Liquidity Void (LV) refers to a situation where there are insufficient orders to fill a rapid price movement within a specific timeframe.
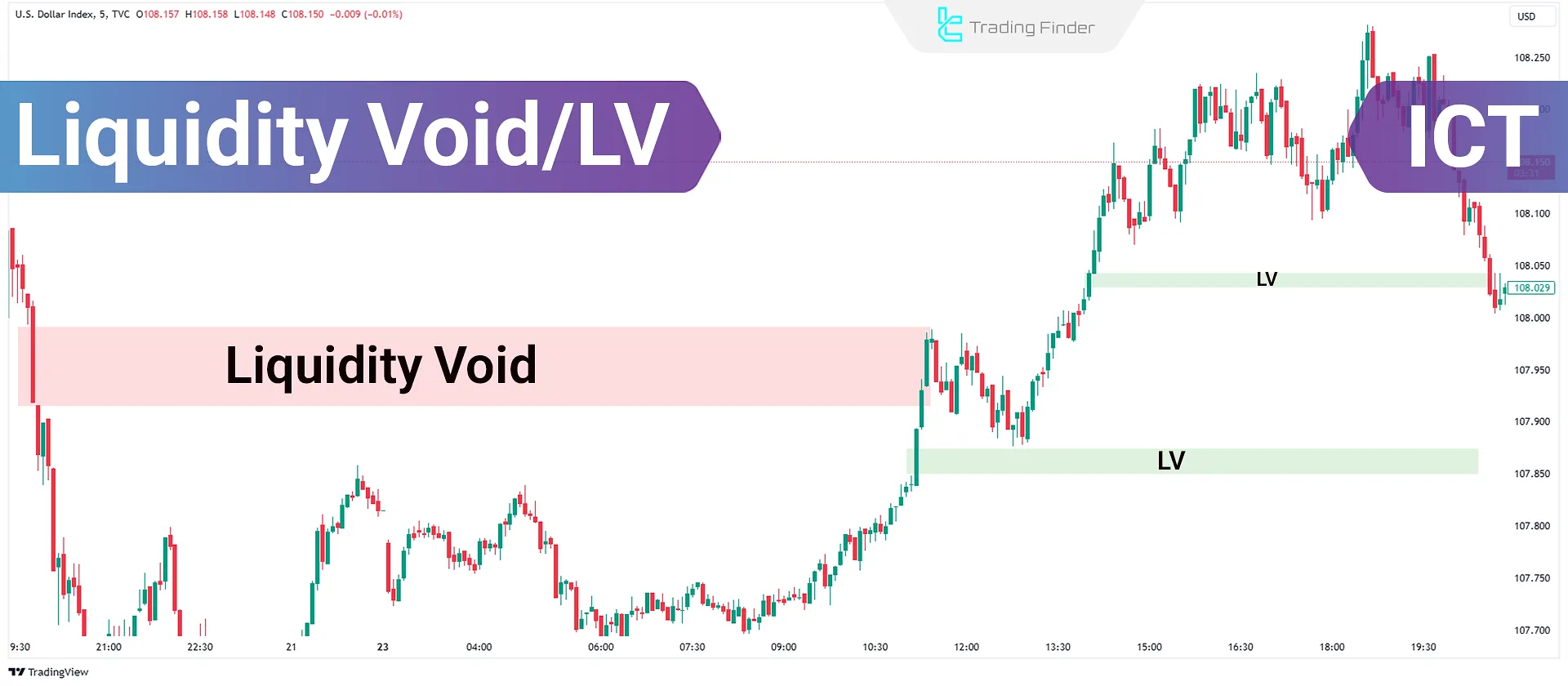
This phenomenon is often considered an indication of strong market movements and a lack of sufficient buyer or seller participation in that area.
What is ICT Liquidity Void?
In financial markets, "liquidity" means the presence of active buyers or sellers, and "void" means the absence or lack thereof.
