Money management encompasses a set of rules designed to maximize investment returns while mitigating risk. Therefore, in the long term, effective money management in trading enhances trading performance and ensures continuity across various markets, such as the Forex market.
In money management, various factors, such as the risk-to-reward ratio, win rate, capital amount, trader personality, and others, are considered to control account losses and plan for potential profits.
Additionally, determining parameters such as Maximum Drawdown and per-trade loss plays a crucial role in optimizing the money management process.

What Is Money Management?
Money management is a key element of account control, where the trader employs various strategies to maximize account returns while minimizing risk.
Proper money management in trading encompasses multiple components, including evaluating returns, investment duration, trade risk, and other key factors.
What Is Capital Management in Trading?
Capital management in trading refers to a set of rules based on which the trader determines how much of the capital is involved in each trade and, in the event of a loss, how much of the account is acceptable.
This concept, commonly known as money management forex in the Forex environment, helps increase returns and control account fluctuations, allowing the trader’s activity in the market to remain stable.
In capital management, factors such as stop loss, position size, and risk to reward ratio play a central role. In the capital management training article in Forex on the MondFX website, this concept is explained in full:
Why Is Capital Management Necessary in All Financial Markets?
Financial markets are always accompanied by volatility, and no analysis has absolute certainty. A capital management plan helps ensure that during losing periods, a large portion of the account is preserved and the possibility of continuing to trade remains.
Using capital management principles also reduces the psychological pressure of trades and allows decisions to be made more rationally.
Key Components of Money Management
To define money management rules, factors such as the risk-to-reward ratio and the success rate of the trading strategy must be analyzed.
Moreover, items such as Maximum Drawdown, per-trade loss, and other limits must be specified.
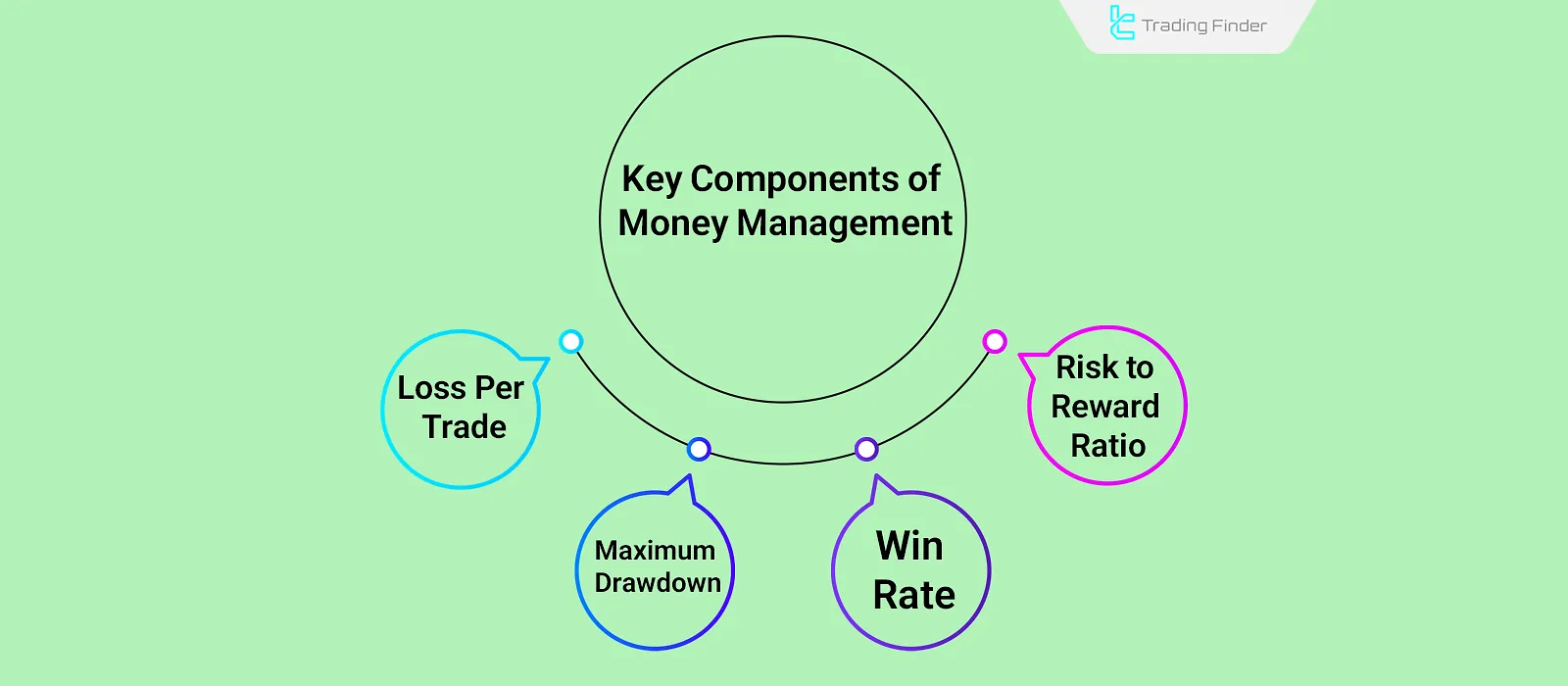
Various components of money management:
- The risk-to-reward ratio of trades: This ratio shows how many units of profit are at stake for every unit of risk;
- Strategy win rate: This shows the percentage of winning trades relative to losing trades;
- Maximum Drawdown: This refers to the maximum loss the total capital can tolerate;
- Loss per trade: This item, more specifically, defines the potential loss in each trade.
