The amount of assets bought or sold in a trade is referred to as the position size. In different markets, position size has a different unit of measurement. For example, in the forex market, this unit is a lot.
Choosing the appropriate forex position sizing directly affects risk and money management. The position sizing in forex trading is calculated using the Risk to Reward Ratio, Stop Loss and Take Profit.
What Is Position Size?
Position size refers to the amount of an asset a trader risks in a trade, aiming to make a profit if their analysis proves accurate.
The trading position size determines the amount of potential loss or gain a trade may bring.
Inside the position size tutorial article on the Investopedia website, this concept is explained in a summarized form.
Forex Position Sizing Formula
To calculate position size, information about lot types and pip value in the trading account is required:
Lot Type | Units | Value Per Pip |
Standard Lot | 100,000 | $10 per pip |
Mini Lot | 10,000 | $1 per pip |
Micro Lot | 1,000 | $0.10 per pip (10 cents) |
Nano Lot | 100 | $0.01 per pip (1 cent) |
To calculate forex position sizing, you need:
- Dollar amount of risk per trade
- Entry-to-Stop Loss distance (in pips)
- Pip value per lot

Position Size Calculation Tools and Mobile Applications
For faster and more accurate calculations, traders can use online tools and mobile applications.
These tools reduce analysis time and minimize the probability of error; they are also useful for calculating various Forex position sizes.
Table of Position Size Calculation Tools:
Tool / Application | Features | Use Case |
OANDA Calculator | Simple interface, live price updates | Suitable for Forex traders |
BabyPips Calculator | Educational design, beginner-friendly | Risk management practice |
Myfxbook Calculator | Precise risk and stop-loss input capability | Professionals with large accounts |
Excel / Google Sheets | Custom formulas, high flexibility | Personal strategy development |
Mobile Applications | Direct connection to trading accounts | Quick on-the-go position sizing |
TradingFinder Position Size Calculator Tool
The TradingFinder Position Size Calculator is one of the most practical risk management tools in financial markets, calculating the optimal trade volume based on capital, risk percentage, stop-loss, and real-time rates.
This tool is available online and free of charge for Forex, cryptocurrency, stocks, and indices, helping traders stay within their personal risk limits.
Input parameters include the trading symbol, account base currency, account balance, risk percentage, stop-loss distance in pips, and the exchange rate.
The exchange rate can be automatically fetched from live market data or entered manually. The output calculations are also performed using a standard formula:
The results are displayed in three formats: standard lot, mini lot, and micro lot, making them suitable for different account types.
For example, with an account balance of €10,000, a 2% risk, and a 5-pip stop-loss, the risk amount equals €200, resulting in a trade size of 0.45 standard lots.
This output allows the trader to enter the exact volume in the trading platform and avoid excessive risk.
However, errors such as ignoring market volatility, setting the wrong risk percentage, or choosing an unrealistic stop-loss can invalidate the calculation results and lead to losses.
Carefully reviewing all parameters before performing the calculation is essential.
In addition to calculating trade volume, using this tool helps create discipline in the trading system and provides better control over emotions.
When the position size is pre-determined, impulsive decisions are reduced, and the risk-to-reward ratio of the strategy is maintained more accurately.
Overall, the TradingFinderPosition Size Calculator is an effective solution for both professional and novice traders who want to execute their trades systematically and measurably while adhering to risk management principles.
How to Choose Position Size Based on Strategy
Selecting the right position size depends on several strategic factors such as time frame, trade goal, trading psychology, and more.
