Crypto yield farming is considered a mechanism based on smart contracts that establishes a direct connection between digital assets and the market without relying on centralized intermediaries. This structure usually distributes returns among participants through native tokens or a share of network fees.
The presence of yield farming on decentralized platforms such as Uniswap, Curve, Aave, and Compound has turned this model into one of the key pillars of capital allocation in decentralized finance.
Entering this process leads to active participation in the DeFi liquidity supply chain and plays a direct role in the dynamism of decentralized markets.
What is Yield Farming?
Yield farming is a method in DeFi for earning passive income by depositing digital assets into liquidity pools. This process is carried out through smart contracts, and in exchange for providing liquidity, reward tokens or transaction fees are allocated to the liquidity provider.
In practice, yield farming allows users to optimize their returns by intelligently reallocating capital between different protocols, especially when reward rates, liquidity volumes, or governance tokens change.
However, factors such as asset price volatility, impermanent loss risk, and the security of smart contracts play a decisive role in final profitability and make risk management an inseparable part of this strategy.
How does Yield Farming Work?
Yield farming is executed based on locking crypto assets in liquidity pools and utilizing smart contracts. These resources provide the necessary infrastructure for activities such as trading, lending, and borrowing.
Users, acting as liquidity providers (LP), earn profits through two methods:
- Transaction fees on platforms such as Uniswap or PancakeSwap;
- Reward tokens issued by the platform, which can be traded or restaked.
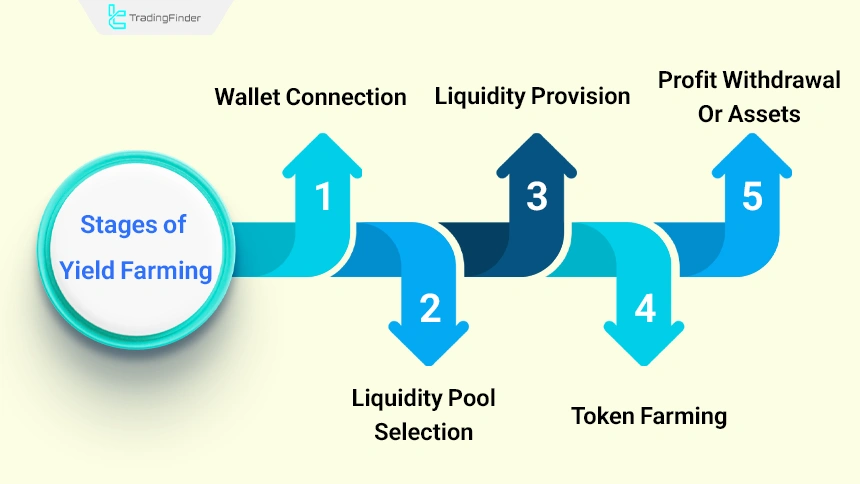
Stages of Yield Farming
The execution sequence of yield farming through smart contracts is carried out automatically. In this mechanism, all stages from asset deposit to reward calculation and distribution are performed without human intervention and based on predefined code.
As a result, transparency, speed, and reduced human error are considered among the most important advantages of using smart contracts in yield farming execution.
Below, the stages of this process are explained in detail:
- Wallet connection: First, the user must connect their cryptocurrency wallet, such as MetaMask or Trust Wallet, to the selected platform;
- Liquidity pool selection: After connecting, a suitable trading pair such as ETH/USDT is chosen to enter the liquidity pool;
- Providing liquidity: The user deposits the desired crypto assets into the pool and receives liquidity tokens (LP tokens) in return;
- Token farming: The LP tokens are deposited in the platform’s farming section to start the process of generating reward tokens;
- Profit or asset withdrawal: At any time, depending on the platform’s conditions, it is possible to withdraw profits or the deposited assets.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Yield Farming
Earning profits from yield farming requires specialized knowledge, continuous analysis, and active risk management. Although this field offers profitable opportunities, ignoring technical and market-related risks can lead to significant losses and early exit.
