In the Forex market, one of the trading costs that directly impacts the performance of trading systems is the Spread. The Spread refers to the difference between the buying and selling price of a currency pair, and serves as a key metric for measuring liquidity, volatility, and even a broker's policy.

What is Spread?
In the Forex market, Spread is the gap between the bid price (the buying price) and the asking price (the selling price) of a currency pair. More precisely, the bid price is the amount the market or broker is willing to pay to purchase an asset, while the asking price is the amount quoted for selling that asset at the same moment.
The difference between these two figures - also referred to as the Bid-Ask Spread - represents the cost a trader pays when entering or exiting a trade.
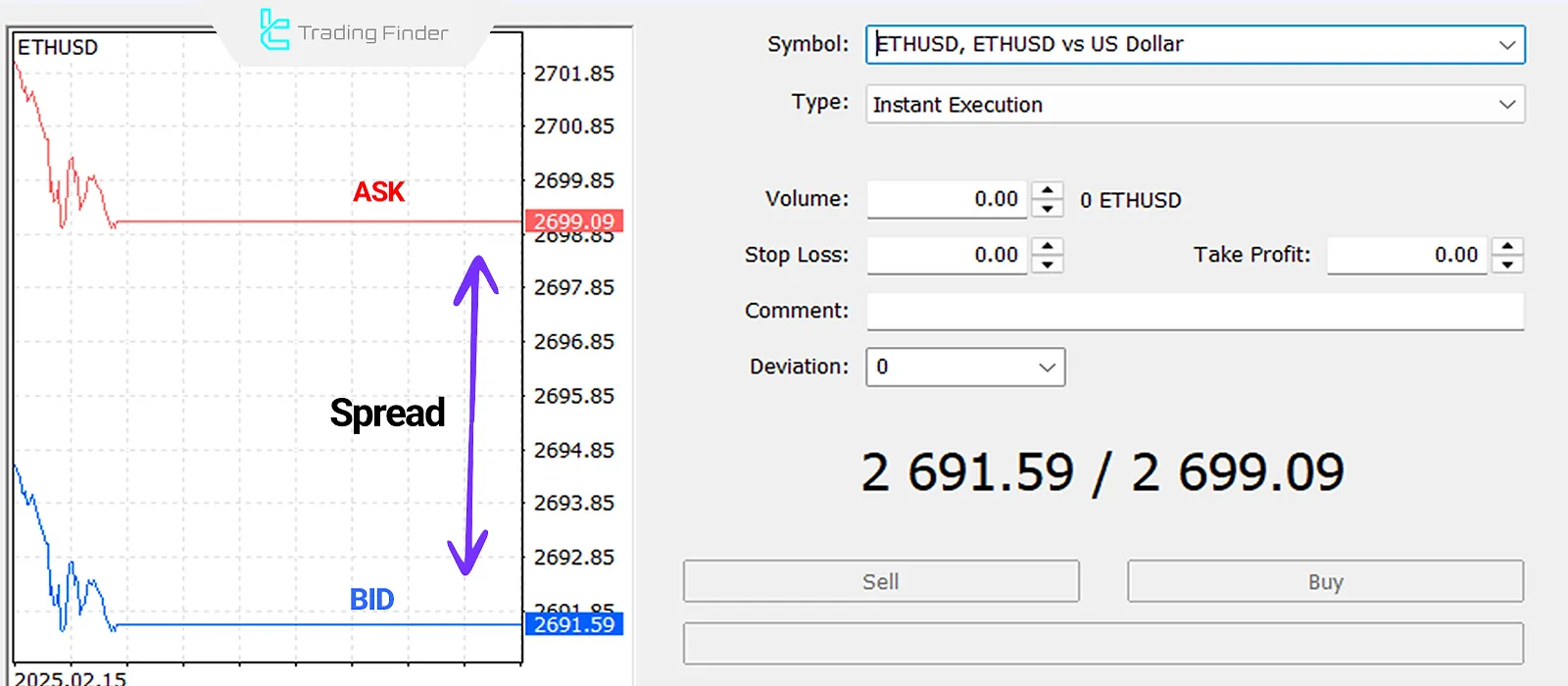
In essence, spread acts as a hidden fee, derived from the difference between the buy and sell prices - even in accounts without explicit commissions.
