The Inverse Fair Value Gap (IFVG) is an advanced ICT trading concept that identifies key supply and demand zones.
This gap occurs when a Fair Value Gap (FVG) is invalidated in one direction but becomes an effective zone for price reversal in the opposite direction.
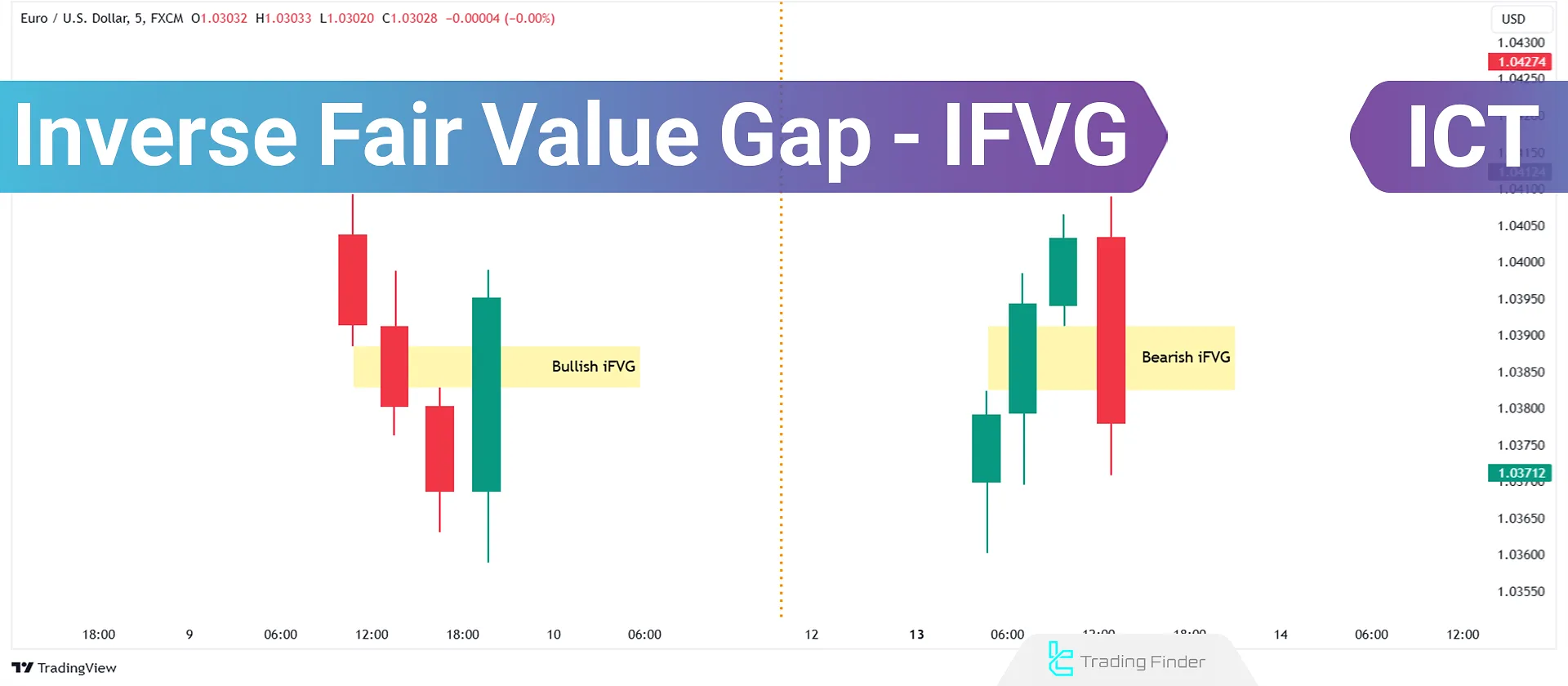
Bullish and Bearish IFVGs, combined with principles like Market Structure Shifts (MSS) and Premium/Discount zones (PD), identify high-probability trading opportunities.
What is the Inverse Fair Value Gap (IFVG)?
The Inverse Fair Value Gap (IFVG) refers to a gap that fails to sustain the price in its initial direction.
Essentially, it is a regular Fair Value Gap (FVG) type that remains a valuable supply or demand zone in the opposite direction despite being invalidated in one specific direction.
