In the Forex market, many investors prefer to use indirect investment methods due to a lack of sufficient knowledge or time to analyze the market.
One of these methods is the PAMM account, which, among models like PAMM forex and mam trading account, has gained great popularity because of its transparent structure and profit-sharing mechanism based on investment proportion.
A PAMM trading account is a sub-category of social trading, in which a professional trader executes trades using the combined capital of several investors, and the resulting profit or loss is distributed among them.
In fact, if we ask what is PAMM or PAMM meaning, the simple answer is that PAMM is a form of co-investment model where a trader operates on behalf of multiple investors, and PAMM forex brokers automatically handle all profit and loss calculations.
Each investor allocates a specific amount of funds to the PAMM account and shares in the profit or loss according to their capital ratio to the total balance.
This mechanism has encouraged many brokers to offer PAMM service for beginner users, allowing them to participate in professional trading activities without the need for direct trading.
What Is a PAMM Account?
The PAMM Account (Percent Allocation Management Module) is a model of social trading in financial markets, in which a professional trader uses pooled capital from multiple investors to execute their trades in the market.
In this type of account, each investor allocates a specific amount to the Forex PAMM Account, and they receive a share of the profit earned in proportion to their investment.
Profits and losses from PAMM trades are distributed among investors based on the ratio of each individual’s capital to the total amount of capital available in the PAMM account.
In this structure, the broker oversees different aspects of the trading process, such as calculating profits, losses, and fees.
PAMM Accounts are mostly used in the forex market, but some brokers also offer the possibility of using this investment model in other markets.
On the FXOpen Official YouTube channel, the operation of a PAMM account is explained in a video format:
How does a PAMM Account Works?
In the PAMM trading system, investors deposit their funds into a PAMM account after opening an account with the supporting broker. The account manager or PAMM account manager executes trades using the total pooled capital.
Profits and losses for each period are calculated based on each investor’s share of the total capital. This process is handled by the broker’s system and is often displayed in the trading dashboard under the title broker PAMM account.
If the PAMM account managers perform successfully in trading, a percentage of the profit is awarded to them as a performance fee.
This model, which is commonly used in most forex PAMM accounts, creates a balance between the interests of the manager and the investors.
In some brokers, the fee payment structure for the account manager is based on the “High Water Mark” method; this means that the manager only receives a fee when the account exceeds the previously recorded highest profit level.
This method ensures that if the account experiences a loss during a month, the manager must recover the previous month’s loss before being eligible to receive any performance fee again.
Numerical Example of High Water Mark Performance
In some PAMM forex trading brokers, the fee structure is based on the High Water Mark model. According to this model, the account manager receives a fee only when new profits are recorded above the previous highest account level (HWM).
Suppose an investor has 1000 USD in a PAMM forex account. If the account earns a 10 percent profit in the first month, 30 percent of that profit (which equals 30 USD) is paid to the manager as a fee.
If a 5 percent loss occurs in the following month, a new fee will be charged only when the balance exceeds 1100 USD.
This mechanism, which exists in many PAMM investments, ensures transparency and fairness in profit distribution between the manager and the investors.
The concept is fully explained with examples in the High Water Mark tutorial article on Investopedia.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of a PAMM Account?
Using PAMM accounts allows individuals to benefit from the skills of professional traders without the need for direct trading.
However, it is important to note that no PAMM trade or investment is without risk, and there is no guaranteed profit.
The table below summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of a PAMM account:
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Possibility to benefit from the expertise of professional traders | No guarantee of profitability |
Profit distribution proportional to the amount of invested capital | Possibility of losses incurred by the account manager |
Transparency in profit and fee reporting | No direct control over trading decisions |
Variety of account managers with different strategies | The quality of the manager’s performance may fluctuate over different periods |
Broker supervision over the profit distribution process | Complete dependence on the trader’s skill and risk management ability |
How to Choose the Right PAMM Account
To select a suitable PAMM account, an investor must understand exactly how PAMM account works and what factors influence its performance.
Reviewing the trading history, risk level, profit-sharing model, and transparency are among the most important criteria.
First of all, it is essential to know that PAMM full form stands for Percent Allocation Management Module, which means a module for percentage-based allocation of capital between investors and the manager. This fundamental definition provides a clear understanding of the nature of a PAMM account.
A proper PAMM account forex should be offered by a broker holding a valid license to ensure investment in a transparent and secure environment.
