The Martingale strategy, originally designed in the 18th century for gambling purposes, is now widely used as a capital management method in financial trading.
Although the Martingale method can be implemented in various ways, its most common form involves position scaling by doubling the trade volume at each successive level of entry.
In essence, the Martingale Strategy is based on the principle of averaging down losses.
This means that after each losing trade, the trader doubles the size of the next position so that a single winning trade can recover all previous losses and generate a profit equal to the amount of the initial trade.
While the Martingale technique may seem simple and logical on the surface, in reality, it requires substantial capital, strong psychological discipline, and a deep understanding of market structure to prevent exponential losses.

What is the Martingale Strategy?
The Martingale strategy is a method used in financial markets in which the amount and volume of investment increase after a loss, with the goal of recovering past losses.
In trading, the Martingale strategy is a type of step-by-step averaging (pyramiding) approach used to return to profitability and eliminate prior losses. A Martingale trader doubles the position size at each new entry stage compared to the previous one.
The execution of the Martingale method is as follows:
Entry Level | Investment Amount |
First Level | 10 |
Second Level | 20 |
Third Level | 40 |
Fourth Level | 80 |
Fifth Level | 160 |
Important Note: Before entering a trade using the Martingale strategy, the total number of entry levels and cumulative losses must be within the risk capacity managed by the trader. Otherwise, there is a high risk of losing the entire capital and facing a margin call.
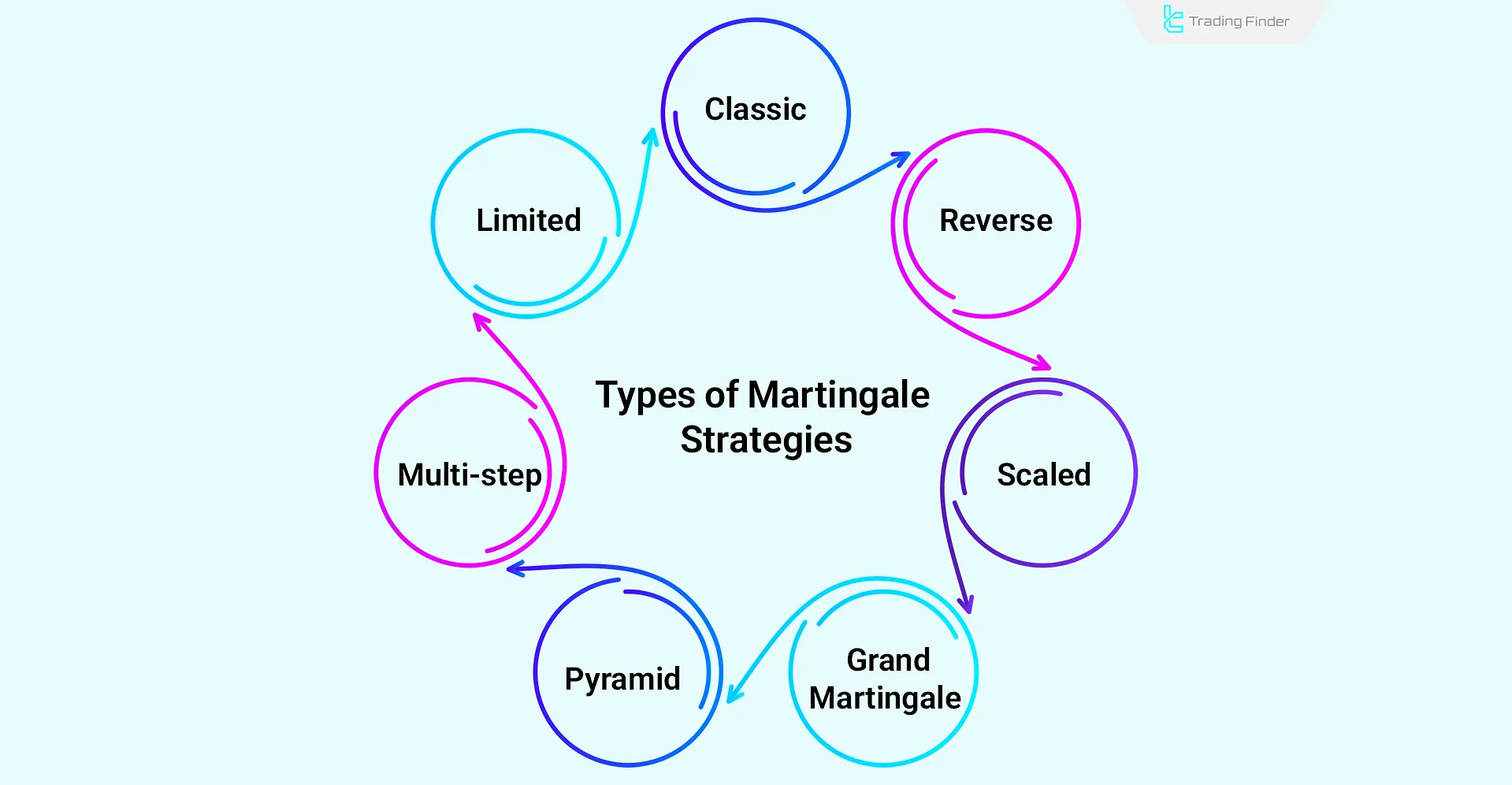
Types of Martingale Strategies
The Martingale in Trading strategy has several variations, which include:
- Classic Martingale
- Reverse Martingale (Anti Martingale)
- Scaled Martingale
- Limited Martingale
- Multi-step Martingale
- Pyramid Martingale
- Grand Martingale
Classic Martingale
In this approach, the position size is doubled after every loss so that a single winning trade can recover all previous losses.
