The Financial Services Authority is an offshore regulator that licenses Forex and CFD brokers in Seychelles, a structure often used for higher leverage access and broader CFD product coverage than Tier-1 regimes.
In this guide, TradingFinder reviews 8 FSA-regulated brokers (Fusion Markets, Eightcap, BlackBull Markets, eToro, Tickmill, FxPro, PrimeXBT and IC Markets) and compares them using 4 data tables covering Trustpilot sentiment (up to 4.8/5), pricing, non-trading fees (as low as $0), and instruments offered.
 | FUSION MARKETS | |||
 | eightcap | |||
 | BlackBull Markets | |||
| 4 |  | eToro | ||
| 5 |  | TICKMILL | ||
| 6 |  | FxPro | ||
| 7 |  | IC Markets | ||
| 8 |  | PRIMEXBT |
Trustpilot Ratings for Forex Brokers Regulated by FSA (Seychelles)
Trustpilot ratings provide an external, user-driven perspective on how FSA-regulated Forex brokers perform in real trading conditions.
This table ranks brokers based on verified client reviews and total review volume, helping identify brands that consistently deliver reliable execution, support quality, and overall platform satisfaction under FSA oversight:
Broker | Trustpilot Rating | Number of Reviews |
IC Markets | 4.8/5 ⭐️ | 50,917 |
4.8/5 ⭐️ | 6,045 | |
BlackBull Markets | 4.8/5 ⭐️ | 3,076 |
eToro | 4.2/5 ⭐️ | 30,370 |
4.0/5 ⭐️ | 3,409 | |
PrimeXBT | 3.7/5 ⭐️ | 443 |
FxPro | 3.5/5 ⭐️ | 813 |
Tickmill | 3.4/5 ⭐️ | 1,070 |
Minimum Spreads in FSA-Regulated Forex Brokers
The table below compares brokers by their minimum advertised spreads, highlighting pricing competitiveness across popular instruments while acknowledging that actual spreads may vary by account type and market conditions:
Broker | Minimum Spreads |
Global Prime | 0.0 Pips |
Tickmill | 0.0 Pips |
IC Markets | 0.0 Pips |
0.0 Pips | |
0.0 Pips | |
Admirals | 0.0 Pips |
PrimeXBT | 0.1 Pips |
Plus500 | 0.5 Pips |
Non-Trading Fees in FSA Regulated Forex Brokers
This table outlines deposit fees, withdrawal costs, and inactivity charges across FSA-regulated brokers, allowing traders to evaluate the hidden operational costs associated with account maintenance and capital movement:
Broker | Deposit Fee | Withdrawal Fee | Inactivity Fee |
$0 | $0 | $0 | |
Fusion Markets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
PrimeXBT | $0 | From 0.05% | $0 |
HF Markets | $0 | $0 | $5 |
Eightcap | $0 | $0 | $10 |
$0 | $0 | $10 | |
Plus500 | $0 | Varies | $10 |
Admirals | 0.9% for Skrill $0 for other Methods | €10 - A free withdrawal per month | €10 monthly |
Number of Tradable Instruments for FSA-Regulated Forex Brokers
The following table compares FSA-regulated Forex brokers based on the total number of tradable instruments, covering Forex pairs, contract for difference (CFDs) on indices, commodities, shares, ETFs, and other derivative products available under each broker’s offering.
Broker | Number of Tradable Assets |
BlackBull Markets | 26,000+ |
Admirals | 8,000+ |
eToro | 7000+ |
Plus500 | 2800+ |
2100+ | |
Eightcap | 800+ |
Fusion Markets | 250+ |
100+ |
Top 7 Forex Brokers Regulated by FSA (Seychelles)
The brokers listed below represent the top Forex trading platforms operating under FSA (Seychelles) regulation, selected based on regulatory structure, trading costs, platform access, and overall market coverage.
While FSA oversight offers greater flexibility than Tier-1 regulators, each broker here is evaluated on execution quality, transparency, and real-world trading conditions, allowing for a balanced comparison across different trading styles and risk profiles.
