The U.S. forex market is governed by one of the world’s most stringent regulatory systems. Brokers must be registered with the Commodity Futures Trading Commission and be members of the National Futures Association, meeting strict capital, reporting, and leverage requirements that significantly enhance trader protection.
With the U.S. Dollar involved in approximately 89% of global FX trades and daily turnover exceeding $9 trillion, selecting a CFTC- and NFA-regulated broker is essential. These brokers offer transparent pricing, regulated trading conditions, and a safer environment compared with unlicensed offshore alternatives.
 | tastyfx | |||
 | OANDA | |||
 | FOREX.com | |||
| 4 |  | Interactive Brokers | ||
| 5 |  | Plus500 | ||
| 6 |  | eToro |
US Forex Brokers Ranked by Trustpilot
Trustpilot data from more than 55,000 verified reviews highlights how U.S. forex brokers are perceived by real traders.
Leading platforms achieve ratings above 4.5/5, reflecting strong execution quality, transparent pricing, platform stability, and consistent customer support under strict CFTC and NFA regulatory oversight.
Broker | Trustpilot Score | Number of Reviews |
4.6/5 ⭐️ | 2,237 | |
eToro | 4.2/5 ⭐️ | 29,889 |
Plus500 | 4.2/5 ⭐️ | 17,664 |
4.0/5 ⭐️ | 1,190 | |
Interactive Brokers | 3.7/5 ⭐️ | 5,015 |
tastyfx | 2.9/5 ⭐️ | 7 |
Forex Brokers in the USA with Lowest Spreads
Spread competitiveness plays a critical role in forex trading costs for U.S. traders operating under CFTC and NFA regulations.
Current comparisons show several regulated brokers offering minimum spreads from 0.0 pips, while others range up to 0.8 pips, reflecting differences in pricing models, liquidity access, and execution structure.
Broker | Minimum Spread |
0.0 pips | |
FOREX.com | 0.0 pts |
0.0 pips | |
OANDA | 0.1 pips |
Plus500 | 0.5 pips |
tastyfx | 0.8 pips |
Forex Brokers in the United States Ranked by Non-Trading Fees
Non-trading costs can materially impact profitability for U.S. forex traders, especially under CFTC and NFA-regulated conditions.
Fee comparisons show several leading brokers offering zero deposit charges, while withdrawal and inactivity fees remain limited, typically ranging from $5 to $15 per month depending on account activity and broker policy.
Broker | Deposit Fee | Withdrawal Fee | Inactivity Fee |
Interactive Brokers | No | 1 free withdrawal/month | No |
No | Up to $15 | No | |
Plus500 | No | No | $10/month |
OANDA | No | No | $14/month |
FOREX.com | No | No | $15/month |
eToro | No | Up to $5 | $10/month |
USA Forex Brokers’ Trading Instruments
Trading instrument diversity is a key differentiator among U.S. forex brokers. Current comparisons show leading platforms offering access to 7,000+ tradable assets, while others focus on a narrower selection, reflecting differences in multi-asset coverage, CFD availability, and market access depth.
Broker | Number of Trading Instruments |
eToro | 7,000+ |
FOREX.com | 5,500+ |
Interactive Brokers | 4,900+ |
2,800+ | |
tastyfx | 80+ |
OANDA | 75+ |
Top 5 Forex Brokers in the USA
The U.S. forex market is one of the most tightly regulated globally, allowing only a small group of brokers to legally serve retail traders.
These top U.S. brokers operate under CFTC, NFA, SEC, or FINRA oversight, offer leverage up to 1:50, and provide access to thousands of instruments through advanced, compliant trading platforms.
FOREX.com
FOREX.com is a globally recognized Forex and CFD broker founded in 2001 and headquartered in the United States. The broker operates as a subsidiary of StoneX Group Inc., a publicly listed financial services firm with $19.68 billion in total assets and a long-standing presence across global financial markets.

The broker serves over 1 million clients worldwide and employs more than 800 professionals, offering access to 5,500+ trading instruments across forex, indices, shares CFDs, commodities, cryptocurrencies, and precious metals.
