Copy Trading is a branch of social trading that allows novice traders and investors to automatically replicate the trades of a professional trader (Signal Provider) in their own account.
This process is carried out via dedicated copy trading platforms such as eToro or Zulu Trade; through direct account connections, trades are executed in real-time and in sync.

What Is Copy Trading?
Copy trading is a model of passive investing in which an investor (Copier) replicates the trading decisions of a professional trader (Signal Provider) instead of analyzing and executing trades independently.
In this method, trades are typically copied automatically via specialized platforms.
The main difference between copy trading and other passive investing methods lies in the automation of all copy processes; by linking the investor’s account to that of the signal provider, all actions of the main account are reflected in the connected account.
This trading model is suitable for those who lack the time for active trading or the necessary knowledge of technical analysis.
History and Evolution of Copy Trading
Copy trading, also known as a copy trading platform, was initially introduced as part of automated trading systems.
The first examples appeared in 2005 with the Tradency platform, and over time, companies such as eToro andZuluTrade brought this concept to a broader audience.
Today, many investors use copy trading services to synchronize their trading strategies with those of successful traders.
In recent years, with the advancement of API infrastructures and the growth of algorithmic trading, both forex copy trading and stock copy trading have become primary methods for new investors to enter financial markets.
Many copy trading websites now offer this functionality directly within their user dashboards, allowing users to benefit from the profits of others’ strategies.
Copy trading advantages and disadvantages
In copy trading, one gains access to the experience and knowledge of a professional trader; however, failing to thoroughly assess the signal provider’s performance or mismanaging risk and capital can lead to significant losses. The pros and cons are outlined below:
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Quick access to professional traders’ experience | Complete dependency on others’ performance |
No need for technical or fundamental analysis | No guarantee of consistent profitability |
Time-saving | Indirect risk-taking |
Investment diversification | Hidden fees and charges |
Transparent view of traders' historical performance | Trade execution delays on some platforms |
How Does Copy Trading Work?
The copy trading process starts by registering on a trading platform. After signing up and connecting your account, you must choose from a list of professional or algorithmic signal providers.