Fusion Markets
Fusion Markets stands out among FSA-regulated options through its Vanuatu oversight (VFSC), paired with Tier-1 supervision by ASIC. Founded by Phil Horner, the broker combines offshore flexibility with institutional governance, serving traders across7 markets, including Forex, indices, commodities, metals, energy, shares, and crypto CFDs.
Registered in Vanuatu (Company No. 40256) under Gleneagle Securities Pty Limited, Fusion Markets follows a multi-jurisdictional compliance model. This structure enhances transparency while allowing competitive conditions such as 0.0-pip average spreads on majors and $0 minimum deposit, appealing to both new and cost-focused traders.
Client funds are held in segregated accounts with HSBC and National Australia Bank (NAB), reinforcing operational safeguards. Backed by Glen Eagle Securities, managing $400M+ in client funds, the broker emphasizes execution quality and pricing efficiency, claiming 36% lower trading costs versus peers.
Traders access a full platform stack, MT4, MT5, TradingView, and cTrader, with features like copy trading, MAM/PAMM, VPS, and fast execution (~0.02 ms) accessible through the Fusion Markets dashboard. Leverage reaches 1:500 under VFSC, while ASIC-regulated accounts apply stricter caps, offering choice by risk profile.
Account Types | Zero, Classic, Swap-Free (Islamic) |
Regulating Authorities | VFSC (Vanuatu Financial Services Commission), ASIC (Australian Securities and Investments Commission), FSA |
Minimum Deposit | $0 |
Deposit Methods | VISA, MasterCard, PayPal, Perfect Money, PayID, Bank Wire, Crypto, Skrill, Neteller, etc. |
Withdrawal Methods | PayPal, Perfect Money, Bank Wire, Crypto, Skrill, Neteller, etc. |
Maximum Leverage | Up to 1:500 (VFSC entity) / Up to 1:30 (ASIC entity) |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), TradingView, cTrader (desktop/web/mobile) |
Fusion Markets Pros & Cons
Below is a concise snapshot to frame the strengths and trade-offs before proceeding with the Fusion Markets registration process.
Pros | Cons |
Ultra-low costs (0.0-pip spreads; $0 Classic commission) | No investor compensation fund |
$0 minimum deposit; wide funding methods | Education resources are limited |
Broad platform choice incl. TradingView & cTrader | No proprietary platform |
Fast execution; copy trading & MAM/PAMM | Instrument range smaller than some rivals |
Eightcap
Founded in 2009 in Melbourne, Eightcap is a multi-asset CFD broker offering 6 tradable markets (Forex, commodities, metals, crypto, indices, shares) with leverage up to 1:500 on eligible entities. The lineup targets active traders who prioritize platform choice and execution simplicity.
Eightcap runs a multi-jurisdiction model regulated by the Australian Securities and Investments Commission, Financial Conduct Authority, Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission, and Securities Commission of The Bahamas. Its entities span Sydney, London, and Limassol, with segregated funds and negative balance protection listed across branches.
Account structure includes Standard, Raw, and TradingView accounts (plus Demo). Standard spreads start from 1.0 pip, while Raw can start from 0.0 pips with commission. The broker supports MT4/MT5 + TradingView, enabling both traditional EA workflows and advanced charting for discretionary setups.
For workflow and execution support, Eightcap offers Capitalise.ai (code-free automation), FlashTrader (faster order + position sizing), and an AI-powered economic calendar with macro-event analytics. There is also an Eightcap rebate program available for the users.
Account Types | Standard, Raw, TradingView, Demo |
Regulating Authorities | ASIC, FCA, CySEC, SCB, FSA |
Minimum Deposit | $100 |
Deposit Methods | Crypto, e-wallets, credit/debit card, bank transfer, online payment systems |
Withdrawal Methods | Crypto, e-wallets, credit/debit card, bank transfer, online payment systems |
Maximum Leverage | 1:500 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MT4, MT5, TradingView |
Eightcap Pros and Cons
Before completing the Eightcap registration process, traders must review the broker’s advantages and disadvantages to make a proper decision.