Average trade execution speed reaches 0.02 seconds, supporting high-frequency and professional trading strategies.
FOREX.com operates under an extensive multi-jurisdictional regulatory framework, including CFTC and NFA (US), FCA (UK), ASIC (Australia), CySEC (EU), MAS (Singapore), CIRO (Canada), and FSA (Japan).
Client protections vary by entity, with EU and UK branches offering investor compensation up to €20,000 and £85,000, respectively.
Traders can access the markets via MetaTrader 5, TradingView, and FOREX.com’s proprietary platform, with support for advanced charting, algorithmic trading, and institutional-grade research tools.
The broker was awarded “Most Competitive Broker” at the Global Forex Awards 2023, reflecting its strong pricing and execution standards.
Account Types | Standard, Raw Spread, MetaTrader |
Regulating Authorities | CFTC, SEC, FCA, ASIC, MAS, CIRO, FSA, CySEC |
Minimum Deposit | $100 |
Deposit Methods | Local Transfer, Credit/Debit Cards, Wire Transfer, Neteller, Skrill |
Withdrawal Methods | Credit/Debit Cards, Wire Transfer |
Maximum Leverage | 1:50 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MT5, TradingView, Proprietary Platform |
FOREX.com Pros and Cons
The following pros and cons outline the broker’s key strengths and potential limitations for retail and professional traders.
Pros | Cons |
Strong Tier-1 regulation across multiple jurisdictions | Higher spreads than some low-cost ECN brokers |
Access to 5,500+ global trading instruments | Inactivity fee after 12 months |
Advanced platforms, including MT5 and TradingView | Geo-restrictions in several countries |
Backed by publicly listed StoneX Group Inc. | No dedicated copy-trading service |
eToro
eToro US is the American branch of the global eToro platform, launched in 2022 to serve U.S. residents. The broker provides access to 3,000+ trading assets across stocks, ETFs, cryptocurrencies, and options, focusing on commission-free investing and social trading features rather than traditional forex trading.
The broker operates through two regulated entities: eToro USA LLC, registered as a Money Services Business, and eToro USA Securities Inc., a FINRA-registered broker dealer and SIPC member. Both entities are headquartered in Hoboken, New Jersey, ensuring compliance with U.S. securities regulations.
By completing the eToro US registration process, traders get access to commission-free stock and ETF trading, a 1% crypto trading fee, and a demo account with $100,000 in virtual funds.
The platform supports investment features such as CopyTrader and Smart Portfolios, although these tools are limited to cryptocurrency portfolios for U.S. clients.
Trading is conducted exclusively through eToro’s proprietary web and mobile platform, which includes advanced charting, customizable watchlists, stop loss and take profit tools, and integrated social sentiment data.
The minimum deposit is $100, and maximum leverage is restricted to 1:1 under U.S. regulations.
Account Types | Standard, Demo |
Regulating Authorities | FINRA, SIPC |
Minimum Deposit | $100 |
Deposit Methods | Online Bank Transfers, Wire Transfer, Credit/Debit Card, PayPal |
Withdrawal Methods | Online Bank Transfers, Wire Transfer, Credit/Debit Card, PayPal |
Maximum Leverage | 1:1 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | Proprietary Platform |
eToro Pros and Cons
The following pros and cons summarize eToro US’s main strengths and limitations for American traders.
Pros | Cons |
Commission-free stock and ETF trading | No traditional forex trading available |
Unique CopyTrader and Smart Portfolio features | 1 percent fee on cryptocurrency trades |
Regulated by FINRA and protected by SIPC | Limited leverage capped at 1:1 |
Beginner-friendly proprietary platform | Crypto restrictions in several U.S. states |
Plus500
Plus500 is a globally recognized CFD broker founded in 2008, offering access to forex, stocks, indices, commodities, ETFs, options, and cryptocurrencies. Headquartered in London and listed on the London Stock Exchange under LSE PLUS, it operates across more than 50 countries through multiple regulated entities.

