In financial markets, none of the trading strategies is reliable in their initial phase. Changes in market structure, price behavior, volatility, and trading volume gradually reduce the effectiveness of a strategy.
Refinement Trading refers to the systematic process of reviewing, enhancing, and re-testing a trading strategy to ensure consistent and reliable performance under real and dynamic market conditions.
What is Refinement Trading Strategy?
Refinement and enhancement of a trading strategy refer to a series of targeted actions aimed at increasing the efficiency, accuracy, and consistency of a trading system under different market conditions.
This process includes analyzing past trading results, identifying flaws and areas of improvement, applying step-by-step changes, and reassessing the strategy's performance after each enhancement.
Analysis and Adjustment in Refinement Trading
Improving the performance of a trading strategy is not possible without a detailed analysis of its results. The refinement process begins at the point where tested data, error patterns, and inefficiencies are accurately identified and categorized. Three key methods for analysis and Refinement:
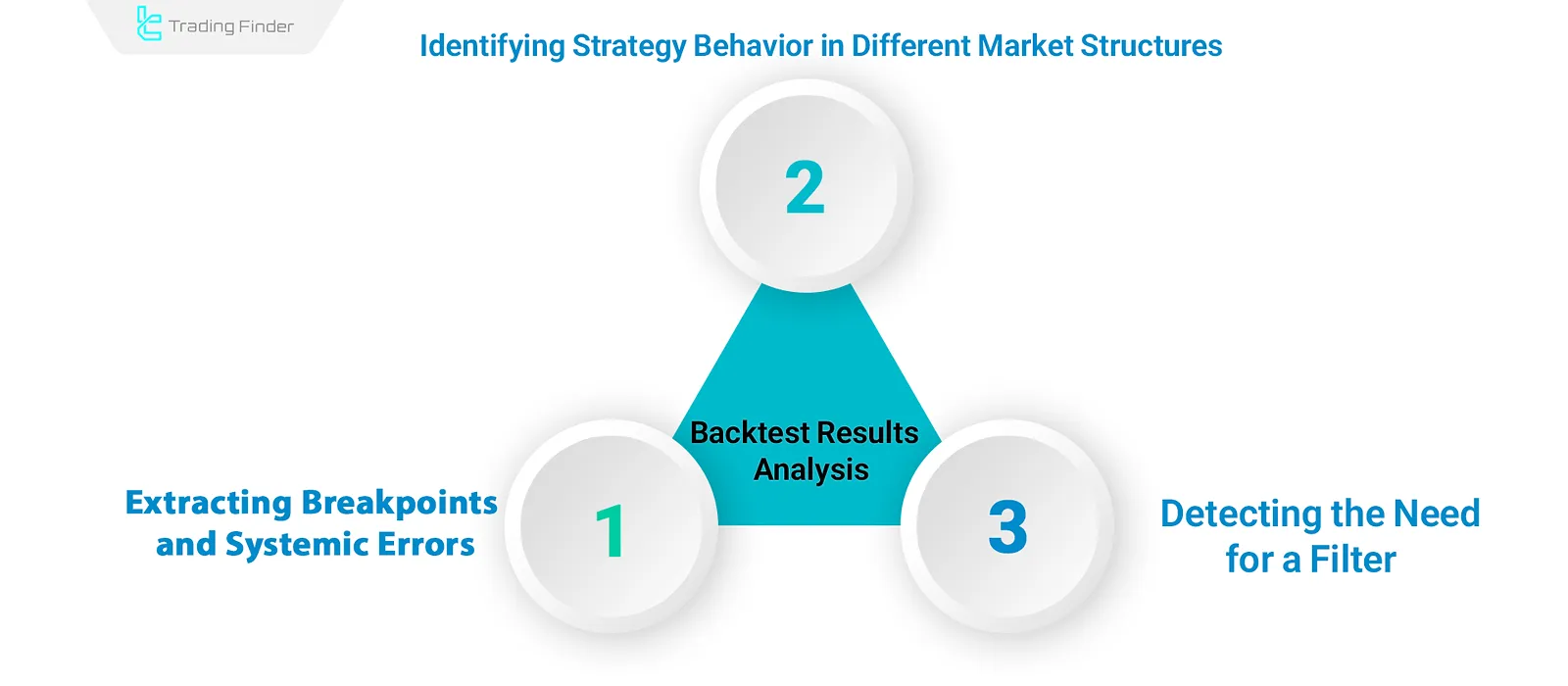
Backtest Results Analysis
Backtest analysis is the first practical step in the refinement process, assessing the real efficiency of the strategy based on historical data and market behavior:
- Identifying strategy behavior across different market structures: Evaluate performance under trending, ranging, or highly volatile conditions. If the strategy underperforms or faces increased drawdown in a specific phase, it needs Refinement;
- Extracting failure points and system errors: Entries occurring at short-term tops, excessively delayed exits, or entries influenced by price noise;
- Detecting the need for filters: Filters are required when the strategy performs poorly in certain market conditions or produces numerous low-quality trades.