Pros | Cons |
Multi-regulated structure (ASIC/FCA/CySEC/SCB) with segregated funds | No copy trading, PAMM, or managed-investment options |
Strong platform coverage: MT4, MT5, TradingView | $100 minimum deposit may be high for some beginners |
Raw pricing option (0.0-pip minimum spreads with commission) | Educational resources are described as relatively basic |
Practical tool stack (automation, fast execution panel, AI calendar) | Platform availability and leverage vary by entity/region |
BlackBull Markets
Founded in 2014 in New Zealand by Michael Walker and Selwyn Loekman, BlackBull Markets positions itself as an ECN-focused broker offering 6 asset classes and 26,000+ instruments. The brand highlights 7 industry awards and partnerships, such as the Starship Foundation and Milford Asset Management.

BlackBull operates through two main regulatory tracks: a Tier-1 route under the Financial Markets Authority and an offshore entity licensed by the Financial Services Authority of Seychelles. Protections listed across entities include segregated client funds and negative balance protection, while dispute coverage differs by jurisdiction.
Account design follows an ECN ladder, ECN Standard, ECN Prime, and ECN Institutional, with minimum spreads, that is only available after BlackBull Markets verification, that can reach 0.0 pips on Institutional, alongside commission-based pricing.
Platform and product access are broad: MT4, MT5, TradingView, cTrader, plus BlackBull CopyTrader and BlackBull Invest for stock investing. Key features include API trading, copy trading, and an economic calendar, with 24/7 support via live chat, phone, email, and WhatsApp, built for traders who value speed, coverage, and multi-platform flexibility.
Account Types | ECN Standard, ECN Prime, ECN Institutional |
Regulating Authorities | FMA (New Zealand), FSA (Seychelles) |
Minimum Deposit | $0 |
Deposit Methods | Visa, MasterCard, Apple Pay, Google Pay, Bank Wire, Crypto, Neteller, Skrill, SEPA, FasaPay |
Withdrawal Methods | Visa, MasterCard, Apple Pay, Google Pay, Bank Wire, Crypto, Neteller, Skrill, SEPA, FasaPay |
Maximum Leverage | 1:500 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MT4, MT5, TradingView, cTrader, BlackBull CopyTrader, BlackBull Invest |
BlackBull Markets Pros and Cons
A wide array of trading markets, ECN execution, comprehensive support, and spreads from 0.0 pips are among the advantages of the broker. However, traders must be aware of the downsides, like GEO restrictions and a high minimum deposit for some accounts, before proceeding with the BlackBull Markets registration.
Pros | Cons |
Very large market range (26,000+ instruments across 6 asset classes) | Entity-based access limits (NZ clients on FMA; offshore restrictions for some regions) |
ECN pricing ladder with spreads down to 0.0 pips (account-dependent) | Offering breadth can feel complex for beginners |
Strong platform coverage + native add-ons (CopyTrader, Invest, API) | An institutional account requires a $20,000 minimum deposit |
24/7 support + segregated funds and negative balance protection | Offshore regulation (Seychelles entity) may not match Tier-1 protections in every area |
eToro
Founded in January 2007 by David Ring, Ronen Assia, and Yoni Assia, eToro operates as eToro Ltd with headquarters in Tel Aviv. The broker is built around investing-first features, combining multi-asset access with a social layer that differentiates it from classic FX-only platforms.
eToro’s core offering centers on 3 investment options: CopyTrader, Smart Portfolios, and Crypto Staking. Alongside a $10 minimum deposit, the platform supports multiple funding rails, including PayPal, Skrill, and Trustly, positioning it as a flexible choice for account funding across supported regions.
Regulatory coverage spans multiple jurisdictions, including Financial Conduct Authority, Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission, Malta Financial Services Authority, Financial Services Regulatory Authority, Australian Securities and Investments Commission, Financial Services Authority Seychelles, and Gibraltar Financial Services Commission.
Account structure includes Personal, Professional, Corporate, and Islamic options, plus a demo balance of $100,000 virtual funds. Platform access is through eToro’s proprietary web and mobile app, meaning no MT4/MT5 support, and customer service is typically handled via email/tickets/live chat, not phone calls.