The broker is supervised by top-tier authorities such as the FCA, CySEC, ASIC, FSCA, DFSA, MAS, and EFSA. This multi-jurisdictional regulation framework ensures strong compliance, fund segregation, negative balance protection, and transparent operating standards for retail and professional traders.
Traders get access to Retail and Professional accounts with a minimum deposit of $100 and maximum leverage reaching 1:300 for eligible professionals by completing the Plus500 registration process.
The broker offers over 2800 CFD contracts through the proprietary Plus500 WebTrader and fully featured mobile applications on iOS and Android.
Designed for self-directed traders, Plus500 emphasizes simplicity, fast onboarding, and a clean trading interface. The platform supports advanced risk management tools, real-time alerts, and commission-free trading via variable spreads, making it suitable for beginners and intermediate CFD traders.
Account Types | Retail, Professional |
Regulating Authorities | FCA, ASIC, CySEC, MAS, EFSA, DFSA, AFSC, FMA |
Minimum Deposit | $100 |
Deposit Methods | Visa/MasterCard, PayPal, Bank Wire, GooglePay, ApplePay, Skrill |
Withdrawal Methods | Visa/MasterCard, PayPal, Bank Wire, GooglePay, ApplePay, Skrill |
Maximum Leverage | 1:300 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | Proprietary platform |
Plus500 Pros and Cons
The following advantages and disadvantages summarize Plus500’s key strengths and limitations:
Pros | Cons |
FSCA regulated entity available for South African traders | No MT4 or MT5 platform support |
Over 2800 tradable CFD instruments across global markets | No copy trading or social trading features |
User friendly proprietary WebTrader and mobile apps | Inactivity fee charged after prolonged account dormancy |
Commission free trading with transparent cost structure | Limited appeal for advanced algorithmic traders |
OANDA
OANDA is one of the longest-established forex brokers in the industry, founded in 1996 in New York and operating globally for nearly three decades. The U.S. entity serves American traders under a highly regulated framework, focusing on transparent pricing, reliable execution, and institutional-grade trading infrastructure.
OANDA US operates under Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) oversight and is a member of the National Futures Association (NFA). Client funds are fully segregated, and the broker follows strict U.S. compliance standards, reinforcing trust, financial integrity, and regulatory accountability for retail traders.
The broker provides access to 68+ forex pairs and 8 spot cryptocurrencies, with trading available on OANDA Web, OANDA Mobile, MetaTrader 4, and TradingView. Cryptocurrency trading in the U.S. is offered through a partnership with Paxos, enabling direct ownership rather than CFDs.
OANDA US offers Standard and Elite Trader accounts, with no minimum deposit for standard users and leverage capped at 1:50 in line with U.S. regulations. Average spreads hover around 2.0 pips, with commission options available for high-volume traders seeking tighter pricing.
Account Types | Standard, Elite Trader |
Regulating Authorities | CFTC, NFA |
Minimum Deposit | $0 |
Deposit Methods | Credit/Debit Cards, ACH Bank Transfers, Wire Transfers, Bpay |
Withdrawal Methods | Credit/Debit Cards, bank transfer |
Maximum Leverage | 1:50 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | OANDA web, OANDA app, TradingView, MT4 |
OANDA Pros and Cons
The following overview highlights the main strengths and limitations of trading with OANDA US.
Pros | Cons |
Strong Tier-1 regulation under CFTC and NFA | Limited tradable markets compared to global brokers |
No minimum deposit for standard accounts | Higher average spreads than ECN competitors |
Multiple platforms, including MT4 and TradingView | An inactivity fee after prolonged dormancy |
Long industry track record since 1996 | No copy trading or investment programs |
Interactive Brokers
Interactive Brokers is a globally established multi-asset brokerage founded in 1977 by Thomas Peterffy and headquartered in Greenwich, Connecticut. Today, the firm serves 2.9 million+ client accounts across 150+ markets, offering institutional-grade access to forex, equities, ETFs, options, futures, bonds, and funds.
The broker operates under a robust regulatory framework that includes SEC, FINRA, NYSE, and FCA, with additional oversight across Europe, Asia, and Canada.
As a NASDAQ-listed company, Interactive Brokers publishes audited financials, reinforcing transparency, capital strength, and long-term operational credibility.