Spread is typically measured in pips and can vary depending on market conditions, account type, and broker policies. The lower the Spread, the higher the liquidity and competition in the market for that currency pair.
How to Calculate Spread?
To calculate the Spread, subtract the bid price from the ask price:
- Ask Price – Bid Price = Spread
For example, if the EUR/USD prices are:
- Ask: 1.1052
- Bid: 1.1050
Then the Spread is:
- 1052 - 1.1050 = 0.0002

Factors Affecting Spread Size
Several factors influence the size of the Spread:
- Liquidity of the asset: Higher trading volume generally means lower spreads;
- Market volatility: Extreme imbalances between buy/sell orders during volatile conditions increase the Spread;
- Broker policy: Brokers may increase spreads to manage resources (e.g., preventing algorithmic scalping);
- Market activity levels: For instance, European currencies see lower activity during nighttime, while Asian currencies become more active;
- Account type: ECN accounts typically offer lower spreads but charge separate commissions per lot.
Types of Spread in Forex
In Forex trading, spreads are typically offered in two main formats:
- Fixed Spread
- Floating Spread
Understanding the difference is crucial for selecting the right account type and designing your strategy.
Fixed Spread
A fixed spread is a predetermined difference between the bid and ask prices that usually don't change under normal market conditions. This type is ideal for traders who require precise cost estimation, such as those using risk-limiting strategies (e.g., short stop-losses).
However, fixed spreads are not always recommended. During major economic news releases or market opening hours, brokers may temporarily widen fixed spreads. Hence, they're only reliable in stable market conditions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fixed Spread
The table below shows the advantages and disadvantages of fixed spreads:
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Transaction costs are usually known in advance | Higher than floating spreads in low-volatility environments |
Good for risk management and precise SL/TP | Can be widened by broker during news or high volatility |
Floating Spread
A floating spread varies in real time based on market supply and demand. It is usually found in ECN and STP accounts, where prices come directly from liquidity providers.
Higher market liquidity—especially during the London session and New York session overlap—leads to narrower spreads. However, during volatile or low-volume conditions, spreads can increase significantly.
Floating spreads suit traders seeking fast execution at low cost under normal market conditions. That said, they can pose challenges for fast-paced styles like scalping, where sudden spread spikes may erode profits or amplify losses.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Floating Spread
The table below shows the advantages and disadvantages of floating spread:
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Starts from 0.1 pip in normal market conditions (cost-effective for short-term trades) | High volatility in risky conditions |
Direct reflection of supply and demand | Fixed commission involved |
Ideal for ECN accounts and direct execution | Requires constant monitoring |
What is Zero Spread?
Brokers often advertise "zero spread" accounts for marketing purposes. However, in reality, the Spread is never truly zero. Even when orders are executed instantly, and are sourced directly from liquidity providers, a minimal bid- prices ask difference always exists.
Sometimes the spread is so small that trading platforms round it down to zero when displaying prices with five decimal places. However, the actual difference may exist in the sixth decimal place. Even so, no trade is ever entirely free from spread costs—this hidden fee, no matter how minimal, should always be taken into account.
How to View Spread in MetaTrader
You can check the Spread in MetaTrader 4 or 5 using these methods:
Order Window
The Spread is the area between the price lines (Quotes) or the difference between Bid and Ask.