Due to the high risk of capital depletion, this method is considered very dangerous during consecutive losing trades. Therefore, strict attention must be paid to risk and capital management.
Reverse Martingale (Anti Martingale)
In the Reverse Martingale or Anti Martingale, the position size is increased after each win and reduced after each loss. The aim is to capitalize on bullish or bearish trends for more efficient trade entries.
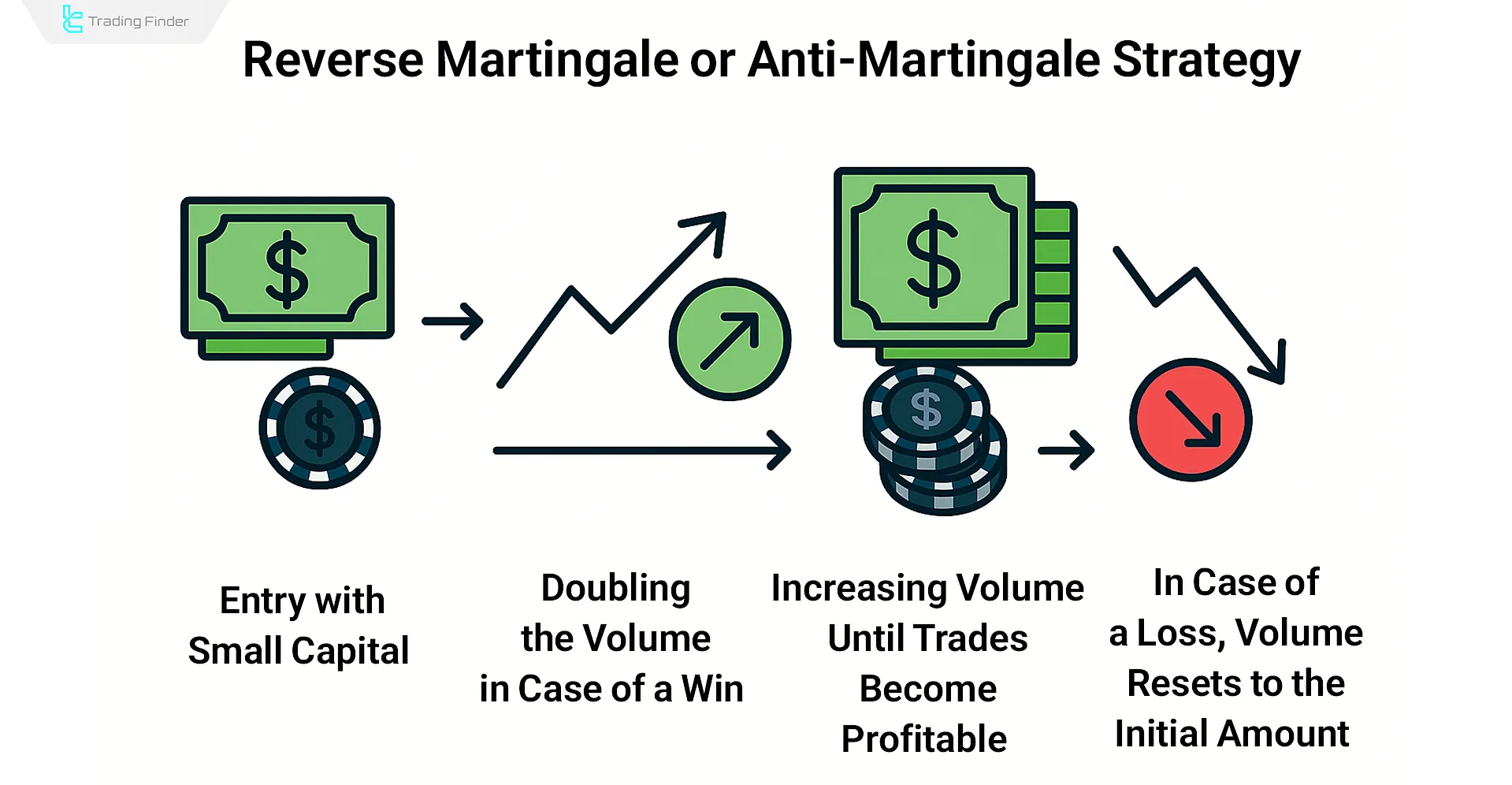
In the educational video on the TRADING RUSH YouTube channel, the Anti-Martingale Strategy is tested and reviewed in real market conditions. Those interested in gaining a better understanding of the Anti-Martingale approach can watch the video here:
Scaled Martingale
In this method, trade volume is gradually increased after losses, based on a fixed percentage scale. The objective is to recover previous losses using a smoother volume curve rather than sharp doubling.
Consecutive losses must be analyzed and diagnosed; otherwise, applying the Martingale method can result in total account depletion.
Limited Martingale
This variation imposes a limit on the number of doubling steps to prevent excessive losses.
Traders define a fixed number of Martingale steps based on their portfolio's capital management, keeping the risk within acceptable bounds.
Multi-step Martingale
Here,trade volume at each step may vary based on extended market analysis. The trader uses discretion and prioritizes support/resistance levels to determine the appropriate volume for each new entry step.
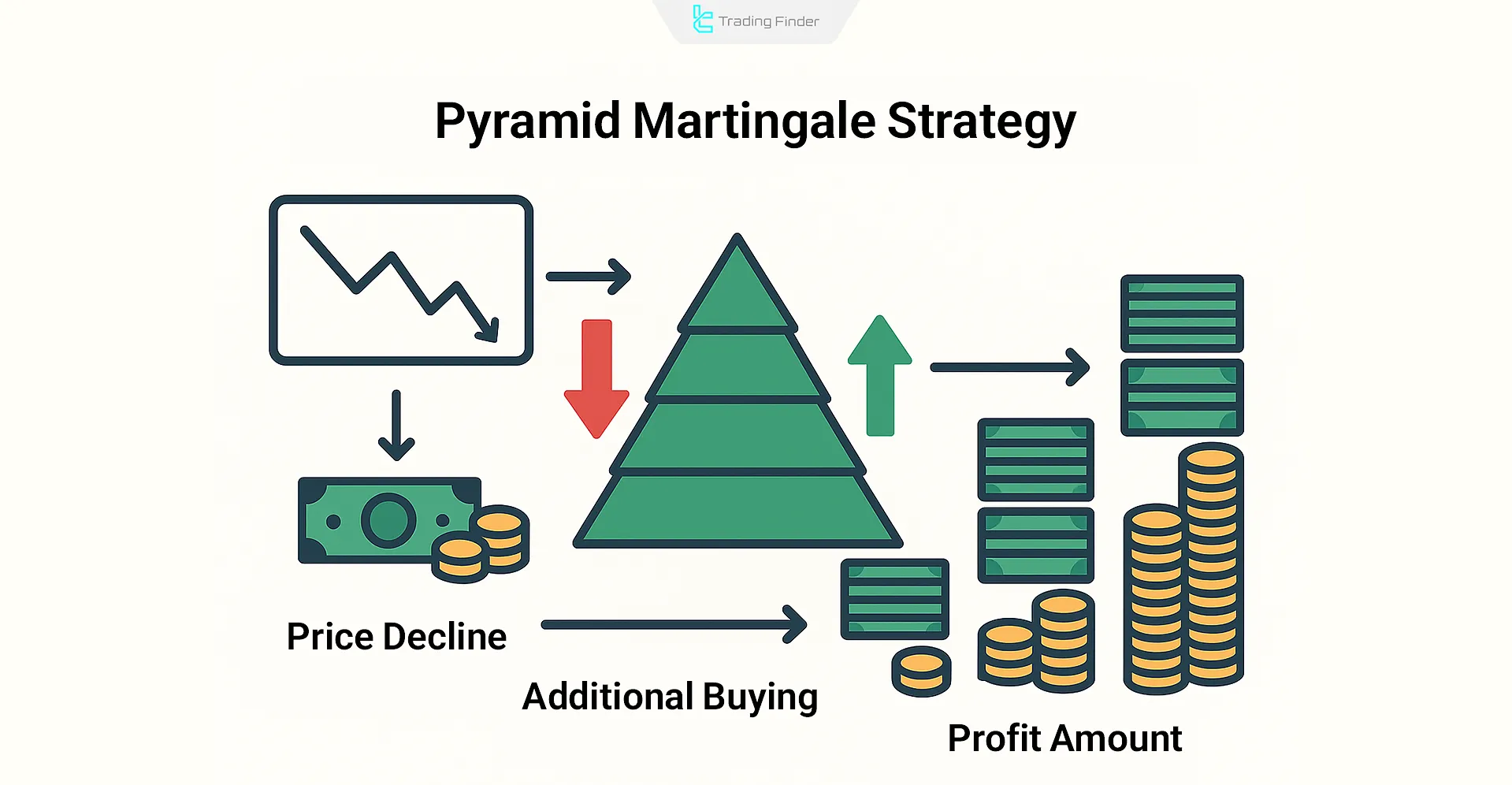
Pyramid Martingale
The Pyramid Martingale strategy is applied in trending markets (clear bullish or bearish directions). When a trader enters a successful trade in the direction of the trend, the next trade will be opened with a larger position size.