Below, the main advantages and disadvantages of yield farming are reviewed:
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Passive income | Smart contract risk |
High returns (APY) | Impermanent loss |
Participation in DeFi | Return volatility |
Automatic compound profit | Rug pull risk |
No need for intermediaries or KYC and | Technical complexity, |
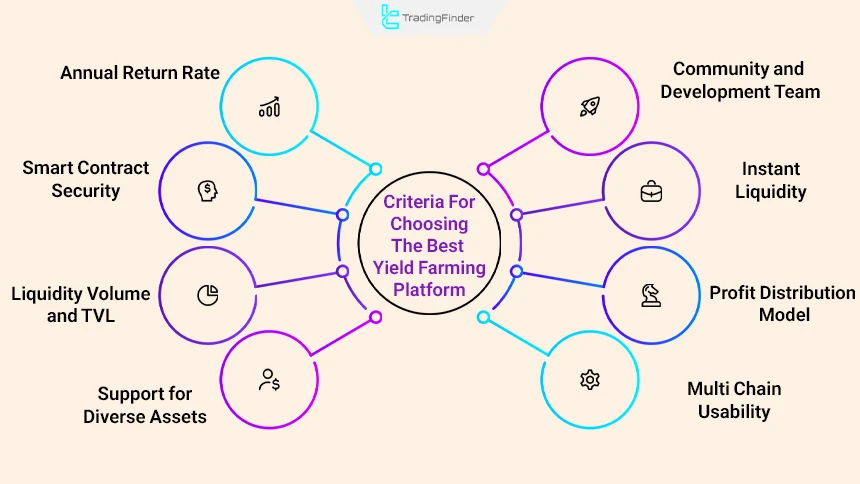
Criteria for Choosing the Best Yield Farming Platform
Choosing the best yield farming platform depends on factors such as capital size, risk tolerance level, type of trading strategy, and the time allocated for continuous monitoring.
A correct choice is achieved when reasonable profitability, high security, and sufficient liquidity exist simultaneously on a yield farming platform.
Criteria for choosing the best yield farming platform:
- Smart contract security: The selected platform must have reputable audits and a history free of hacks;
- Annual return rate (APY/APR): The return rate should be realistic, sustainable, and analyzable; a high APY is not necessarily a sign of long-term profitability;
- Liquidity volume and TVL: High total value locked indicates user trust and the platform’s ability to pay consistent rewards;
- Support for diverse assets and trading pairs: Variety in assets and reputable pairs provides strategic flexibility and reduces the risk of extreme volatility;
- Multi-chain support: Support for multiple blockchains offers easier access, lower fees, and a more optimized user experience;
- Yield model: The profit distribution model should be transparent and preferably based on the platform’s real revenue;
- Community and development team: Transparency of the development team and active community engagement indicate project commitment and investment security;
- Instant liquidity and withdrawal policy: Easy withdrawal and the absence of hidden penalties ensure liquidity and better control over capital.
Difference Between Yield Farming and Staking
Yield farming and staking are both recognized as methods for earning passive income from crypto assets; however, they have fundamental differences in operational structure, risk level, and return rates.
Understanding these distinctions plays a decisive role in choosing an effective investment strategy within the DeFi ecosystem. The table below examines the differences between yield farming and staking:
Feature | Staking | Yield farming |
Profit mechanism | Through locking coins in the network to validate transactions | Through providing liquidity to pools and receiving transaction fees and reward tokens |
Platforms | Proof-of-stake blockchains such as Ethereum 2.0 and Cardano | Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and DeFi protocols |
Risks | Dependent on price fluctuations and network characteristics | Includes impermanent loss and smart contract vulnerabilities |
Typical income | More stable with a defined annual rate or APR | Variable and often with high APY rates |
Strategy composability | Limited to the internal structure of the network | Can be used in multi-stage farming strategies |
Capital lock-up | Often includes a fixed lock-up period such as 15 or 30 days | Instant withdrawal possible in most cases |
Types of Yield Farming
Modern yield farming is not limited to depositing assets into liquidity pools, but also includes a combination of lending, leverage, and simultaneous use of multiple DeFi platforms.
Success in this investment model depends on accurate risk analysis, APY rates, collateralization, and protocol sustainability.
Traditional Yield Farming Methods
Classic crypto yield farming methods are designed based on direct liquidity provision and simple staking on platforms such as Uniswap and PancakeSwap.