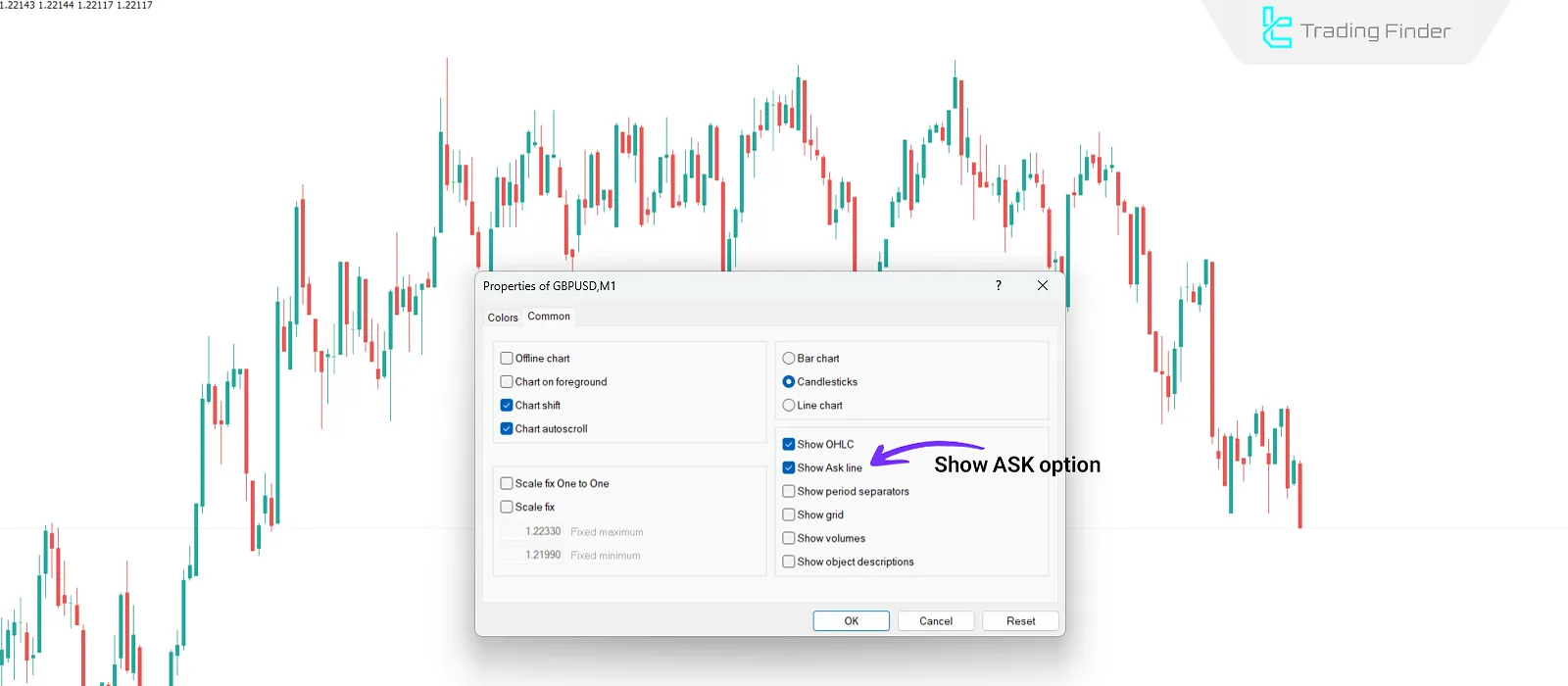
Ask Price on Chart
Right-click the chart, select "Properties", go to the "Common" tab, and enable the option to display the Ask price.
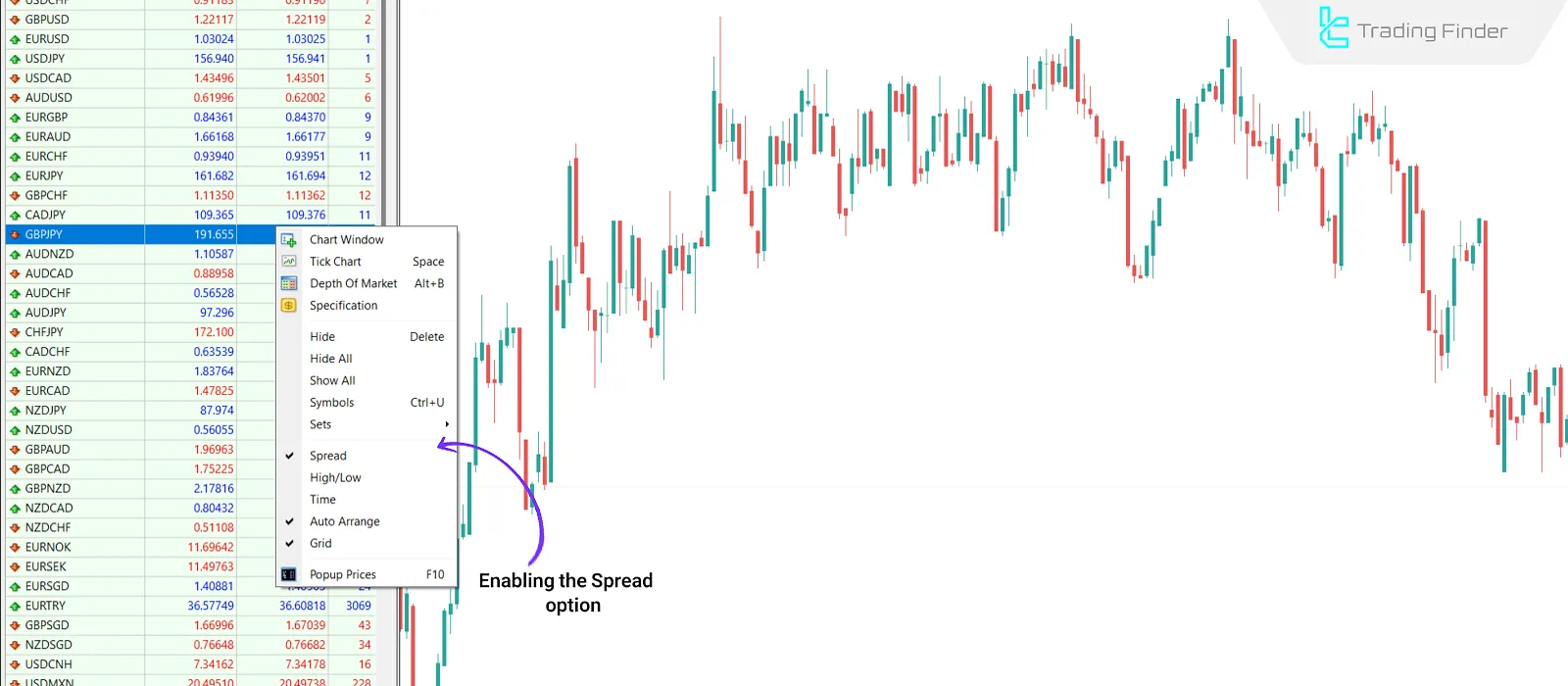
Contract Specifications
In the "Market Watch" window, right-click the desired instrument and select "Specification". The spread type will be listed. Also, you can enable the Spread option in Market Watch to display it directly.
Impact of Spread on Forex Trading Strategies
As a fixed cost in every trade, the Spread plays a key role in the performance of different trading strategies. Its impact varies depending on trading style:
Scalping
Scalping involves executing many trades with small profits (a few pips). Spread is critical here—if too high, it can wipe out potential profits or even lead to losses. Thus, scalpers need very low spreads (preferably under one pip) and fast execution. ECN accounts with raw spreads and transparent commissions are essential.
Day Trading
Day traders open and close multiple positions daily, aiming for medium-range movements (e.g., 20–50 pips). Lower spreads help increase net profitability, especially for high-frequency trades.
Swing Trading
Swing trades stay open for several days to capture larger moves, typically over 100 pips. Here, the Spread has minimal effect compared to swap and holding conditions.
Position Trading
