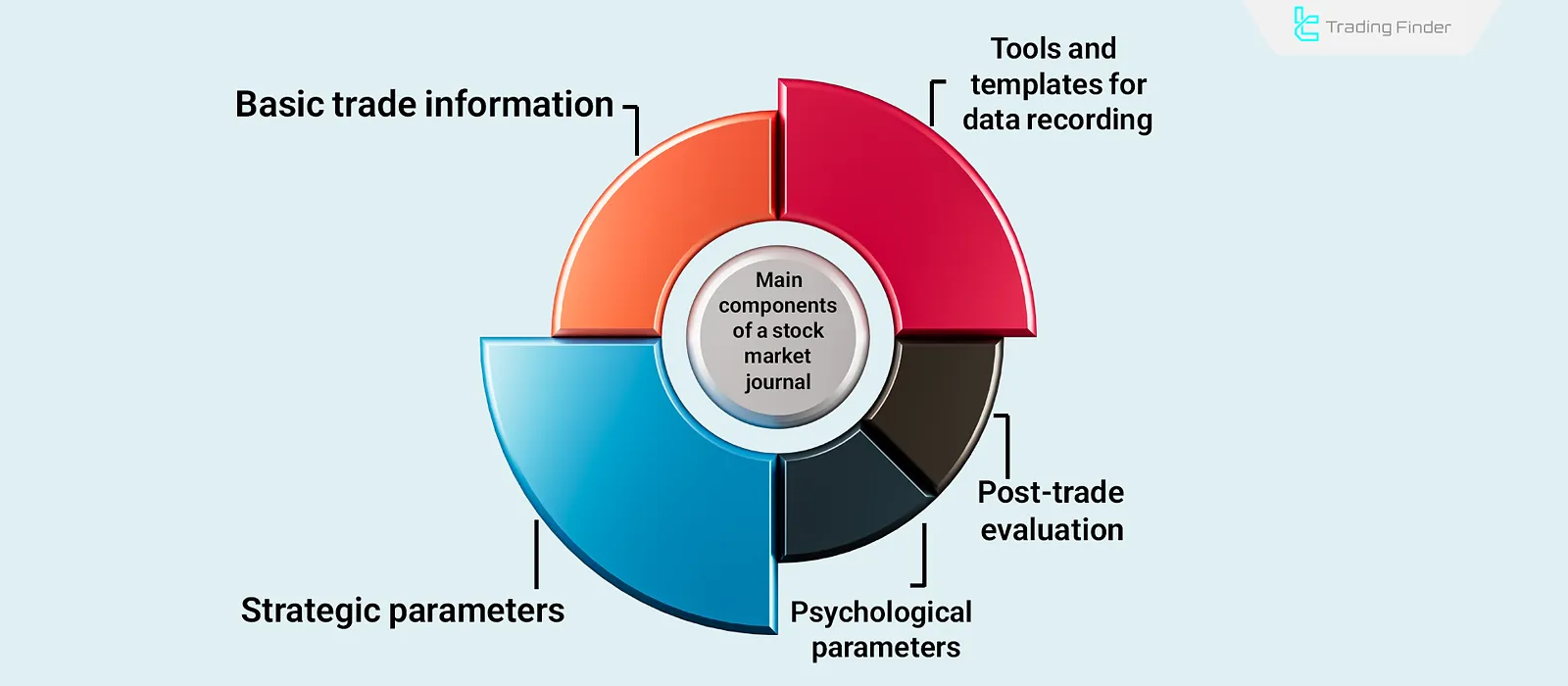
Main Components of a Stock Market Journal
To maintain its analytical function, a stock market journal must have a structured and data-driven format. This structure allows traders to document every decision, outcome, and influencing factor in a measurable way.
The following are the main components of a standard stock market journal:
- Basic Trade Information in the Journal
- Strategic Parameters in the Journal
- Psychological Parameters in the Trading Journal
- Post-Trade Evaluation
- Tools and Templates for Recording Data in a Stock Market Journal
Basic Trade Information
The initial section of the journal is dedicated to recording quantitative data information directly extracted from the trading platform:
- Date and exact time of the trade
- Symbol or stock traded
- Type of operation (buy or sell)
- Entry and exit price
- Trade volume and total value
- Final profit or loss as a percentage or amount
This foundational information serves as the basis for further statistical analysis and for calculating indicators such as average return, win rate, and risk-to-reward ratio (R/R).