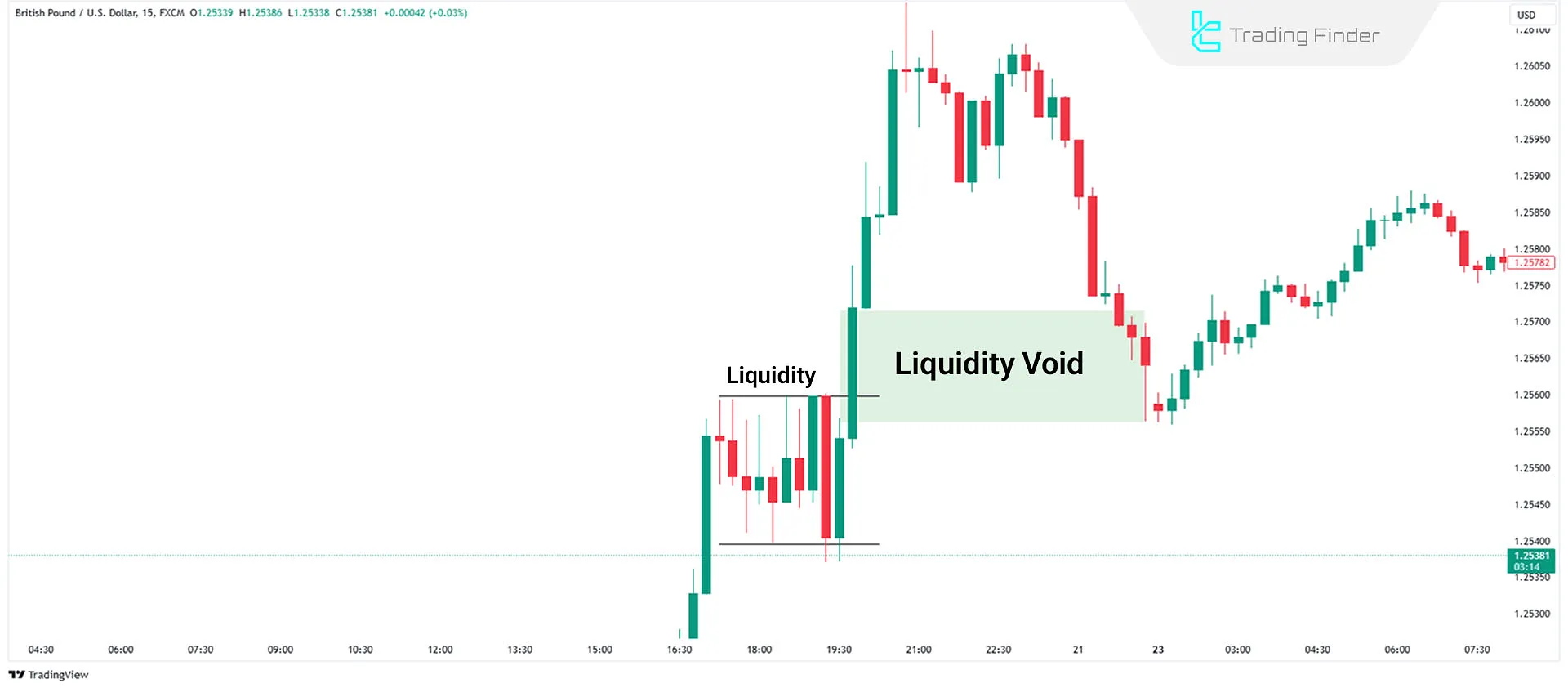
Liquidity void in the ICT style occurs when the price breaks out of a consolidation phase and moves aggressively in one direction without returning or forming shadows in the previous candles' range. This imbalance between buyers and sellers is known as the ICT liquidity void.
Bullish ICT Liquidity Void
A bullish liquidity void occurs when the price breaks out of a consolidation range (a narrow price fluctuation zone) and moves strongly upward, absorbing sell-side liquidity.
Insufficient sell-side liquidity causes the price to surge upward and creates an imbalance in the market, which is called a "bullish liquidity void."
For more information on liquidity voids, you can use the TradingFinder indicator set:
- Liquidity Void (LV) Indicator for MetaTrader 4
- Liquidity Void (LV) Indicator for MetaTrader 5
- Liquidity Void (LV) Indicator for TradingView
How to Trade Bullish Liquidity Void?
To trade bullish liquidity void, consider the following three steps:
- Market Analysis: First, determine whether the market is bullish or bearish.
