The UK’s FCA is one of the most stringent financial authorities in Forex industry that supervises brokers offering services in the United Kingdom. These brokerages are limited in terms of leverage, promotional offers, instrument classes, and other parameters.
The list below contains some of the best choices regulated by the FCA.
 | eightcap | |||
 | Pepperstone | |||
 | FXCM | |||
| 4 |  | eToro | ||
| 5 |  | IronFX | ||
| 6 |  | TICKMILL | ||
| 7 |  | CMC Markets |
Trustpilot Ratings in FCA Brokers
The ranking in this section is based on the Trustpilot scores submitted for the mentioned Forex brokerages regulated by the FCA in UK.
Broker Name | Trustpilot Rating | Number of Reviews |
842 | ||
CMC Markets | 2,850 | |
Pepperstone | 3,156 | |
30,360 | ||
Eightcap | 3,406 | |
STARTRADER | 893 | |
Tickmill | 1,069 | |
IronFX | 671 |
Trading Spreads in FCA Brokers
The table in this section ranks the FCA brokers by their minimum spread across all account types and instruments.
Broker Name | Min. Spread |
CMC Markets | 0 Pips |
0 Pips | |
eToro | 0 Pips |
0 Pips | |
Eightcap | 0 Pips |
Swissquote | 0 Pips |
FXCM | 0.2 Pips |
Plus500 | 0.5 pips |
Non-Trading Fees in FCA Brokers
Brokers usually charge inactivity, deposit, withdrawal, and conversion costs as non-trading fees for users. Mentioned brokerages are ranked based on it here.
Broker Name | Deposit Fee | Withdrawal Fee | Inactivity Fee |
STARTRADER | $0 | $0 | $0 |
Pepperstone | $0 | $0 | $0 |
Plus500 | $0 | $0 | $10 |
From $0 | $0 | 10 EUR | |
Swissquote | From $0 | $0 | €15 |
From $0 | $0 | $10 | |
eToro | $0 | $5 | $10 |
FXCM | $0 | $0 Except for Bank Transfers | $50 Annually |
Tradable Instruments in FCA-Regulated Brokerages
The ranking in this section mentions the number of tradable instruments for each of the mentioned brands.
Broker Name | Number of Instruments |
eToro | 6,000+ |
Plus500 | 2,800+ |
Pepperstone | 1,200+ |
STARTRADER | 1,000+ |
600+ | |
500+ | |
Swissquote | 400+ |
Axi | 220+ |
Top 6 Brokers Regulated by FCA
Five of the recommended brokerages under the supervision of the UK’s financial authority are reviewed in summary in the following sections.
FXCM
Founded in 1999, FXCM (Forex Capital Markets) is a long-running Forex and CFD provider with a strong footprint in the UK, one reason it’s frequently shortlisted in “Best Financial Conduct Authority forex brokers” roundups. Its UK entity operates from London and is built for multi-asset CFD trading.
From a regulation perspective, FXCM runs a multi-entity structure that includes oversight beyond the FCA, such as Australian Securities and Investments Commission, Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission, Israel Securities Authority, and Financial Sector Conduct Authority.
Client-safety features highlighted across regulated entities include segregated accounts, negative balance protection, and recurring audits.
For trading access, FXCM lists three primary account tracks, CFD, Active Trader, and Corporate, starting from a $50 minimum deposit, with floating spreads from 0.2 pips on supported instruments. Platform coverage is a key selling point: MT4 plus integrations with TradingView and TradeStation, alongside algorithmic and copy-trading style options.
FXCM’s brand history is also part of its due-diligence story: it faced major U.S. enforcement action in 2017 by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission and scrutiny tied to National Futures Association, followed by a restructuring period and acquisition by Jefferies Financial Group.
For UK-eligible clients, investor coverage is commonly referenced via the Financial Services Compensation Scheme (up to £85,000). If you are interested, check out our FXCM registration guide.