Account Types | Personal, Professional, Corporate, Islamic |
Regulating Authorities | FCA, CySEC, MFSA, FSRA (ADGM), ASIC, FSA (Seychelles), GFSC |
Minimum Deposit | $10 |
Deposit Methods | eToro Money, Credit/Debit Card, Bank Transfer, PayPal, Neteller, Skrill, Trustly, iDEAL, Sofort, Przelewy24 |
Withdrawal Methods | eToro Money, Credit/Debit Card, Bank Transfer, PayPal, Neteller, Skrill, Trustly, iDEAL, Sofort, Przelewy24 |
Maximum Leverage | 1:400 (noted in your specs table; entity-based) |
Trading Platforms & Apps | Proprietary App (Web + Mobile) |
eToro Pros and Cons
The strengths below explain why eToro often ranks highly in “best regulated brokers” lists, while the limitations clarify when it may not fit a platform-first FX workflow:
Pros | Cons |
Social investing suite: CopyTrader + Smart Portfolios + staking | No MT4/MT5 support |
Multi-jurisdiction regulation with entity-level protections | No phone-call support channel |
Wide multi-asset coverage (stocks, ETFs, FX, indices, crypto) | Fees/spreads vary by asset and region (less uniform pricing) |
Low entry point ($10 minimum deposit) + many payment methods | Professional accounts can reduce some retail protections |
Tickmill
Tickmill is a multi-asset broker with 785,000+ registered users, operating in 180+ countries and reporting an average monthly trading volume above $129 billion. It offers spreads from 0.0 pips and leverage that can reach 1:300 (entity- and client-status dependent), built around fast execution and a Tickmill rebate program.

Founded in 2014, Tickmill runs a no-dealing-desk (NDD) model that routes orders to liquidity providers rather than internalizing flow. Accounts support 6 base currencies: USD, EUR, GBP, ZAR, PLN, and CHF, helping traders reduce conversion friction when funding and managing margin across different regions.
Its multi-jurisdiction framework includes the Financial Services Authority, Financial Conduct Authority, the Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (ICF up to €20,000), Labuan Financial Services Authority, and Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSP 49464). Segregated funds and negative balance protection are listed across entities.
Trading is centered on Classic and Raw accounts (plus demo), with MT4/MT5 + web + mobile support and features such as scalping and hedging. Tickmill also offers Social Trading (availability can vary by entity), along with promotions like a $30 welcome bonus account upon completing the Tickmill registration.
Account Types | Classic, Raw, Demo, Islamic |
Regulating Authorities | FSA (Seychelles), FCA, CySEC, LFSA, FSCA |
Minimum Deposit | $100 |
Deposit Methods | Crypto, Payment Systems, Credit/Debit Cards, Bank Transfers (also listed: Skrill, Neteller, UnionPay) |
Withdrawal Methods | Crypto, Payment Systems, Credit/Debit Cards, Bank Transfers (also listed: Skrill, Neteller, UnionPay) |
Maximum Leverage | 1:1000 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, MetaTrader Web, Mobile App |
Tickmill Pros and Cons
The following snapshot frames Tickmill’s strongest differentiators and the limitations to weigh before choosing the broker as your forex trading platform:
Pros | Cons |
Multi-regulated group (FCA/CySEC/FSCA/FSA/LFSA) with entity-based protections | Limited account variety (mainly Classic + Raw) |
NDD execution model + spreads from 0.0 pips (Raw) | Product depth may be narrower than “mega-brokers” |
Multiple base currencies (USD, EUR, GBP, ZAR, PLN, CHF) | Leverage/protections vary significantly by entity |
MT4/MT5 + web/mobile support; social trading options | Some features (social/bonuses) can be restricted by jurisdiction |
PrimeXBT
PrimeXBT is a multi market broker launched in 2018, offering Forex, 100+ CFDs, and Spot plus Futures crypto trading through web and mobile platforms. Traders get TradingView charts, market execution, and access from a low $15 minimum deposit, which suits smaller accounts and frequent traders.
PrimeXBT operates through a multi entity structure with oversight across several jurisdictions. Listed registrations and licenses include FSA Seychelles (SD162), Lithuania FCIS (306038128), South Africa FSCA (45697), Banco Central de Reserva (66d10393e8a00a3181b8e457), and Mauritius FSC (GB24203383), supporting international client onboarding.