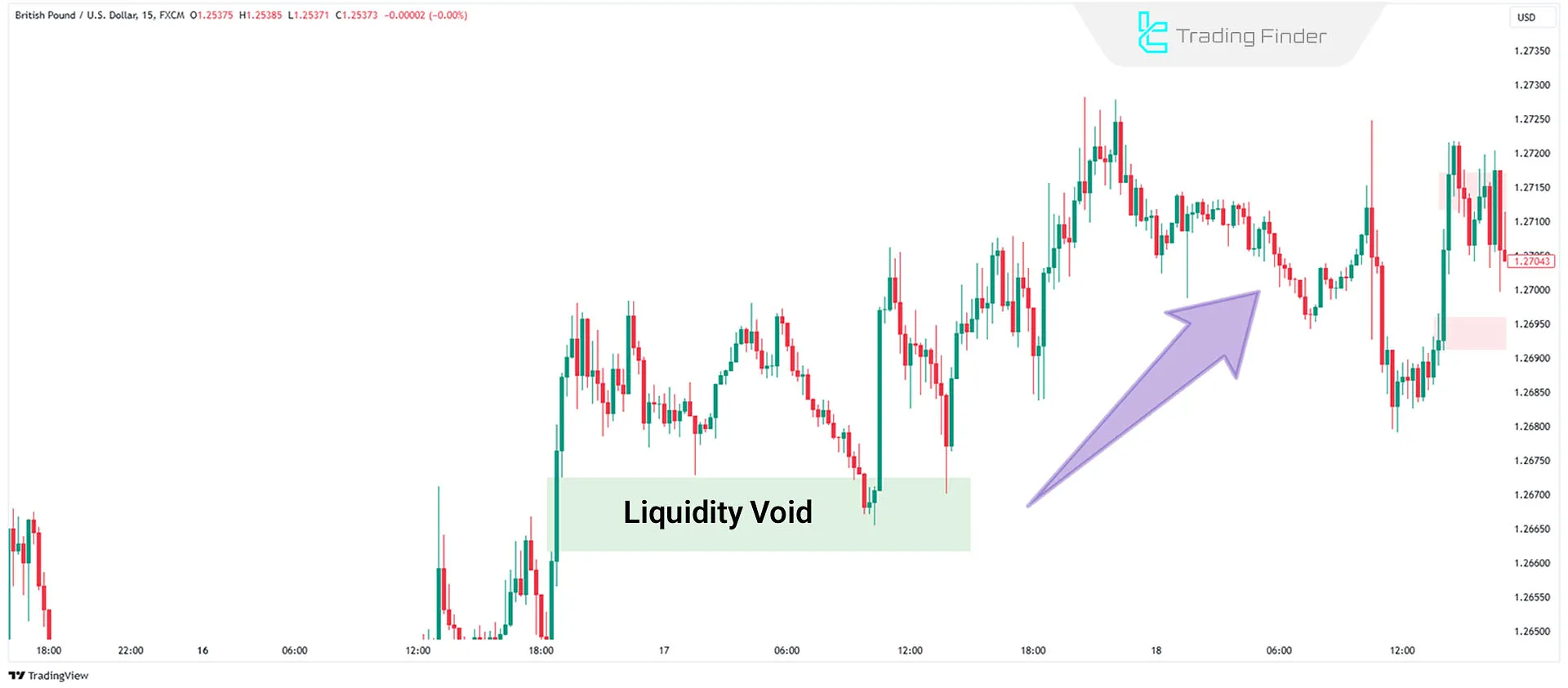
- Bullish Market: In a bullish market, the price usually retraces downward to fill the liquidity void, after which the upward move resumes. In these conditions, you can find buy setups within the void.
- Support Level: A bullish liquidity void in an uptrend is a strong support level.