In most cases, the price retraces to this zone from the opposite direction and uses it as a new supply or demand level.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Inverse Fair Value Gap (IFVG)
Like any technical concept or tool, trading based on the Inverse Fair Value Gap has unique strengths and weaknesses. Pros and Cons of IFVG:
Advantages | Limitations |
Provides an early signal for reversal points | It can sometimes produce false signals |
Enables early trade entries | Dependent on market conditions |
Improves risk-reward ratio | Requires integration with other tools |
Types of Inverse Fair Value Gaps
Inverse Fair Value Gaps (IFVG) are divided into Bullish IFVGs and Bearish IFVGs.
Bullish Inverse Fair Value Gap (Bullish IFVG)
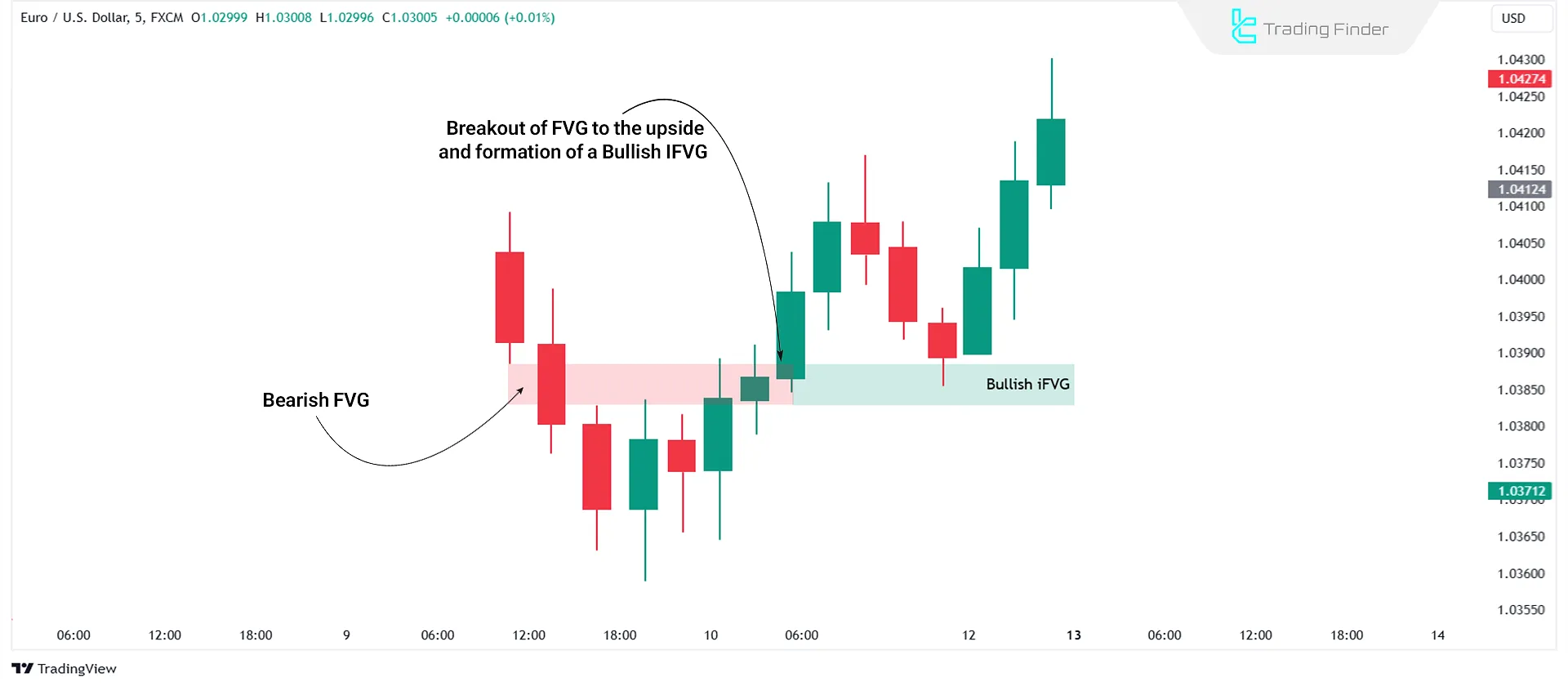
This type of gap forms when a Bearish FVG fails to push the price downward. The price then breaks upward through the gap, invalidating it. Ultimately, this level acts as a demand zone, triggering a bullish movement.