Specifics and Features
Account Types | CFD account, Active Trader account, Corporate account |
Regulating Authorities | FCA, ASIC, CySEC, ISA, FSCA |
Minimum Deposit | $50 |
Deposit Methods | Visa/MasterCard, Bank wired, Neteller, Skrill |
Withdrawal Methods | Visa/MasterCard, Bank wired, Neteller, Skrill |
Maximum Leverage | 1:1000 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MT4, TradingView, TradeStation |
FXCM Pros and Cons
FXCM fits FCA-focused comparisons when the priority is a long operating track record, recognizable regulatory coverage, and broad platform connectivity, while the trade-off assessment usually comes down to fee points (like inactivity/bank-wire costs) and how much weight you place on its past regulatory and corporate events.
Pros | Cons |
FCA-regulated UK entity with investor-protection framework (FSCS eligibility where applicable) | Notable regulatory/corporate setbacks in 2017 remain part of due diligence |
Multi-regulated group footprint across several jurisdictions | $50 annual inactivity fee after prolonged non-use (as stated in broker materials) |
Strong platform mix: MT4 + TradingView + TradeStation connectivity | Bank wire withdrawals can carry a $40 fee |
Low barrier to entry with $50 minimum deposit and spreads from 0.2 pips (instrument-dependent) | Account conditions and leverage vary by entity/account type, which can complicate comparisons |
CMC Markets
CMC Markets is a London-based brokerage with over 30 years of industry experience and more than 1 million clients across four continents. The company is publicly listed on the London Stock Exchange (LSE), reinforcing its transparency and financial accountability.
Operating through its UK entity, CMC Markets UK Plc, the broker is regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) and several other Tier-1 regulators worldwide. FCA oversight ensures strict compliance with client fund segregation, negative balance protection, and FSCS coverage up to £85,000 for eligible UK clients.
CMC Markets provides access to Spread Betting, CFD Trading, and FX Active accounts, supporting retail and advanced traders. Clients can trade 12,000+ instruments across forex, indices, commodities, shares, ETFs, treasuries, and cryptocurrencies, with floating spreads from 0.0 pips and leverage aligned with regulatory limits.
The broker’s proprietary Next Generation platform, alongside MetaTrader 4, delivers advanced charting, institutional-grade execution, and multi-device access. With no minimum deposit, broad base-currency support, and professional-grade tools, CMC Markets positions itself as a technology-driven FCA-regulated broker. Here’s a summary of the broker’s details.
Account Types | Spread Betting, CFD Trading, FX Active |
Regulating Authorities | FCA, ASIC, CySEC, DFSA, NFRA, FMA, BaFIN |
Minimum Deposit | $0 |
Deposit Methods | Visa/MasterCard, Bank wired, Online Banking |
Withdrawal Methods | Visa/MasterCard, Bank wired, Online Banking |
Maximum Leverage | 1:500 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MT4, Next Generation web trading platform |
CMC Markets Pros & Cons
CMC Markets combines long-standing market presence, top-tier regulation, and a highly sophisticated trading infrastructure. Before opening an account through the CMC Markets registration, check out this balanced overview of the broker’s main strengths and limitations to help evaluate its suitability for different trading styles.
Pros | Cons |
FCA-regulated and LSE-listed company | Higher commissions on share CFDs |
12,000+ tradable instruments across global markets | Limited deposit and withdrawal methods |
Advanced proprietary Next Generation platform | Inactivity fee after prolonged non-trading |
No minimum deposit requirement | No PAMM or managed account solutions |
Pepperstone
Pepperstone is a high-volume global forex and CFD broker founded in 2010 in Melbourne. The company processes over $9.2 billion in daily trading volume for more than 400,000 clients, supporting flexible trade sizes from 0.01 to 100 lots across multiple markets.
From a regulatory standpoint, Pepperstone’s UK entity is authorized by the FCA, complemented by oversight from ASIC, CySEC, BaFin, DFSA, and CMA. This multi-jurisdiction structure enforces segregated client funds, negative balance protection, and strict compliance standards.
Pepperstone offers Standard and Razor accounts with pricing models designed for different trading styles. Spreads start from 0.0 pips on Razor accounts, while commission-free trading is available on Standard accounts. You can participate in Pepperstone rebate program for a discount on costs.
Leverage reaches up to 1:500 under non-EU entities, with FCA clients trading under ESMA limits.
On the technology side, Pepperstone supports MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, cTrader, TradingView, and proprietary platforms. Traders gain access to Forex, indices, commodities, crypto CFDs, shares, and ETFs, alongside support for scalping, Expert Advisors, and hedging strategies. The table below summarizes the broker’s specifics.