In exchange for depositing assets, users receive LP tokens and benefit from additional rewards. Despite their simplicity and transparency, the returns of these models have gradually declined compared to more advanced structures. Types of traditional yield farming methods:
- Providing liquidity on decentralized exchanges (DEX liquidity farming)
- Depositing LP tokens into farms
- Simple staking (single asset staking)
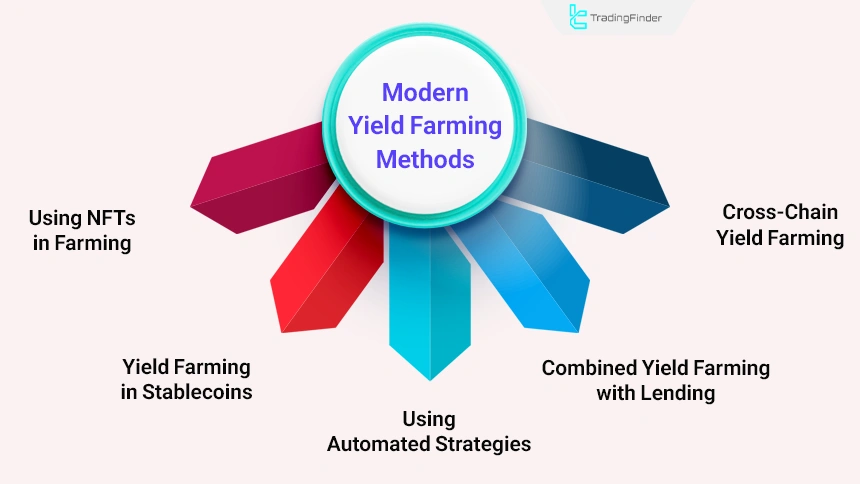
Modern Yield Farming Methods
Modern yield farming uses automation, strategy aggregation, and platforms such as Yearn and Beefy to execute profit compounding without manual user intervention.
Integration with lending, income-generating non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and multi-chain functionality has made it an efficient option for professional users with a long-term perspective.
Types of modern yield farming methods:
- Using automated strategies (auto-compounding vaults)
- Combined yield farming with lending
- Farming with stablecoins and low-risk assets
- Using NFTs in farming
- Cross-chain yield farming
Role of Reward Tokens in Yield Farming
Many yield farming platforms offer their native tokens as rewards to attract liquidity. These tokens may generate high returns initially, but they usually experience price declines as supply increases.
If the value of the reward token decreases, high nominal returns can turn into low real profits or even losses. For this reason, evaluating the token’s real utility and its tokenomics plan is highly important.
How does Yield Farming Generate Income?
In this process, the protocol uses the deposited assets to provide liquidity, facilitate trades, or issue loans, and returns part of the generated value to the user in the form of fees, interest, or incentive tokens.
The level of income depends on factors such as the type of protocol, participation volume, deposit duration, and market conditions; therefore, returns can be variable and dynamic.
Example of Earning Income from Yield Farming
For example, assume you have 1,000 dollars in capital and deposit it into a liquidity pool. This capital enables traders to buy and sell without intermediaries. In return, you receive a portion of the transaction fees and, in some cases, the protocol’s native token as a reward.
Simply put, you make your capital available to the system and earn income from the activity of other users.
Note: The profit figures displayed on DeFi platforms are not necessarily the final profit, as gas fees, withdrawal costs, price fluctuations, and impermanent loss affect actual returns. Therefore, before entering any pool, nominal returns should be compared with real costs.
Difference Between APR and APY in Yield Farming?
In the field of yield farming and investment in DeFi protocols, understanding the difference between APR and APY is highly important for evaluating the real return on capital.
- Annual percentage rate: The annual return rate calculated without considering compound interest and represents the base profit earned on capital over one year, without reinvesting rewards;
- Annual percentage yield: The yearly return rate that includes compound interest, where earned rewards are regularly reinvested to generate additional returns.
Best Yield Farming Platforms in DeFi
Along with the significant growth of decentralized finance, a large number of yield farming protocols with diverse mechanisms have entered the market.
However, not all of them meet acceptable standards in terms of security, liquidity sustainability, and profitability. Below, a selection of the top yield farming platforms is introduced along with their yield models, advantages, and distinctive features.