For trading conditions, PrimeXBT combines spreads from 0.1 pips with $0 commission on CFDs, while crypto costs follow a maker taker model on Futures. Maker fees are 0.01% and taker fees start from 0.02%, plus blockchain network fees on crypto withdrawals, which matters for active crypto users.
Account access stays simple with one main Standard setup and a $10,000 demo account for practice, available after completing the PrimeXBT registration. Key specs include 0.01 lots minimum order size, leverage up to 1:1000, Islamic account availability, and copy trading features that let followers mirror strategies and providers monetize performance through profit share models.
Account Types | Standard, Demo account |
Regulating Authorities | FSA, FCIS, FSCA, BCR, FSC |
Minimum Deposit | $15 |
Deposit Methods | Visa/Mastercard, E-Wallet, International Bank Wire Transfer, Crypto |
Withdrawal Methods | Visa/Mastercard, E-Wallet, Bank cards, Crypto |
Maximum Leverage | 1:1000 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | Proprietary Mobile App, WebTrader, MT5 |
PrimeXBT Pros and Cons
Before choosing PrimeXBT, it helps to compare its strengths and trade offs, especially around platform features, fees transparency, and the level of top tier licensing. Below, the pros and cons highlight what typically matters most for Forex CFD and crypto active traders.
Pros | Cons |
Low minimum deposit of $15 for CFDs and crypto access | No tier 1 regulator license listed |
TradingView charts plus web and mobile proprietary platform | Fee transparency can feel limited beyond headline spreads |
Crypto Futures maker 0.01% and taker from 0.02% | Limited account variety compared with multi account brokers |
Copy trading with follower and provider profit share options | Restricted countries include USA, Japan, Canada, Iran, and more |
IC Markets
Founded in 2007 in Australia, IC Markets is a multi-asset brokerage that supports 10 base currencies (USD, AUD, EUR, GBP, SGD, NZD, JPY, CHF, HKD, CAD) and sets a $200 minimum deposit, positioning itself for traders who prefer flexible funding and account configuration.
On the product side, IC Markets highlights broad CFD coverage, including 2,100+ stock CFDs, alongside core CFD markets such as FX, indices, commodities, bonds, crypto, and shares. This breadth makes it practical for multi-asset watchlists without switching brokers.
Regulation is split across multiple entities: the Australian Securities and Investments Commission, the Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission, and the Financial Services Authority of Seychelles. The broker also emphasizes operational controls such as external audits, AML procedures, and segregated client funds held with top-tier banks.
Execution and platform choice are a major focus: MetaTrader 4/5 and cTrader (including web and mobile) are supported, with account types structured around pricing needs, Standard (spread-only) and Raw Spread (tight spreads + commission). In addition, traders can earn up to 21.5% of their paid commission with the IC Markets rebate program.