Benefits of Money Management in Trading
Effectivemoney management in trading supports sustained marketactivity andenhances the returnrate of the trading strategy. Key benefits include:
- Continuity in the market
- Preserving a large portion of capital during losing trades
- Reducing stress and pressure during trades
- Increasing the account’s return rate
Why Is Money Management Important?
In financial markets, no strategy offers a 100% success rate. Thus, there is always a possibility that prices will move against the trader’s analysis.
Effective money management helps preserve a large part of the capital in such situations, creating opportunities for additional trades and offsetting previous losses.
It also aids in increasing profits and maintaining the ability to keep operating in the market.
Factors Influencing Money Management
The implementation of money management depends on several factors, including the trader’s personality, available capital, market type, trading goals, and others.
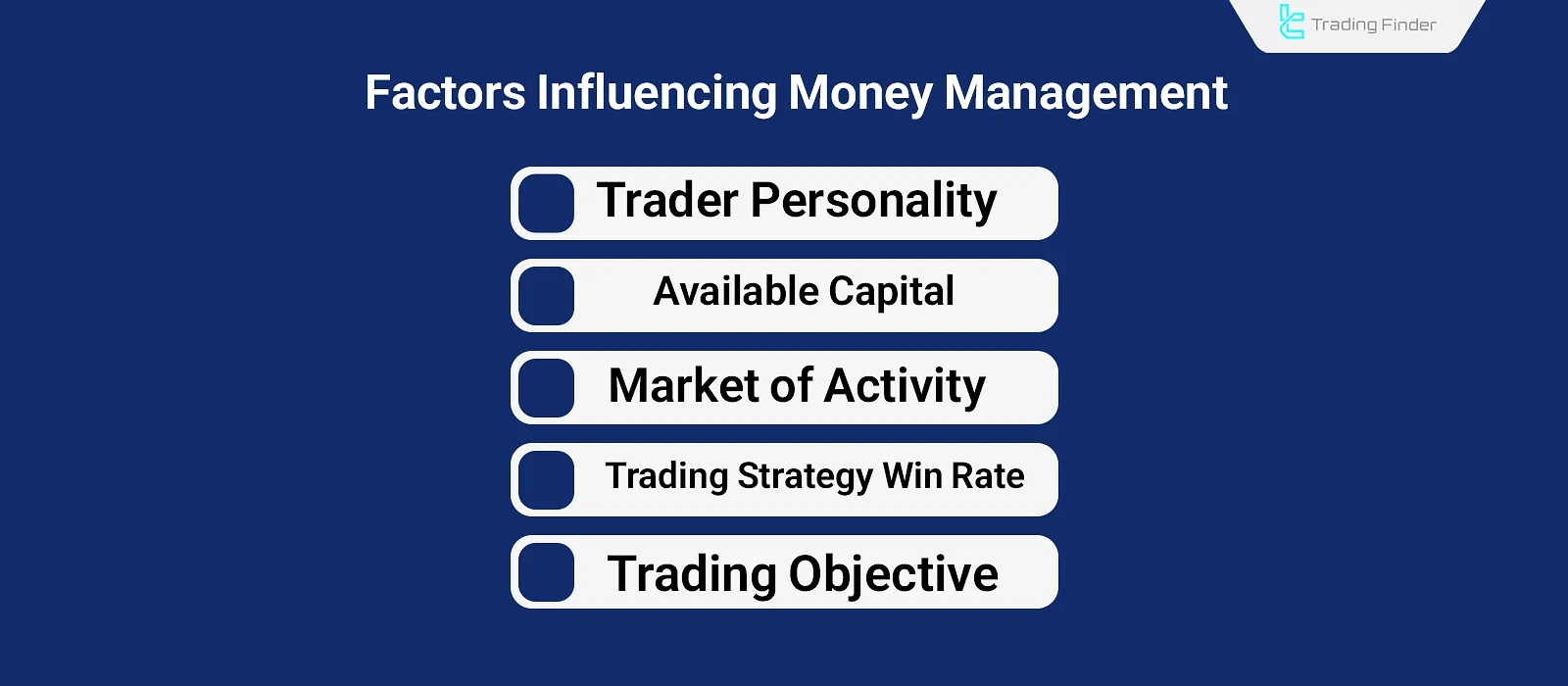
Factors affecting money management:
- Trader Personality: Based on a trader’s risk tolerance, trade size, and selected markets may vary;
- Capital size: The available capital for trading directly influences market activity and reasonable risk levels per position;
- Market type: Different markets come with different levels of volatility and risk, which affects how risk is assessed and managed;
- Win Rate: Each trading strategy has a different success rate; thus, different money management techniques apply to each;
- Trading goals: Based on whether the objective is long-term or short-term, money management styles differ across trading plans.
Difference Between Money Management and Risk Management
Money management, in general, encompasses both aspects of trading, meaning that money management covers both profits and losses.
On the other hand, risk management takes a more specific approach by focusing on managing losses and preserving assets during critical situations.