Introduction and comparison of 10 leading yield farming platforms in DeFi:
Platform name | Yield farming model | Special feature | Advantages |
Aave | Earning returns through lending assets | Borrowing with variable and fixed interest rates | High security, support for multiple networks such as Ethereum, Optimism, and Polygon |
Compound | Depositing crypto assets and receiving automatic yield | Integration with reputable wallets such as Coinbase Wallet | Stable annual yield, COMP governance token |
Uniswap V3 | Depositing trading pairs into pools and earning transaction fees | Ability to select price ranges to optimize returns | High liquidity, no need for secondary farming |
Curve Finance | Providing liquidity for similarly priced pairs such as USDT/USDC | Yield boost through locking veCRV | Low fees, attractive APY with minimal volatility risk |
Yearn Finance | Depositing into vaults to execute automated strategies | Decentralized and community-driven structure | Passive management optimized compound yield |
Beefy Finance | Automated farming with reinvested yield across multiple vaults | Simple interface, high returns | Support for multiple networks such as BSC, Arbitrum, and Polygon |
GMX | Staking GMX/GLP and earning real fees from user activity | Suitable for conservative investors with a real yield model | No need for inflationary rewards, sustainable income |
Convex Finance | Staking Curve LP tokens for enhanced rewards | Increased voting power in Curve DAO | Accumulated yield from CRV and CVX fees |
Pancake Swap | Providing liquidity and farming LP tokens on BNB Chain | Suitable for beginners with a simple interface | Low gas fees, fast returns, CAKE token |
Balancer | Multi-asset liquidity provision in weighted pools | High APY for lesser-known assets | Automated portfolio construction with asset diversification |
Risks and Challenges of Yield Farming
Despite its high profitability, yield farming is not risk-free. The decentralized nature of DeFi, reliance on smart contracts, and market volatility make it a challenging field, and awareness of these risks before investing is essential.
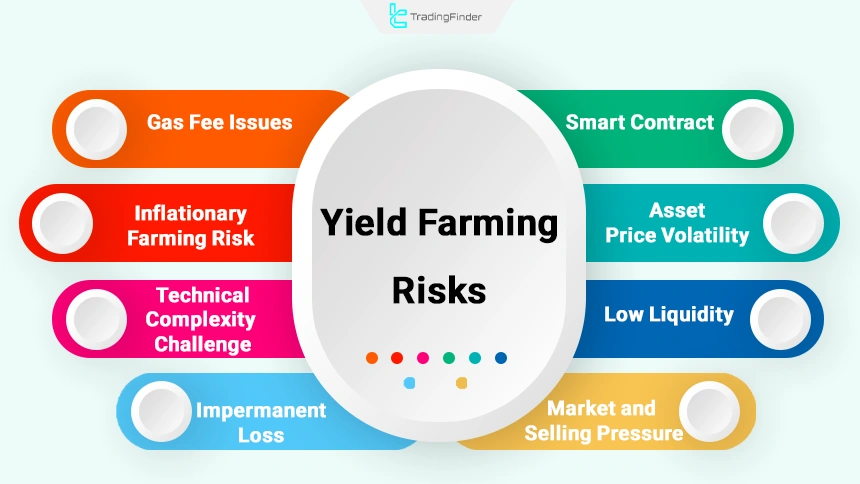
Risks and challenges of yield farming:
- Smart contract risk
- Asset price volatility risk
- Low liquidity risk
- Gas fee–related issues
- Inflationary farming risk
- Technical complexity challenge
- Market risk and selling pressure
- Impermanent loss risk
Smart Contract Risk
All crypto yield farming processes are fully executed on smart contracts. Any coding error, security bug, or structural vulnerability can lead to the loss of assets.
Even reputable platforms are not immune to hacking or exploits; therefore, carefully reviewing audit reports before entering any yield farming platform is critical.
Asset Price Volatility Risk
Although some platforms offer farming with stablecoins, a significant portion of profitable opportunities is built on highly volatile tokens. In such conditions, sharp price declines can not only eliminate profits but also result in investor losses.
As a result, managing entry and exit timing from pools and paying attention to overall market trends become highly important, since even high nominal returns lose real value when token prices fall.
For this reason, assessing volatility risk and diversifying assets are considered key factors in reducing the negative impact of this type of risk in yield farming.
Low Liquidity Risk
In some platforms or low-volume pools, insufficient liquidity leads to high slippage, delays in asset withdrawal, or even pool closure. Reviewing indicators such as total value locked (TVL) and daily trading volume is essential for evaluating a liquidity pool.
Under such conditions, entering or exiting capital may involve significant hidden costs and reduce investor flexibility.
Therefore, choosing pools with stable liquidity and a solid operating history plays an important role in reducing liquidity risk and maintaining fast access to assets.