The main and essential factors in a PAMM trading account include:

Checklist Before Choosing a PAMM Account
Before investing in a PAMM account, it is essential to follow several key points. Paying attention to these factors can help prevent risks associated with unstable accounts.
- Review at least three months of the account’s performance history;
- Compare the profit-to-drawdown ratio;
- Examine the consistency of returns and recovery time from losses;
- Ensure that HWM is active and the manager’s fees are transparent;
- Choose a reputable broker with an independent PAMM management system.
What Are the Rules of PAMM Accounts?
In PAMM accounts, the broker acts as a supervisor and controls the processes of profit distribution, capital withdrawal, and fee calculation based on a set of transparent rules.
These rules define what is PAMM account and how it differs from other managed account types. For example, in many PAMM forex accounts, the payment structure for the manager is activated only when the account is profitable.
Below, we will review the key parts of these regulations:
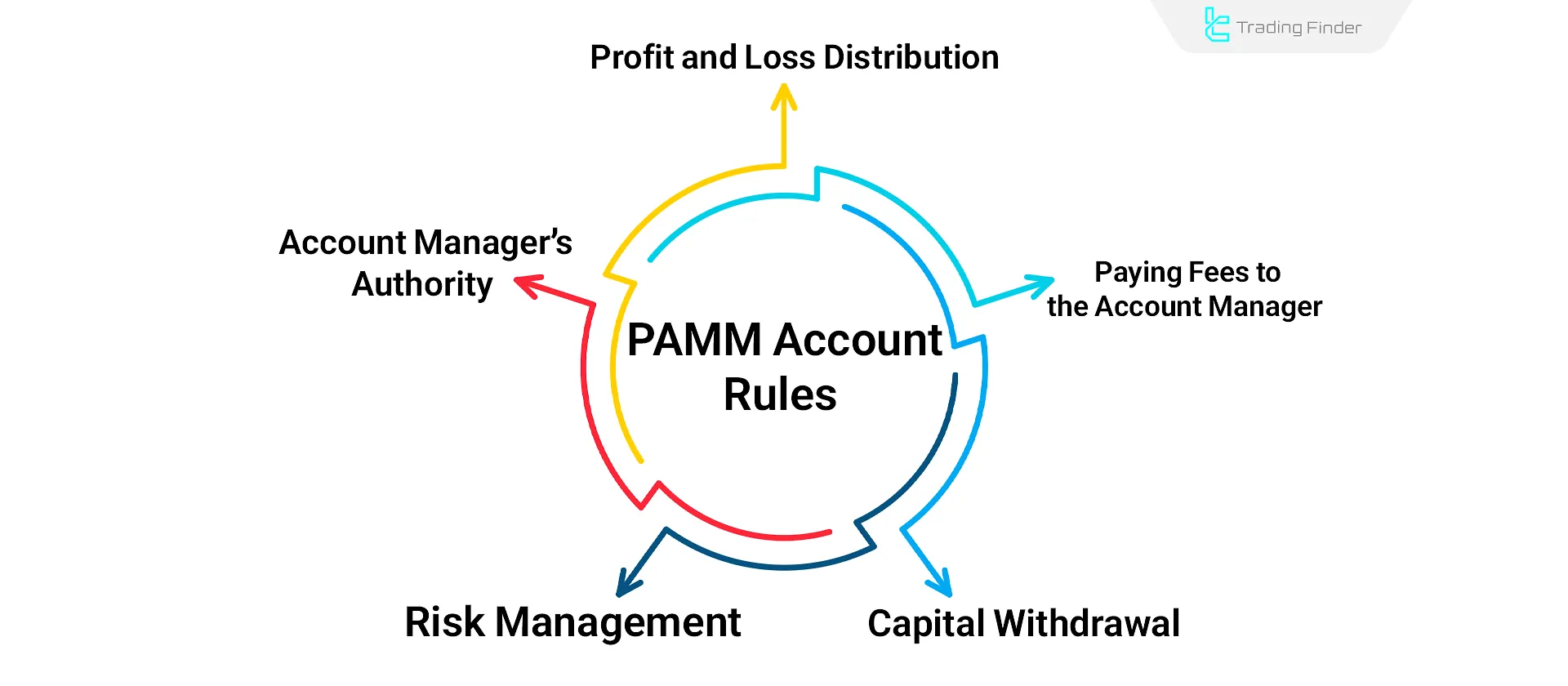
Rules Related to Profit and Loss Sharing
Transparent rules on profit and loss sharing are a critical factor in a PAMM Account. In this investment model, the share of profit is calculated based on the percentage of capital each investor has relative to the total account.