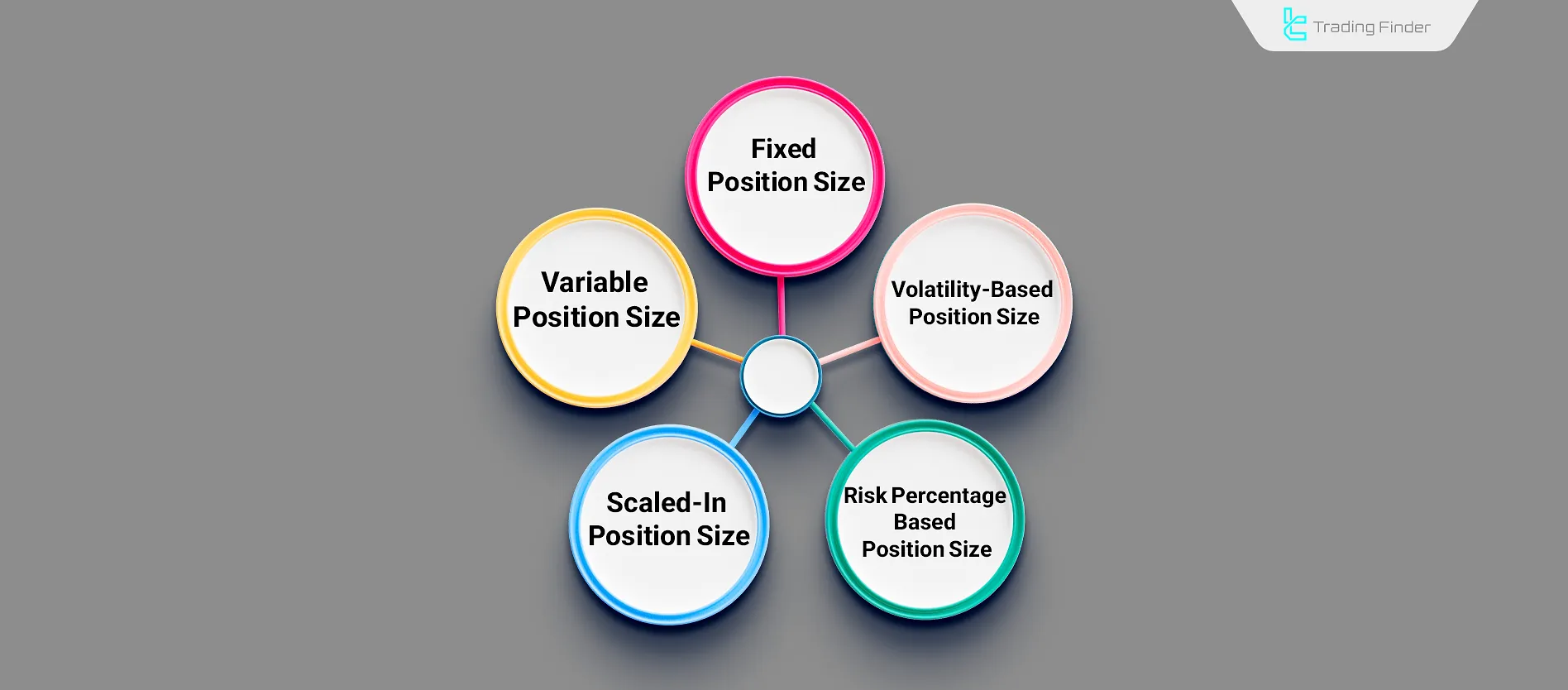
Fixed Position Size
In this method, the position size is calculated based on a fixed percentage of the total account balance (usually 2%). This is the same approach as the position sizing formula and position sizing forex trading.
While it's the simplest method, in trades with high risk and wide Stop Loss, it increases the risk to the entire account.
Position Size Based on Risk Percentage
In this method, a fixed percentage of the entire account (usually 2%) is used to determine the position size.
This is the most common approach, but since it requires calculation, entry opportunities may be missed.
Variable Position Size
In this method, there is no fixed formula for determining the position size in each trade; instead, the position size is defined based on the trade’s validity and market conditions.
This approach is an example of a position sizing strategy and offers high flexibility.
Though flexible and potentially more effective, it carries higher risk and requires strong strategy experience mistakes can lead to account-level risks.
Scaled-In Position Size
In medium- and long-term trades such as swing or position trading, there are multiple entry and exit points for each trade.
In this method, a percentage of the total trade volume is allocated based on the importance of each point. Using this approach in combination with volatility position sizing helps achieve optimal risk management.
This reduces missed entry risk but may lead to unused volume, which reduces overall profit.
Volatility-Based Position Size
This method uses volatility indicators like ATR to determine position size.
This method is related to the ATR position sizing formula forex. Depending on the level of volatility, the distance between the entry point and the stop-loss is determined.
The Stop Loss distance is based on volatility more volatility means a wider Stop Loss.
This can improve risk-to-reward by aligning Stop Loss with market volatility, but in short-term trades like scalping, the error rate of indicators increases risk.
Position Sizing Based on Account Balance
In this method, the position size changes along with fluctuations in the account balance.
If the account is in an uptrend, the position size for each trade increases compared to the previous one.
This method is sometimes referred to in educational materials as fixed ratio position sizing.
If the account is in a downtrend, the position size for each trade decreases compared to the previous one.
With this method, the account balance grows faster during an uptrend, and during a downtrend, it helps slow down the rate of capital decrease.
Position Sizing Based on the Kelly Criterion
The Kelly Criterion is a mathematical formula used to determine the position size best suited to a trading strategy and is considered part of professional position sizing formulas.