This volume increase is done in anticipation of trend continuation and to maximize potential profits.
Grand Martingale
In the Grand Martingale method, after each losing trade, the position is not only doubled but also increased by an additional fixed unit to accelerate recovery of losses.
This is considered an advanced form of the Martingale strategy, which goes beyond simple doubling.
The key difference between Grand Martingale and the regular method is that it adds one more unit (double + one unit) to the position size in each step after a loss.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using the Martingale Strategy in Trading
Below are the key benefits and limitations of the Martingale method:
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Fast recovery of previous losses | High risk of capital loss |
High return potential | Requires large investment |
Simple to implement | Negative psychological impact |
– | Lack of proper risk management |
– | No guarantee of long-term profitability |
– | High potential for misuse |
Comparison Between the Martingale and Classic Averaging (Pyramiding) Methods
Although the Martingale strategy may appear similar to a classic averaging approach, it differs fundamentally in structure and risk level:
Comparison Parameters | Classic Averaging (Pyramiding) | Martingale |
General Structure | Gradual entry with equal position sizes at each step | Gradual entry with exponentially increasing position sizes (usually double each step) |
Main Objective | To lower the average entry price and manage risk during a downtrend | To quickly recover previous losses with a short-term price reversal |
Trade Size per Step | Fixed and consistent at all stages | Increasing geometrically (1, 2, 4, 8...) |
Risk Management | Lower risk; limited loss per step | Higher risk; potential losses grow at each level |
Liquidity Requirement | Requires less capital to fully execute the plan | Requires significantly higher liquidity in later stages |