This list displays data such as past profitability, drawdown, number of trades, and trading strategy in aPerformance Dashboard.
Once a trader is selected and the amount of allocated capital is defined, all future trades made by that signal provider are mirrored in the copier’s trading account.
Some platforms offer tools like Risk Multiplier and Stop Copying, which allow users to customize risk levels and manage their portfolio more flexibly.
Capital Allocation and Position Sizing Models in Copy Trading
In forex copy trade systems, the method of allocating capital to the reference trader’s positions can be implemented in various ways. The most common models include the following:
- Equity-Proportional: Allocation of trade volume based on the proportion of available capital in the user’s account;
- Fixed Lot: Replicating trades with a fixed volume, regardless of capital fluctuations;
- Risk Multiplier: Setting a risk factor to increase or decrease the size of positions;
- Equity-to-Equity: Automatically matching trade volume between the user and the trader based on their equity ratio.
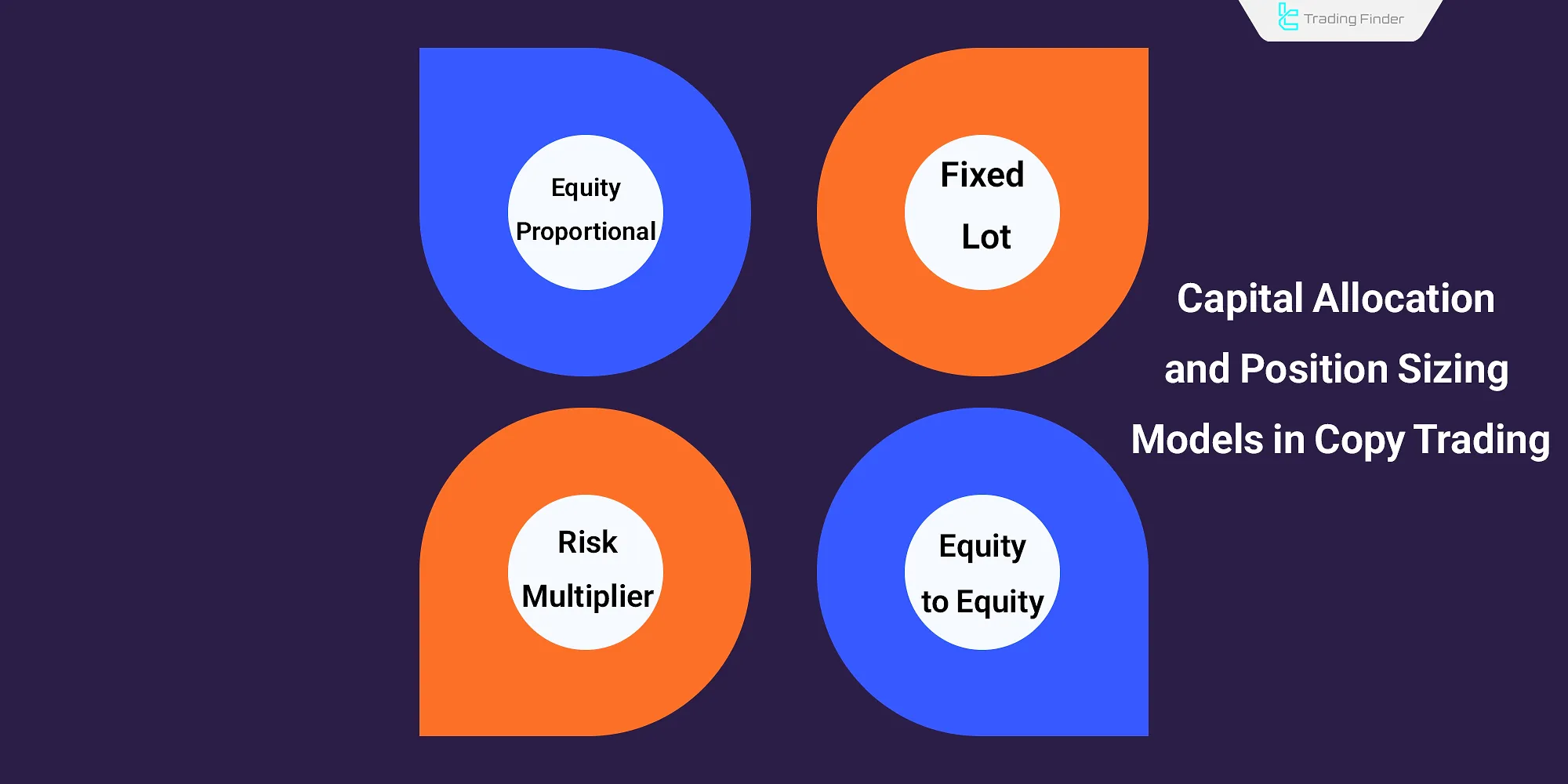
Each model within a copy trade platform carries its own advantages and risks
For example, the Fixed Lot model provides greater control but may cause risk fluctuations in accounts with variable equity.
In contrast, the Equity-Proportional model is a balanced option for beginners and well-suited for manual copy trading.
Real Example of Copy Trading in Action
To better understand how copy trading works, imagine a user with a 1,000-dollar balance decides to follow an experienced trader’s positions. This trader opens a trade on the EUR/USD pair with a volume of 1 standard lot.
Under the Equity-Proportional model, the system automatically replicates the same trade proportionally to the user’s capital, meaning a 0.1-lot position is opened in the user’s account.
If the main trader earns a 2 percent profit from the trade, the user will also gain approximately 20 dollars.
However, if the trader closes the position with a 3 percent loss, the user will incur around a 30-dollar loss. Therefore, even in copy trading, personal risk control and proper trader selection are highly important.
Types of Copy Trading
Copy trading can be categorized into three types depending on the investor’s involvement and the method of trade execution:
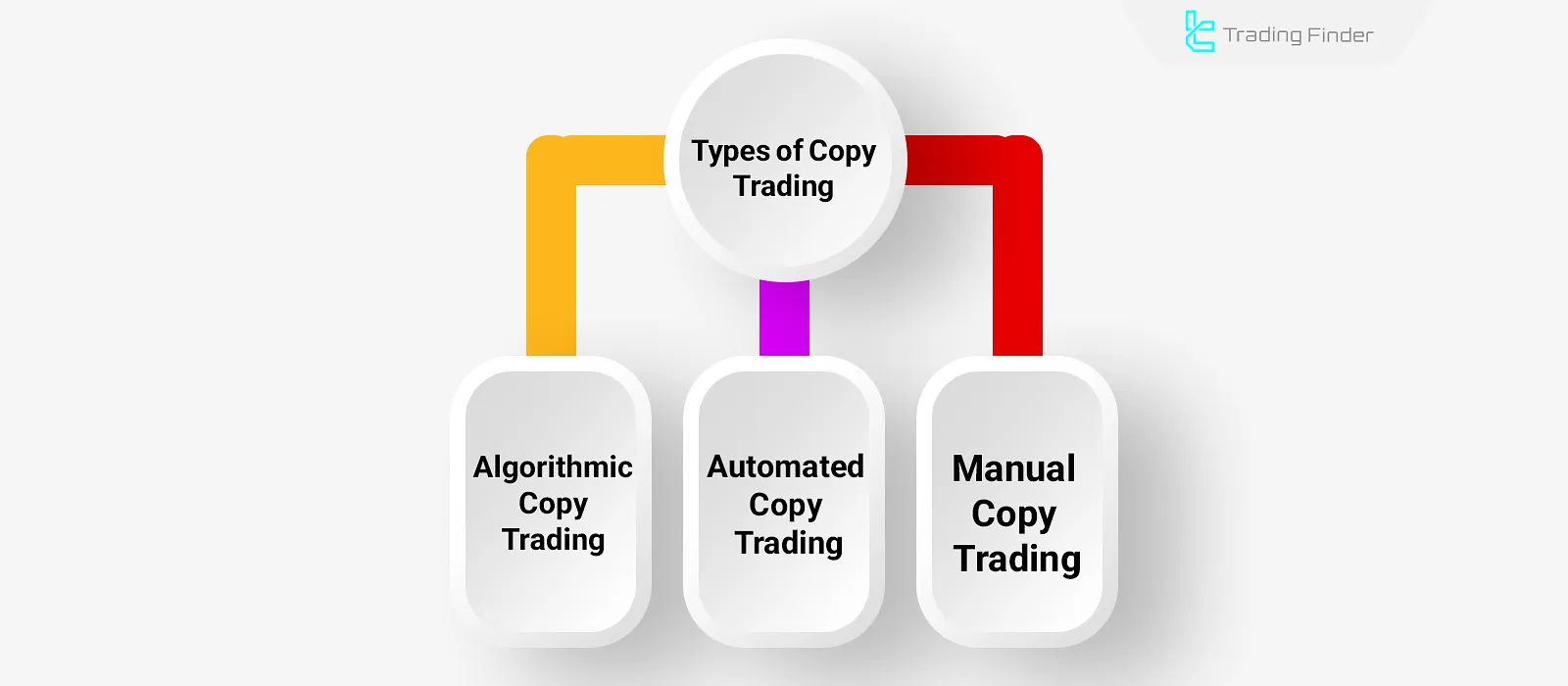
Manual Copy Trading
In this model, the investor manually executes trades after viewing the signals or performance of a professional trader.
This approach is more similar to taking consultation from an expert than a fully automated system.
Automated Copy Trading
In this method, the Copier’s account is directly connected to the Signal Provider’s account, and trades are automatically and simultaneously executed in both accounts.