Adding Filters and Enhancing Entry & Exit Zones
In the strategy refinement process, technical filters play a key role in improving entry and exit accuracy. Tools like the RSI indicator, ATR indicator, and volume analysis help eliminate high-risk setups and confirm optimal conditions. Additionally, candlestick patterns and price action techniques enhance decision-making precision.
Using lower timeframes or complementary signals further refines entries and allows for more timely exits. These adjustments ensure the strategy activates only in high-quality trading conditions.
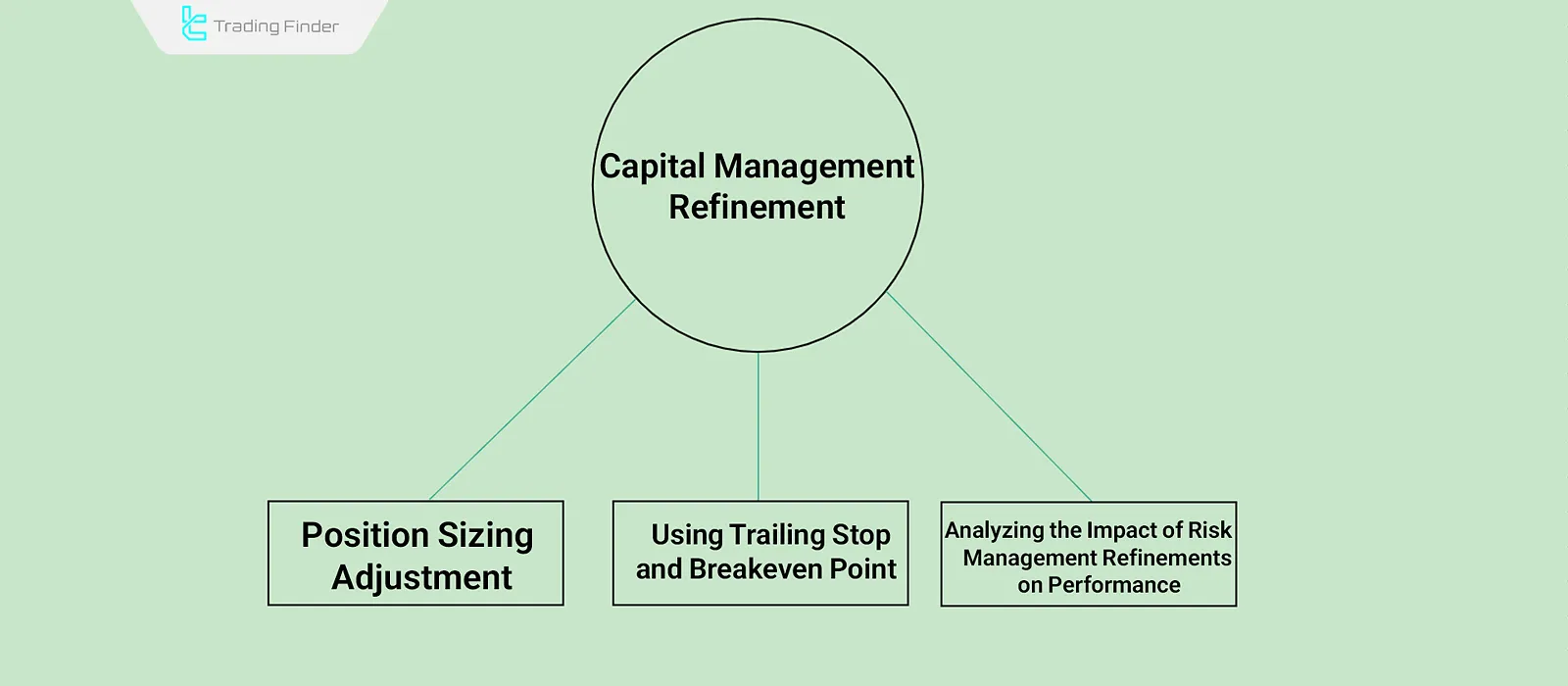
Capital Management Adjustment
Capital management refinement is a critical phase that directly impacts risk control, profit preservation, and the overall sustainability of trading performance. Three core components of capital management refinement:
Position Size Adjustment
Trade size should be proportional to signal strength, market risk level, and analytical confidence. Strategies with fixed position sizes often underperform under high volatility or weak signals. Dynamic and adaptive position sizing helps balance risk and return.