In summary, decisions regarding how capital is allocated and utilized fall under the scope of money management in trading. In contrast, strategies for dealing with investment risks are classified as risk management.
Stages of Implementing Capital Management
Implementing capital management is a step-by-step process that includes the following elements; these stages ensure that the way capital is used remains coordinated and controllable:
- Analyzing market conditions and the level of volatility;
- Defining trading objectives and the acceptable level of risk;
- Selecting the appropriate position size for each trade;
- Executing the trade with a defined stop loss;
- Evaluating trade performance and adjusting the capital management method.
Capital Management in the Forex Market
In the Forex market, due to the presence of leverage, the importance of capital management forex is greater. The trader must choose a position size that is aligned with their level of risk tolerance.
Using an appropriate stop loss, selecting a logical risk to reward ratio, and avoiding excessive use of leverage are among the core principles of forex money management.
Types of Money Management Methods
Money management strategies can be divided based on the trader’s risk appetite into three main categories: conservative, aggressive, and hedging.
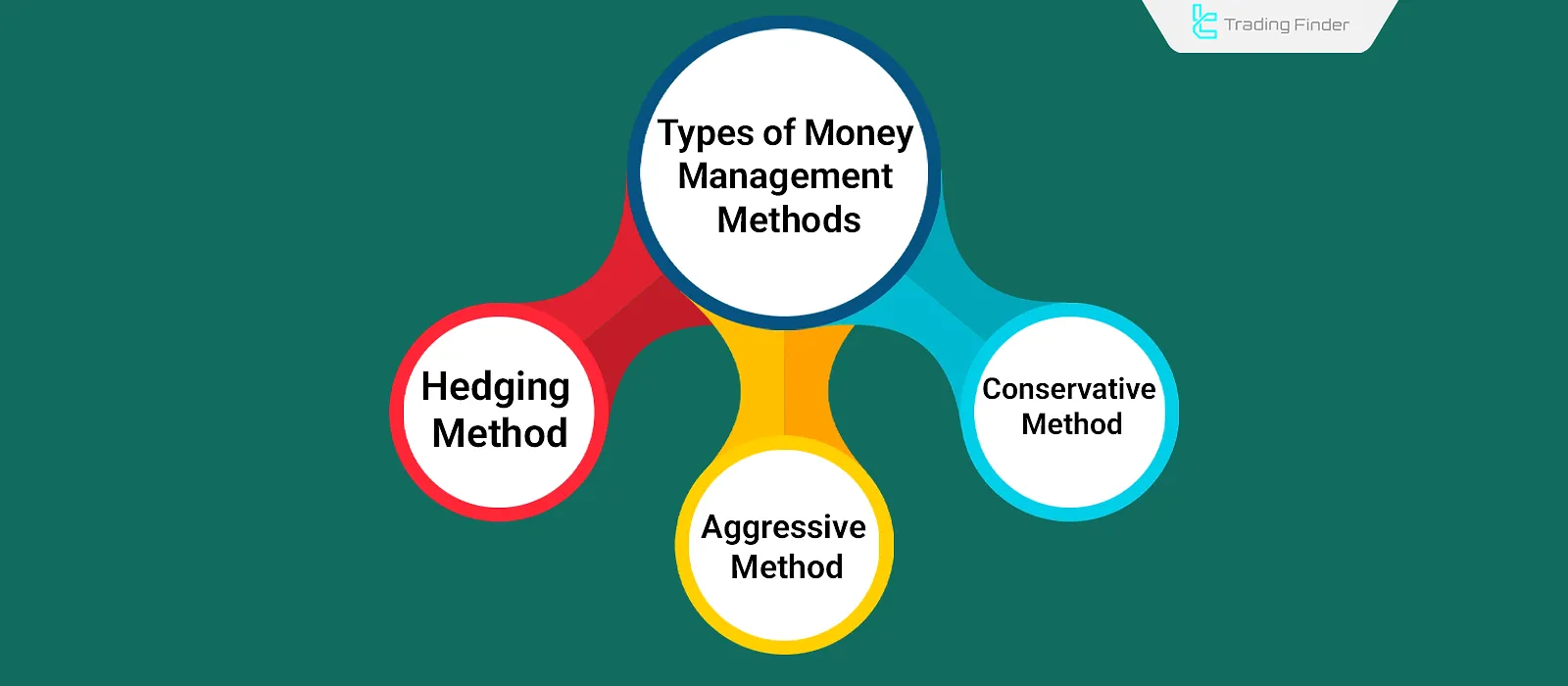
Conservative Method
In this method, investment risk is reduced by diversifying assets across different markets and instruments.
Additionally, a significant portion of the capital remains in cash, ensuring that the required funds are available to enter a trade when a suitable investment opportunity arises.
Aggressive Method
In the aggressive method, the focus is on maximizing profits and accepting higher levels of risk. This means that by investing in high-risk assets and allocating a large portion of capital to each trade, the potential return on investment increases.
In this method, leverage is used to amplify profits; therefore, the risk associated with this type of money management also increases.
Hedging Method
