Trading psychology has a direct connection with a set of specific emotions and behavioral patterns. Emotional behaviors in the market attribute a large portion of impulsive trades to greed and fear, diverting the path of rational decision-making.
One of the most decisive factors for success in financial markets is paying attention to trading psychology, which in many cases is overlooked.
Professional traders believe that sustainable results in trading depend more on the individual’s level of mastery over the mind, emotions, and behavioral reactions than on reliance on technical analysis and fundamental analysis.

What is Trading Psychology?
Trading psychology examines the impact of traders’ emotions, behavioral patterns, and mental processes on their performance in financial markets.
This field analyzes factors such as fear, greed, self-confidence, and other emotions, and demonstrates their role in shaping trading decisions.
Uncontrolled emotions create irrational decisions and result in significant losses; therefore, mastery of the psychology of trading is recognized as one of the foundations of success in financial markets.
Key Concepts and Principles of Trading Psychology
Understanding the concepts and principles of trading psychology is highly vital for success in financial markets. Below, we address the key concepts and fundamental principles of trading psychology.
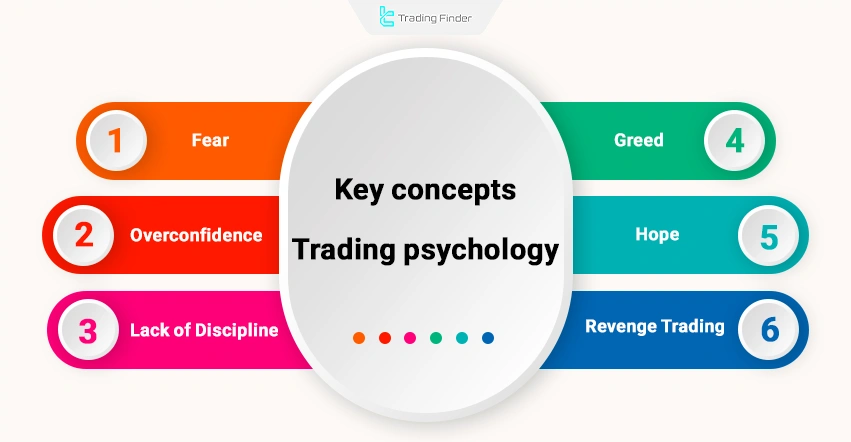
Key concepts of trading psychology:
- Fear: A natural reaction to loss or market instability, but if not controlled, it leads to premature exits from trades or delayed entries;
- Greed: Causes holding positions for too long or entering trades without a plan and is the main cause of overtrading;
- Hope and correction illusion: The trader does not accept the loss and hopes for a price reversal; this condition prevents the execution of a stop loss;
- Revenge trading: An attempt to quickly compensate for losses through emotional and illogical entries, which usually leads to greater losses;
- False confidence: After several successful trades, the trader becomes overly confident and abandons risk management;
- Lack of mental discipline in trading: The inability to adhere to a defined strategy, which is one of the most important reasons for failure in trading.
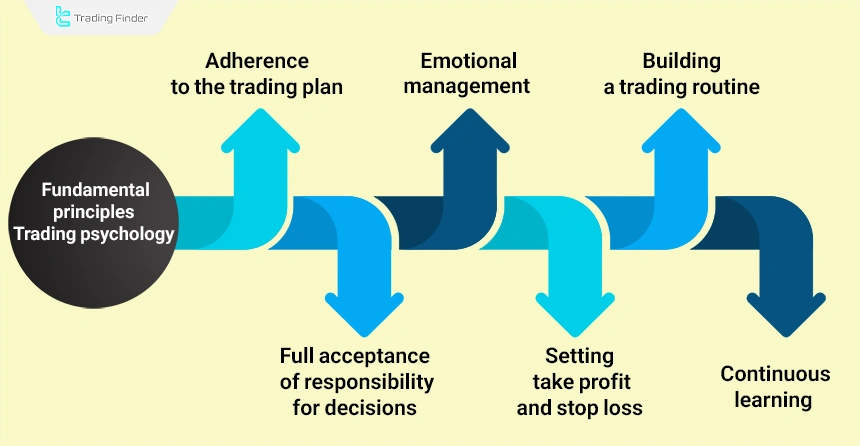
Fundamental principles of trading psychology:
- Adherence to the trading plan: No decisions should be made outside the plan, and the written trading strategy should be defined as the main reference;
- Emotional control: Emotions should be controlled in sensitive situations such as consecutive losses or high-risk positions;
- Full acceptance of responsibility for decisions: Positive and negative results should arise from individual choices, and blaming the market, broker, or other factors should be eliminated;
- Setting take profit and stop loss: The risk and profit range should be determined before entering a trade to prevent emotional reactions;
- Continuous self-reflection: Past mistakes should be reviewed, emotions during trading should be recorded, and results should be analyzed for mental and technical growth;
- Building a trading routine: A daily routine combining market analysis, mindfulness, note-taking, and performance review to maintain a trader’s mental stability.