Use of Trailing Stop and Break-even Point
Implementing Trailing Stops allows for securing open profits, especially in strong trends. Moving the stop-loss to the break-even point once the price hits a certain level structurally removes trade risk.
Analyzing the Impact of Risk Management Adjustments
Every capital management change must be supported by data and quantitative analysis. Reduction in drawdown, improved profit-to-loss ratio, and sustained profitability despite fewer trades indicate effective adjustments.
If changes only cosmetically improve results without enhancing quality, they're not considered real improvements.
Mental Improvement and Trader Psychology
In many cases, failure to execute a strategy arises not only from technical weaknesses but also from the trader's emotional reactions and behavioral inconsistencies.
Mental improvement extends beyond code or parameter optimization and includes redesigning the human decision-making process at the moment of execution.
Identifying Emotional Behaviors in Strategy Execution
Abandoning a strategy prematurely after a few losses, doubting valid entries, or rushing into trades without following rules are all signs of emotional decision-making. These behaviors typically stem from fear, greed, or lack of trust in the system. Identifying these mental patterns is the first step to improving trader behavior.
Enhancing Trader Behavior
Strategy consistency requires psychological discipline, continuous focus, and physical readiness (e.g., sleep and proper nutrition).
Tools like a psychological journal, daily emotional monitoring, and tracking mental mistakes alongside trades help the trader refine their thought process. Successful trading is the outcome of mental strength combined with analytical ability.
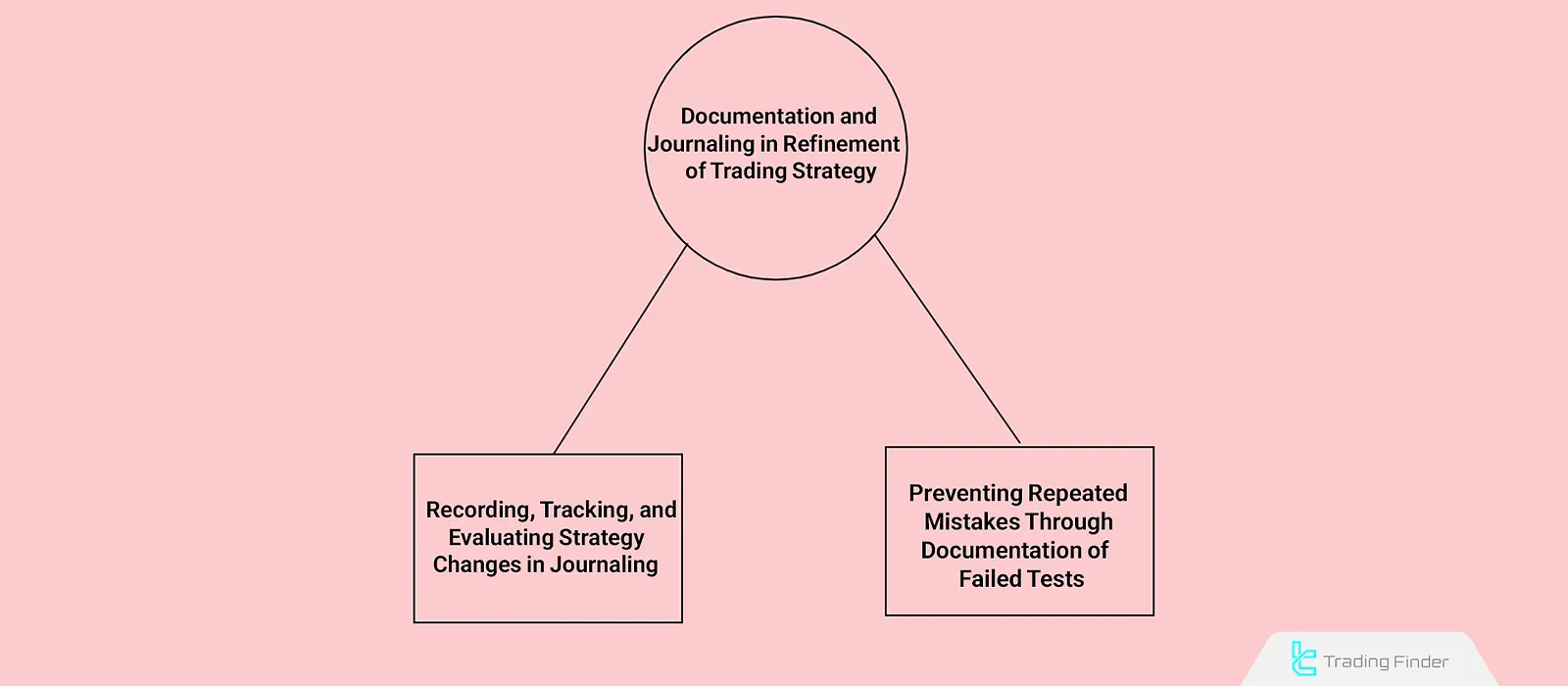
Documentation and Journaling in Refinement Trading Strategy
Accurate documentation is a vital part of the Refinement process; without it, analyzing the effects of changes and replicating successes becomes impossible. Journaling allows traders to track, review, and refine their strategy optimization journey.
Creating a Journal
In the refinement process, journaling is the main method for recording, tracking, and evaluating strategy changes. Every modification (from parameter adjustments to entry and exit refinements) should be documented with reasons, dates, and impact on metrics like drawdown or win rate.