Behavior in Prolonged Downtrends | Controlled and tolerable loss | High probability of capital depletion or lock-up |
Profitability on Price Recovery | Gradual and steady | Fast and concentrated during short reversals |
Best Suited For | Medium-term investors with a fundamental outlook | Short-term, high-risk traders |
In conclusion, the Martingale strategy is riskier but faster, while the classic averaging method carries lower risk and is more suitable for long-term investment.
In the article martingale strategy tutorial on the website corporatefinanceinstitute.com, various aspects of this strategy have been examined.
Using the Martingale Strategy in Forex and Cryptocurrency Markets
Implementing the Martingale strategy in the forex market is more challenging compared to other platforms. It demands strong skills in trade volume calculation and a deep understanding of market behavior and influencing factors, making it unsuitable for beginners.
Implementing the Martingale method in crypto is challenging, but thanks to spot market buying, it has become a popular averaging strategy for generating profits.
When used correctly and with disciplined capital management, even novice traders can apply the Martingale strategy in crypto markets to seek profits from price rebounds.
Real Example of Implementing the Martingale Strategy in Forex
Suppose a trader opens a sell position on the EUR/USD pair at a price of 1.1095. If the price rises and the trade ends in a loss, the trader doubles the position size and opens another sell order at 1.1125.
In the third stage, the trader again doubles the position size so that, in the event of even a small market retracement, all previous losses can be recovered. Finally, if the price drops by only 15 pips, the profit from the third trade can offset the losses from the first two.