Interactive Brokers provides access to 100+ currency pairs and trading on 90+ global exchanges, supported by advanced platforms such as Trader Workstation (TWS), IBKR Mobile, and Client Portal. Spreads and commissions start from 0, execution is electronic, and leverage varies by jurisdiction.
After completing the Interactive Brokers registration process, clients can choose from six account types, including Individual, Joint, Retirement, Institutional, and Advisor accounts, with a minimum deposit as low as $1.
Funding is handled via bank transfers and checks, and negative balance protection applies to most retail leveraged accounts outside the U.S.
Account Types | Individual, Joint, Trust, Retirement, Institutional, Non-Professional Advisor |
Regulating Authorities | SEC, FINRA, NYSE, FCA, etc. |
Minimum Deposit | $1 |
Deposit Methods | Bank Transfer, Check |
Withdrawal Methods | Bank Transfer, Check |
Maximum Leverage | 1:1000 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | Proprietary platform |
Interactive Brokers Pros and Cons
The following pros and cons summarize its main strengths and limitations for active and professional traders.
Pros | Cons |
An extremely wide range of global trading instruments | Limited funding methods with no cards or e-wallets |
Strong Tier-1 regulation and public company transparency | Platform complexity for beginners |
Low commissions and tight spreads | Customer support experience can vary |
Advanced trading platforms and APIs | No built-in copy trading or PAMM services |
Is Forex Trading Legal in USA?
Forex trading is legal in the United States, but retail traders must use brokers that are formally authorized. Only firms registered with the Commodity Futures Trading Commission and members of the National Futures Association can legally offer retail spot forex to U.S. residents.
This strict framework limits broker choice but significantly reduces exposure to fraud and undercapitalized firms. U.S. rules also impose leverage caps and execution restrictions designed to protect retail traders and maintain overall market integrity.
- Trade only with CFTC-registered and NFA-member brokers;
- Avoid offshore firms soliciting U.S. residents;
- Expect stricter leverage and execution rules than most jurisdictions.
Understanding the Forex Regulatory Framework in the US
The U.S. retail forex market is overseen by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission, with supervision and enforcement supported by the National Futures Association. Brokers must comply with strict reporting, disclosure, and conduct standards designed to protect traders from manipulation and fraud.
A major barrier to entry is capitalization. Retail Forex Exchange Dealers and eligible Futures Commission Merchants must maintain at least $20 million in regulatory capital, which is why only a small number of brokers can legally serve U.S. retail forex traders.
- Primary oversight by CFTC and NFA
- Minimum capital requirement of $20 million
- Uniform nationwide rules for retail forex access

How can I Verify CFTC and NFA Authorization?
Verification begins on the broker’s U.S. website, where authorized firms disclose their regulatory status. The most reliable confirmation method is the NFA BASIC database, which lists registration status, authorization category, and disciplinary history.
Verifying Broker Authorization with the CFTC
Confirming CFTC registration ensures a broker is legally permitted to offer retail forex services in the United States and meets strict capital, reporting, and conduct requirements.
- Visit the broker’s official U.S. website and locate the regulatory disclosure section, usually found in the footer;
- Confirm that the broker explicitly states registration with the Commodity Futures Trading Commission;
- Identify whether the broker is registered as a Retail Foreign Exchange Dealer or a Futures Commission Merchant;
- Cross check the legal entity name used for U.S. clients, not just the brand name;
- Treat missing or unclear CFTC registration details as a warning sign and avoid opening an account.