Importance and Application of Trading Psychology
Trading psychology is considered one of the key pillars of success in financial markets, which receives less attention compared to technical analysis or fundamental analysis.
In practice, a significant portion of trading failures stems from weaknesses in emotional management and the trader’s mental instability.
Reasons for the importance of trading psychology:
- Emotional control: Emotions such as fear, greed, hope, and anxiety can disrupt rational decision-making and must be controlled;
- Behavioral stability: Strong psychology enables traders to adhere to their plans and avoid emotional behavior;
- Risk management: Accepting losses and maintaining calm in unfavorable conditions requires psychological discipline;
- Increasing trader confidence: Mental focus combined with identifying cognitive biases significantly improves the quality and accuracy of decision-making.
Without mastery of trading psychology, even the best strategies will not lead to sustainable profitability.
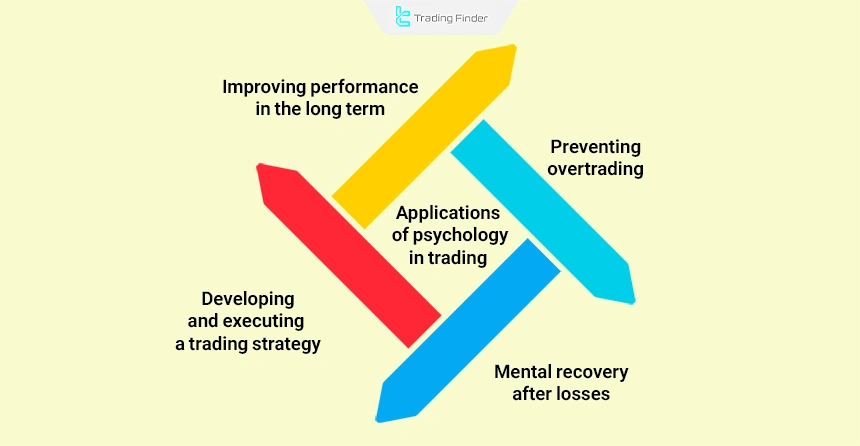
Applications of psychology in trading:
- Developing and executing a trading strategy: Prevents momentary temptations and enables accurate execution of the trading plan within the trading routine;
- Preventing overtrading: Traders who are not psychologically prepared usually trade excessively without sufficient analysis;
- Mental recovery after losses: The ability to return to the market after failure is one of the signs of psychological maturity in trading;
- Improving long-term performance: Healthy psychology allows decisions to be made without influence from momentary events and solely based on data and logic.
Effects of Trading Psychology on Successful Traders
Trading psychology includes a set of rules and techniques that, by focusing on experiences of failure and mental development, control trading behavior.
These rules and frameworks have had positive effects on the performance and returns of successful traders, as outlined below.
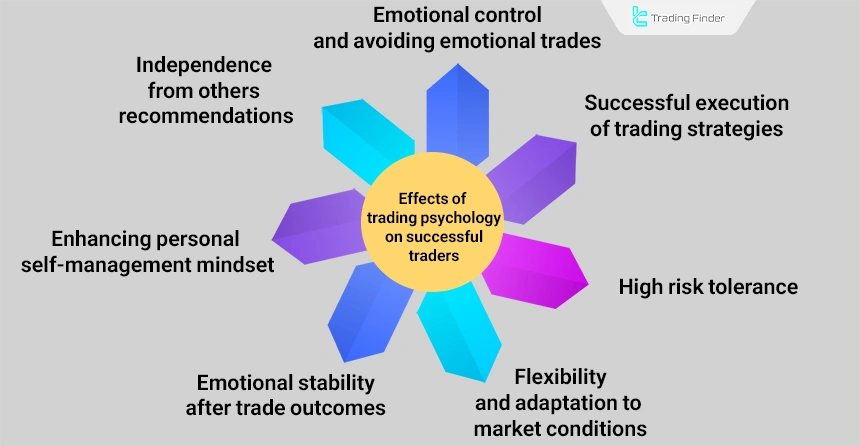
Effects of trading psychology on successful traders:
- They can make decisions without being dependent on others’ suggestions;
- They control their emotions and never trade based on emotions;
- With the help of trading psychology, they can execute strategies more successfully;
- They have developed their minds, are not afraid of taking risks, and have a high level of risk tolerance;
- They are highly flexible and can easily adapt themselves to market conditions without fear or stress;
- After a win or loss in a trade, they do not become quickly overly happy or upset and remain committed to their path;
- They enhance their self-management skills and manage capital in the best possible way.