Account Types | Standard, Razor |
Regulating Authorities | ASIC, SCB, FCA, DFSA, CMA, BaFin, CySEC |
Minimum Deposit | $1 |
Deposit Methods | Apple Pay, Google Pay, Visa, Mastercard, Bank transfer, PayPal, Neteller, Skrill, Union Pay, USDT, ZotaPay |
Withdrawal Methods | Apple Pay, Google Pay, Visa, Mastercard, Bank transfer, PayPal, Neteller, Skrill, Union Pay, USDT, ZotaPay |
Maximum Leverage | 1:500 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | Proprietary Platform, cTrader, Trading View, MetaTrader 4&5 |
Pepperstone Pros & Cons
Pepperstone focuses on execution quality, tight pricing, and regulatory credibility rather than promotional incentives. Below is a balanced overview of the broker’s key strengths and limitations to help assess its suitability.
Pros | Cons |
FCA-regulated with strong global oversight | No bonuses or promotional programs |
Tight spreads from 0.0 pips on Razor accounts | No PAMM or managed account solutions |
Wide platform selection incl. MT4, MT5, cTrader, TradingView | Leverage capped at 1:30 for FCA retail clients |
No inactivity or account maintenance fees | Demo account availability can be limited |
eToro
eToro is a global multi-asset brokerage founded in 2007 and headquartered in Tel Aviv, Israel. The company is best known for pioneering social trading, allowing users to invest across Forex, stocks, ETFs, commodities, indices, and cryptocurrencies through an integrated, proprietary platform.
From a regulatory perspective, eToro operates under several authorities, including the FCA for its UK entity. This ensures compliance with MiFID II standards, client fund segregation, and investor protection under the FSCS scheme, covering eligible clients up to GBP 85,000.
eToro offers four account types, Personal, Professional, Corporate, and Islamic, designed for different trader profiles. For a guide on opening an account, visit our eToro registration guide.
Retail clients can access leverage up to 1:30 under FCA rules, while eligible professional traders may unlock higher limits with reduced regulatory protections.
Instead of MetaTrader platforms, eToro relies exclusively on its in-house web and mobile trading system. The platform integrates CopyTrader, Smart Portfolios, and crypto staking features, positioning eToro closer to an investment ecosystem than a traditional Forex-only broker.
eToro stands out for its regulatory depth, intuitive platform, and unique copy trading infrastructure. Here’s a summary of its specifics.
Account Types | Personal, Professional, Corporate, Islamic |
Regulating Authorities | FCA, CySEC, MFSA, FSRA, ASIC, FSA, Gibraltar FSC |
Minimum Deposit | $10 |
Deposit Methods | eToro Money, Credit/Debit Card, Bank Transfer, PayPal, Neteller, Skrill, Online Banking (Trustly), iDEAL, Sofort, Przelewy24 |
Withdrawal Methods | eToro Money, Credit/Debit Card, Bank Transfer, PayPal, Neteller, Skrill, Online Banking (Trustly), iDEAL, Sofort, Przelewy24 |
Maximum Leverage | 1:400 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | Proprietary App |
eToro Pros & Cons
The following pros and cons summarize its strengths and limitations for traders evaluating FCA-regulated Forex brokers.
Pros | Cons |
FCA regulation with FSCS protection up to GBP 85,000 | No MetaTrader 4 or MetaTrader 5 support |
Innovative CopyTrader & Smart Portfolio features | $10 monthly inactivity fee after 12 months |
Very low minimum deposit ($10) | Proprietary platform only |
Wide range of tradable markets and assets | No phone-based customer support |
Eightcap
Eightcap is a multi-asset Forex and CFD broker founded in 2009 in Melbourne, offering access to six major markets, including Forex, indices, commodities, shares, metals, and crypto CFDs. The broker supports leverage up to 1:500 under non-EU entities and provides over 800 tradable instruments globally.
Eightcap operates under a strong multi-jurisdiction regulatory framework, with oversight from the Financial Conduct Authority, Australian Securities and Investments Commission, and Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission.
FCA-regulated UK clients benefit from FSCS protection up to £85,000, segregated funds, and negative balance protection.