This is a fully hands-off passive investment method that does not require real-time monitoring or manual intervention.
Algorithmic Copy Trading
Instead of copying a trader’s activities, algorithmic copy trading executes trades based on coded strategies using APIs.
This method allows setting custom parameters for risk control and position sizing.
Step-by-Step Guide to Starting Copy Trading
To begin operating on copytrading platforms, follow the steps below:
- Register and complete verification on your chosen platform;
- Fund your account and allocate a specific budget for copying;
- Review trader performance and select one based on analytical metrics;
- Choose your capital allocation model and set an overall stop-loss limit;
- Start copying and continuously monitor the trader’s performance.
By following these steps, you can reduce initial risks and experience a more controlled environment during your first copy trading periods.
Many platforms, such as eToro and ZuluTrade, are recognized as the best copy trade service providers because they offer analytical tools, performance reports, and detailed charts for evaluating how to copy other traders.
Best Copy Trading Platforms
Among the many copy trading platforms, only a few deliver acceptable quality in terms of technical structure, data transparency, and risk control.
Key factors in evaluating copy trading platforms include account integration, execution models, customization features, and trader ranking systems.
eToro
The eToro platform launched in 2007 and is regulated by institutions such as ASIC, FCA, and CySEC. Copy trading is a core service offered on this platform.
It provides a transparent dashboard displaying trader performance including returns, risk level, follower count, and trading strategy.
Introduction video of eToro’s copy trading services on the official eToro YouTube channel:
The minimum investment to start copy trading on this platform is $200, and tools like stop copying and custom risk management settings are also available.
ZuluTrade
This platform operates as a dedicated marketplace for traders, where investors and signal providers interact without broker intermediaries.
It features ZuluRank, a trader ranking system that evaluates performance based on factors like return consistency, drawdown, trade duration, and risk management style.
Another notable feature is ZuluGuard, an automatic protection system that disconnects your account if the trader exhibits unusual behavior or excessive risk.

Covesting
A component of the PrimeXBT exchange, Covesting offers a transparent structure for signal providers to compete.
Its core feature is the Leaderboard, a public, real-time index showing trader performance and updated strategies across multiple timeframes.
