The Proof of Stake (PoS) algorithm, by introducing staking as a means to enhance blockchain security and functionality, offers aneco-friendly solution that also conserves energy.
Staking is a form of passive income generation from cryptocurrency assets where block information is verified and validated without the need for mining systems.
However, like any other type of investment, this method also comes with risks such as impermanent loss.

What Is Staking?
Staking refers to the process in which users earn rewards by holding or locking their digital assets within a blockchain network.
By staking assets on blockchains that operate under the Proof of Stake (PoS) algorithm, individuals contribute to the security and efficiency of that network.
This process is similar to earning interest by depositing funds in a traditional bank account.
Crypto staking does not require advanced technical skills, and anyone with basic knowledge can enter this space.
Networks such as Solana (SOL), Cardano (ADA), and Ethereum (ETH) are among the projects that offer cryptocurrency staking options.
In the Coinbase website’s staking tutorial article, this investment method is fully explained and provides a clear staking definition for beginners.

The History and Evolution of Staking
The idea of staking first emerged in 2012, alongside the introduction of the Peercoin network. This concept later expanded with the development of projects such as Cardano and Tezos.
In recent years, with the rise of Liquid Staking and Restaking, the possibility of reusing locked assets and increasing liquidity in PoS networks has become available.
What Is the Proof of Stake (PoS) Algorithm?
The Proof of Stake (PoS) algorithm is a method for verifying blockchain transactions and creating new blocks.
Instead of using mining devices, users stake a portion of their cryptocurrency and, in return, receive rewards for generating new blocks.
The locking of users’ assets within the blockchain increases the credibility of that blockchain.
Delegated Stake Based Algorithms (DPoS and the Delegation Model)
In the delegation model, users assign their tokens to selected nodes so these nodes can validate transactions. This mechanism improves network speed and reduces the need for advanced hardware, although it is less decentralized compared to classic PoS.