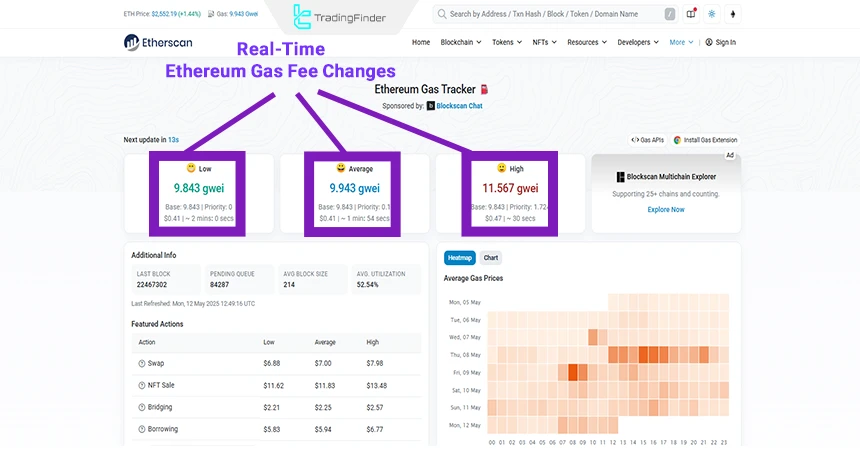
Gas Fee Related Issues
In networks such as Ethereum, sharp increases in transaction fees during high-traffic periods may reduce the net profit generated from yield farming or even make the activity uneconomical.
As a result, choosing the right timing and evaluating costs before entering is highly important. For this reason, using alternative networks with lower fees or layer-two solutions can have a significant impact on increasing real returns.
Additionally, accurately calculating the ratio of gas costs to expected profit helps investors avoid entering positions with only apparent profitability.
Inflationary Farming Risk
In some projects, farming rewards are generated through the continuous issuance of new tokens. This process leads to a gradual decline in token value and, as a result, a decrease in users’ real returns; a situation often observed in newly launched projects.
Under these conditions, selling pressure caused by increased supply can quickly neutralize received rewards, especially if there is no real demand for the token.
Therefore, reviewing the tokenomics model, issuance rate, and real utility of the token before entering farming plays an important role in assessing profit sustainability and preventing capital value erosion.
Technical Complexity Challenge
Many crypto yield farming strategies, especially combined or multi-stage models, require technical knowledge, continuous monitoring, and a precise understanding of smart contracts.
For beginner users, this level of complexity can lead to execution errors and ultimately asset loss.
As a result, using automated management tools, simpler user interfaces, and reputable platforms can partially reduce this risk; however, education and gradual familiarity with core DeFi concepts remain essential.
Without a proper understanding of mechanisms, even the most profitable strategies can result in costly and irreversible decisions.
Market Risk and Selling Pressure
When users cash out farming profits, selling pressure on the platform’s native token increases. In the absence of sufficient demand, this pressure can lead to sharp price declines and, consequently, a reduction in the total value of users’ capital.
In such conditions, token price stability becomes highly dependent on the balance of supply and demand, and the lack of real utility or long-term incentives can disrupt this balance.
Therefore, evaluating user behavior, reward release volume, and the project’s control measures for managing selling pressure plays an important role in reducing market risk and preserving capital value.
An educational article on yield farming risks on the quantstamp.com website provides additional explanations regarding enhanced security in yield farming, which interested users can benefit from.
Impermanent Loss Risk
When users deposit assets into a liquidity pool and one of the assets experiences severe and asymmetric price volatility, they may face a phenomenon known as impermanent loss. This issue is very common in many DEX pools, especially when volatile tokens are involved.
Even if a user ultimately exits the pool with nominal profit, the value of their assets may be lower compared to simply holding the tokens.
For this reason, selecting highly correlated pairs, using pools with impermanent loss mitigation mechanisms, and carefully comparing farming returns with price volatility risk play an important role in controlling the impact of this risk.
How Does Yield Farming Differ in Bull and Bear Markets?
In a bull market, rising asset prices can amplify yield farming profits, but at the same time increase impermanent loss risk. In a bear market, although nominal returns decline, stablecoin pools can serve as an option for preserving capital value.
An educational video from the CryptoLabs Research YouTube channel provides further explanations about yield farming in bear markets, which interested users can watch.
Difference Between Yield Farming and Staking
Staking refers to locking assets to participate in network consensus and security; Its returns are usually more stable and lower-risk and do not require active management.