Paying attention to trading psychology increases the ability to control emotional reactions and high-risk behaviors when facing losses and provides the groundwork for accurate and rational decision-making.
Market Psychology vs Trader Psychology
Market psychology and trader psychology form two distinct dimensions of mental behavior in trading that mutually influence each other’s decision-making and performance. In the table below, we compare market psychology and trader psychology:
Comparison criteria | Market psychology | Trader psychology |
Conceptual definition | The collective emotions, attitudes, and behaviors of market participants and their effect on price movement | The individual mental states, emotions, and thought patterns of the trader in decision-making |
Level of analysis | Macro, collective, and systemic level | Micro, individual, and personal level |
Focus axis | Collective fear and greed, public excitement, herd behavior, market optimism and pessimism | Fear of loss, profit greed, excessive self-confidence, stress, personal discipline |
Source of formation | Simultaneous interaction of a large number of traders | Personality traits, experiences, beliefs, and individual emotional control |
Relation to price | Formation of trends, bubbles, corrections, and price crashes | Timing of entries and exits, trade size, and adherence to strategy |
Degree of controllability | Not individually controllable, but identifiable and interpretable | Manageable and improvable through training and practice |
Analysis tools | Market sentiment, fear and greed index, trading volume, price action | Trading journal, risk management, trading rules, mental practice |
Impact on trading performance | Creating an environment of opportunities and threats | Quality of the individual’s reaction to market conditions |
Common errors | Price bubbles, collective panic, widespread emotional decisions | Overtrading, revenge trading, violation of the trading plan |
Importance in long-term success | Alignment with the overall market flow | Mental stability and sustainable profitability |
Mutual relationship | Influencing the trader’s mind and emotions | Being influenced by the market’s psychological environment |
An educational video published on the OPTO channel on the YouTube platform addresses the psychology of trading in the process of income generation, and interested individuals can watch it to gain further insights.
Trading Psychology of the Cryptocurrency Market
Trader psychology in the cryptocurrency market is very similar to other financial markets in terms of mental structure; however, differences in operating conditions and the composition of the active community in this market create clear distinctions.
The absence of traditional fundamentals, unpredictable volatility, and widespread emotional behavior are among the factors that differentiate cryptocurrency trading psychology from other markets and influence the decision-making framework.
Differences in trading psychology between the cryptocurrency market and traditional markets:
Cryptocurrency market | Traditional markets | Differentiating factor |
Very high | More controlled | Volatility |
Very limited | Structured and analyzable | Access to fundamental data |
Lower, newer population | Higher, more professional | Traders’ experience level |
24/7 and uninterrupted | Defined trading hours | Market operating time |
Very intense fear and greed | Relatively balanced | Intensity of psychological emotions |
The Role of Trading Psychology in Proper Execution of a Trading Plan
Many traders develop a trading plan, but weak trading psychology prevents its accurate execution. Trading psychology directly affects the execution of trading plan components and defines the gap between planning and actual performance.
At the entry point, emotional traders often enter trades earlier or later than the optimal time and ignore the analytical structure. In setting a stop loss, fear of loss leads to moving the stop loss or rendering it ineffective.
At the exit point, greed causes traders to remain in profitable positions for too long and disrupts the risk-to-reward balance.
In practice, a trading plan without mental control turns into a non-executable document, and its success remains dependent on the trader’s psychological stability and behavioral management.
In the trading psychology educational article published on the IG.com website, more detailed and specialized explanations are provided, and interested readers can refer to this educational resource.