Concepts such as bitcoin staking also illustrate how stake based participation can differ across networks.
Comparison of Proof of Work and Proof of Stake
In the Proof of Work (PoW) algorithm, network security is provided through computational power, while in PoS the locked assets determine participation.
Comparison table of Proof of Work and Proof of Stake:
Features | Proof of Work (PoW) algorithm | Proof of Stake (PoS) algorithm |
Network security basis | Computational power of miner devices | Amount of locked assets in the network |
Energy consumption source | Very high due to electricity and hardware requirements | Very low and environmentally friendly |
Required equipment | Mining devices and GPU | Wallet and network token |
Node selection method | Through computational competition solving blocks | Based on the amount of locked stake |
Main risks | Hardware failure, energy cost, hash rate concentration | Asset price volatility, slashing risk |
Block reward | From mining output and transaction fees | From token inflation and block validation |
Network examples | Bitcoin, Litecoin | Ethereum, Cardano, Solana |
Advantages and Risks of Staking
While crypto staking offers passive income for investors, it also comes with risks such as Price Volatility Risk.
Benefits of Staking
Staking cryptocurrencies not only generates income but also contributes to energy efficiency and improved environmental conditions.
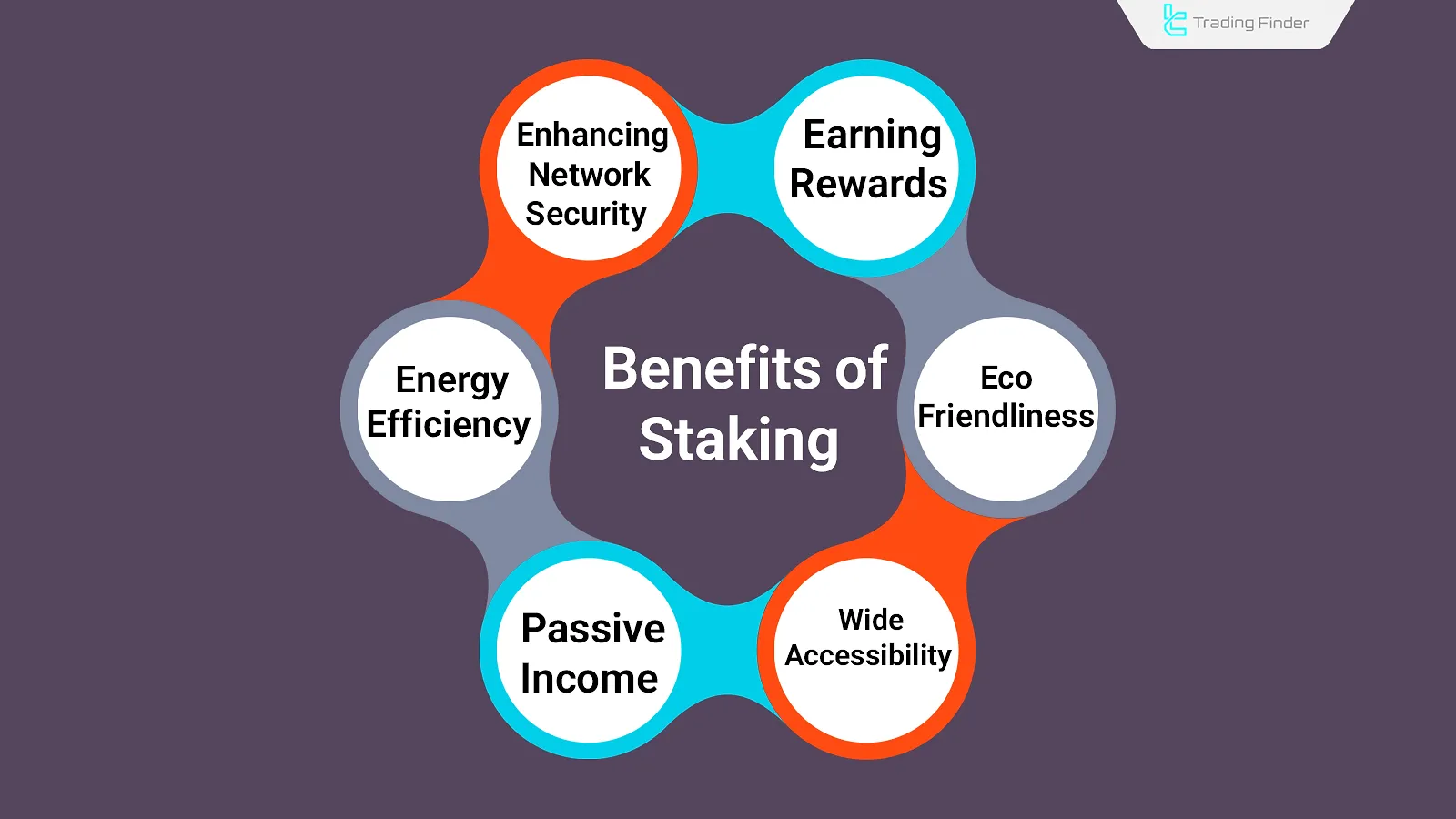
- Earning Rewards: Similar to earning interest in a bank, staking allows users to receive periodic returns;
- Enhancing Network Security: Participating in the transaction validation process improves the stability and security of the network;
- Eco-Friendly: Unlike PoW, the PoS algorithm does not require heavy hardware resources and is environmentally sustainable;
- Energy Efficiency: Energy consumption and related costs are significantly lower compared to mining;
- Passive Income Generation: One can earn profits without daily activity or constant trading;
- Wide Accessibility: Many exchanges (such as ByBit, CoinBase, Binance) and wallets offer crypto staking services.
Staking not only strengthens network security, but also provides a more sustainable alternative to mining by reducing energy consumption and offering passive income.