The main elements of these rules include:
- Profit and loss division based on each investor’s capital share;
- Automatic calculations by the broker's system;
- Time-based restrictions on profit withdrawals (e.g., monthly or weekly).
Rules Regarding Payment of Fees to the Manager
In the PAMM trading platform structure, fee payments are made only in cases of profitability. Usually, a percentage of the net profit is allocated to the manager, and all details are clearly defined in the initial agreement.
Rules for paying fees to the account manager:
- The fee is paid only in case of profitability (Performance Fee);
- The fee rate is determined in the initial agreement;
- Some brokers use the High Water Mark model.
Rules Regarding Capital Withdrawal
Capital withdrawal in PAMM investments is usually allowed on a weekly or monthly basis, and for mid-term withdrawals, a fee or time restriction may apply.
Topics covered in these rules include:
- Ability to withdraw all or part of the capital with prior notice (e.g., 24 or 48 hours);
- Designated timeframes allowed for withdrawal;
- Penalties are imposed for early withdrawals before the set schedule.
Investment Cycles and Withdrawal Periods in PAMM Accounts
In most brokers, PAMM accounts operate with regular investment cycles (weekly or monthly). At the end of each cycle, profit and loss are calculated, and investors can withdraw their principal or earned profit.
The duration of each cycle and the withdrawal conditions are defined by the manager when creating the account and can be viewed on the account information page within the PAMM trading platform. Mid-cycle withdrawals may involve fees or require prior notice to the broker.
Rules Related to Risk Management
Risk management is one of the essential elements in every forex PAMM account. Brokers usually implement limits such as maximum drawdown and trade stop levels within their system to prevent significant losses.
A professional trader in a PAMM trading setup must maintain an appropriate risk-to-reward ratio and define a specific stop-out level for investors. These rules are stated in the main agreement, and the broker monitors their enforcement.
To enforce these considerations, the following contractual terms are included:
- Setting a maximum drawdown threshold;
- Defining the stop-out level by the investor or broker;
- Enforcing capital management rules and requiring the manager to comply.
Rules Regarding the Manager's Authority
The PAMM Account manager has limited authority. The manager is not allowed to withdraw or transfer funds from the account.
The framework of the manager’s authority includes:
- The manager is only authorized to execute trades and cannot access funds for withdrawal;
- Restrictions may be applied to permitted trading symbols;
- The manager’s responsibilities must be clearly defined for all trades.
Role of the PAMM Agent and Reward Distribution
In some PAMM forex trading platforms, a person known as a PAMM agent is defined, who introduces investors to managed accounts and receives a percentage of the manager’s fee as a reward.
This model creates a broad investment network and enhances the transparency of managers’ performance. As a result, both the manager and the agent benefit from the account’s successful performance.
This structure expands the investment network and increases transparency in capital acquisition without requiring investors to pay any additional costs.
In a PAMM contract, the manager can independently determine the agent’s reward percentage, the investment period, and the performance fee rate.
Difference Between PAMM, MAM, and Copy Trading
The PAMM Account, Copy Trading, and MAM (Multi-Account Manager) are three different models for utilizing the skills and experience of a professional trader.

One of the key topics frequently discussed among traders and investors is the difference between pamm and mam.
Both structures are designed based on the management of multiple clients’ capital by a single account manager, but there are notable differences between them:
Feature | PAMM Account (PAMM) | Copy Trading | MAM Account (MAM) |
Capital Management | All investor funds are pooled in one account | Each investor has a separate account | Funds are pooled; trade volume can be customized |
Investor Control | No control over trades | Investors can close or change trades | Control over trade volume depends on the broker |
Risk Management | Managed by the account manager | Managed by investor or through copy settings | Combination of manager and investor control |
Fee Payment | Percentage of net profit | Percentage of profit or fixed fee | Percentage of profit or based on trade volume |
Trade Execution Structure | Trades executed on a pooled account | Trades are copied to individual investor accounts | Trades are executed on a pooled account, but the volume can be adjusted for each investor |
Fast Trade Copier Expert Advisor (Trade Copier)
One of the most useful tools for synchronizing trades in PAMM forex trading accounts is the Trade Copier expert. This tool, developed by Trading Finder, enables traders to automatically transfer trades between multiple accounts.