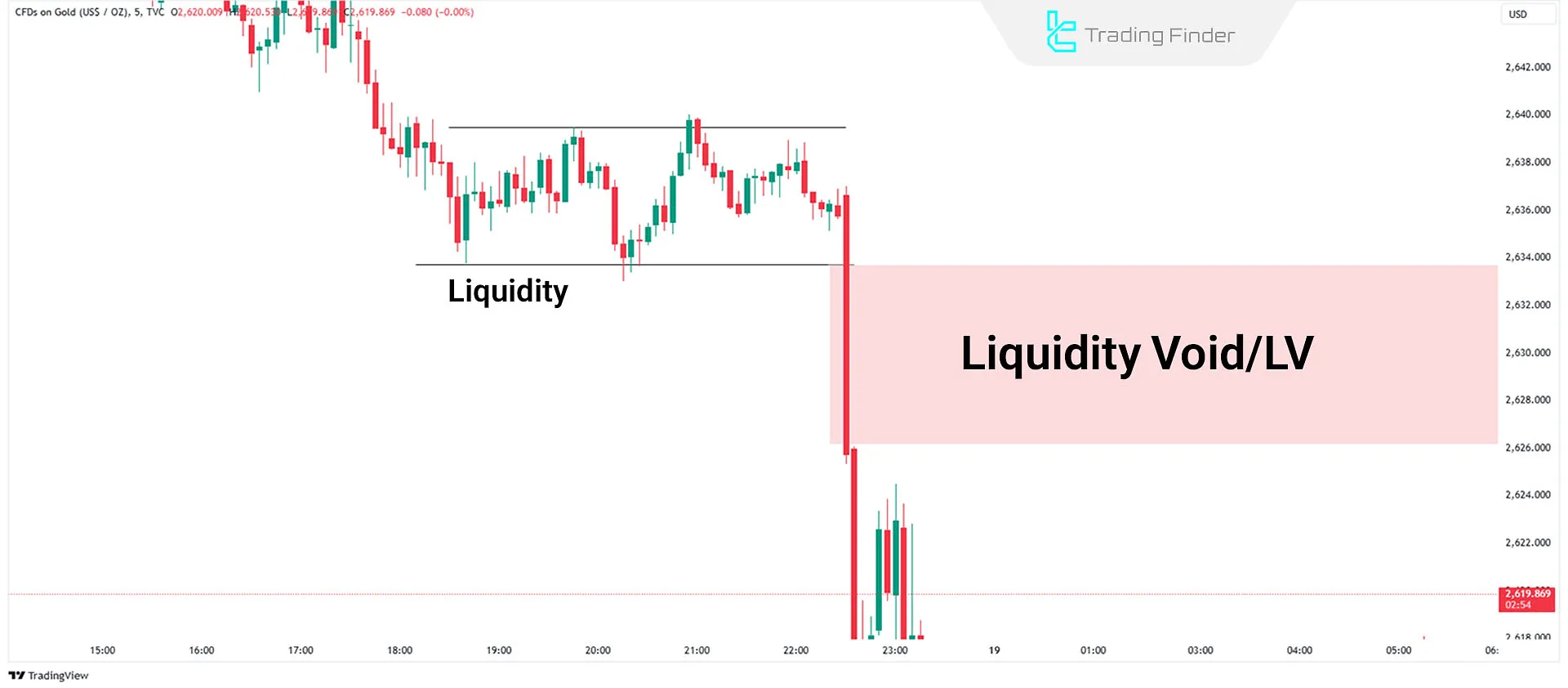
Bearish ICT Liquidity Void
A bearish liquidity void occurs when the price breaks strongly downward from a consolidation phase with large candles, absorbing buy-side liquidity.
This void occurs due to the absence of sufficient buy-side liquidity. The price moves downward without returning, creating an imbalance in the market.
How to Trade Bearish Liquidity Void?
To trade bearish liquidity void, consider the following three steps:
- Market Structure: First, determine the market trend (bullish or bearish).
- Bearish Market: In a bearish market, the price usually retraces upward to fill the liquidity void before resuming its downward In these conditions, you can look for sell setups within the void.
- Resistance Level: A bearish liquidity void in a downtrend is a strong resistance level.
Do Liquidity Voids Always Get Filled?
There is no specific timeframe for filling or rebalancing a liquidity void. The price may fill the void immediately or return to fill it days later.
Is Filling a Liquidity Void Guaranteed?
No, there is no guarantee that a liquidity void will be filled. The price may continue without returning to the previous liquidity void or create new voids.
Price behavior depends on market conditions, structure, and liquidity flow.
Differences Between Liquidity Void (LV) and Fair Value Gap (FVG)
A liquidity void is a larger pattern that encompasses several fair value gaps. Some of the key differences between these two models are as follows:
Pattern | Liquidity Void (LV) | Fair Value Gap (FVG) |
Definition | An area with rapid movements and imbalance in trading volume | A gap between candles due to price imbalance |
Cause | Lack of liquidity and volume in the market | Strong price movements and mismatched orders |
Appearance on Chart | Long, rapid candles with no price retracement | Gap between the high and low of candles |
Purpose in Technical Analysis | Filling the gap to rebalance liquidity | Identifying areas for price reversal or trend continuation |
Signs | Sharp decrease in trading volume and rapid price movement | Visible gap between candles |
Conclusion
Liquidity voids occur when the price moves rapidly and aggressively without retracement or balance in trading, creating an imbalance between buyers and sellers.
Although these voids can be used as trading opportunities, there is no guarantee that they will be filled or rebalanced, as it depends on market conditions.
Use this concept in combination with structural changes for better analysis and confirmation.