Bearish Inverse Fair Value Gap (Bearish IFVG)
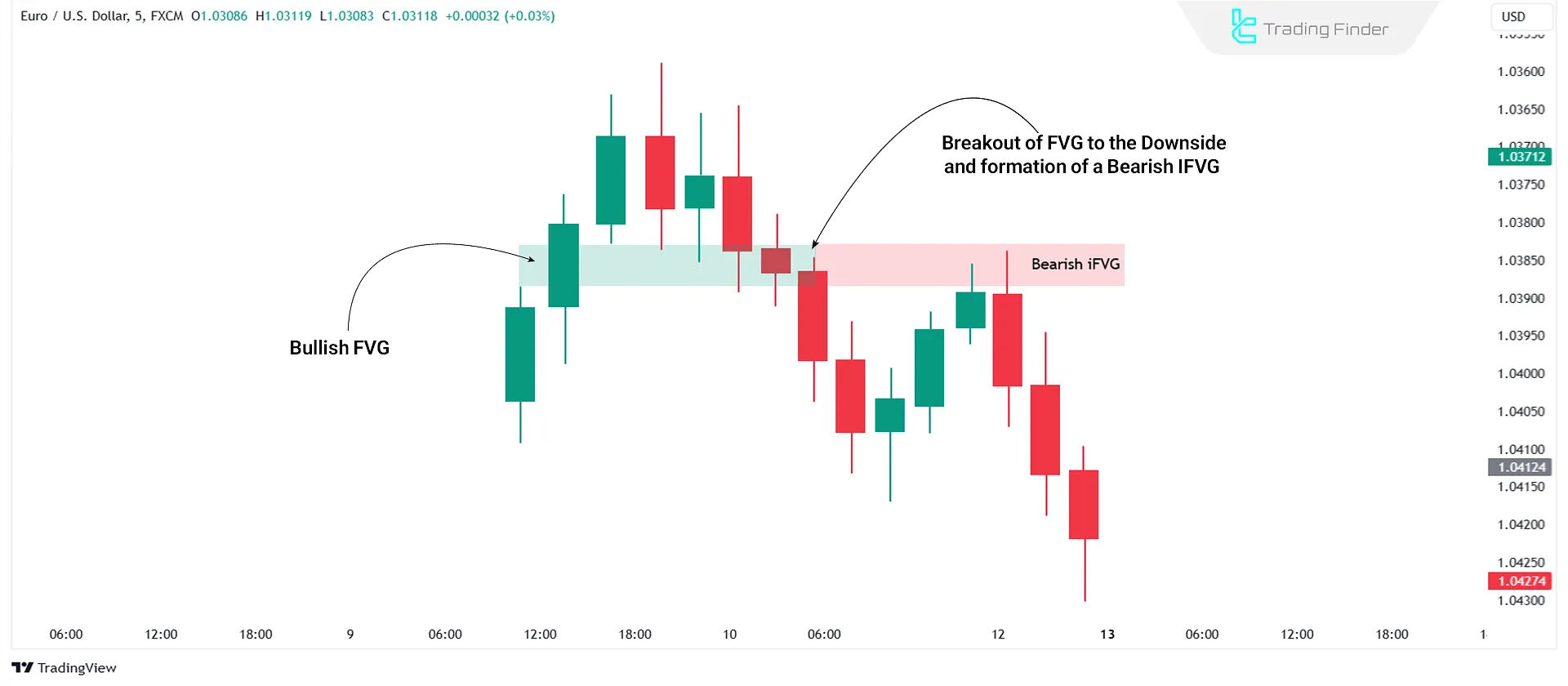
In this scenario, a Bullish FVG is broken downward by the price, losing its validity. This zone then transforms into a supply area where a bearish movement begins.