With this tool, users who manage several accounts or PAMM investor accounts can copy their trades simultaneously and minimize human errors.
In the latest versions of MetaTrader 4 and 5, this expert supports multiple master and slave accounts, making it highly beneficial for professional traders and broker PAMM account managers.
From a technical standpoint, the Trade Copier supports multiple master accounts and can convert symbols if brokers use different naming conventions.
It also includes options for selecting allowed trading days, synchronizing with Market Watch, and receiving data from one or multiple charts.
The expert works in both single and multi-timeframe modes and performs accurately across Forex, cryptocurrency, stock, index, and commodity markets.
In tests conducted on GBP/USD pairs and BTC trades, buy and sell positions with TP and SL levels were precisely copied to the destination account.
Thanks to its speed, accuracy, and simple setup, this tool is highly popular among scalpers and day traders.
As a result, the TradingFinder Fast Trade Copier Expert offers a reliable and free solution for traders who want to synchronize their trades across multiple accounts or platforms without human error.
Another major advantage of the TradingFinder Fast Trade Copier Expert is its extensive customization options and precise control over the trade-copying process.
Users can define position size as a percentage of the master account, exclude certain symbols from copying, or choose to transfer only specific types of trades such as buys or sells.
These features allow traders to execute their strategies more flexibly and prevent discrepancies in position size or risk levels between accounts.
Additionally, with support for simultaneous multi-broker trading, this expert is an ideal choice for investment account managers (PAMM/MAM) and traders working with multiple brokers.
The combination of high transfer speed and a user-friendly interface has made this tool one of the most popular and practical free experts available on TradingFinder.
- Download Fast Trade Copier Expert (Trade Copier) for MetaTrader 4
- Download Fast Trade Copier Expert (Trade Copier) for MetaTrader 5
Difference Between a PAMM Account and a PAMM Portfolio
In a PAMM account, all invested funds are pooled into a single account managed by one account manager.