The broker offers three main live account types, Standard, Raw, and TradingView, alongside a demo account. Spreads start from 1.0 pip on Standard accounts and from 0.0 pips on Raw accounts, with competitive commission structures. For discounts on spreads or trading fees, check out the Eightcap rebate program.
All accounts support scalping, EAs, and market execution with an 80% margin call and 50% stop-out level.
Eightcap distinguishes itself through advanced trading technology and platform choice. Traders can access MT4, MT5, and full TradingView integration, complemented by tools such as Capitalise.ai, FlashTrader, and an AI-powered economic calendar designed to enhance automation, execution speed, and macro-driven analysis.
Overall, Eightcap combines top-tier FCA regulation, modern trading platforms, and strong crypto-CFD depth, making it a competitive choice among FCA-regulated Forex brokers.
Summary of Parameters
Account Types | Standard, Raw, TradingView, Demo |
Regulating Authorities | ASIC, FCA, CySEC, SCB |
Minimum Deposit | $100 |
Deposit Methods | Crypto, e-wallets, credit/debit card, bank transfer, Online Payment Systems |
Withdrawal Methods | Crypto, e-wallets, credit/debit card, bank transfer, Online Payment Systems |
Maximum Leverage | 1:500 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MT4, MT5, TradingView |
Eightcap Pros & Cons
Below is a concise overview of its key advantages and limitations, which are essential to be aware of before Eightcap registration.
Pros | Cons |
Regulated by FCA, ASIC, and CySEC | No copy trading or PAMM accounts |
Tight spreads with Raw accounts from 0.0 pips | Educational resources are relatively basic |
Full TradingView integration with auto-subscription perks | Inactivity fee after prolonged dormancy |
Wide crypto CFD offering (outside UK retail limits) | Weekend customer support not available |
STARTRADER
Founded in 2012 and headquartered in Seychelles, STARTRADER runs a multi-entity brokerage model that includes a Tier-1 Financial Conduct Authority licence for its UK branch. FCA supervision typically means strict conduct rules, segregated client money, and FSCS eligibility up to £85,000.
On the trading side, STARTRADER offers STP and ECN pricing with micro-lot sizing from 0.01 lots, spreads from 0.0 pips (ECN), and a $50 minimum deposit. The broker lists 1,000+ instruments across Forex, indices, commodities, metals, and share CFDs, including 50+ FX pairs and 70+ equities.
Platform coverage spans MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, WebTrader, and a proprietary mobile app, with market execution as the default model. Check out the STARTRADER dashboard article for a review of the broker’s user interface and account management features.
For account security, the broker highlights SSL encryption and segregated accounts, while negative balance protection is available under specific regulated entities (including the FCA unit).
Because STARTRADER is also regulated by Australian Securities and Investments Commission, Financial Sector Conduct Authority, and offshore authorities, leverage and protections vary by jurisdiction (e.g., up to 1:30 under FCA, higher elsewhere). The CEO, Peter Karsten, focuses on execution infrastructure, liquidity partnerships, and regional growth.
Overall, STARTRADER’s strengths and trade-offs come down to entity selection: the FCA branch prioritizes safeguards (segregation, NBP, FSCS eligibility), while non-UK entities emphasize higher leverage and broader flexibility.
STARTRADER Pros and Cons
The pros and cons below summarize what’s typically assessed before listing the full broker breakdown. Pay attention to them before going on with the STARTRADER registration procedure.
Pros | Cons |
FCA-regulated UK entity with FSCS eligibility up to £85,000 | Protections and leverage differ materially by entity/jurisdiction |
1,000+ tradable instruments across major CFD markets | ECN pricing can add commission costs (instrument/account dependent) |
STP + ECN accounts, micro-lots from 0.01, spreads from 0.0 pips (ECN) | Research/education depth is relatively limited vs. top research-led brokers |
Multiple platforms: MT4, MT5, WebTrader, and mobile app | Crypto product access is restricted for UK retail under FCA rules; availability depends on registration entity |
How Were the Brokerages Selected?
Choosing the Best FCA-Regulated Forex Brokers requires more than comparing spreads or platform names. At TradingFinder, each broker is evaluated using a 19-metric review methodology designed to reflect real trading conditions, regulatory strength, and long-term reliability under Financial Conduct Authority supervision.