Strategic Parameters
In this section, the reasoning and analytical logic behind the trade are recorded to clarify the trader’s decision-making foundation. Strategic parameters in the stock market journal include:
- Strategy or signal used (technical, fundamental, algorithmic, etc.)
- Take Profit (TP) and Stop Loss (SL) levels
- Timeframe of analysis (daily, weekly, mid-term)
- Market conditions at the time of entry (trend, trading volume, relevant news)
Recording this data enables review of each strategy’s performance under various market conditions and provides a basis for improving trading methods.
Psychological Parameters
One of the distinguishing features of a stock market journal is documenting mental and emotional components. Key elements that should be recorded in the psychological section of the journal include:
- The trader’s mental state at the time of decision (confidence, doubt, anxiety)
- Reaction to market fluctuations or temporary losses
- Degree of adherence to trading rules and risk management principles
This data helps traders recognize behavioral patterns and minimize the effect of emotions on financial decisions.
Post-Trade Evaluation
The analytical section of the journal focuses on reviewing the results of each trade. The most important items for post-trade evaluation in a forex or stock journal include:
- Whether the trade followed the initial plan
- Factors that led to profit or loss
- Mistakes that must be corrected in future trades
- Lessons that can be extracted from this experience
The goal of this stage is to extract practical knowledge from raw data and turn each trade into a learnable experience.
Tools and Templates for Data Recording
The method of implementing a journal can vary depending on experience level and trading volume:
- Paper notebook: for beginners or low-frequency traders
- Excel or Google Sheets file: for automatic calculation of profit, loss, and analytical ratios
- Specialized stock journal software: for statistical analysis and in-depth data evaluation
The key factor is consistency in recording and updating data a journal that is not maintained regularly loses its analytical value.
Educational video of Building a trading journal Using Excel from the YouTube channel Disciplined Trader:
How to Implement and Maintain a Stock Market Journal in Practice?
A stock market journal is most effective when its implementation is consistent, accurate, and aligned with the investor’s goals. Proper execution requires a step-by-step approach so that the data is not only recorded but also utilized analytically.
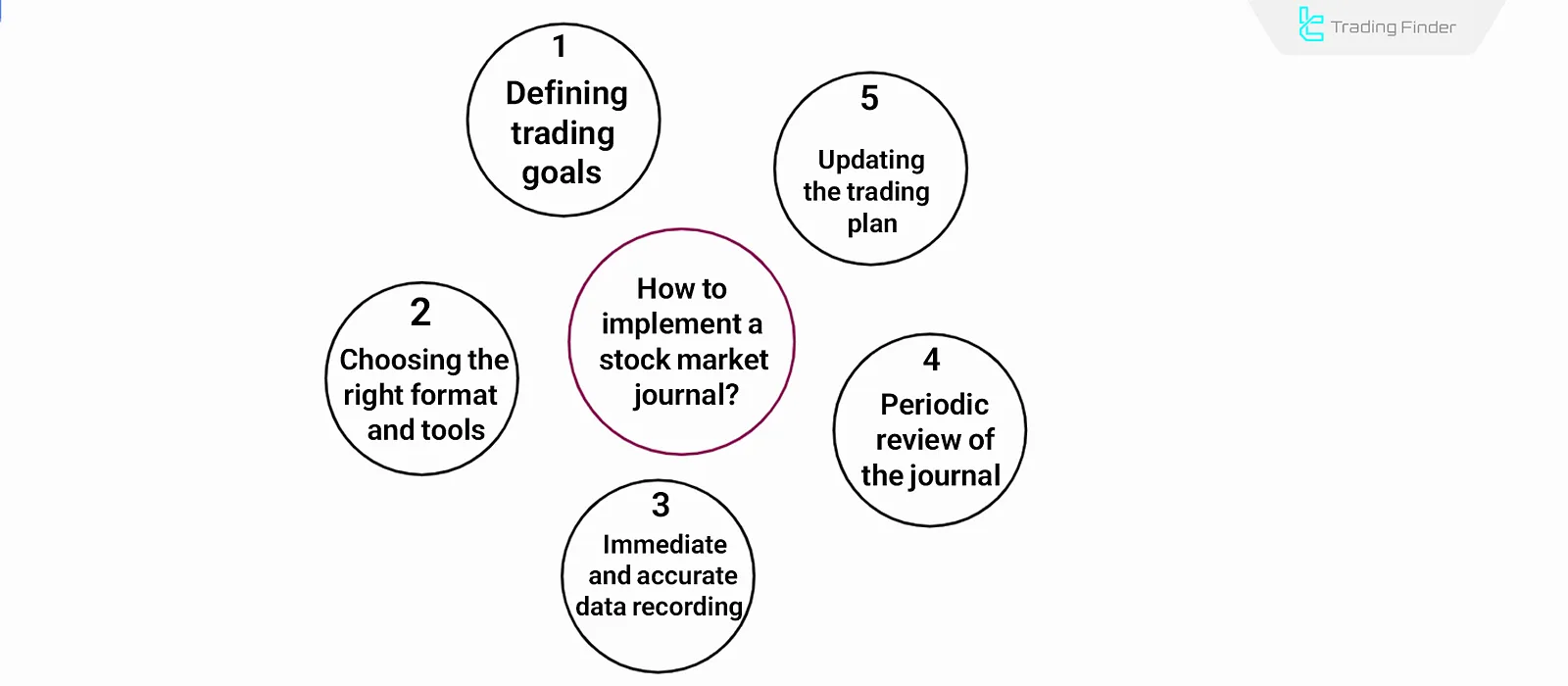
#1 Defining Trading Goals
Before anything else, the journal’s objectives must be specified; for example, analyzing the profit-to-loss ratio, number of trades per month, or evaluating a specific strategy’s performance. Setting goals ensures that collected data remains focused and purposeful.
#2 Choosing the Right Format and Tools
Depending on activity level and experience, journal formats can vary. Beginners typically use notebooks or Excel files, while professional traders may rely on specialized software for statistical analysis.
#3 Immediate and Accurate Data Recording