NAGA
NAGA Platform combines copy trading with a financial social network. Traders share their experiences in a social setting and engage with others.
Its main feature is Auto-Copy, if a trader’s analysis or trade idea interests a user, they can copy it instantly into their account via a single click.
What Is the Difference Between Mirror Trading and Copy Trading?
In copy trading, the investor directly replicates the trades of a professional trader. This means every trading decision is mirrored live from the signal provider’s account into the copier’s account.
In this method, the investor has control over trader selection, capital allocation, and even stopping the copy process.
The concept of mirror trading vs copy trading is one of the most common questions among users. Mirror trading focuses more on the automated execution of algorithms, while a copy trade system replicates the actual behavior of traders.
According to learning mirror trading article on the Investopedia website, it fully explains how does mirror trading work and what differences exist between these two approaches.
The following table compares the two methods:
Feature | Mirror Trading | Copy Trading |
Basis of Operation | Follows pre-programmed trading strategies | Replicates live trades of a real trader |
Decision-Making Nature | Algorithmic, based on backtested models | Human, real-time decisions |
Ability to Change Trader/Strategy | Not available | Available |
User Control Level | Low; no direct access | Medium; ability to stop or adjust capital |
Human Behavioral Risk | Limited; algorithm-driven behavior | Present; subject to human error |
What Is the Difference Between Social Trading and Copy Trading?
In social trading, users enter a social environment, where they can observe analyses, trades, ideas, and opinions from other traders.
Here, the user makes the final trading decision, unlike in copy trading, where once the accounts are connected, all trades are executed automatically by the signal provider.
Comparison table of copy trading and social trading:
Feature | Copy Trading | Social Trading |
Nature of Execution | Automatic execution based on another trader’s activity | Observation and personal decision-making |
Trade Execution | Instant and without manual intervention | Executed manually by the user |
User Involvement Level | Low | High |
Social Interaction | Limited to trader selection and performance viewing | Extensive; includes analysis sharing, discussions, etc. |
Control Over Trades | Low | Full |
Main Objective | Simplify investing without the need for analysis | Learn from the community and enhance personal decision-making |
Comparison of Copy Trading, Mirror Trading, and Social Trading
This table helps users choose the most suitable model based on their level of knowledge and investment goals.
Feature | Copy Trading | Mirror Trading | Social Trading |
Trade Execution | Automatic based on the performance of the selected trader | Automatic based on a predefined algorithm | Manual based on user analysis and ideas |
User Role | Selecting the trader and parameters | Minimal direct interaction | Learning, sharing opinions, and making personal decisions |
Risk Control | Moderate and adjustable | Limited to system parameters | High, but dependent on user experience |
Suitable For | Beginner to semi-professional users | Structured investors | Social and educational traders |
This table is particularly useful for those who want to copy stock traders or copy forex traders. Each of these methods can be chosen depending on the user’s level of control and financial knowledge.
Risks of Copy Trading
Copy trading involves various systematic and behavioral risks, primarily due to the lack of direct control over trades and platform limitations. Key risks include:
- Strategy misalignment with the investor’s risk profile;
- Sudden fluctuations in trader performance;
- Lack of true transparency in platforms;
- Concentration of capital in a single trader;
- Platform or technical infrastructure risk;
- Limited full control over the trading account.
Copy Trading Fees
Depending on the platform and integration model, fees and charges in copy trading vary. These directly affect investment returns.

Types of Copy Trading Fees:
- Performance Fee: The most common fee model where the platform or trader charges a percentage of net profits;
- Monthly Subscription Fee: Instead of profit-based fees, some platforms charge a fixed monthly fee for access to trading signals;
- Increased Spread or Broker Commission: Many copy trading, platforms apply higher spreads or commissions to copied trades;
- Withdrawal or Internal Transfer Fees: Some platforms charge extra for-profit withdrawal or internal fund transfers, often beyond the user’s control;
- Hidden Infrastructure Costs: On platforms lacking proper execution speed or server quality, slippage or execution delays may cause pricing differences between the trader and copier - considered a hidden cost.
Operational Risks in Copy Trading
In addition to financial risks, technical factors can also affect the results of a copy trader platform.
Delays in order execution (latency), price slippage during entry or exit, and reduced liquidity during periods of high volatility are among the most significant operational risks.
To manage these issues, it is recommended to use copy trading apps or brokers with fast and reliable infrastructure, and to set limits such as maximum slippage and position size caps.
Moreover, paying attention to the copy trading signal and verifying the credibility of its source is highly important.