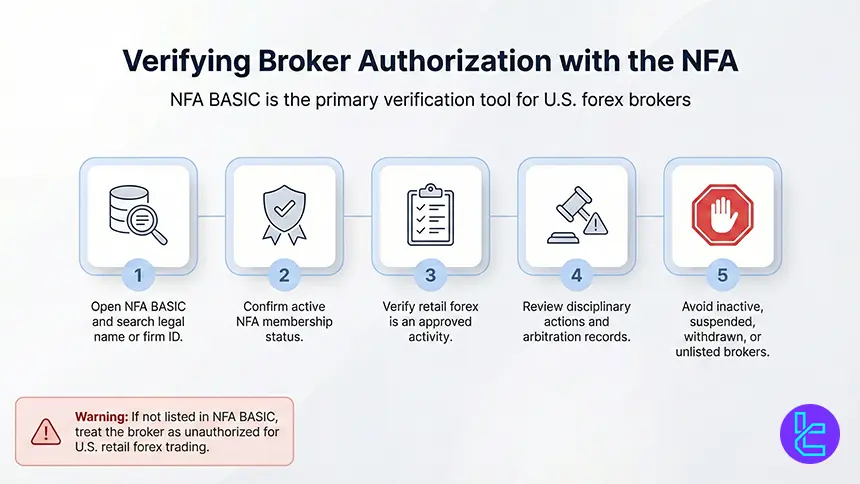
Verifying Broker Authorization with the NFA
Checking NFA membership validates a broker’s compliance status, approved activities, and disciplinary history, providing essential insight into regulatory oversight and trader protection.
- Access the NFA BASIC database and search using the broker’s legal name or firm ID;
- Confirm the broker holds active membership status with the National Futures Association;
- Verify that retail forex trading is listed as an approved activity for the broker;
- Review disciplinary records, arbitration cases, or enforcement actions shown in the profile;
- Avoid brokers that are inactive, suspended, withdrawn, or not listed in NFA BASIC.
If a broker does not appear in NFA BASIC, it should be considered unauthorized for U.S. retail forex trading. Traders should also review any past regulatory actions or arbitration records before opening an account.
USA Trading Rules and Client Protections
U.S. client protection relies on structural safeguards rather than compensation schemes. Brokers must meet capital adequacy rules, undergo audits, and follow strict conduct standards.
Retail accounts operate under FIFO execution rules and a ban on holding opposing positions in the same currency pair.
Execution standards favor non-dealing desk models, reducing conflicts of interest. These rules aim to ensure transparent pricing, fair order handling, and consistent execution across regulated U.S. forex brokers.
- FIFO execution applies to same pair positions;
- Hedging within a single account is prohibited;
- Emphasis on transparent execution and oversight.

How to Start Forex Trading in the USA
Starting legally requires selecting a CFTC-registered and NFA member broker, completing identity verification, and funding the account through approved banking methods such as ACH or wire transfer.
Before trading live, using a demo account helps traders understand margin behavior, order types, and platform tools. A structured trading plan with defined risk limits improves long term consistency.
- Choose a CFTC and NFA authorized broker;
- Complete identity verification;
- Fund via bank based methods;
- Practice on a demo account;
- Apply risk management rules.
Is Forex Income Taxable in the US?
Forex trading profits are taxable and must be reported to the Internal Revenue Service. Spot forex trades are usually taxed as ordinary income under Section 988, while certain futures and options may qualify for Section 1256 capital gains treatment.
Tax outcomes depend on the elections made and the trader’s income level. Ordinary income rates range up to 37%, while capital gains rates range from 0% to 20%, making accurate record keeping essential.
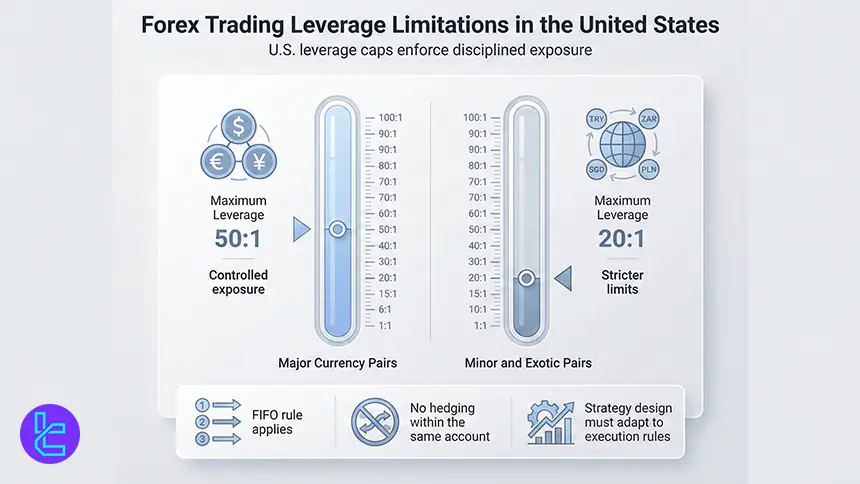
Forex Trading Leverage Limitations in the United States of America
Leverage is strictly capped in the United States. Brokers may offer up to 50:1 leverage on major currency pairs and 20:1 on minor or exotic pairs. These limits are designed to reduce excessive risk for retail traders.