On the Financial Wisdom YouTube channel, position sizing based on the Kelly Criterion is explained in a detailed video:
Using this formula requires having a trading journal with at least 60 trades reviewed.
This formula consists of two main components:
- Win Rate (W): Calculated by dividing the number of winning trades by the total number of trades;
- Win/Loss Ratio (R): Calculated by dividing the average profit of winning trades by the average loss of losing trades.
position calculation formula:
Martingale
In the Martingale method, the position size of a trade is calculated based on the previous trade.
If the previous trade resulted in a loss, the position size for the next trade is doubled so that, if the new trade is profitable, both the previous loss is recovered and the profit from the new trade is added to the account balance.
This technique can be used in some buy market position sizing systems; however, it carries a high level of risk.
Position Size Management in Profit and Loss Conditions
Trade volumes should adjust according to recent performance to prevent large losses and optimize profits.
Gradually increasing position size after several consecutive wins, reducing it after two or three consecutive losses, and using trailing position sizing during strong trends are among the common approaches for dynamic management.
Gradual size increases after multiple wins and reductions after consecutive losses are examples of trade sizing and risk size approaches that help preserve capital.
Advanced Position Sizing Methods
In professional accounts, simply using a fixed risk percentage is not enough. Advanced methods help traders align with market volatility and their own trade statistics.
Examples include position calculation based on ATR, the fixed percentage method, and the advanced Kelly Criterion, which are all part of position sizing strategies .
Advanced Position Sizing Methods:
- ATR-Based Position Calculation: Adjusting position size dynamically according to real market volatility using the Average True Range (ATR) indicator;
- Fixed Fractional Method: Gradually increasing trade volume in sync with account growth;
- Advanced Kelly Criterion: Optimizing trade size based on win rate and win/loss ratio.
Practical Example of Position Size Calculation
A numerical example simplifies understanding of the formula and shows how much position size should be chosen in practice; in this example, the account risk is set at 2%.
This example is directly related to how to calculate position size forex.
Table below is an example of position size calculation:
Parameter | Value | Description |
Account Balance | $1,000 | Initial Capital |
Risk Percentage | 2% | Equivalent to $20 |
Stop-Loss Distance | 20 pips | Exit level of the trade |
Pip Value | $1 | Based on EUR/USD pair |
Calculated Position Size | 0.1 lot | Suggested trade volume |