However, in a PAMM portfolio, the investor can distribute their capital among several different managers.
This approach helps reduce the risk associated with relying on a single manager’s strategy, although the profit and fee calculation structure in a PAMM portfolio is more complex.
PAMM portfolios are usually offered by brokers that host a large number of active managers.
What Are the Criteria for Choosing a PAMM Account Manager?
For success in PAMM trading, selecting the right account manager is one of the most crucial steps. The manager must have a proven track record of profitability, strong risk management skills, and transparent performance.
Below are the key factors that influence the selection of the best PAMM account manager:
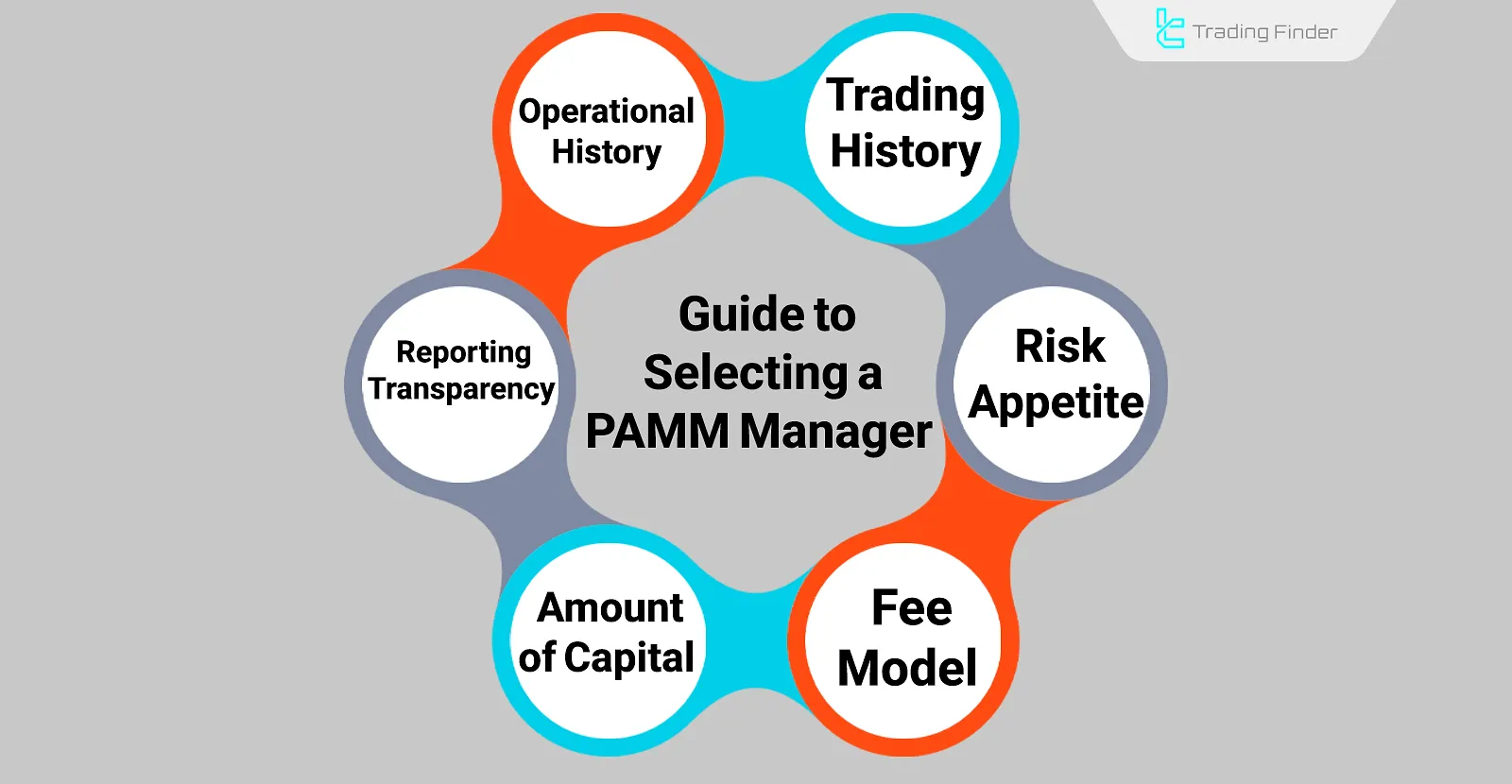
- Trading History: Review profit percentages, drawdown rates, and performance consistency across various timeframes;
- Risk Tolerance: Analyze the manager's trading strategy in terms of risk control and win/loss ratio;
- Fee Model: Examine the performance fee rate and how it is applied;
- Capital Under Management: Consider the total capital that the manager has handled;
- Transparency: Assess how openly the manager reports on performance, losses, and strategy updates;
- Broker Affiliation: Prefer managers with long and stable track records with reputable brokers.
These factors help investors make more informed decisions and choose, among multiple managers, the one with a higher rating or PAMM scores.
Top Brokers Offering PAMM Accounts
These factors help investors make more informed decisions and choose, among multiple managers, the one with a higher rating or PAMM scores.
The table below presents a few brokers such as OnEquity and GO MARKETS, which provide PAMM Account services:
Broker Name | Key Features | Regulation | Important Notes |
OnEquity | Access to top trading experts | SVJFSA, FSA, FCSA | Investor funds safeguarded in segregated accounts |
AUS GLOBAL | Regulated and secure licensing | CySEC | Offers PAMM accounts with advanced risk management structure |
GO MARKETS | PAMM accounts with strong regulatory oversight and fast execution | CySEC | No account limits for PAMM, and the deposit amount is unlimited |
Investors should choose a broker that, in addition to providing high security, offers comprehensive analytical tools for the PAMM trading platform, taking into account their level of experience and investment goals.