Yield farming is a DeFi investment strategy based on providing liquidity or lending, which can generate higher returns but is exposed to risks such as return volatility, impermanent loss, and smart contract threats.
The table below compares yield farming and staking:
Criterion | Staking | Yield farming |
Source of return | Block rewards + network fees | Trading fees + incentive tokens |
Annual return stability | Relatively stable and predictable | Unstable and liquidity-dependent |
Main risk | Slashing, liquidity lock-up | Impermanent loss, hacks, smart contract risk |
Management requirement | Minimal | Active and continuous |
Technical complexity | Low to medium | High |
Liquidity | Limited until lock-up ends | Usually higher but variable |
Suitable for | Conservative investors | Risk-tolerant and professional investors |
Economic objective | Network security and stability | Return optimization |
Can Yield Farming Replace Traditional Investment?
Yield farming can be attractive due to its high potential returns; however, because of technical risks and market volatility, it is not considered a suitable option for fully replacing low-risk investment methods.
From a professional perspective, yield farming should only represent a portion of a diversified portfolio and be used alongside traditional or lower-risk financial instruments to create an appropriate balance between risk and return.
The table below provides a professional comparison of the differences between yield farming and traditional investment:
Comparison criterion | Yield farming | Lower-risk / traditional investments |
Potential return level | High and sometimes very attractive, but unstable | Low to medium, usually stable |
Technical risk | High (smart contract risk, bugs, hacks, oracles) | Very low or close to zero |
Market risk | High (severe asset price volatility, impermanent loss) | Low to medium |
Technical complexity | High; requires DeFi knowledge, wallet management, and protocol interaction | Low; suitable for the general public |
Liquidity | Usually high, but dependent on protocol and market conditions | Medium to high, often with defined rules |
Operational transparency | High (on-chain data visibility) | Dependent on financial institutions and reports |
Income sustainability | Unstable and variable | More stable and predictable |
Role in investment portfolio | Complementary tool to increase overall portfolio return | Core of the portfolio for capital preservation |
Recommended strategy | Limited and controlled use alongside other instruments | Broad use to create stability |
Common User Mistakes in Yield Farming
Despite the strong appeal of yield farming, many users-especially less experienced ones-encounter mistakes that result in reduced returns or capital loss.
These challenges usually stem from a lack of thorough analysis, improper risk assessment, and a superficial understanding of decentralized finance mechanisms.
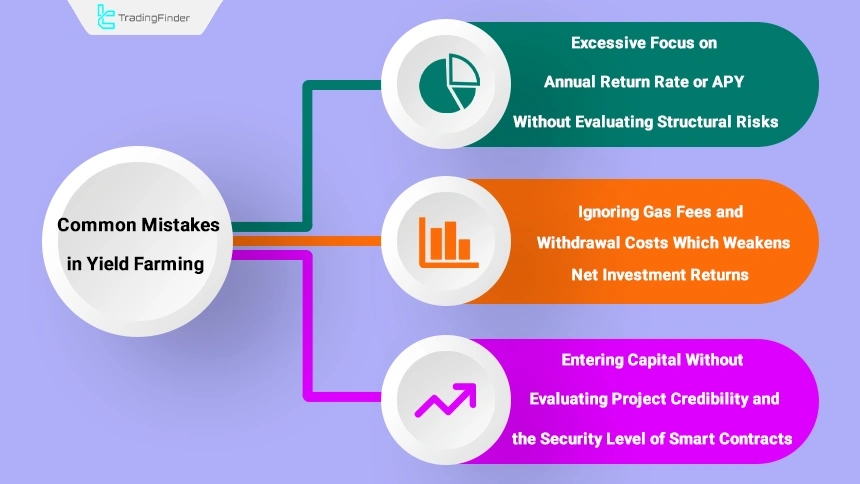
Common mistakes in yield farming:
- Excessive focus on annual percentage yield (APY) without evaluating structural risks;
- Ignoring gas fees and withdrawal costs, which weakens net returns;
- Entering with capital without reviewing project credibility and the security level of smart contracts.