Impact of Leverage and Margin on Position Size
Understanding the relationship between leverage and margin is essential to avoid margin calls.
Choosing a position size without considering these two parameters can wipe out an account within just a few trades.
Impact of leverage and margin on position size can be seen in the table below:
Account Leverage | Margin Required for 1 Lot EUR/USD | Risk Recommendation |
1:50 | $2,000 | Suitable for large accounts |
1:100 | $1,000 | Commonly used by retail traders and part of understanding forex position sizing formula |
1:500 | $200 | High risk, using less than 50% of available margin is recommended |
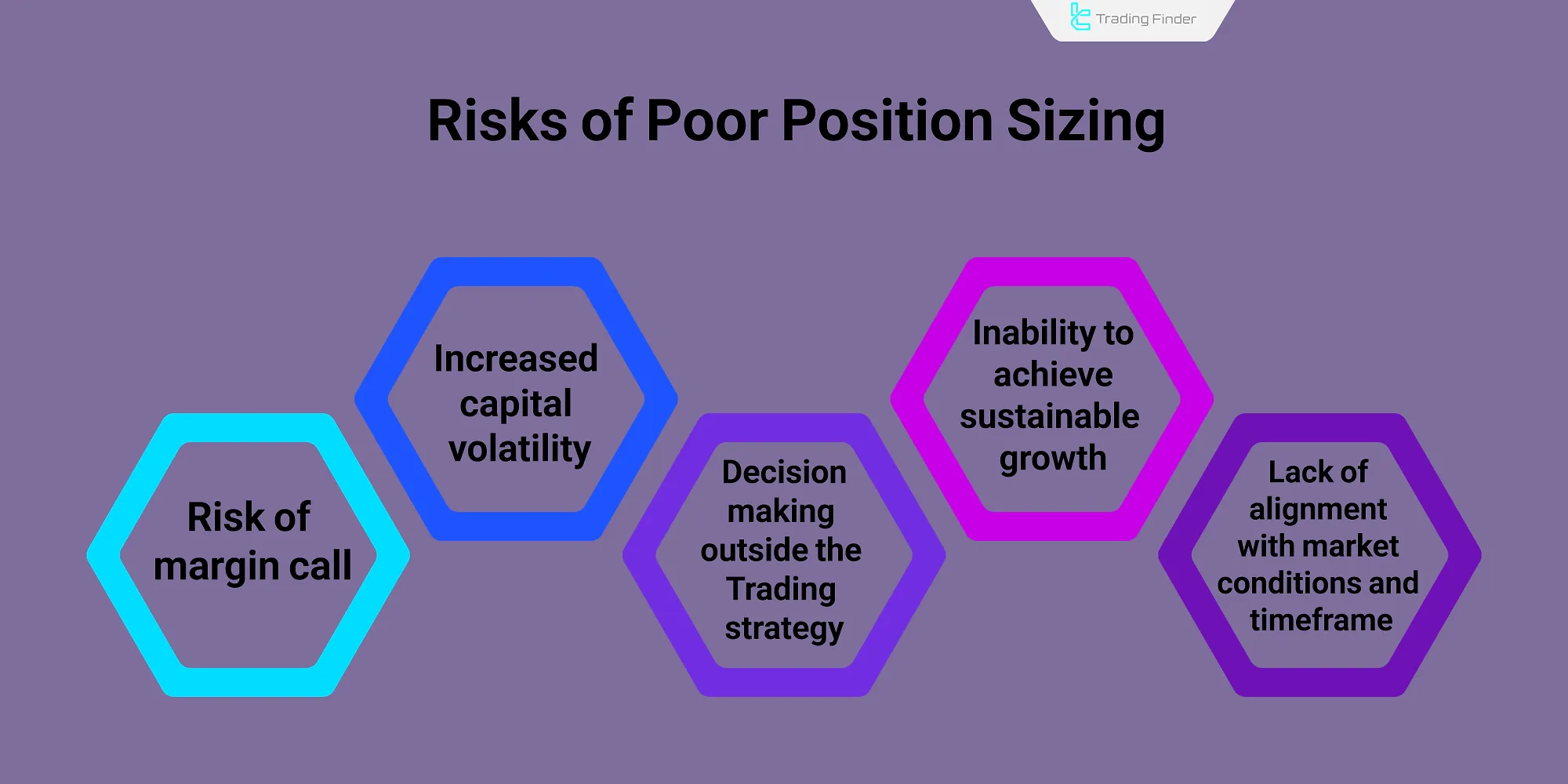
Risks of Ignoring Forex Position Sizing
Neglecting position sizing in forex trading leads to long-term capital loss.
Failing to manage position size affects account performance and introduces various risks:
Position Size in Different Trading Styles
Each trading style requires selecting a position size that matches the risk and market volatility.
Understanding these differences ensures your position size aligns with your overall strategy; this choice is particularly important in styles such as forex position trading:
Trading Style | Position Size Characteristics | Key Point |
Scalping | Small volume, short stop-loss | Large number of trades |
Day Trading | Medium volume, fixed risk | Suitable for M15 to H1 timeframes |
Swing Trading | Larger volume, deeper stop-loss | A few trades per week |
Position Trading | Volume aligned with long-term trend | Ability to withstand multi-day volatility |
Applications of Position Sizing
Choosing the correct position size has applications that ensure continuity in market participation and, over the long term, improve the risk-to-reward ratio while aligning with position sizing strategies.
- Controls risk in every trade
- Maintains trading strategy consistency
- Matches trade volume with market volatility
- Improves risk-to-reward ratio
- Prevents emotional decisions
Entry TP & SL Time Trader Manager Expert Advisor
The Entry TP & SL Time Trader Manager expert advisor is a semi-automated solution for precise management of fx position trades.
This tool combines timing and price condition settings to structure the execution process of trading orders and minimize manual errors.
In the trade entry section, it allows you to specify the type of position (buy/sell), the desired volume in lots, and the exact activation time.
By dragging the green line on the chart, the order execution time is defined, and if it coincides with the specified entry level, the trade is automatically triggered.
This feature is particularly useful for scenarios that require entry at a specific time.
Initial configuration is done by enabling the options Allow DLL imports , Allow imports of external experts, and Allow live trading to allow the expert to run and send orders.