This example demonstrates that in the Martingale strategy, the timing of the market reversal and the trader’s ability to endure consecutive losses are two critical factors.
Stage | Trade Type | Entry Price (EUR/USD) | Trade Volume (Lots) | Distance from Previous Trade (Pips) | Trade Result | Profit/Loss (Pips) | Description |
1 | Sell | 1.1095 | 1 | - | Loss | -30 | The market moved against the position |
2 | Sell | 1.1125 | 2 | +30 | Loss | -30 | Position size doubled to recover the first loss on the next reversal |
3 | Sell | 1.1155 | 4 | +30 | Profit | +15 | A 15-pip decline generated enough profit from the larger position to cover the losses from the |
How to Execute the Martingale Strategy More Safely in the Cryptocurrency Market?
Implementing the Martingale strategy in the crypto market requires a precise combination of technical analysis and risk management to avoid heavy losses during periods of high volatility.
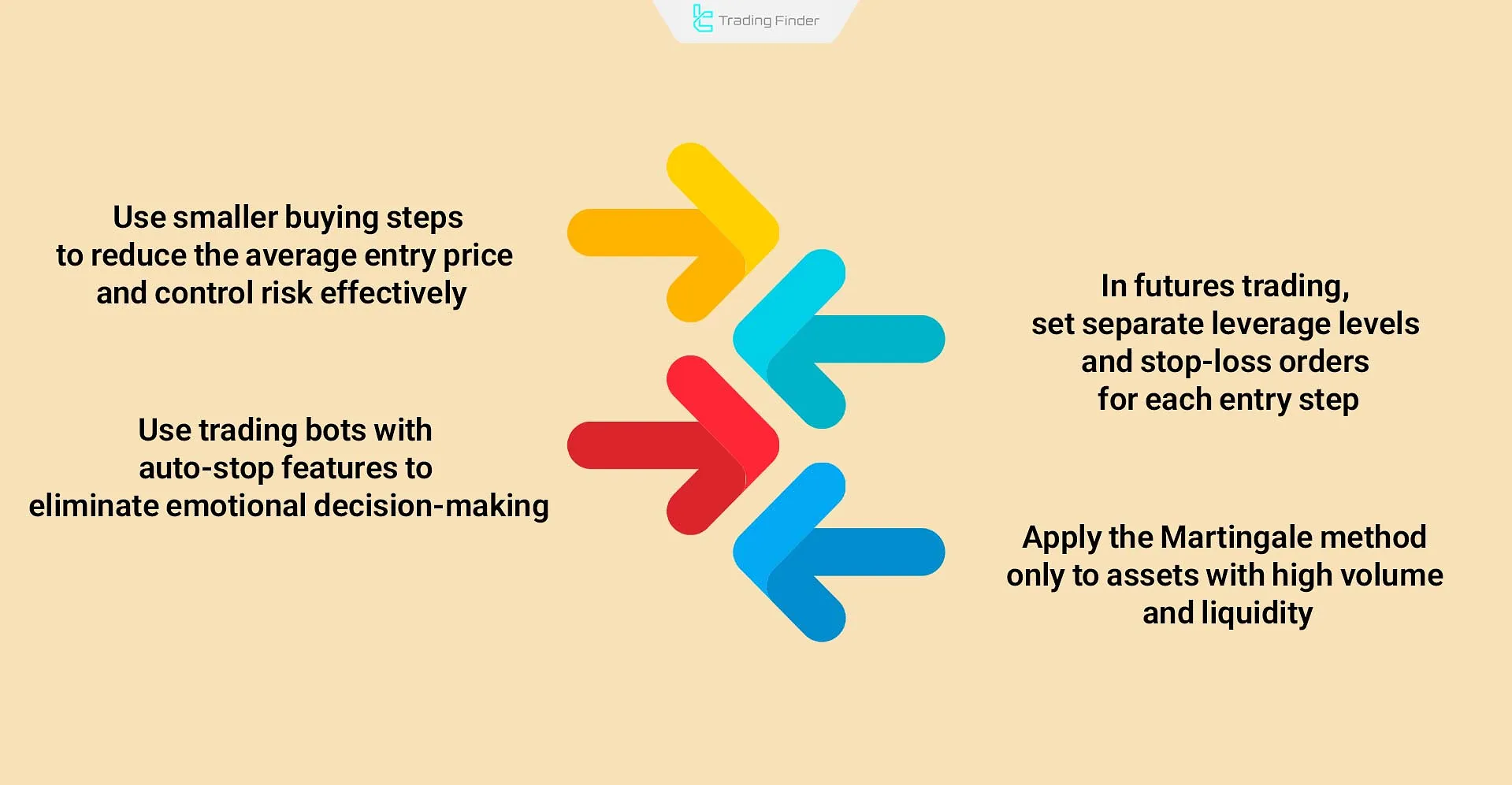
- In spot trading, use smaller buy steps so that the average entry price gradually decreases while keeping overall risk pressure limited;
- In futures trading, set different leverage levels and separate stop-loss orders for each step to prevent margin calls;
- Utilize trading bots equipped with auto-stop functions to eliminate emotional decision-making;
- Before applying the strategy, analyze the historical performance of cryptocurrencies and use it only on assets with high liquidity and large trading volume.