Regulation and licensing form the foundation of our analysis. We verify FCA authorization, client money segregation under CASS rules, negative balance protection, and eligibility for the Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS), which may protect retail traders up to £85,000 in case of broker insolvency.
Beyond compliance, our analysts examine broker background data such as establishment year, corporate structure, headquarters, and global office presence. We then assess account type diversity, including Standard, ECN, Micro, PAMM, and professional accounts, alongside leverage policies and risk controls aligned with FCA guidelines.
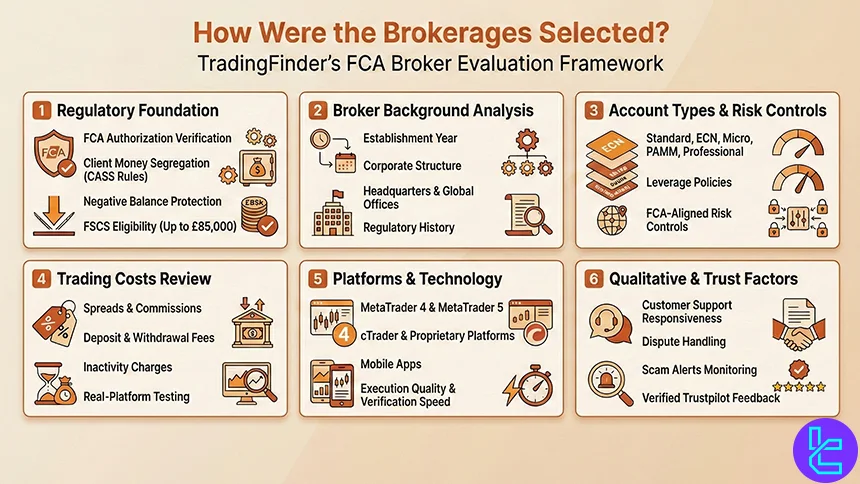
Trading costs are reviewed in detail. This includes spreads, commissions, deposit and withdrawal fees, and inactivity charges, all tested through direct platform usage where possible. We also evaluate tradable asset coverage, from major and minor forex pairs to CFDs on indices, commodities, stocks, ETFs, and crypto derivatives.
Technology and usability play a critical role. Brokers are tested across MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, cTrader, proprietary platforms, and mobile apps, with close attention to execution quality, account-opening workflows, and verification speed. Copy trading, investment tools, and educational resources are assessed for transparency and practical value.
Finally, qualitative factors complete the review. We analyze customer support responsiveness, broker communications, scam alerts, dispute handling, and verified user feedback from Trustpilot.
What is the United Kingdom’s FCA?
The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) is the primary financial regulator responsible for overseeing financial markets, firms, and services in the United Kingdom. Established in 2013, the FCA replaced the Financial Services Authority (FSA) as part of the UK’s post-financial-crisis regulatory reforms, with a stronger focus on consumer protection, market integrity, and competition.
The FCA regulates a wide range of financial institutions, including forex and CFD brokers, investment firms, banks, and asset managers. Its core objectives include protecting retail clients, ensuring that financial markets operate fairly and transparently, and reducing the risk of systemic failures.
FCA-authorized brokers must comply with strict rules on client fund segregation, capital adequacy, risk disclosures, and conduct of business.
One of the FCA’s most important safeguards for retail traders is mandatory participation in the Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS). Under this scheme, eligible clients may be compensated up to £85,000 per person per firm if an FCA-regulated broker becomes insolvent.
Following Brexit, the FCA operates independently from EU regulators, but it has largely retained MiFID-based standards, maintaining high regulatory consistency. As a result, FCA regulation is widely regarded as Tier-1, making it one of the most trusted benchmarks for forex broker safety and regulatory credibility worldwide.
What Are the Pros and Cons of the FCA Regulation on Brokers?
FCA regulation is widely regarded as one of the strongest supervisory frameworks in the global forex industry. Brokers authorized by the Financial Conduct Authority operate under strict legal, financial, and conduct standards designed to protect retail traders and ensure market integrity.
However, this high level of oversight also introduces certain limitations compared to offshore or lightly regulated jurisdictions.