In this method, various trading styles, such as hedging, are used to reduce risk and enhance the return on investment.
Additionally, investments are made in markets with negative correlation so that if one position results in a loss, the profit from the opposite trade can offset the loss.
To evaluate the correlation between Forex currency pairs, you can use the Forex Pair Correlation Tool provided by the TradingFinder.
Popular Money Management Techniques
There are various techniques to tailor money management in trading to specific strategies. These techniques vary in risk tolerance and expected return.
The 2% Rule
According to this method, regardless of prior trade outcomes, only 2% of the account balance is risked per trade. As capital grows, so does the potential profit per trade, while the downside per trade decreases during losses.
Consistently applying this technique accelerates account growth during profitable streaks and slows down capital depletion during losing streaks.
Example of Capital Management Calculation Based on the 2% Rule
Assume the account balance is 1000 dollars and the acceptable risk level is 2 percent. In this case, the allowable loss for each trade within trading capital management is 20 dollars.
If the stop loss of the trade is 20 pips, the position size should be selected in such a way that each pip equals 1 dollar in loss. This method ensures that the position size is determined based on risk, not emotions.
When a trade ends in a loss, the size of the next position is recalculated using the updated account balance, which gradually slows the rate of capital decline during a losing sequence.
Conversely, during a winning sequence, position sizes increase with account growth, accelerating capital expansion, unlike methods such as Martingale money management.
On the YouTube channel Spencer Li - Synapse Trading, this capital management method is taught in video format:
Martingale Technique
Martingale is a high-risk money management technique. After every losing trade,the position size is doubled. Thus, a winning trade can recover prior losses and add to the account's profit.