Key Points Before Applying the Martingale Strategy
Before implementing the Martingale strategy in highly volatile markets such as Forex, it is essential to follow these guidelines to preserve capital and manage risk effectively:
- Set a Clear Stop-Loss Limit: Always define your maximum acceptable loss in advance, and stop using the strategy after a series of consecutive losses;
- Start with Small Position Sizes: Begin with low trade volumes to minimize the impact of consecutive losses and prevent total capital depletion;
- Perform Statistical Analysis of Past Trades: Review historical data to assess the probability of price reversals in the chosen market, ensuring decisions are based on statistical evidence;
- Understand Currency Pair Behavior: Before applying the Martingale method, study the volatility patterns and movement characteristics of the currency pair to avoid entering trades under unfavorable conditions.
Key Considerations When Using the Martingale Strategy
The Martingale strategy is among the high-risk techniques in financial markets. If applied without proper risk management, it may lead to significant capital loss. Below are essential points for effective implementation:
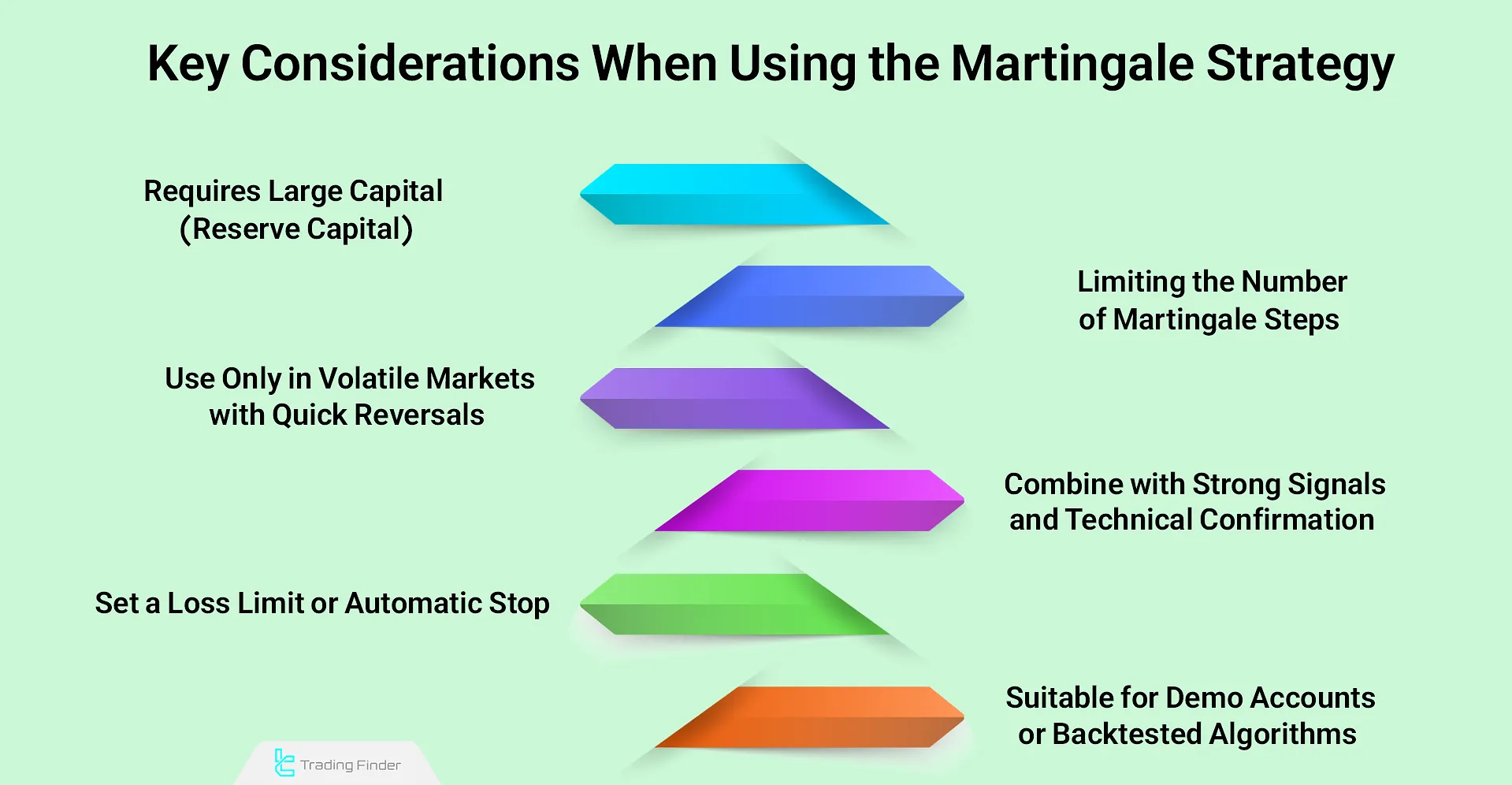
- Large capital reserve required: The Martingale method carries high risk and requires substantial backing capital to withstand multiple losses. Without it, accounts are quickly margin called;
- Limit the number of steps: It is recommended not to exceed 3 to 5 levels, as the risk of hitting the loss ceiling and full capital depletion increases drastically;
- Apply only in volatile markets with quick reversals: It works better in highly volatile markets like forex or crypto, and carries higher risk in strongly trending environments;
- Combine with strong entry signals and technical confirmation: Always base the initial entry on precise technical analysis. The Martingale strategy must not be used without a valid analytical setup;
- Define a strict loss cap or stop limit: Predetermine a loss threshold (e.g., stop after 4 losing steps). This reduces the risk of full account wipeout;
- Start with demo accounts or backtested algorithms: Always test the strategy on a demo or with backtesting. Applying it directly on a live account without prior testing is extremely risky.