Pros | Cons |
Strong investor protection through strict conduct-of-business rules and continuous supervision | Lower leverage limits for retail traders (typically capped at 1:30 for major FX pairs) |
FSCS coverage up to £85,000 per eligible client in case of broker insolvency | Higher compliance costs for brokers, which may translate into wider spreads or fewer promotions |
Mandatory client fund segregation under UK CASS rules | No trading bonuses for retail clients due to product intervention rules |
Negative balance protection for retail traders | More complex onboarding due to enhanced KYC and AML requirements |
High transparency standards for pricing, execution, and risk disclosures | Restricted product offerings for high-risk instruments compared to offshore brokers |
Strong enforcement powers, including fines, license suspension, and criminal referrals | Limited flexibility for traders seeking aggressive risk exposure |
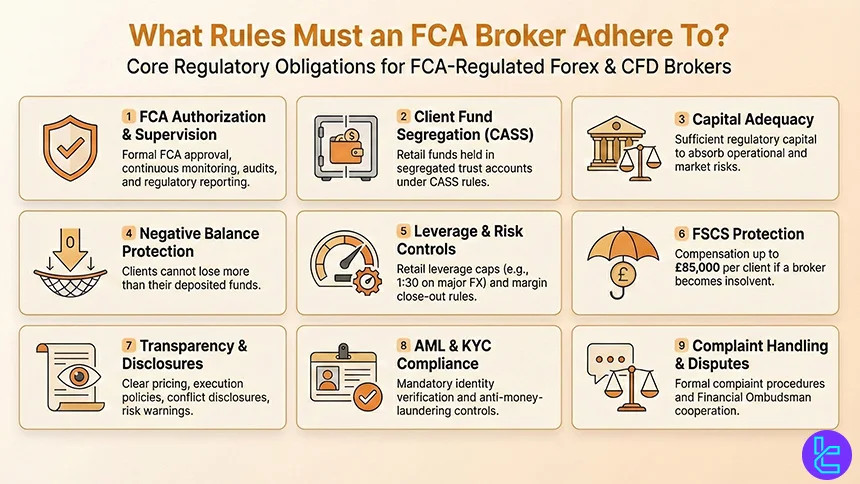
What Rules Must an FCA Broker Adhere To?
Forex and CFD brokers regulated by the FCA are required to comply with one of the most comprehensive regulatory frameworks in the global financial industry. These rules are designed to protect retail traders, ensure financial stability, and promote transparent and fair market practices across the UK.
Key regulatory obligations for FCA-regulated brokers include:
- Authorization and Ongoing Supervision: Brokers must be formally authorized by the FCA and are subject to continuous monitoring, periodic audits, and detailed regulatory reporting;
- Client Fund Segregation (CASS Rules): Retail client funds must be held in segregated trust accounts, completely separate from the broker’s operating capital, in accordance with the UK Client Assets Sourcebook (CASS);
- Capital Adequacy Requirements: FCA brokers must maintain sufficient regulatory capital to cover operational risks and client exposures, ensuring financial resilience during market stress;
- Negative Balance Protection: Retail clients cannot lose more than their deposited funds, even during extreme market volatility or price gaps;
- Leverage and Risk Controls: In line with FCA product intervention rules, leverage is capped (e.g., 1:30 for major forex pairs), and standardized margin close-out rules apply;
- Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS): Eligible retail clients are protected by the Financial Services Compensation Scheme, which may compensate up to £85,000 per client per firm if a broker becomes insolvent;
- Transparency and Disclosure Obligations: Brokers must publish clear pricing, execution policies, conflict-of-interest statements, and standardized risk warnings, including the percentage of losing retail accounts;
- Strict AML and KYC Compliance: Enhanced identity verification and anti-money-laundering controls are mandatory to prevent fraud and financial crime;
- Complaint Handling and Dispute Resolution: Brokers must maintain formal complaint procedures and cooperate with the Financial Ombudsman Service when disputes arise.
How Can I Check if a Broker Is Regulated by the FCA?
Verifying a broker’s regulatory status with the FCA is a critical step before opening a trading account. The process is straightforward, but it must be done carefully to avoid cloned firms or misleading regulatory claims.