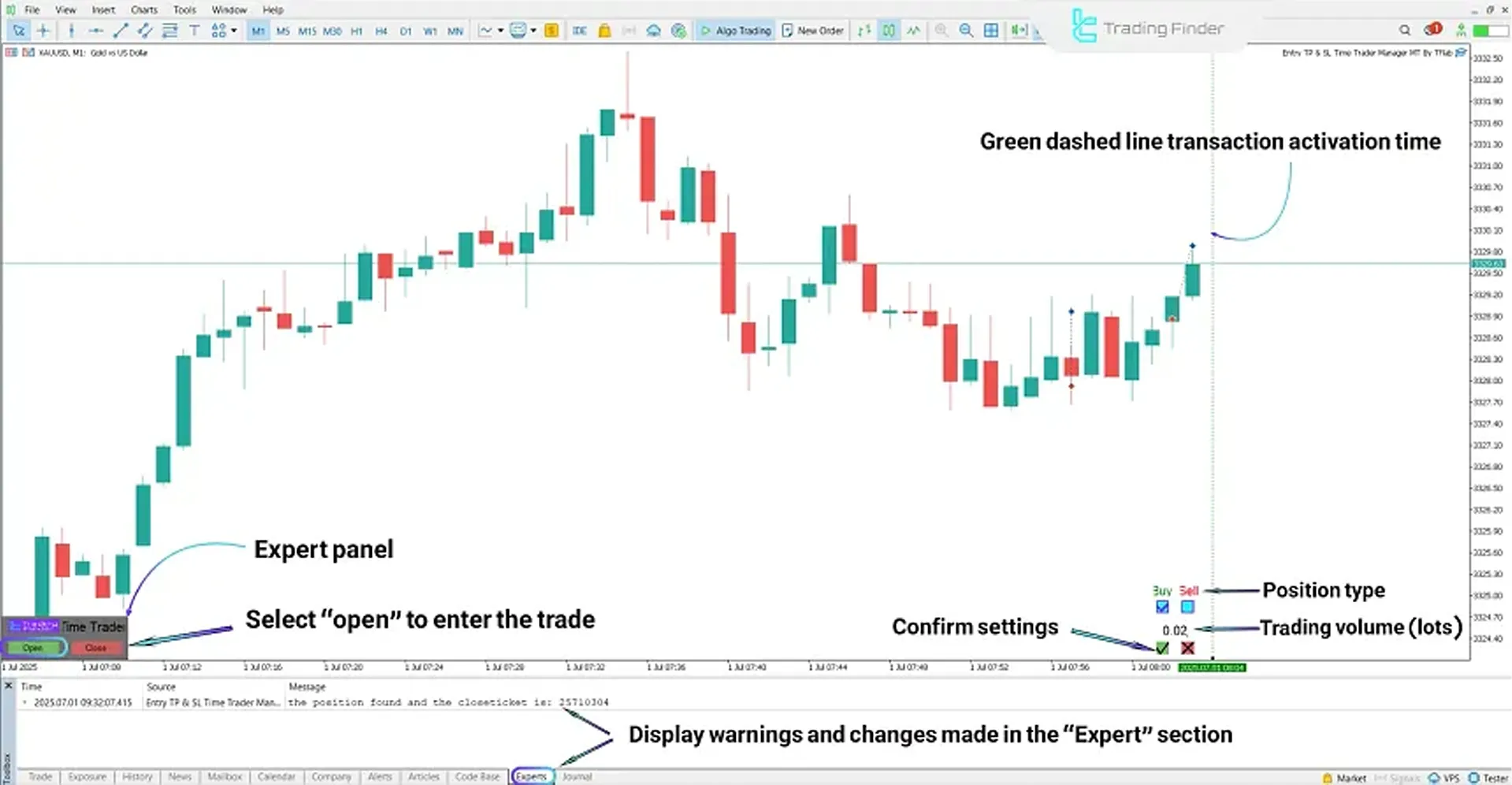
This expert advisor not only manages trade entries but also provides intelligent trade exit management.
TheClose panel displays three options: closing positions in profit, in loss, or both. You can also choose to close a portion of the trade volume (25%, 50%, or 100%) and set the red timeline for a scheduled exit on the chart.
Once confirmed, the position is closed automatically without real-time manual intervention.
Another advantage of this tool is the ability to set both price and time conditions simultaneously, ensuring trades are executed only when both conditions are met.
This feature is very important for reducing false entries and improving risk control.
Additionally, the ability to schedule partial position closures allows traders to implement multi-stage exit strategies.
This feature is particularly useful in highly volatile markets, enabling partial profit locking and gradual risk reduction.
- Download link for Entry TP & SL Time Trader Manager for MetaTrader 4
- Download link for Entry TP & SL Time Trader Manager for MetaTrader 5
Conclusion
The core of capital and risk management is choosing the right position size. Incorrect trading position sizing leads to account volatility and unstable returns.
Approaches like volatility-based sizing add flexibility under different market conditions.
Improving strategy performance in financial markets depends on time in the market. Managing position size ensures trading longevity.