Identifying High-Probability Inverse Fair Value Gaps
The likelihood of spotting an Inverse Fair Value Gap (IFVG) exists across any point on the chart. To identify high-probability IFVGs, consider the following key points:
#1 Liquidity Areas
IFVGs that emerge after clearing liquidity zones are more likely to hold prices. These liquidity zones include:
- Highs and Lows of the Day (HOD/LOD)
- Session Highs and Lows
- Equal Highs and Lows
- Support and Resistance Zones
- Swing Highs and Lows
In a downtrend, lower highs often act as liquidity inducement zones (IDM), which the price clears before continuing the bearish move.
#2 Premium and Discount Zones (PD Zones)
Identifying premium and discount zones is another effective method to locate high-probability IFVGs. Here's how to define these zones:
- In an uptrend, the discount zone is the lower half of the move, while the premium zone is the upper half.
- Typically, prices retrace at least 50% before continuing. Thus, supply or demand zones within the discount area are more likely to hold prices.
How to Trade Using Inverse Fair Value Gap (IFVG)?
IFVG is not a standalone trading strategy but a concept that enhances understanding of price behavior. To use it effectively, combine it with other ICT principles.
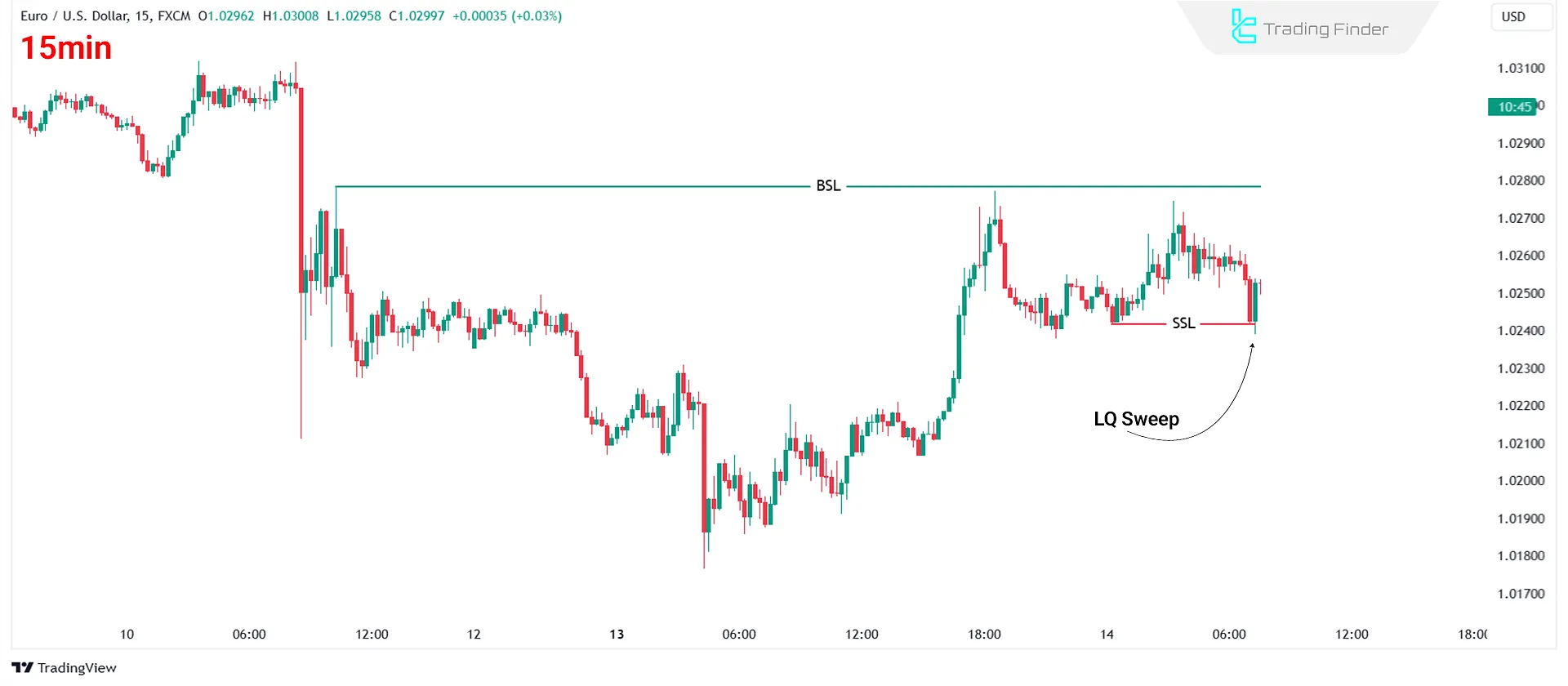
#1 Identifying Liquidity Sweep
The first step is recognizing the liquidity area likely to be swept before the trend continues. Ideally, liquidity should exist on the side opposite your expected trend.