Best Strategies for Successful Yield Farming
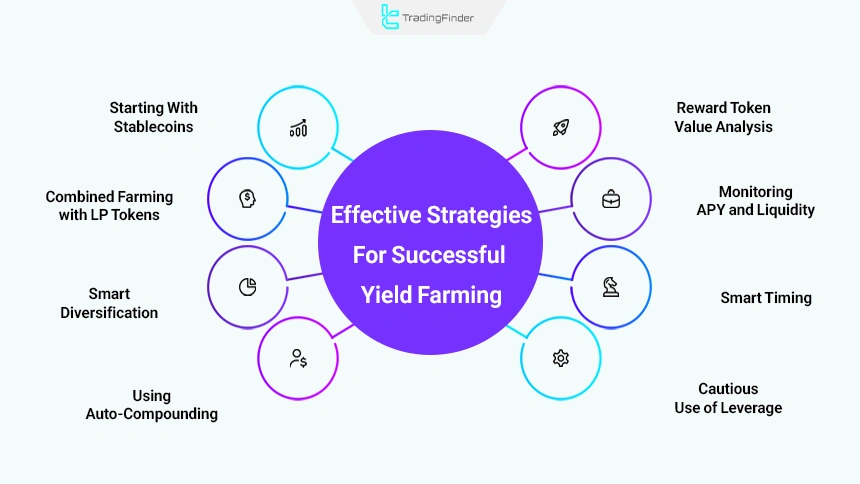
To succeed in yield farming, simply depositing assets is not sufficient. Professional users increase returns and keep risk at an acceptable level by implementing precise strategies. Effective approaches for successful yield farming:
- Starting with stablecoins: Using pools such as USDC/DAI minimizes price volatility and impermanent loss risk;
- Combined farming with LP tokens: Depositing LP tokens into secondary platforms such as Convex or Yearn results in automatic compound returns;
- Smart diversification: Distributing assets across different pools and platforms reduces systemic risk and prevents capital concentration;
- Using auto-compounding: Platforms such as Beefy Finance automatically compound rewards, eliminating manual management and increasing efficiency;
- Monitoring APY and liquidity: Continuous monitoring of annual percentage yield, TVL, and market conditions is critical to maintaining profitability;
- Smart timing: Early entry into new farms and timely exit enables optimized short-term profit opportunities;
- Cautious use of leverage: Leveraged yield farming generates profit only in low-volatility markets with precise risk management;
- Analyzing reward token value: Thorough evaluation of backing, utility, and liquidity of reward tokens is a fundamental requirement for rational and professional decision-making.
Ai-Based Trend Navigator Indicator for Trend Detection in Yield Farming
The AI-based trend navigator indicator, known as AI Trend Navigator, is a modern analytical tool designed for users who focus on identifying the dominant market trend for yield farming in bullish markets and reducing investment risk within their asset portfolios.
This indicator has been specifically developed for the MetaTrader platform and uses the K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) machine learning algorithm to analyze price data.
The operational logic of AI Trend Navigator is based on reducing market noise and clearly displaying the price movement structure. The indicator output consists of a main trend line and a signal line.
The trend line defines the overall market direction, while the signal line functions as a trade-timing tool.
- AI-based trend navigator indicator in MT5 (AI Trend Navigator)
- AI-based trend navigator indicator in MT4 (AI Trend Navigator)
A color change in this line is the primary basis for generating signals; in bullish conditions, a color change from red to green may indicate a buying opportunity, while in bearish trends, a color change from green to red is considered a warning for entering a sell position.
This indicator is usable across multiple timeframes and is designed for various trading styles such as scalping, intraday trading, and day trading. Traders can use it for trend analysis and improving decision-making accuracy without dependence on a specific symbol or market.
One of the standout features of AI Trend Navigator is its flexible settings.
Users can select the price source from price action, VWAP, and various moving averages, and parameters such as moving average length, the number of KNN neighbors, and smoothing allow traders to adjust the indicator’s sensitivity according to their trading strategy.
Increasing the number of neighbors results in a smoother trend line, while higher smoothing makes the indicator’s response more stable.
Overall, the AI-based trend navigator indicator is a practical tool for identifying market direction and optimizing entry and exit points, which, when used alongside proper risk management, can significantly enhance trading performance.
Conclusion
Crypto yield farming, also known as yield cultivation, is one of the most profitable mechanisms within decentralized finance. In this method, users earn passive income by depositing digital assets into liquidity pools and utilizing smart contracts.
This model generates returns through reward tokens and a share of network fees, circulating capital dynamically within the DeFi ecosystem.
On the other hand, factors such as impermanent loss, price volatility, and technical vulnerabilities make successful yield farming dependent on specialized knowledge, accurate data analysis, and careful evaluation of reputable platforms.