Psychology and Emotional Control in the Martingale Strategy
Executing the Martingale strategy is not limited to volume calculations alone; the trader’s psychological discipline plays a decisive role in the success of this approach.
During consecutive losses, a trader must be able to remain calm and make decisions without emotional reactions or fear of further loss.
Emotional control, consistent strategy execution, and avoidance of impulsive responses to short-term market fluctuations are key traits of successful Martingale practitioners.
Practicing mental meditation and trading stress management techniques can also help maintain mental discipline and behavioral stability when applying the Martingale strategy.
MorFX Gold Digger A Expert Advisor Based on the Martingale Strategy for MetaTrader
The MorFX Gold Digger A Expert Advisor is an intelligent and fully automated trading robot designed specifically for the gold market (XAU/USD). Its primary function is to analyze market volatility and execute trades with precision in real time.
This EA (Expert Advisor) utilizes the Martingale strategy along with a set of advanced algorithms to identify price trends, determine optimal entry and exit points, and carry out trading operations without the need for manual intervention.
- Download MorFX Gold Digger A Expert Advisor for MetaTrader 5
- Download MorFX Gold Digger A Expert Advisor for MetaTrader 4
Operating on the MetaTrader platform, this Martingale-based EA falls under the category of AI Indicators and Machine Learning tools. Thanks to its user-friendly interface, traders at all level from beginners to professionals can easily use it.
The performance of MorFX Gold Digger A is built upon Multi-Timeframe Analysis, meaning it examines the market across different timeframes and combines historical data to identify high-probability trading opportunities.
A standout feature of this EA is its ability to add new positions when the market moves against the active trade. This approach helps adjust the average entry price, increasing the chance of returning to profit while controlling overall risk.
The 30-minute XAU/USD chart is a clear example of this system’s precise performance.