This approach helps beginners understand what is staking means in a practical and accessible way.
On the CoinGecko YouTube channel, the concept of staking is explained in a video format:
Risks of Staking
Staking involves risks such as Price Volatility Risk or project failure. Key risks of cryptocurrency staking include:
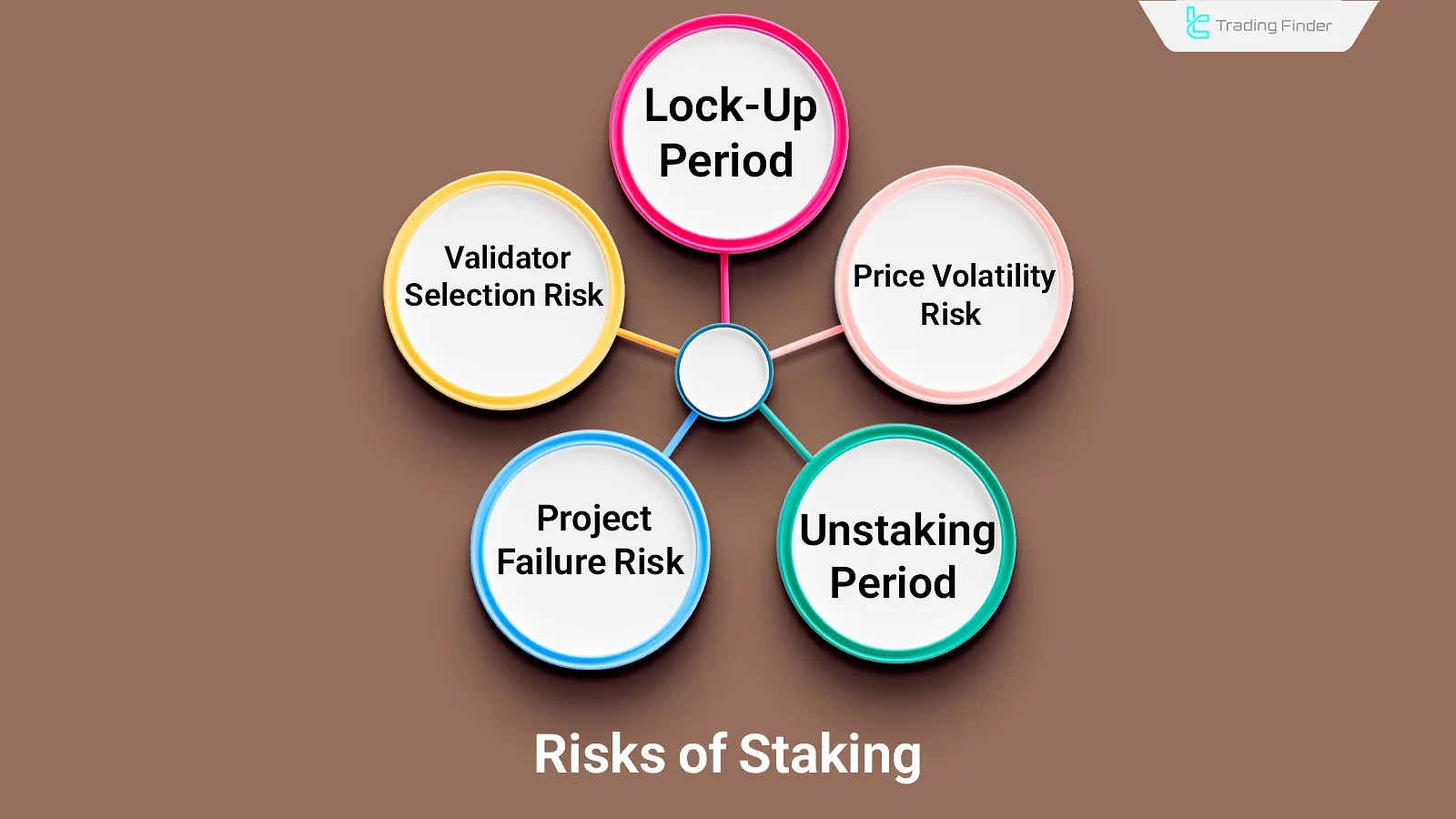
- Lock-Up Period: During this time, users cannot sell or transfer their cryptocurrency;
- Price Volatility Risk: The value of the asset may decline during thestaking period;
- Validator Selection Risk: Choosing an unreliable validator may result in partial loss of funds;
- Unstaking Period: After stopping staking, users might need to wait before their assets become withdrawable;
- Project Failure Risk: If the project fails, there's a possibility of losing the staked funds.
Economic Analysis of Price Risk
In staking, the real profit is positive only when the asset’s price growth surpasses market fluctuations.
For example, if the annual staking yield is 8 percent while the cryptocurrency price drops by 15 percent, the final outcome becomes negative. Therefore, assessing the long term market trend before staking is highly important.
Reward Models and Staking Economics
In PoS networks, staking rewards are calculated according to the amount of locked assets, the duration of participation, and the token’s inflation rate.
The more participants engage in staking, the lower the individual reward share becomes. In some networks, rewards are paid in a compounding format.
What Is a Staking Pool?
The chance of successfully validating a block is directly related to the amount of cryptocurrency locked in the network; the higher the amount, the better the chances of being selected to validate a block.
Given the large number of validators and their substantial holdings, small investors typically have a low probability of receiving block rewards.
Staking pools allow smaller crypto stakers to combine their assets with others, increasing their chances of being chosen for block validation.
Consequently, the reward for validating a block is distributed among participants based on each staker’s contribution to the pool.
Different Methods of Staking
To stake cryptocurrencies, users can either connect directly to the blockchain or use intermediaries such as staking pools.