Trade information should be recorded immediately after execution to preserve accuracy. Delays in recording can distort memory-based details and reduce analytical value.
Required data includes time, symbol, volume, prices, reasons for entry or exit, and the trader’s emotional state at the time of decision-making.
#4 Periodic Performance Review of Journal Performance
Analysis without regular review is ineffective. Weekly or monthly evaluation helps traders identify behavioral patterns, analytical weaknesses, and recurring mistakes.
At this stage, indicators such as average profit per trade, percentage of successful trades, maximum drawdown, and risk-to-reward ratio are calculated.
#5 Updating the Trading Plan
Insights derived from the journal should be directly applied to improving strategies and future decisions.
When recurring patterns of errors or weaknesses are identified, traders should rewrite their entry, exit, or position-sizing rules. A journal without corrective action is merely a record book.
Example of Using a Stock Market Journal
Suppose a trader buys a company’s stock based on a breakout above 4,500, with a stop loss at 4,300 and a profit target at 5,000.
Three days later, the price reaches the target, and the trade closes with an 11% gain. The trader records all details, emotions, and reasoning in the journal.
After three months, reviewing the journal reveals that out of 25 trades, 16 were profitable (64%), and the most frequent mistake was entering too early before breakout confirmation. This insight helps the trader operate more systematically and data-driven in future trades.
Challenges and Suggestions in Stock Market Journals
During the journaling process, traders face multiple challenges that can affect accuracy and consistency. The table below presents the challenges and recommendations for maintaining an effective stock trading journal:
Challenges | Suggestions |
Consistency and discipline in data recording; decreased motivation to continue regular documentation | Start with a simple, scalable structure; focus on essential data such as time, price, and outcome, then gradually add advanced analytical sections |
Turning data into analysis; recording information without processing or drawing conclusions | Use digital analytical tools such as Excel files or specialized software to automate calculations and analyses |
Cognitive bias in recording; tendency to write down successes and omit failures | Conduct periodic analysis of results to identify mistakes, review patterns, and refine trading strategies |
High volume and variety of data in frequent trades, resulting in time consumption | Select key performance indicators and remove non-essential data to increase the speed and efficiency of recordkeeping |
Conclusion
A stock market journal is a systematic analytical tool for documenting and evaluating investor performance in the stock market. By combining quantitative data, behavioral analysis, and post-trade evaluation, it enables traders to make data-driven and logical decisions.
Regular use enhances trading discipline, reduces recurring mistakes, and improves the risk-to-reward ratio.
Ultimately, the stock market journal is not merely a trade recording but a continuous learning method, a form of financial self-awareness, and a path toward professional growth in the capital market.