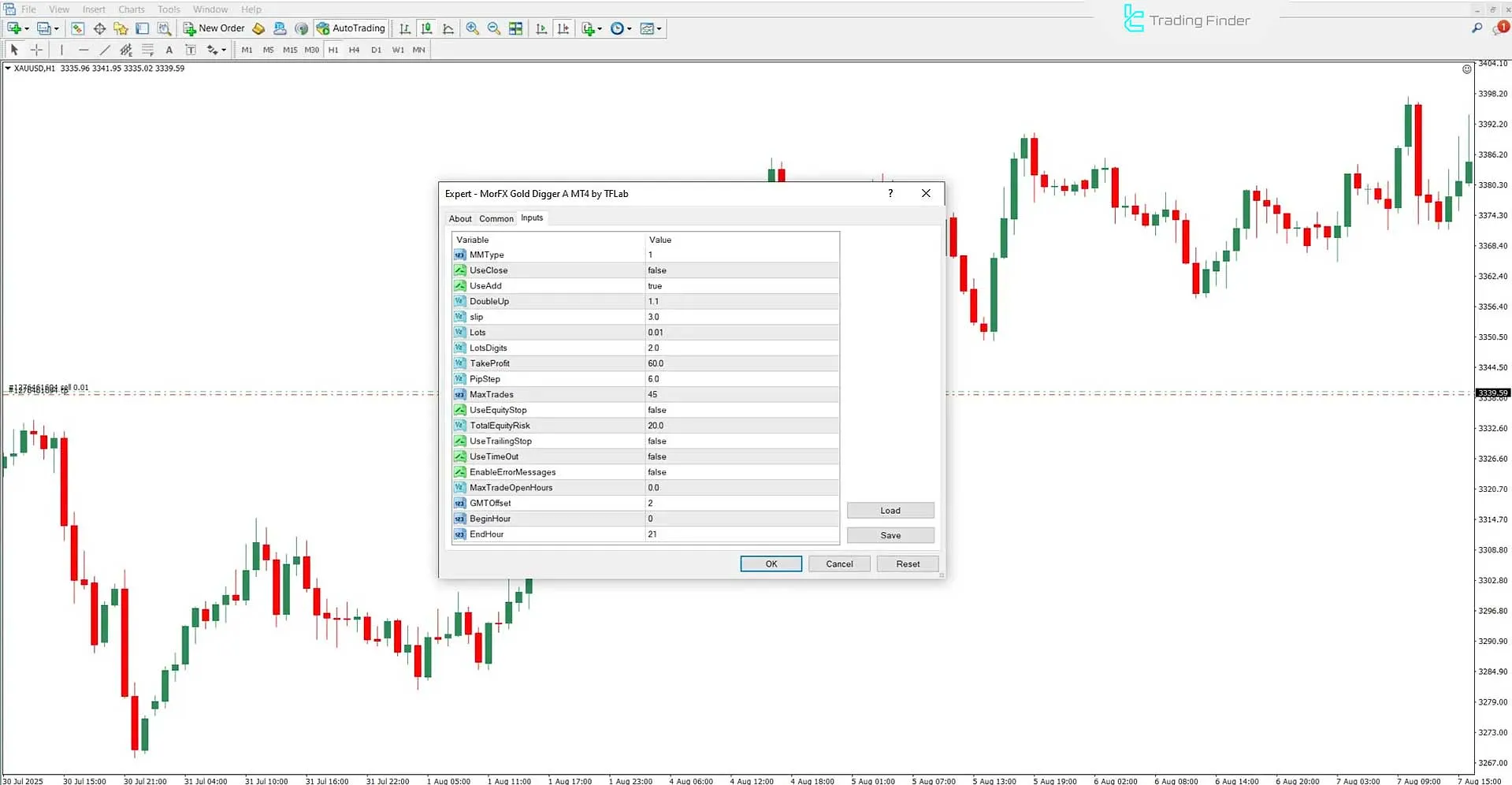
Within the settings panel, there are numerous parameters, including:
- MM Type to select the type of money management;
- Use Close to enable automatic trade closure;
- Use Add to activate additional position entries.
Other parameters such as Double Up (volume multiplier), Slip (price slippage control), Lots (initial trade volume), and Take Profit (target profit) are also available.
Additional settings like UseTrailingStop, MaxTrades, UseTimeOut, GMTOffset, BeginHour, and EndHour allow for precise control of trading conditions and time-based restrictions.
Overall, MorFX Gold Digger A, by combining artificial intelligence technology, the Martingale strategy, and flexible parameter customization, serves as a powerful tool for automated trade management in the gold market.
Conclusion
The Martingale strategy is a well-known capital management technique used in financial trading, where position size increases after each loss.
This method comes in multiple variations such as Classic Martingale, Reverse, Pyramid, and Grand Martingale and while it can potentially recover losses and restore profitability, it also carries a high risk of margin calls if poorly managed.
Successful application of this strategy requires technical knowledge, accurate market analysis, and strict risk control, especially in highly volatile markets like forex and cryptocurrency, where technical and emotional demands are greater.