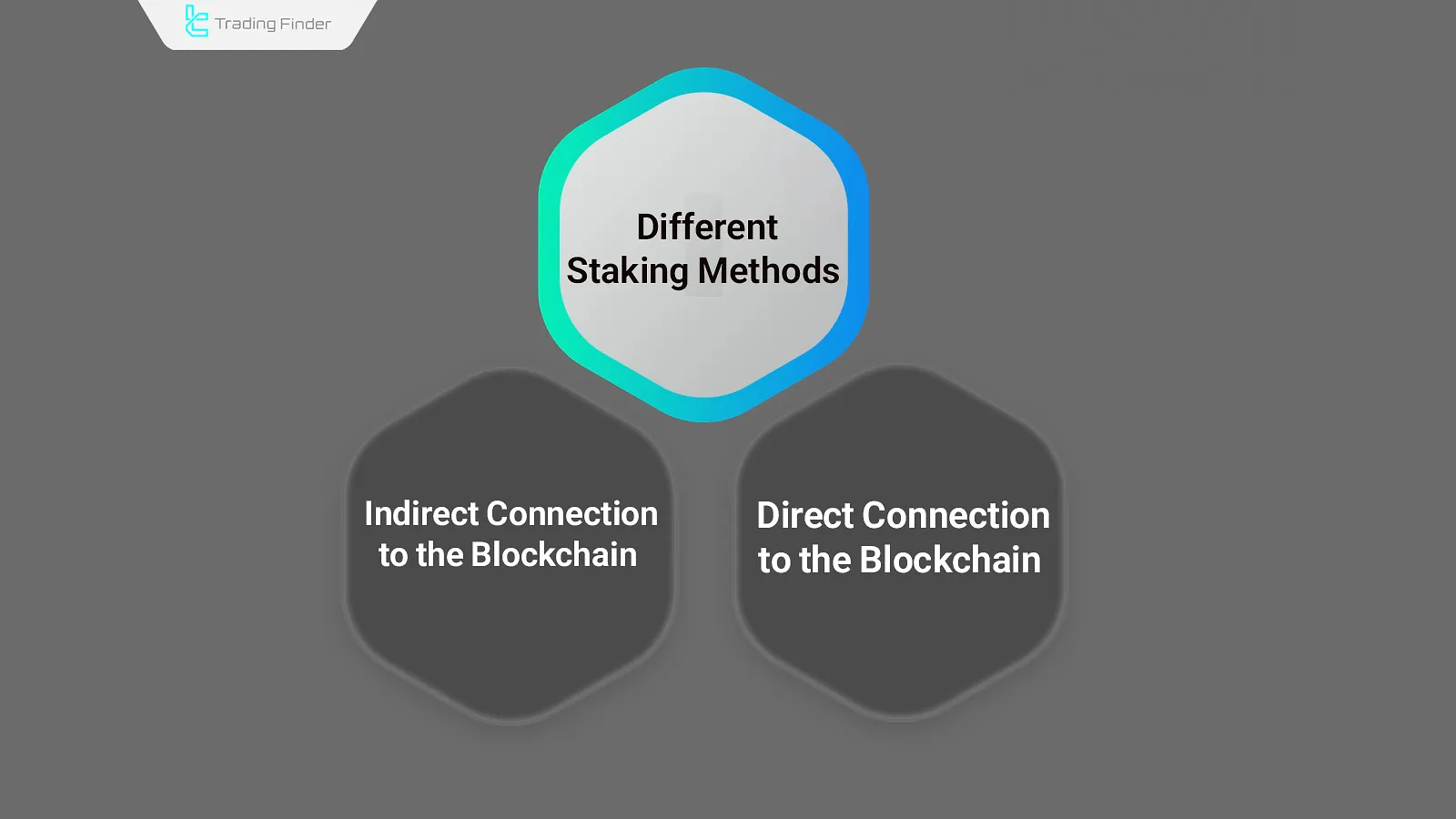
Direct Connection to the Blockchain
In this method, the staker becomes a validator within the network and plays a direct role in the block validation process. To do this, a certain amount of the network’s native cryptocurrency must be locked directly on the blockchain.
Once the asset is locked, a computer must remain continuously online to stay connected to the blockchain and validate blocks.
This method typically yields higher rewards than other crypto staking methods, but it requires significant capital, advanced blockchain knowledge, and technical setup.
If any issue or disruption occurs in the validator’s block validation process, a portion of the locked funds may be penalized and deducted.
Using an Intermediary to Connect to the Blockchain
In this method, users connect to a validator’s liquidity pool and do not participate directly in the block validation process. This is a fully passive investment strategy that does not require advanced blockchain knowledge.
One simply locks their funds into a staking platform; naturally, the reward received from this approach is lower compared to direct connection to the blockchain.
There are various methods for connecting to a staking intermediary, each offering different levels of rewards.