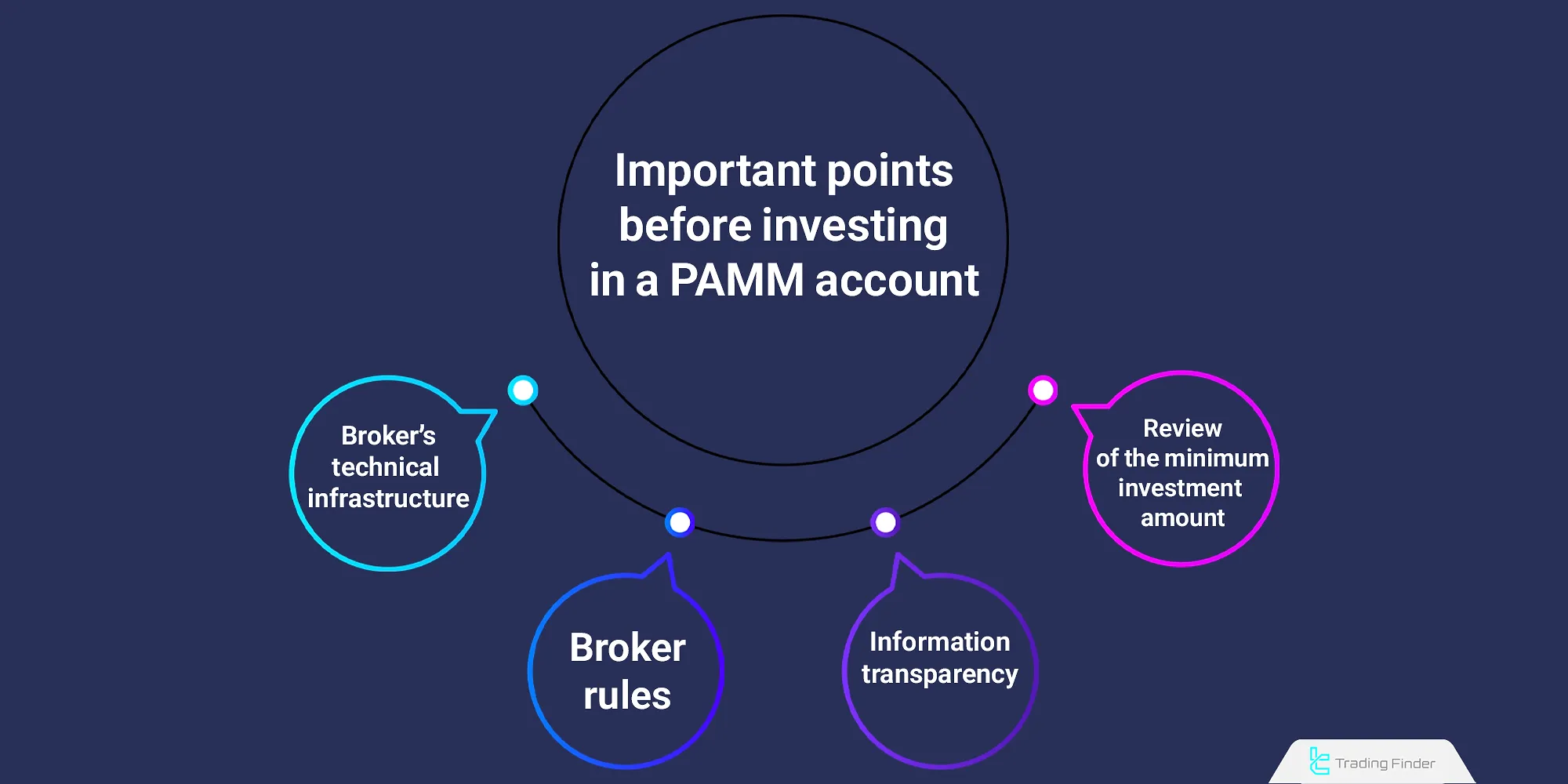
Importnt Points Before Investing in PAMM Account
Before depositing funds into the account, it is necessary to ensure that the broker holds an official license and that the rules for withdrawal and profit distribution are clearly defined.
In reputable forex PAMM systems, all transactions are carried out through the broker’s official platform, and no direct payments should be made to the manager or any third party.