Account Types | Standard, Raw Spread, Islamic |
Regulating Authorities | FSA (Seychelles), CySEC, ASIC |
Minimum Deposit | $200 |
Deposit Methods | Bank Cards, Wire Transfers, Electronic payments (also listed: PayPal, Neteller, Skrill, UnionPay, Bpay, POLi, etc.) |
Withdrawal Methods | Bank Cards, Wire Transfers, Electronic payments (also listed: PayPal, Neteller, Skrill, etc.) |
Maximum Leverage | 1:500 |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MT4, MT5, cTrader, cTrader Web, IC Markets Mobile |
IC Markets Pros and Cons
Below is a quick overview of what typically stands out with IC Markets and what may be limiting, especially when comparing EU-leverage rules and minimum-deposit expectations across brokers:
Pros | Cons |
Multi-regulated structure (ASIC, CySEC, FSA) with segregated funds emphasis | $200 minimum deposit may be higher than “low-entry” brokers |
Strong platform lineup (MT4, MT5, cTrader, web + mobile) | Leverage is more restricted under EU/EEA regulation (e.g., 1:30) |
Competitive pricing options (Standard spread-only; Raw Spread for active traders) | Entity differences matter (protections and NBP can vary by jurisdiction) |
Large instrument range, including 2,100+ stock CFDs | No PAMM account structure listed in the provided specs |
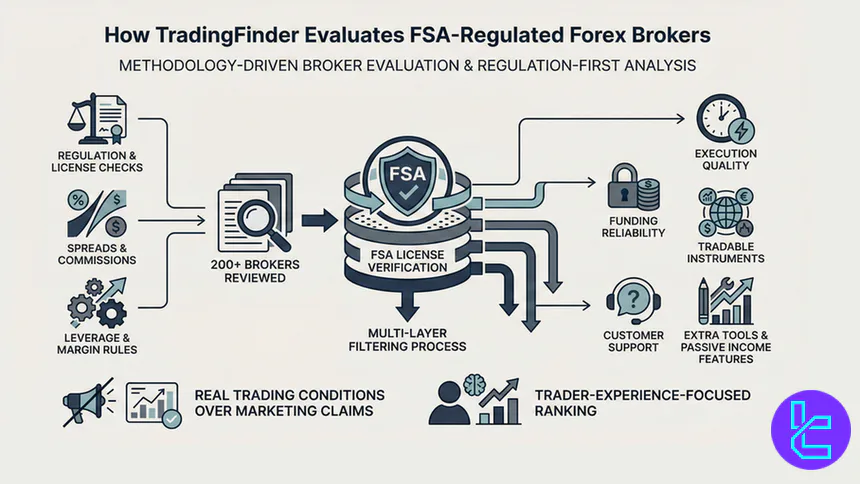
How the Selection for the Best FSA-Regulated Forex Brokers Works in TradingFinder?
TradingFinder’s evaluation of FSA-regulated Forex brokers is based on a multi-layer review of regulation strength, trading conditions, and operational transparency.
Our analysts reviewed 200+ brokers, filtering only those holding an active license from the Financial Services Authority and meeting minimum credibility standards.
Beyond licensing, each broker is stress-tested across real trading metrics such as spreads, commissions, execution quality, leverage structure, and funding reliability. This approach avoids ranking brokers purely on marketing claims and instead reflectsactual trader experience in offshore-regulated environments.
Key evaluation criteria:
- Regulatory status & license verification
- Average spreads and commission models
- Maximum leverage and margin rules
- Range of tradable instruments
- Deposit & withdrawal methods
- Customer support responsiveness
- Additional tools or passive income features
What is FSA?
The Financial Services Authority (FSA) of Seychelles is the primary regulator overseeing non-bank financial services, including Forex and CFD brokers operating under an offshore framework. Established under the Financial Services Authority Act, it supervises licensing, conduct, and reporting obligations for investment firms.
Unlike Tier-1 regulators, the FSA focuses on market accessibility and business flexibility, allowing higher leverage and broader product offerings. While investor protection mechanisms are lighter, FSA regulation still provides a formal legal structure, public registries, and supervisory oversight for licensed brokers.
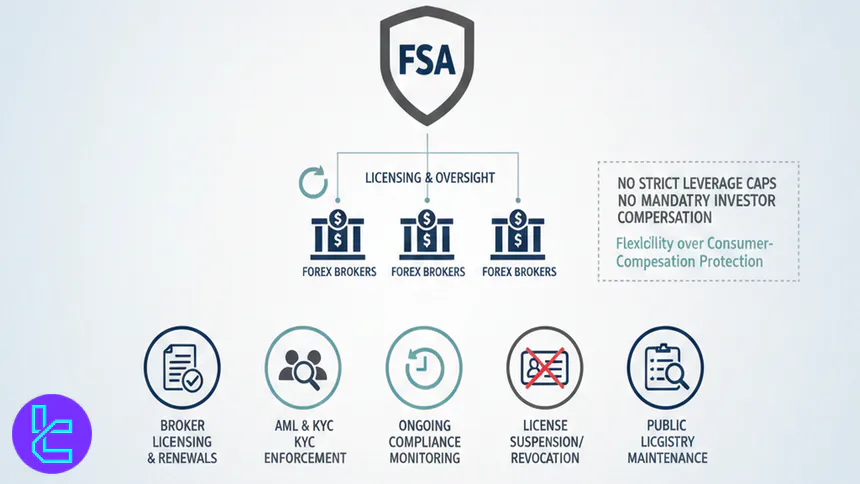
What are the capabilities of FSA?