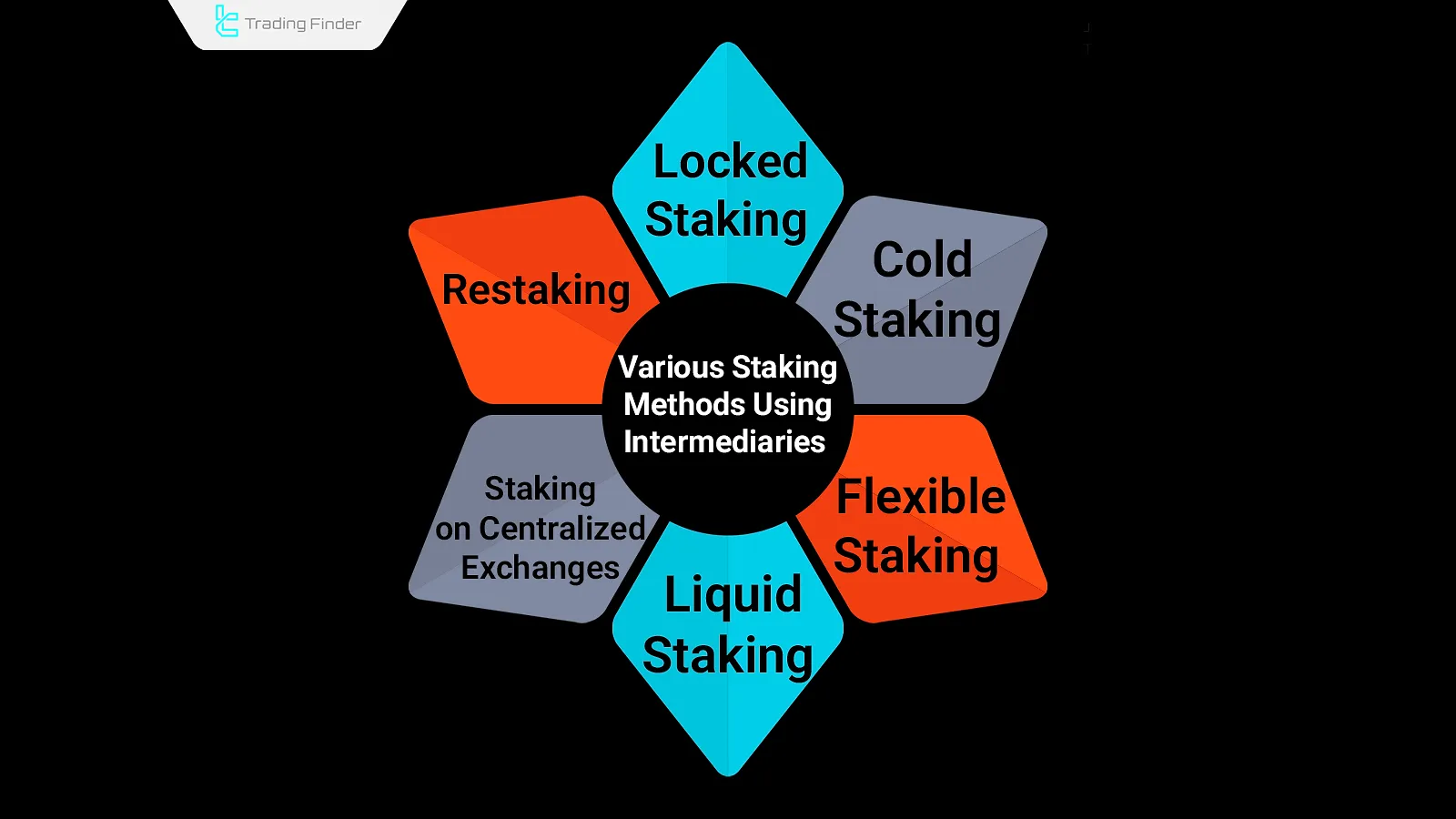
Locked Staking
In this method, the staker connects to a validator’s liquidity pool and locks a certain amount of cryptocurrency in a wallet or exchange for a predetermined period.
The lock-up duration is set in advance, and if the user cancels participation before the agreed time, the locked asset is released with a penalty deduction.
Cold Staking
In this method, the asset is locked in a cold wallet that is not connected to the internet, and the staker retains control over the private keys.
By signing a smart contract, the staker delegates the use of their digital asset for block validation to a validator, while still holding the asset in their cold wallet.
If the asset is removed from the cold wallet, the reward distribution stops. Afterward, the accumulated rewards from the locked asset will be paid to the staker.
Flexible Staking
In this approach, the asset is held in an exchange or wallet without being locked.
There is no penalty for early withdrawal, which makes this method more convenient, though it offers lower rewards compared to other crypto staking methods.
Liquid Staking
In this method, after the selected asset is locked, the staker receives a derivative token with the same name as the locked token, prefixed with "ST", representing the same value and quantity.
This token retains all functionalities of the original locked token, allowing the staker to trade it freely.
After initiating liquid staking, whenever the staker decides to end the process, they must return the derivative token in order to retrieve their original asset. After this step, the derivative token is burned.
Staking on Centralized Exchanges
In this method, the staker deposits their asset into a centralized exchange (CEX) and leaves the rest of the staking process to the platform.
This approach requires no technical knowledge of blockchain. However, the selected exchange must be validated, and its staking rewards should be reviewed carefully.
Restaking
The concept of restaking is defined within Ethereum’s consensus layer. This mechanism, through its own protocols, enables locked tokens to be reactivated.
Restaking allows the crypto staker to use their tokens across multiple networks to enhance network security andincrease rewards.
Top restaking protocols include:

Differences Between Cold and Hot Staking
In cold staking, the assets are stored in a non custodial wallet and the private key remains under the user’s control.