- Check the Broker’s Legal Disclosure: Review the broker’s website footer or legal documents for its registered company name and FCA reference number (FRN). FCA-authorized firms are required to clearly disclose this information;
- Visit the FCA Financial Services Register: Go directly to the official FCA Register and search for the broker using the legal entity name or FRN. Avoid using links provided by the broker itself to reduce the risk of redirection to fake registries;
- Confirm Authorization Status: Ensure the firm’s status is listed as “Authorised”. The register should display the approval date, permitted regulated activities, and current standing of the license;
- Match the Trading Domain: Verify that the broker’s website domain you are using is explicitly listed on the FCA register under the authorized firm. Many scam operations use similar brand names but operate on unregistered domains;
- Review Client Protection Details: Confirm participation in the Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS) and check whether retail clients are eligible for compensation of up to £85,000 in case of insolvency;
- Watch for “Clone Firm” Warnings: The FCA regularly publishes alerts about cloned firms. If a broker claims FCA regulation but is not listed correctly, or appears in FCA warnings, it should be avoided immediately.
Are Crypto Trading Services Available in FCA-Regulated Brokers?
Yes, FCA-regulated brokers can offer crypto-related trading services, but only within a strict and clearly defined regulatory framework enforced by the Financial Conduct Authority. The availability of crypto products depends primarily on how cryptocurrencies are offered, rather than on the assets themselves.
Under current FCA rules, brokers are permitted to offer cryptocurrency CFDs (Contracts for Difference). These products allow traders to speculate on the price movements of digital assets such as Bitcoin or Ethereum without owning the underlying crypto.
Crypto CFDs are classified as high-risk derivative instruments and are subject to enhanced risk disclosures, margin requirements, and negative balance protection.
However, since January 2021, the FCA has banned the sale of crypto derivatives and ETNs to UK retail clients. This means that UK retail traders cannot legally trade crypto CFDs with FCA-regulated brokers, even though professional clients may still have access under stricter eligibility criteria.
This ban was introduced due to concerns over extreme volatility, valuation challenges, and consumer harm.
It is also important to distinguish crypto derivatives from spot cryptocurrency trading. FCA regulation of forex brokers does not automatically permit spot crypto trading or custody services.
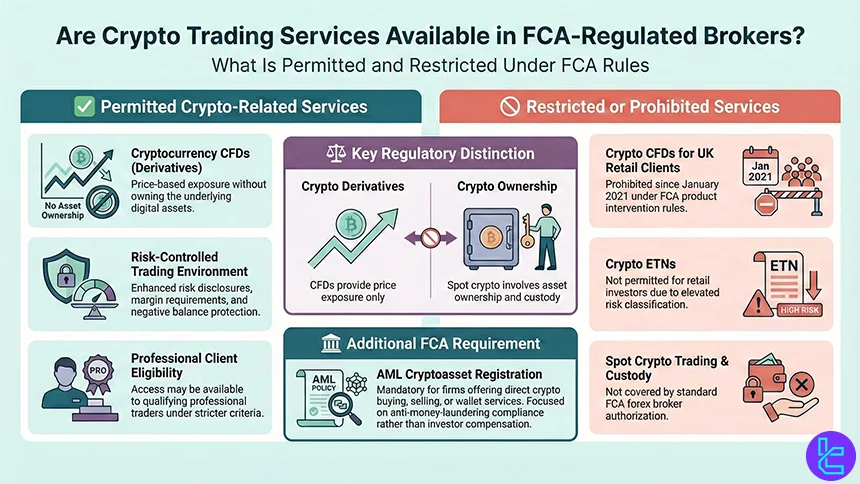
Firms offering direct crypto buying, selling, or wallet services must register separately with the FCA under the UK’s AML cryptoasset registration regime, which focuses on anti-money-laundering compliance rather than investor protection.
In practice, most FCA-regulated forex brokers either exclude crypto products for UK retail clients or limit access to non-UK entities. Understanding these distinctions is essential when evaluating crypto trading availability under FCA supervision, as FCA authorization prioritizes consumer protection and risk limitation over product flexibility.
Customer Protections Offered by the FCA
The FCA enforces one of the most robust investor-protection frameworks in the global forex industry. Its regulatory rules are designed to safeguard retail traders, limit excessive risk exposure, and ensure fair treatment across all authorized financial firms.
A core protection is client fund segregation. FCA-regulated brokers must hold retail client funds in segregated trust accounts under the UK Client Assets Sourcebook, ensuring that customer money is kept separate from the broker’s operational capital and protected in the event of financial distress.