Before investing in a PAMM Account, due to the nature of indirect profit generation, certain technical and operational factors must be considered:
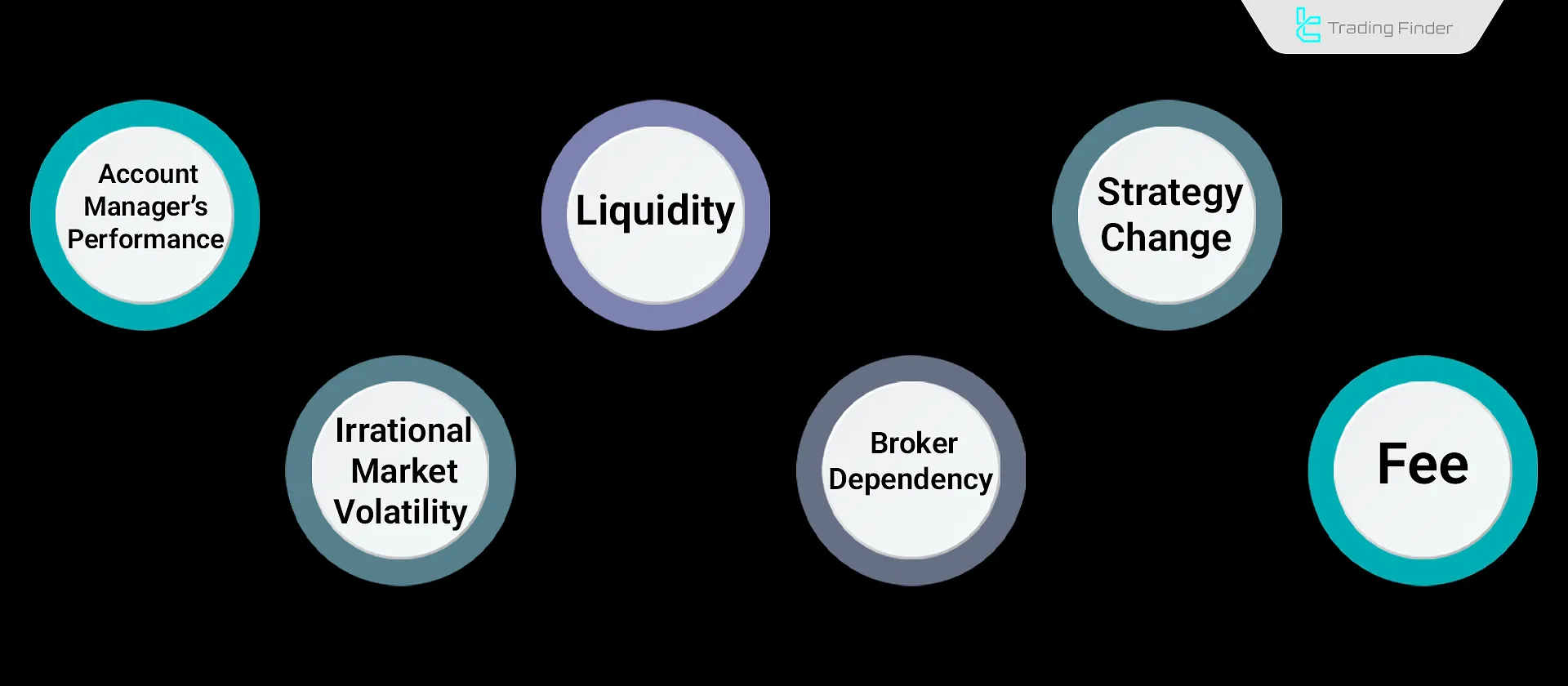
What Are the Risks of Using a PAMM Account?
Risks associated with using a PAMM Account are typically related to the performance of the manager, market conditions, and regulatory limitations of the broker.
These factors must be evaluated before depositing capital in a PAMM account.
Security Tips and Fraud Warnings in PAMM Accounts
In PAMM accounts, the security of capital is of utmost importance. Investors should always proceed through the broker’s official channels and avoid making direct payments to unknown individuals.
Promises of guaranteed profit or fixed returns are usually signs of fraud.
Reputable managers typically have verified track records, transparent reports, and high PAMM scores. Reviewing these factors before investing is essential.
Serious investors usually use only those accounts that provide transparent reports, real trading history, and verifiable withdrawal conditions.
Costs of Using a PAMM Account
In PAMM accounts, the costs include a performance fee, management fee, and withdrawal charges. Generally, the performance fee is paid only when the account is profitable.
This cost structure ensures transparency in the relationship between the manager and the investor and demonstrates what is PAMM forex in terms of its financial structure.
The costs of using a PAMM Account typically depend on profitability, investment volume, and the services offered by the broker and account manager. PAMM Account Fees:
Fee Type | Description |
Performance Fee | Percentage of the investor’s net profit paid to the manager (typically 20%–30%) |
Management Fee | Fixed annual or monthly fee charged even if the account is not profitable (applied by some brokers) |
Capital Withdrawal Fee | Some accounts charge fees for early withdrawal before the scheduled period |
Platform Fees | Some brokers may charge for using PAMM infrastructure |
Banking/Payment Fees | Includes fees for transferring funds to the broker or withdrawing profits |
Step-by-Step Process of Opening a PAMM Account
This process may vary depending on the broker and can be completed either through the web platform or the personal client area. To start investing in a PAMM account, the following steps are carried out in order.