In hot or custodial staking, the assets are delegated to a platform so that the technical operations are handled by it. Security is higher in the cold model, while accessibility is easier in the hot model.
Differences Between on Chain Staking and DeFi Staking
Staking in PoS blockchains is performed to maintain network security, while staking in DeFi is usually used for providing liquidity and earning fees.
In the first type, rewards are paid from block validation, while in the second type they come from transaction fees and reward tokens.
Steps to start staking
To begin staking and become a Staker, it is essential to first choose a staking method based on one’s individual investment strategy.
Steps to perform staking:
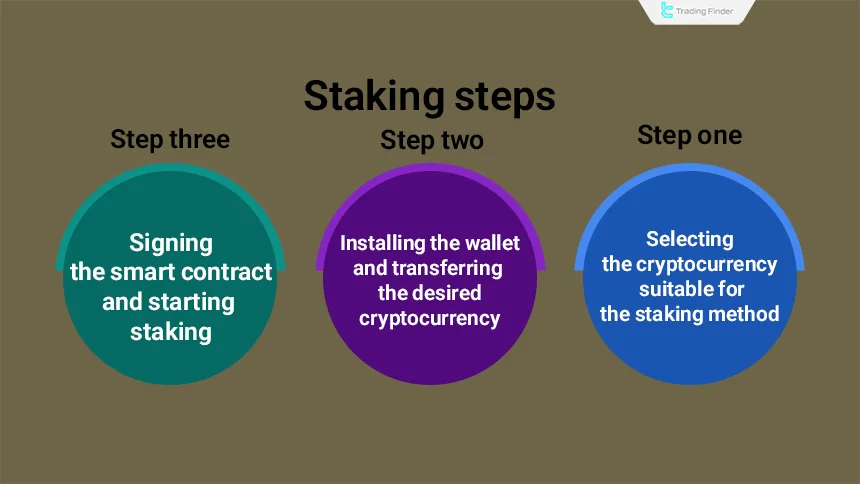
#1 Choosing the Right Cryptocurrency for Staking
To choose a cryptocurrency, the investment goal must first be defined.
If the objective is to earn passive income by staking an asset alongside long-term holding profits, the long-term trend of that asset should be analyzed to avoid Price Volatility Risk.
To eliminate the risk of Price Volatility Risk, it is recommended to use stablecoins for staking, as their value is always pegged to 1 USD.
#2 Installing a Wallet and Transferring Your Cryptocurrency
In this step, the wallet setup and preparation process is completed:
- Preparing the wallet for staking;
- Downloading a trusted wallet from platforms such as App Store or Google Play;
- Creating a user account within the wallet;
- Setting up security measures such as two-factor authentication (2FA);
- Transferring your selected cryptocurrency to the wallet.
#3 Signing a Smart Contract and Starting the Staking Process
Next, access the DApp section of your wallet to locate the staking platform and connect your wallet to it.
At this point, the chosen amount of cryptocurrency is locked, and with the signing of a smart contract, the staking process officially begins.
Liquid Staking Tutorial
Liquid Staking is a method in DeFi that allows users to stake their assets while maintaining liquidity at the same time.
In this model, after locking the assets, a derivative token such as stETH is received, which represents the underlying asset and can be used in other DeFi protocols for lending or yield farming.
The main advantage of this method is increased capital efficiency, because the user earns staking rewards while also using the derivative token to generate additional yield.
However, it carries two main risks: the possibility of the token depegging and the vulnerability of the smart contract, both of which can threaten the value or security of the assets.
In summary, liquid staking combines profitability with liquidity, but requires choosing reputable platforms and evaluating smart contract security.
Restaking and Layer Two Security
In Restaking, the staked asset is used to secure layer two services or new protocols.
By doing so, the existing capital secures multiple networks simultaneously. Projects such as EigenLayer are among the pioneers of this model.
Key Considerations for Staking Cryptocurrency
Before starting staking, several factors must be reviewed such as platform credibility, fees, and the duration of the smart contract to minimize investment risks as much as possible.