Leverage restrictions interact with FIFO and no hedging rules, influencing strategy design. Traders must adapt position sizing and exits to comply with U.S. execution requirements.
- Maximum leverage 50:1 on majors
- Maximum leverage 20:1 on minors and exotics
- FIFO and no hedging rules apply
Is Mobile Trading Available in US Forex Brokers?
Mobile trading is widely available among U.S. forex brokers through proprietary apps and web-based platforms. These apps allow order execution, position monitoring, charting, and alerts directly from mobile devices.
Modern mobile platforms often integrate advanced charting and research while maintaining compliance with U.S. execution and disclosure standards. Stability and risk controls are more important than interface design during volatile market conditions.
What Forex Fees Should US Traders Expect?
U.S. brokers generate revenue through spreads, commissions, and overnight financing charges. Some accounts bundle costs into spreads, while others offer raw spreads with separate commissions.
Non-trading fees, such as inactivity or withdrawal charges, may apply depending on the broker. Traders should estimate total costs based on trading frequency and holding duration.
How to Select the Best Forex Broker in the US?
Broker selection starts with legality. Only CFTC-registered and NFA member brokers can legally serve U.S. retail forex traders. After eligibility, traders should compare execution quality, pricing structure, and platform reliability.
Evaluating real trading costs, rollover policies, and customer support responsiveness helps identify a broker that matches trading frequency and strategy requirements.
- Confirm CFTC and NFA authorization;
- Compare live spreads and commissions;
- Assess execution quality and platform stability;
- Review funding and support services.

Forex Trading Platforms in US Brokers
U.S. brokers offer platforms optimized for compliance, execution, and risk control. Traders access markets through proprietary platforms, web terminals, and selected third-party tools, depending on the broker.
The most effective platforms combine stable connectivity, advanced charting, flexible order types, and detailed reporting that supports regulatory compliance and tax preparation.
- Proprietary and web-based platforms dominate;
- TradingView integration is increasingly common;
- Focus on stability, order tools, and reporting.
What Hours Are Important in US Forex Trading?
Forex markets operate 24 hours during the trading week, but U.S. activity is concentrated around Eastern Time. Liquidity often increases around the U.S. market open when European markets remain active.
The overlap period typically delivers tighter spreads and stronger price movement. Traders should also monitor economic releases, which can increase volatility regardless of session timing.
- Liquidity often peaks near 8:00 AM ET;
- London overlap supports higher volume;
- News events can increase volatility.
Can I Trade CFDs in the United States of America?
Retail CFD trading is not permitted in the United States. Brokers offering CFD contracts to U.S. residents are operating outside the legal framework and expose traders to significant legal and financial risks.
U.S. traders typically use futures or options as alternatives for leveraged exposure. Any CFD marketing aimed at U.S. retail clients should be treated as a serious warning sign.
- CFDs are banned for U.S. retail traders;
- Futures and options are common alternatives;
- CFD offers to U.S. residents signal illegality.

Can US Residents Use International Brokers?
U.S. residents are generally required to trade with CFTC and NFA-authorized brokers. Offshore brokers that accept U.S. clients may expose traders to legal uncertainty, weak protections, and limited dispute resolution.
Because the authorized broker list is small, verification through NFA BASIC is essential before funding any account.