Long-term positions may remain open for weeks or months, focusing on macroeconomic trends. With targets of thousands of pips, spreads have negligible impact. Instead, interest rates (swap), broker credibility, and geopolitical risks are more important.
Spread vs Commission
Spread and commission are separate trading costs. Spread is a hidden, variable cost built into the Bid-Ask difference, while commission is a fixed, transparent fee per trade or lot. Low-spread accounts usually charge a commission, whereas commission-free accounts compensate with wider spreads.
Comparison Between Spread and Commission:
eature | Spread | Commission |
Type of Cost | Difference between bid and ask prices (implicit cost) | Fixed, explicit fee per trade |
Application | Built into price quotes | Shown separately alongside trade |
Market Dependency | Varies in volatile conditions | Fixed, unaffected by market fluctuations |
Typical Use | Standard or Micro accounts | ECN, Raw Spread, or Pro accounts |
Transparency | Low transparency | High transparency |
Conclusion
Spread is a core trading cost in Forex that directly affects strategy profitability. This difference between buy and sell prices can be the deciding factor between profit and loss—especially in scalping and day trading.
By understanding the distinction between fixed and floating spreads, traders can choose the right account type and align their strategy with cost structures. Additionally, knowing how spreads differ from commissions helps clarify hidden fees and choose brokers with realistic terms.