Important crypto staking considerations include:
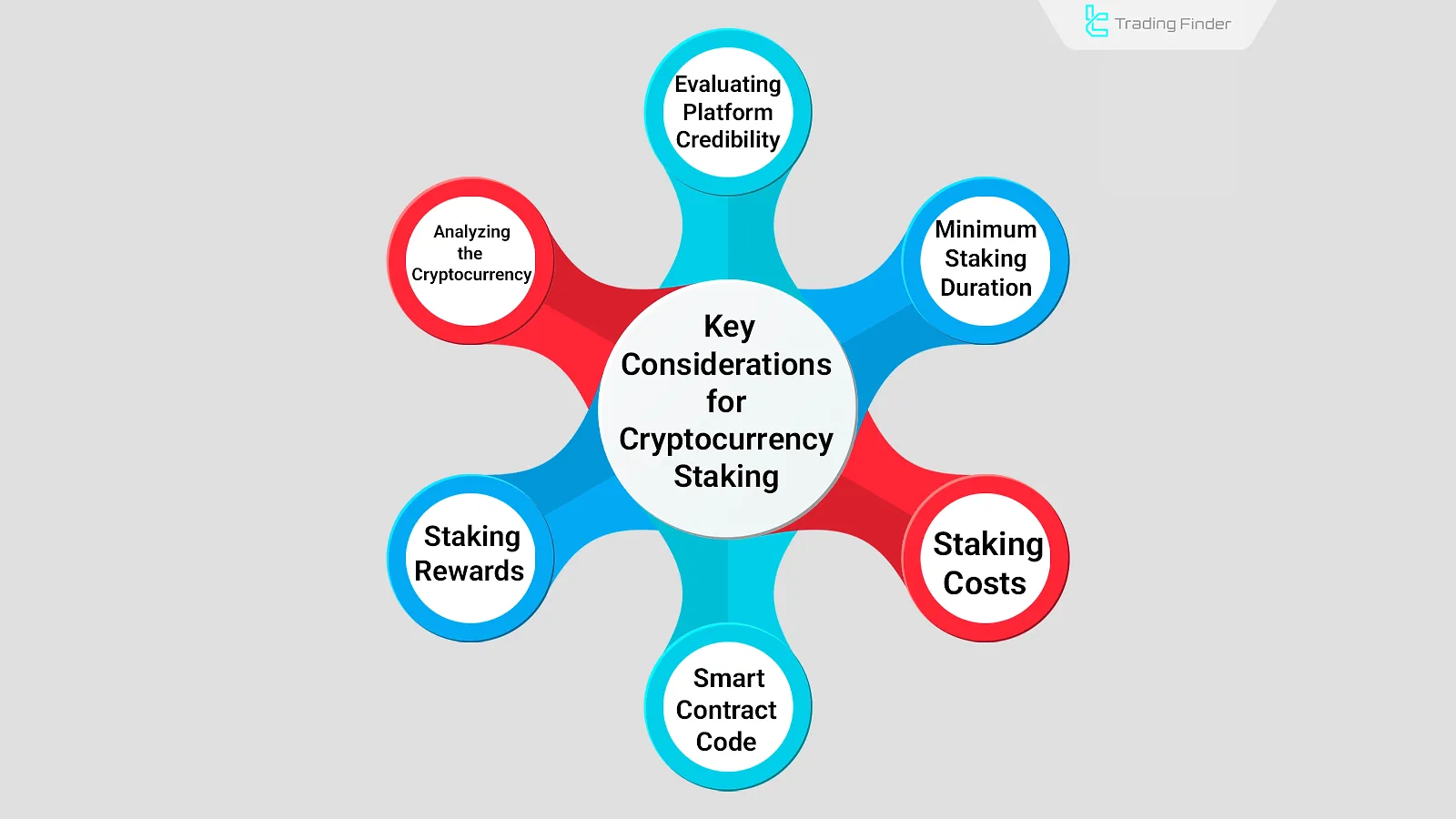
- Evaluating Platform Credibility: The reputation and track record of astaking platform should be assessed through expert reviews and user feedback;
- Reviewing Minimum Lock-Up Period to Earn Rewards: This duration can vary from a few days to several months and should be considered based on the investor’s goals;
- Staking Costs: It’s essential to estimate costs such as transfer fees, custody fees, and staking service charges;
- Analyzing Smart Contract Instructions: Some smart contracts may include hidden clauses beyond staking instructions; reading the underlying code can help identify them;
- Staking Rewards: Staking platforms offer different reward percentages depending on the cryptocurrency and lock-up duration;
- Analyzing the Cryptocurrency: To avoidPrice Volatility Risk, the long-term trend of the chosen asset should be examined using both technical and fundamental analysis.
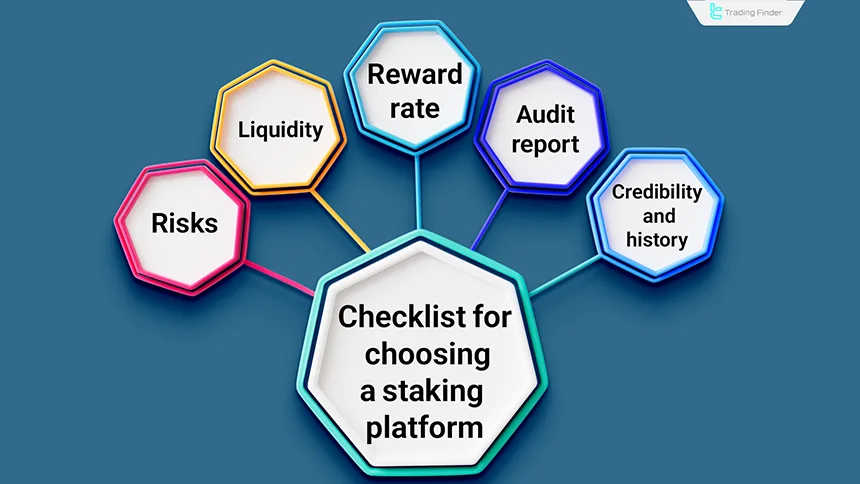
Checklist for Choosing a Staking Platform
Before selecting any platform for staking, it is necessary to review several key criteria to ensure its security, transparency, and actual return. The following points can serve as a practical checklist to guide your decision making:
- Checking the platform’s credibility and its activity history on social networks;
- Analyzing the smart contract and verifying the existence of an audit report;
- Comparing reward rates, fees, and lock up periods;
- Evaluating emergency withdrawal conditions and user support;
- Reviewing the liquidity of the derivative token in liquid staking.