Steps to Create a PAMM Account:
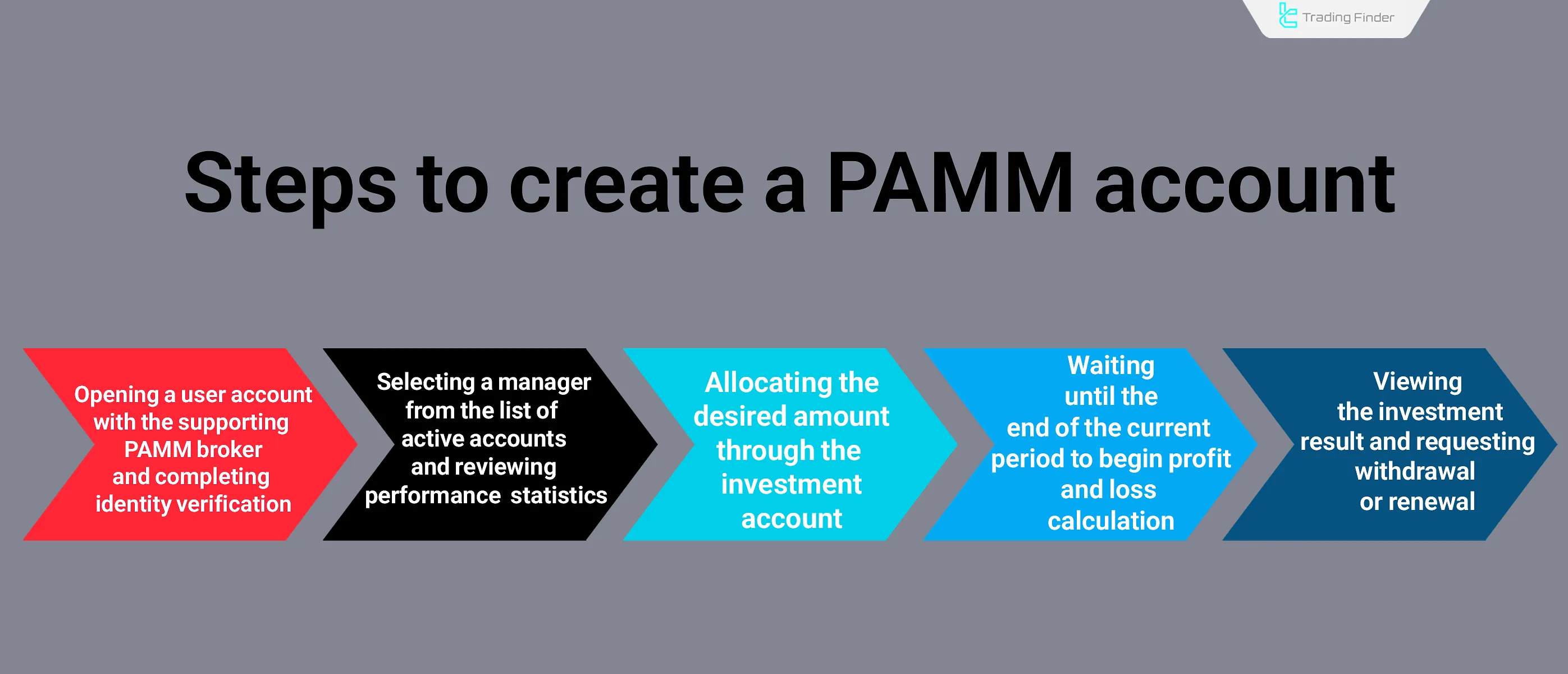
At this stage, the investor enters the PAMM investment environment and can view the manager’s trades.
Conclusion
PAMM Accounts are a form of indirect investment in financial markets. These accounts utilize the experience and skill of a professional trader to execute trades, making them suitable for individuals with limited time or trading experience.
To succeed with a PAMM account, it's essential to analyze several key factors such as the account manager’s performance history, fee structure, risk management strategy, and the credibility of the broker.