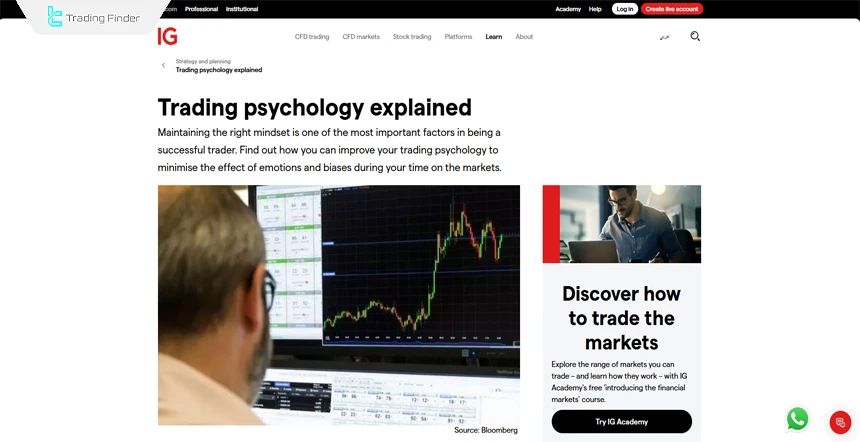
Common Trader Problems in Trading Psychology
Various psychological problems can challenge traders along the trading path. Overcoming these challenges through self-awareness, emotional management, and developing a successful trading strategy is essential.
Common problems in trader psychology:
- Fear: Fear of loss prevents the trader from entering a trade or exiting logically and eliminates profitable opportunities;
- Greed: Greed leads to ignoring secured profits and remaining in a trade until it turns into a loss;
- Anxiety: Mental pressure caused by tracking trade outcomes reduces focus and disrupts decision-making;
- Lack of concentration: Stress, mental fatigue, and environmental factors weaken accuracy and mental control in the trading process;
- Hasty decisions: Emotions such as fear and greed override logical analysis and create impulsive behavior;
- Failure to adhere to strategy: Psychological pressure causes the trader to deviate from the defined trading strategy;
- Overtrading: Increasing the number of trades without clear logic intensifies financial losses and mental tension;
- Revenge trading: Attempting to compensate for losses with higher-risk trades increases the likelihood of heavier losses;
- Ego and false confidence: Consecutive profits create an illusion of control and push risk management principles aside;
- Hopelessness and loss of focus: Repeated failures exhaust the mind and perpetuate a cycle of behavioral errors.
A Real Example of Trading Psychology Errors
For example, in one trade, the price moved according to the trader’s analysis after entry, and the position reached a profit zone of $350.
Based on the trading plan, this area was the best point to close the trade or at least secure profit; however, due to greed and expectation of higher gains, the trader refrained from closing the position.
With a shift in market momentum, the price gradually reversed, and eventually the trade was not only closed without profit, but first reached the breakeven point and then closed with a $120 loss.
Whereas if the trader had adhered to the principles of trading psychology and controlled emotions, the same trade could have been concluded with a definite $350 profit.
This example shows that lack of mental discipline and inability to execute the trading plan can completely reverse the outcome, even in correct and profitable trades.
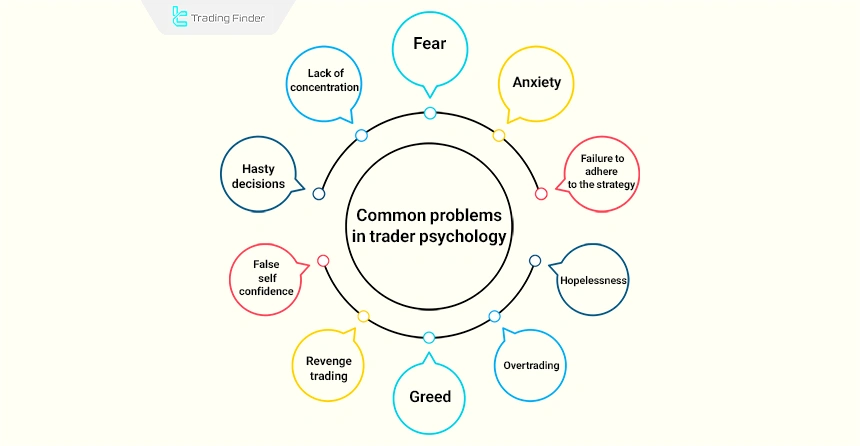
Methods for Solving Trading Psychology Problems
Solving trading psychology problems is one of the most vital components of success in financial markets. Many traders, despite having strong analytical knowledge, suffer heavy losses due to mental and emotional challenges.