A well-kept journal serves not only as a report but also as a learning path. Comparing performance before and after each change helps determine if the modification was effective or needs reconsideration. This ongoing documentation prevents repeating mistakes.
Using Failures to Improve the System
Every failed test is part of the learning curve. Negative results highlight which paths are inefficient and which conditions should be avoided. Documenting failed tests helps traders avoid repeating similar mistakes and gain a deeper understanding of strategy performance.
In Refinement Trading, both successes and documented failures carry analytical value.
Live Execution and Iterative Refinement
Live execution and iterative Refinement are stages where the strategy leaves the testing environment and is evaluated in real market conditions to measure and strengthen its long-term reliability and practicality.
Gradual Execution in a Real Environment
After completing testing and improvement phases, live strategy execution should begin gradually—first in a demo account, then with limited real capital.
This controlled transition allows the strategy's performance to be evaluated under real-world conditions like slippage, execution speed, and trader psychological response, without exposing main capital to serious risk.
Developing Adaptive Versions of the Strategy
To enhance strategy resilience against market changes, it's essential to create specialized versions of the core system. Separate versions for trending, ranging, and volatile markets provide the trader with suitable tools for each condition. This structural diversity turns the trading system into a flexible and multi-purpose tool.
Conclusion
Refinement Trading Strategy involves a step-by-step review and modification of a trading system to improve its real-market performance. It includes analyzing past results, applying filters, adjusting position sizing, managing trader emotions, and thoroughly documenting all changes.
Ultimately, the strategy must be executed in real conditions, with adaptive versions developed to match various market scenarios. The primary goal is to build a trustworthy system for live and ever-changing financial markets.