However, a series of consecutive losses can lead to margin calls due to the increasing size of positions.
Anti-Martingale Technique
With the Anti-Martingale technique, after a losing trade, the position size is halved. This dramatically reduces the rate of capital depletion and almost eliminates the chance of a margin call.
However, since the trade size is reduced after each loss, it takes more winning trades to recover the previous losses fully.
Portfolio Rebalancing
In thismoney management method, when one investment becomes profitable, a portion of the profit is withdrawn from that position and added to another active trade that has not yet yielded a profit.
For example, consider a portfolio consisting of 50% gold and 50% silver.
If the price of gold increases, the portfolio shifts to 70% gold and 30% silver. In this case, part of the profit from the gold position should be converted into silver.
This way, the capital distribution in the portfolio is rebalanced equally between gold and silver.
Factors Affecting Capital Management
The quality of capital management in trading depends on a set of factors. The most important of them include the following; these factors determine to what extent capital management trading can prevent severe account fluctuations:
- The trader’s level of risk tolerance as a money management trader
- The expected return
- Asset diversification
- Trade timing
- Trading costs
- Analytical ability and adherence to the trading plan
Advantages of Capital Management in Trading
One of the advantages of following trading money management is that the amount of trading losses is limited and the trading activity in the market becomes continuous.
Advantages of capital management trading in trading:
- Limiting the amount of trading losses and preventing severe account drawdowns;
- Maintaining continuity of activity in the market and reducing the probability of early exit;
- Reducing stress and psychological pressure during trading;
- Creating the ability to recover previous losses during suitable periods;
- Improving the return rate of the trading strategy through precise position sizing based on the money management ratio.
Common Mistakes in Capital Management
Some errors cause capital management in trading to fail to perform properly; recognizing these errors makes the trading process more controllable:

Capital Management Across Different Time Frames
The method of trading money management differs across various time frames.
In short term trading, smaller position sizes and closer stop losses are usually selected. In medium term trading, a larger risk to reward ratio is defined. In long term trading, the focus is on controlling drawdown and holding positions.
Capital Management in Diversified Portfolios
In diversified portfolios, the rebalancing method is used.
In this method, when one asset shows greater growth, part of its profit is withdrawn and added to the remaining assets.
This process keeps capital distribution among assets stable and controls the overall portfolio risk, regardless of approaches such as the martingale technique.
Capital Management Expert Advisor and Trading
The Forex trade management expert advisor is designed with the aim of creating full control over the trading flow and is suitable for traders who value discipline, principled capital management trading, and strict compliance with prop firm account rules.
With a modular and multi section structure, this tool provides the ability to manage all stages of entry, exit, volume control, setting take profit and stop loss, and configuring Break Even and Partial Close in a simple and fast environment.
Traders in the Forex market and prop firm accounts can use this tool to define their trading structure precisely within the framework of what is money management.
Features such as limiting Drawdown in dollar or percentage form, automatic stop of trading after reaching the maximum allowable loss or profit, controlling the number of trades per day and week, and applying time filters during the release of high impact news create operational discipline and prevent emotional behavior.
By providing a complete graphical panel, this expert simplifies and accelerates the order execution process.
Setting multiple take profit and stop loss levels on the chart, graphical position management, activating trailing stop, determining trade volume based on capital, risk percentage, or stop loss distance, and displaying the remaining time until candle close are among the professional features of this tool for every money management trader.
The Account Protector section consists of seven specialized tabs that provide control over volume, activity time, profit and loss sequence, daily and weekly profit and loss limits, allowed symbols, and trade entry conditions.
This structure creates a structured framework for users who operate with styles such as ICT, Smart Money, or Scalping, allowing the execution of the trading plan without deviation.
Ultimately, the Forex trade management expert advisor is a complete tool for capital management in trading and risk management that makes trade execution in the Forex market and prop accounts more precise, faster, and more controllable.
Conclusion
Money management rules are defined based on various elements of a trading plan, including the trader's personality, trading objectives, strategy win rate, capital size, and other factors.
Additionally, factors such as the risk-to-reward ratio, Maximum Drawdown, and stop-loss for each trade play a crucial role in the effectiveness of money management.
In general, money management in trading is categorized into the three types of conservative, aggressive, and hedging. Each of these approaches involves a different level of risk tolerance and offers varying return potentials.