Below, we address the most important scientific and practical methods for dealing with trading psychology problems:
- Having a precise trading plan: A trading plan includes entry rules, exit rules, stop loss, capital management, and psychology. When decision-making is predefined, momentary emotions have less impact;
- Capital management and risk control: No strategy works without risk management; using stop losses, clear risk-reward ratios, and limiting risk per trade reduces stress and fear;
- Recording and analyzing a trading journal: Recording emotions, reasons, and outcomes for each trade helps identify negative behavioral patterns;
- Practicing mindfulness and meditation: Practices such as daily meditation or deep breathing before trading increase awareness of emotions;
- Defining realistic expectations of the market: Much stress comes from unrealistic expectations, and accepting losses as part of the market reduces psychological pressure;
- Creating a daily trading routine: Having specific times for analysis, trading, and rest creates mental order. Trading without structure disturbs the mind and allows emotions to dominate;
- Avoiding revenge and emotional trades: If you have incurred consecutive losses in one day, not trading is better than trading under high emotional pressure;
- Setting rewards for discipline in trading: Reward yourself for following plan rules; this leads to forming correct behavioral habits;
- Working with a trading psychologist or professional coach: If you feel your problems are deep and beyond control, consulting a trading psychology specialist can be an effective solution.
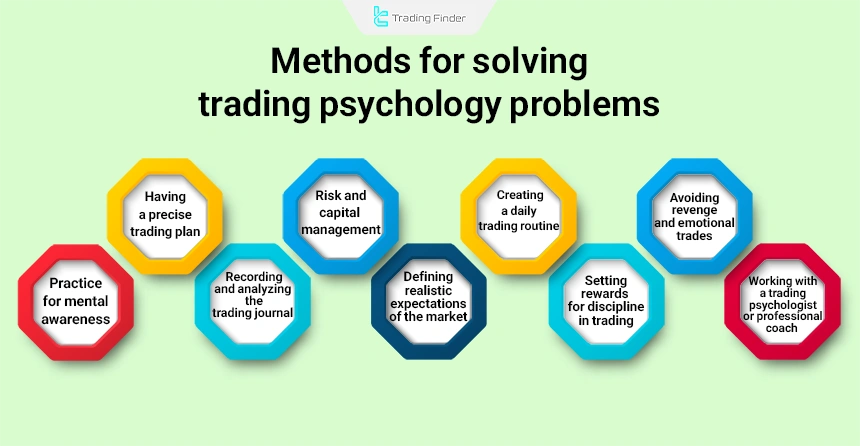
Important trading psychology tips
Below, we discuss the most important key points of trading psychology in a practical manner. Paying attention to these points is essential for success in financial markets, especially in highly volatile markets such as cryptocurrencies.
Key points regarding trading psychology:
- Controlling emotions and overcoming fear and greed in trading;
- Overcoming fear of missing out;
- Maintaining personal discipline;
- Accepting losses as part of the nature of the market;
- Using risk and capital management intelligently;
- Continuous learning and maintaining a sustainable growth mindset;
- Avoiding excessive trading or overtrading;
- Maintaining psychological balance during severe market volatility;
- Independent thinking and avoiding blind imitation of others in trading;
- Rest and mental recovery.
Trader Mental Burnout and its Impact on Decision-Making
One of the less-discussed challenges in trading psychology is mental burnout caused by continuous and uninterrupted trading.
Traders without a defined time schedule gradually experience reduced concentration, increased decision-making errors, and intensified emotional reactions.
Signs of mental burnout include impatience, impulsive decision-making, ignoring trading rules, and reduced motivation in the trading process.
Defining specific time intervals for trading, creating regular breaks for mental rest, and limiting the number of trades reduce psychological pressure and maintain mental stability.
At a deeper level, mental burnout leads to a reduction in cognitive processing capacity and weakening of the brain’s executive control; meaning the trader loses the ability to evaluate alternative scenarios and identify personal mental and behavioral errors.
This condition increases the likelihood of biases such as false confidence or avoidance of accepting losses and transforms trading performance from a systematic process into a reactive and unstable one.