Another key safeguard is negative balance protection, which prevents retail traders from losing more than the funds deposited in their accounts. This rule applies across leveraged products such as forex and CFDs and is particularly important during periods of extreme market volatility.
The FCA also enforces leverage caps and margin close-out rules. Retail leverage is typically limited to 1:30 on major forex pairs, with lower limits on more volatile instruments. Brokers must automatically close positions when margin levels fall below regulatory thresholds, reducing the risk of catastrophic losses.
In the event of broker insolvency, eligible retail clients may be protected by the Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS), which can compensate up to £85,000 per person per firm, subject to eligibility conditions.
Additional protections include strict risk disclosure requirements, transparent pricing, best-execution obligations, and mandatory complaint-handling procedures. FCA-regulated brokers must also cooperate with the Financial Ombudsman Service, giving retail traders access to independent dispute resolution.
How Does the FCA Differ from Offshore Regulatory Authorities?
The difference between brokers regulated by the FCA and those licensed in offshore jurisdictions lies mainly in regulatory strength, investor protection, and legal accountability. While both frameworks allow brokers to operate legally, the level of oversight and trader safeguards varies significantly.
Key Characteristics of FCA Regulation:
- Tier-1 regulatory status with strict supervision and enforcement powers
- Mandatory client fund segregation under UK CASS rules
- Negative balance protection for retail traders
- Leverage caps (e.g., 1:30 on major forex pairs) to limit excessive risk
- FSCS protection up to £85,000 per eligible client in case of insolvency
- High transparency requirements, including standardized risk warnings and best-execution policies
- Strong legal recourse, including access to the Financial Ombudsman Service and UK courts
Key Characteristics of Offshore Regulation:
- Lighter regulatory requirements and reduced ongoing supervision
- No mandatory compensation schemes in most jurisdictions
- Higher leverage offerings (often 1:500 or more) with fewer risk controls
- Weaker fund-segregation rules, depending on the regulator
- Limited transparency and reporting obligations
- Restricted legal protection, making dispute resolution more complex for clients
From a trader’s perspective, FCA regulation prioritizes capital protection, transparency, and fair market conduct, making it particularly suitable for risk-aware retail traders and long-term investors.
Offshore regulation, while often attractive due to higher leverage and fewer restrictions, places a greater burden on traders to assess counterparty risk and operational reliability.
In practice, the choice comes down to security versus flexibility. FCA-regulated brokers emphasize regulatory certainty and consumer protection, whereas offshore brokers typically offer more aggressive trading conditions at the cost of reduced legal safeguards.
FCA in Comparison to Other Financial Regulatories
The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK is widely recognized for its robust, transparent regulatory framework that prioritizes investor protection, market integrity, and compliance standards.
When compared with other top-tier authorities like CySEC (EU), ASIC (Australia), and JFSA (Japan), the FCA maintains strict capital requirements, client segregation, and compensation schemes.
Each regulator has unique approaches to leverage, reporting, and risk controls, with the Japanese JFSA standing out for its conservative retail leverage and trust-based client fund rules.
Parameter | FCA (UK) | CySEC (Cyprus) | ASIC (Australia) | FSA (Japan) |
Minimum Capital Requirement | £125,000–£730,000+ depending on model | €750,000+ depending on firm type | Not Specified | Based on net capital and exposure (strict supervision) |
Client Fund Segregation | Required | Required | Required | Required |
Compensation Scheme | FSCS (~£85,000) | Investor Compensation Fund (~€20,000) | No statutory compensation fund | Japan Investor Protection Fund exists |
Leverage Limits | Retail max ~1:30 on majors | Set under MiFID (often 1:30 for retail in EU) | Retail up to ~1:30 under ASIC reg. | Strict cap ~1:25 for retail |
Negative Balance Protection | Required | Often required | Common but not statutory | Required |
Reporting & Audits | Ongoing reporting standard | Ongoing financial reporting | Regular compliance reporting | Frequent reporting and compliance monitoring |
Conclusion
There is a certain group of Forex brokers regulated by the FCA in United Kingdom; the number might not be so large because there are limitations and strict rules for those regulated by it. FXCM, CMC Markets, Pepperstone, and eToro are some of the reputable brands in the list.
For a detailed explanation of the framework for the broker selection, check out the Forex methodology page.