The FSA holds statutory powers to license, supervise, and enforce compliance among Forex brokers operating under its jurisdiction. It can issue licenses, request financial records, conduct inspections, and revoke authorization if regulatory breaches are identified.
However, the FSA does not impose strict leverage caps or mandatory investor compensation schemes. Its capabilities are best described as administrative and supervisory, rather than consumer-compensation driven, making it suitable for traders prioritizing flexibility over maximum regulatory protection.
FSA regulatory powers:
- Licensing and renewal of Forex brokers
- AML and KYC enforcement
- Ongoing compliance monitoring
- Authority to suspend or revoke licenses
- Maintenance of public license registry
How to Check if a Forex Broker is FSA Regulated
Verifying an FSA-regulated broker is a straightforward but essential due-diligence step. Traders should rely only on the official FSA registry, not claims displayed on a broker’s website or marketing material.
The verification process ensures the broker’s legal entity, license number, and authorization status match official records. This step helps avoid cloned brokers or false regulatory claims common in offshore markets.
Step-by-Step Verification Process:
- Identify the exact legal entity name: Locate the broker’s full registered company name in its legal documents or website footer. Do not rely on brand names, as brokers often operate multiple entities;
- Find the claimed license number: Check whether the broker clearly lists an FSA license or registration number. This number is essential for accurate cross verification in the official registry;
- Visit the official FSA website: Access the official website of the relevant Financial Services Authority. Ensure the domain is authentic and secure before using its regulatory database;
- Open the public register: Navigate to the regulator’s official register of licensed entities. Most FSA authorities provide a searchable database for public verification purposes;
- Search by company name and license number: Enter the legal entity name and license number separately in the registry. Confirm that both searches return matching and consistent results;
- Check authorization status: Review the company’s status in the registry. Ensure it is listed as Authorized or Active, not Suspended, Revoked, Expired, or Under Investigation;
- Confirm permitted business activities: Verify that the license covers Forex, CFD, or investment services. Some firms may be registered but not authorized to offer trading products;
- Match contact and address details: Compare the registered address, phone number, and website listed in the FSA registry with those shown on the broker’s official site;
- Review regulatory warning lists: Search the regulator’s warning section for alerts involving the broker’s name or similar entities that may indicate cloning or impersonation risks;
- Contact the regulator if uncertain: If discrepancies remain, contact the FSA directly using official contact details to confirm whether the broker is genuinely licensed and authorized.
List of FSA Rules Set for Forex Brokers
FSA-regulated Forex brokers must comply with a defined operational framework focused on financial reporting, AML controls, and fair conduct. While capital requirements are lower than Tier-1 regulators, licensed brokers must still maintain proper records and internal controls.
Unlike FCA or ASIC regimes, the FSA does not mandate negative balance protection or leverage caps. This regulatory flexibility explains why many high-leverage Forex brokers operate under FSA supervision.
Core FSA requirements:
- Valid FSA investment dealer license
- AML & KYC compliance procedures
- Annual reporting and audits
- Operational transparency
- Client complaint handling processes

What are the Tradable Instruments in the FSA-Regulated Brokers?
FSA regulated Forex brokers typically provide broad multi asset access, often wider than brokers operating under stricter tier one regulators. Traders commonly gain exposure to high leverage pairs from the Forex market and diversified CFD markets spanning global financial sectors.
Due to lighter product restrictions, many FSA brokers offer expanded instrument lists, including exotic currency pairs, crypto CFDs, and emerging market indices. Instrument availability is usually determined by the broker’s internal liquidity providers and risk management framework.
This flexible structure allows brokers to tailor product offerings to regional demand. However, traders should evaluate liquidity depth, spread structure, and execution quality before trading higher risk or less liquid instruments.
Common tradable markets in FSA brokers:
- Forex: Including major pairs such as EURUSD and GBPUSD, minor crosses, and high volatility exotic currency pairs linked to emerging economies;
- Indices: CFDs covering major benchmarks like S&P 500, NASDAQ 100, DAX 40, FTSE 100, Nikkei 225, and other regional stock indices;
- Commodities: Including spot gold, silver, crude oil, natural gas, and industrial metals offered through leveraged CFD contracts;
- Cryptocurrencies: CFDs, commonly including Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, Ripple, and selected altcoins, depending on liquidity access;
- Shares and ETFs: CFD products, enabling speculation on global equities and sector focused exchange traded funds without direct ownership.