Example of Choosing a Staking Platform
Below is a real example of evaluating a staking platform to show how the above checklist is applied. Suppose you intend to stake your assets on the Lido platform
- Credibility and history: Lido has been active since 2020 and holds the largest share of liquid staking on the Ethereum blockchain;
- Audit report: It has been audited multiple times by companies such as Quantstamp;
- Reward rate: The average annual yield is around 4 to 5 percent which varies depending on market conditions;
- Liquidity: The derivative token stETH is tradable on major exchanges and has high liquidity;
- Risks: There is a possibility of depegging between ETH and stETH but due to high liquidity volume it remains manageable.
Best Cryptocurrencies for Staking
Only cryptocurrencies that use the Proof of Stake (PoS) algorithm are eligible for staking.
Cryptocurrencies offer different annual percentage yields (APY), depending on the nature of each project. Here’s a list of the best cryptocurrencies for staking in 2025:
Cryptocurrency Name | Percentage Yield (APY) |
Ethereum (ETH) | 4% |
Avalanche (AVAX) | 7% |
Binance Coin (BNB) | 2% |
Aptos | 7% |
Matic | 4% |
Polkadot (DOT) | 11% |
Cardano (ADA) | 3% |
Tron (TRX) | 5% |
Cosmos | 20% |
Algorand (ALGO) | 11% |
Solana (SOL) | 8% |
HyperLiquid (HYPE) | 2% |
Future of Cross Chain Staking
With the development of cross chain standards, users will be able to lock their assets on one blockchain and receive rewards across other networks.
This trend increases capital efficiency and expands the concept of shared security between chains.
Using the AI Based Trading Connection Expert Advisor in the Cryptocurrency Staking Process
Just as artificial intelligence has transformed financial market analysis, it can also make the staking process smarter and more precise by predicting network behavior, optimizing node selection, and analyzing returns.
The AI Trading Connection expert advisor is one of TradingFinder’s advanced tools that allows traders to receive intelligent and accurate technical, fundamental, and news based analysis using AI models such as ChatGPT and Claude.
This expert advisor connects directly with the APIs of these models through the WebRequest feature in the MetaTrader 5 platform and delivers the data to the user in the form of analytical text responses.
The main purpose of the AI Trading Connection expert advisor is to provide fast and reliable access to real time analysis of the forex and crypto markets.
This tool can interpret key price levels, market trends, reactions to economic data, and even news based insights in a structured format. Unlike automated trading robots, the function of this expert advisor is purely analytical and does not execute trades automatically.
To activate this tool, the user must go to the Expert Advisors section from the Options menu in MetaTrader and enable the option Allow WebRequest for listed URL. Then, by adding the official API addresses including https://api.openai.com and https://api.anthropic.com, the connection between the platform and the AI models will be established.
After that, by entering the dedicated OpenAI or Anthropic token in the Inputs section and selecting the desired model such as gpt 4 or claude opus, the tool will be ready to use.
Once the expert advisor is executed on the chart and the analytical prompt is written, the text is sent to the AI model and the precise output is displayed in the Output window. These responses may include market structure analysis, interpretation of supply and demand zones, market sentiment evaluation, and analytical suggestions.
In the end, the AI Trading Connection expert advisor for MetaTrader 5 creates a bridge between artificial intelligence and professional trading, and serves as a practical and transformative tool for all traders seeking smarter, data driven decision making.
- Download AI Trading Connection expert advisor for MetaTrader 5
- Download AI Trading Connection expert advisor for MetaTrader 4
Conclusion
Proof of Stake (PoS) allows users to earn cryptocurrency by staking instead of mining. Staking involves locking a portion of a blockchain’s native token to help secure and operate the network. In return, stakers receive token rewards.
There are two main staking methods: direct staking, which requires expertise and high capital, and indirect staking, where users participate via intermediaries through options like Locked Staking, Cold Staking, and Liquid Staking.