Important Notes Before Starting Copy Trading
Before connecting your account, consider the following to avoid unnecessary losses:
- Analyze the trader’s historical performance
- Review drawdown levels
- Diversify capital across multiple traders
- Examine the trader’s trading duration and experience
- Carefully assess the trader’s profile
- Use a demo account before risking real capital
- Set an overall stop-loss limit
Key Metrics for Evaluating Traders
Before selecting a trader for copy trade services, it is advisable to assess their performance using quantitative indicators.
Metrics such as maximum drawdown, win rate, profit factor, expectancy, and Sharpe ratio are essential in determining the trader’s consistency and trade quality.
Analyzing trading history, average holding duration, number of monthly trades, and capital drawdowns during volatile periods provides a more realistic perspective on each trader’s trading style.
Some platforms also allow users to compare multiple copy trade capital accounts, enabling them to evaluate actual returns more accurately.
Comparison of Copy Trading with Other Passive Investment Methods
Copy trading falls under the category of variable-return investments. Instead of investing in a specific asset, the investor is essentially investing in a person’s performance.
Compared to methods like ETFs, crypto staking, or robo-advised portfolios, copy trading carries higher risk.
The following table compares copy trading with other passive investment options:
Feature | Copy Trading | ETF (Exchange-Traded Funds) | Crypto Staking | Robo-Advised Portfolios |
Return Potential | High (variable, trader-dependent) | Medium (market index-based) | Low to Medium (stable, long-term) | Medium (controlled risk) |
Overall Risk | High | Medium | Relatively Low | Relatively Low |
User Control Level | Medium (choose trader, define capital) | Low | Very Low | Low |
Liquidity | High (on most platforms) | High | Depends on blockchain network | High |
Technical Knowledge Need | Medium | Low | Medium | Very Low |
Predictable Performance | Low (high volatility) | High | High (in defined periods) | High (algorithm-based) |
Fees and Costs | High (performance fees, spread) | Low | Very Low | Medium |
Fast Trade Copier Expert Advisor (Trade Copier)
The Fast Trade Copier Expert Advisor (Trade Copier) by TradingFinder is designed to automatically synchronize trades between multiple accounts.
With its smooth interface and floating control panel, this tool enables traders to instantly transfer trades across different accounts while simultaneously copying stop loss (SL) and take profit (TP) settings.
This expert advisor is particularly useful for those who manage multiple trading accounts simultaneously and want to instantly mirror open positions from the main (Master) account to the sub (Slave) accounts.
Simply set one account as the sender and another as the receiver, and every new trade or modification to existing orders will automatically be reflected in the second account.
From a technical standpoint, Trade Copier supports multiple master accounts and can convert symbols in cases where broker naming conventions differ.
It also includes options for selecting permitted trading days, synchronizing with Market Watch, and receiving data from one or several charts.
The Expert Advisor operates in both single and multi-timeframe modes and delivers precise performance not only in the forex market but also in cryptocurrencies, stocks, indices, and commodities.
In tests conducted on GBP/USD and BTC pairs, buy and sell positions along with their TP and SL levels were accurately copied to the target account.
Due to its speed, precision, and simplicity of setup, this tool is highly popular among scalpers and day traders.
As a result, the TradingFinder Fast Trade Copier Expert Advisor serves as a reliable and free solution for those seeking to synchronize their trades across multiple accounts or platforms without human error.
Another major advantage of the TradingFinder Fast Trade Copier is its extensive customization options and precise control over the trade-copying process.
Users can set each position’s volume as a desired percentage of the main account, exclude certain symbols from copying, or choose to replicate only specific trade types such as buy or sell orders.
These features enable traders to execute their strategies with greater flexibility and prevent discrepancies in trade size or risk among accounts.
Furthermore, with its support for simultaneous and multi-broker operations, this Expert Advisor is an ideal choice for investment account managers (PAMM/MAM) and traders operating across several brokers.
The combination of high transfer speed and a simple interface has made this tool one of the most popular and practical free Expert Advisors on TradingFinder.
- Download Fast Trade Copier Expert Advisor (Trade Copier) for MetaTrader 4
- Download Fast Trade Copier Expert Advisor (Trade Copier) for MetaTrader 5
Conclusion
Copy trading is a form of passive investing that allows inexperienced or time-constrained individuals to benefit from the expertise of professional traders.
However, this model requires thorough analysis, platform understanding, and risk management.
Before starting, one should understand the differences between mirror trading and copy trading, as well as social trading and copy trading, and be aware of hidden fees and other important platform aspects.
Platforms like eToro, ZuluTrade, Covesting, and NAGA are among the best copy trading platforms, offering high-quality services in this domain.