While the product range may appear extensive, traders should assess contract specifications such as leverage ratios, margin requirements, overnight swap rates, and trading hours before selecting specific instruments.

Comparison Between FSA-Regulated and Unregulated Forex Brokers
The key difference between FSA-regulated and unregulated brokers lies in legal accountability. While both may offer high leverage, only FSA-licensed brokers operate under a recognized authority with enforceable rules.
Unregulated brokers may provide similar trading conditions but lack oversight, public registries, or formal complaint channels, significantly increasing counterparty risk:
Parameters | FSA Regulated (Seychelles) | Unregulated Brokers |
Application Fees | Varies by license type; typically ranges from USD 15,000 to USD 25,000, including application and annual regulatory fees | No regulatory application fees; only company registration costs if incorporated offshore |
Capital Requirement | Generally USD 50,000 to USD 100,000, depending on license scope and business model | No mandatory minimum capital requirement |
Application Assessment Timeframe | Usually 2 to 4 months, subject to documentation completeness and due diligence | No formal regulatory assessment or approval timeframe |
Physical Presence Required | Not mandatory; local representative or registered agent usually sufficient | Not required |
Corporate Tax Rates | 0% corporate tax in Seychelles for licensed international companies | Depends on incorporation jurisdiction; often unclear or unverified |
Client Funds Segregation | Required, but with fewer prescriptive rules than Tier 1 regulators | Not legally required or independently monitored |
Investor Protection Scheme | No statutory compensation fund or guaranteed investor insurance | No compensation scheme or investor protection mechanism |
Leverage Limit | No regulatory cap, often up to 1 to 500 or higher, broker defined | Fully broker defined, potentially unlimited and unrestricted |
This comparison highlights that even though FSA regulation is considered offshore and flexible, it still imposes formal entry requirements and compliance standards, unlike unregulated brokers operating without supervisory control.
FSA (Seychelles) vs Other Top Regulatory Entities
When compared to Tier-1 regulators like the Financial Conduct Authority or Australian Securities and Investments Commission, FSA regulation offers greater trading flexibility but fewer investor safeguards. In the table below, we have compared them in detail:
Parameter | FSA (Seychelles) | ASIC (Australia) | CySEC (Cyprus) | FCA (UK) |
Minimum Capital Requirement | Typically USD 50,000 - USD 100,000, depending on license scope | AU$500,000 - AU$1,000,000 | €750,000+, depending on firm type | £125,000 - £730,000+, depending on business model |
Client Fund Segregation | Required, but with less prescriptive rules | Required | Required | Required |
Compensation Scheme | No statutory investor compensation fund | Investor compensation fund (~AU$10,000) | Investor Compensation Fund (~€20,000) | FSCS (~£85,000) |
Leverage Limits | No regulatory cap (broker-defined, often 1:500+) | 1:30 | Set under MiFID (often 1:30 for EU retail) | Retail max ~1:30 on major FX pairs |
Negative Balance Protection | Not mandatory | Required | Often required | Required |
Reporting & Audits | Regular compliance reporting, lighter supervisory audits | Ongoing financial reporting | Ongoing financial reporting | Ongoing reporting and supervisory audits |
Conclusion
Our review of the best Forex brokers regulated by the Financial Services Authority (Seychelles) shows that Fusion Markets, Eightcap, BlackBull Markets, eToro, Tickmill, Plus500, and IC Markets stand out as the most competitive options available under this regulatory framework.
Access to high leverage (often up to 1:1000), tight spreads from 0.0 pips, broad multi-asset coverage, and flexible trading platforms are the main characteristics shared by top FSA-regulated brokers, making them suitable for experienced traders seeking fewer regulatory constraints.
All brokers featured in this article were assessed using TradingFinder’s Forex methodology, which evaluates key factors such as regulation structure, spreads and commissions, tradable instruments, leverage policies, non-trading fees, platform availability, and customer support quality.