Top U.S. Regulated Forex Brokers Shortlist
Because U.S. rules require CFTC registration and NFA membership, only a limited set of firms can legally offer retail forex. This constraint reduces choice, yet it concentrates activity among brokers able to meet strict capital, reporting, and conduct requirements demanded by the U.S. retail forex framework.
A commonly referenced legal availability shortlist includes tastyfx, FOREX.com, OANDA, Trading.com, and Charles Schwab for certain forex access models, with Interactive Brokers often positioned toward institutional spot forex participation.
Always confirm the exact entity and authorization using NFA BASIC before opening an account.
Helpful Links for Forex Traders in the US
Official regulatory and tax resources help traders verify brokers, understand rules, and meet reporting obligations. These tools are essential because only a limited number of firms can legally offer retail forex in the United States.
Using official databases improves broker due diligence and supports accurate tax reporting and compliance.
- CFTC: U.S. regulator overseeing futures, options, and retail forex markets to protect traders and ensure market integrity
- NFA BASIC: Official database for verifying broker registration, authorization status, and disciplinary history in the U.S
- FINRA BrokerCheck: Tool for researching broker-dealer backgrounds, licenses, and regulatory or disciplinary records
- IRS: U.S. federal tax authority providing tax rules, reporting requirements, and guidance for individuals and traders
- IRS Direct Pay: Secure service allowing taxpayers to pay federal taxes directly from a bank account
Forex Trading in the US vs Other Countries
Forex trading rules in the United States differ sharply from other major financial hubs such as Cyprus, Canada, and Singapore.
While all four jurisdictions enforce strong oversight, the U.S. applies the most restrictive leverage limits, tighter broker eligibility, and unique execution rules that significantly shape retail trading conditions.
Comparison Factor | United States of America | |||
Primary Regulator | CFTC and NFA | Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC) | Canadian Investment Regulatory Organization (CIRO) | Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) |
Regulatory Framework | Commodity Futures Trading Commission and National Futures Association | EU wide MiFID II and ESMA compliance | National Tier 1 framework under CIRO | National framework under MAS (non-EU) |
Retail Leverage Cap Forex Majors | 1:50 | 1:30 | Up to 1:50 | 1:20 |
Investor Protection Level | High | High | High | High (prudential & conduct-based) |
Negative Balance Protection | Mandatory | Mandatory | Mandatory | Not mandatory; applied by many brokers |
Client Fund Segregation | Mandatory | Mandatory under CySEC rules | Required under CIRO rules | Mandatory under MAS rules |
Broker Transparency Requirements | Strict reporting, disclosure, and conduct standards | Strict EU disclosure rules | Strict compliance and disclosure standards | Strict disclosure, capital, and reporting standards |
Broker Availability | Domestic brokers | Broad EU access via passporting | CIRO authorized and international brokers | MAS-licensed local and global brokers |
Access to International Brokers | No | High via EU passporting | Yes | High (regional financial hub) |
Typical Trading Platforms | MT5, TradingView, Proprietary apps | MT4, MT5, cTrader, TradingView | MT4, MT5, cTrader, TradingView, ProRealTime | MT4, MT5, cTrader, TradingView |
Maximum Loss Protection | Mandatory for retail traders | Cannot lose more than deposit | Cannot lose more than the deposit | Entity-dependent |
Tax Treatment of Forex Profits | Variable up to 37% | Capital gains tax applies | Gains are treated as capital gains with 50% taxable | Taxable as income depending on activity (IRAS rules) |
Conclusion and Expert Suggestions
The United States offers one of the safest environments for retail forex trading, driven by strict CFTC andNFA oversight, high capital requirements, and disciplined execution rules. While broker choice is limited, authorized U.S. brokers provide transparent pricing, controlled leverage, and strong structural protections.
Selecting a U.S. forex broker should focus on regulatory authorization, execution quality, real trading costs, and platform stability rather than marketing claims. Brokers that meet U.S. standards operate under consistent nationwide rules.
“All brokers featured in this guide are evaluated using the TradingFinder Forex methodology, which analyzes regulation strength, pricing transparency, execution reliability, platform performance, and long-term operational credibility to identify brokers best suited for U.S. retail forex traders.”