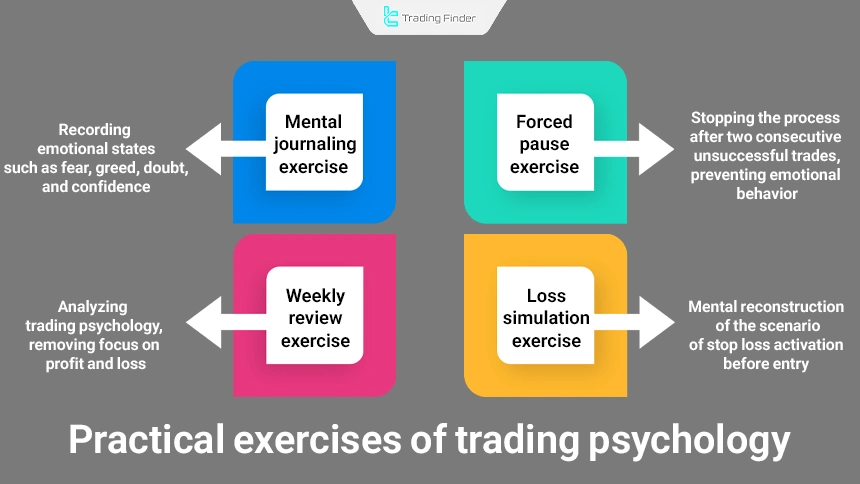
Practical trading psychology exercises
Trading psychology is not strengthened solely through study and requires continuous practical practice. Some effective exercises include:
- Mental journaling exercise: Before each trade, emotional states such as fear, greed, doubt, or confidence should be recorded;
- Forced pause exercise: After 2 consecutive unsuccessful trades, the trading process should be stopped to prevent emotional behavior from forming;
- Loss simulation exercise: Before entering a trade, the scenario of the stop loss being triggered should be mentally reconstructed;
- Weekly review exercise: The week’s trades should be analyzed solely from a trading psychology perspective, with the focus removed from profit and loss.
Identifying personality type facilitates choosing an appropriate trading strategy and strengthens targeted emotional management in the decision-making process.
Risk Reward Indicator in MetaTrader for Better Trade Risk Management
The Risk Reward Indicator is considered one of the specialized tools in capital management, which numerically and transparently displays the ratio between potential risk and expected profit before entering any trading position.
The main output of this tool determines the risk-to-reward ratio and shows what level of potential return justifies accepting a certain amount of risk.
In the MetaTrader trading environment, this indicator is designed as a risk management tool and visually defines the trade structure by drawing 3 horizontal lines on the chart. These lines include the entry price, stop loss, and take profit.
At the same time, the value of the risk-to-reward ratio is displayed in a section of the chart so that trade quality can be evaluated without manual calculations. The calculation basis of the Risk Reward Indicator is designed to be simple yet precise.
In buy trades, the price distance between the entry point and the stop loss is considered the risk, and the price difference between the entry and the take profit represents the trade’s reward.
In sell trades, the same logic is applied with reversed calculation direction. In both cases, the main focus is on assessing the justification of potential profit against possible loss.
This indicator is applicable in various trading styles, including day trading and multi-timeframe analysis, and its simple structure makes it usable even for beginner traders.
The scope of use of this tool is not limited to a specific market and can be applied in markets such as Forex, Cryptocurrency, and Stocks.
In the settings section, various options are defined for customization, ranging from changing the colors of entry, stop loss, and take profit lines to adjusting font size, information display position, and line styles.
This flexibility turns the Risk Reward Indicator into a practical tool for risk control, optimizing trade structure, and making informed decisions in financial markets.
Conclusion
In the complex world of trading, trading psychology is not only a complement to technical and fundamental analysis, but is also recognized as the main pillar of intelligent decision-making.
Mastery over emotions such as fear, greed, false confidence, and revenge trading distinguishes a professional trader from an emotional trader.
Successful traders, by using tools such as a precise trading plan, trading journal, risk control, and even a daily psychological routine, train their minds in a sustainable way to remain resilient against the volatility of high-risk markets such as cryptocurrencies.
A deep understanding of trader and market psychology concepts, along with the use of techniques such as pre-trade meditation, forms the foundation of proper performance in financial markets.