Example: An uptrend is expected on EUR/USD chart. However, a notable swing low serves as sell-side liquidity.
#2 Trade Entry
First, identify the regular FVG that forms after liquidity is swept on the chart:
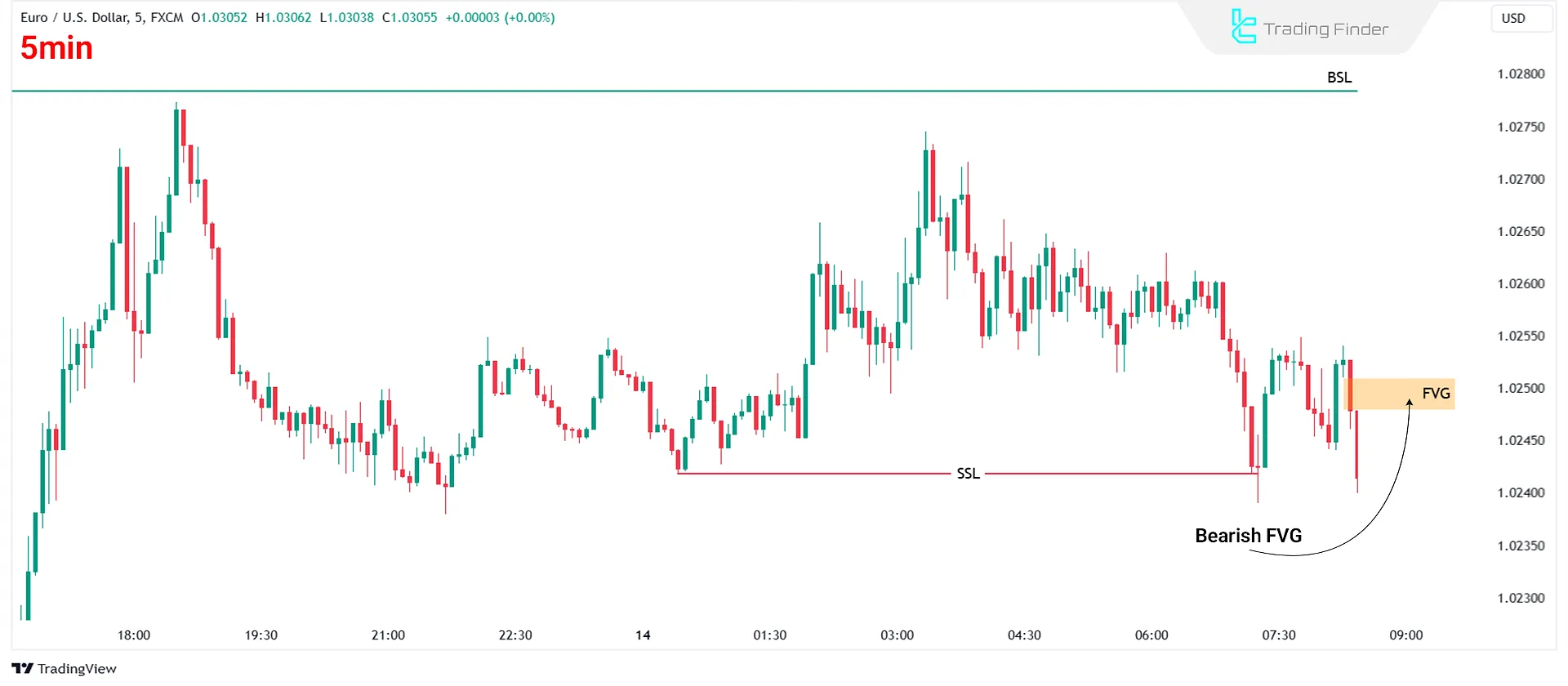
Next, wait for the price to break through the FVG in the opposite direction, forming an IFVG:
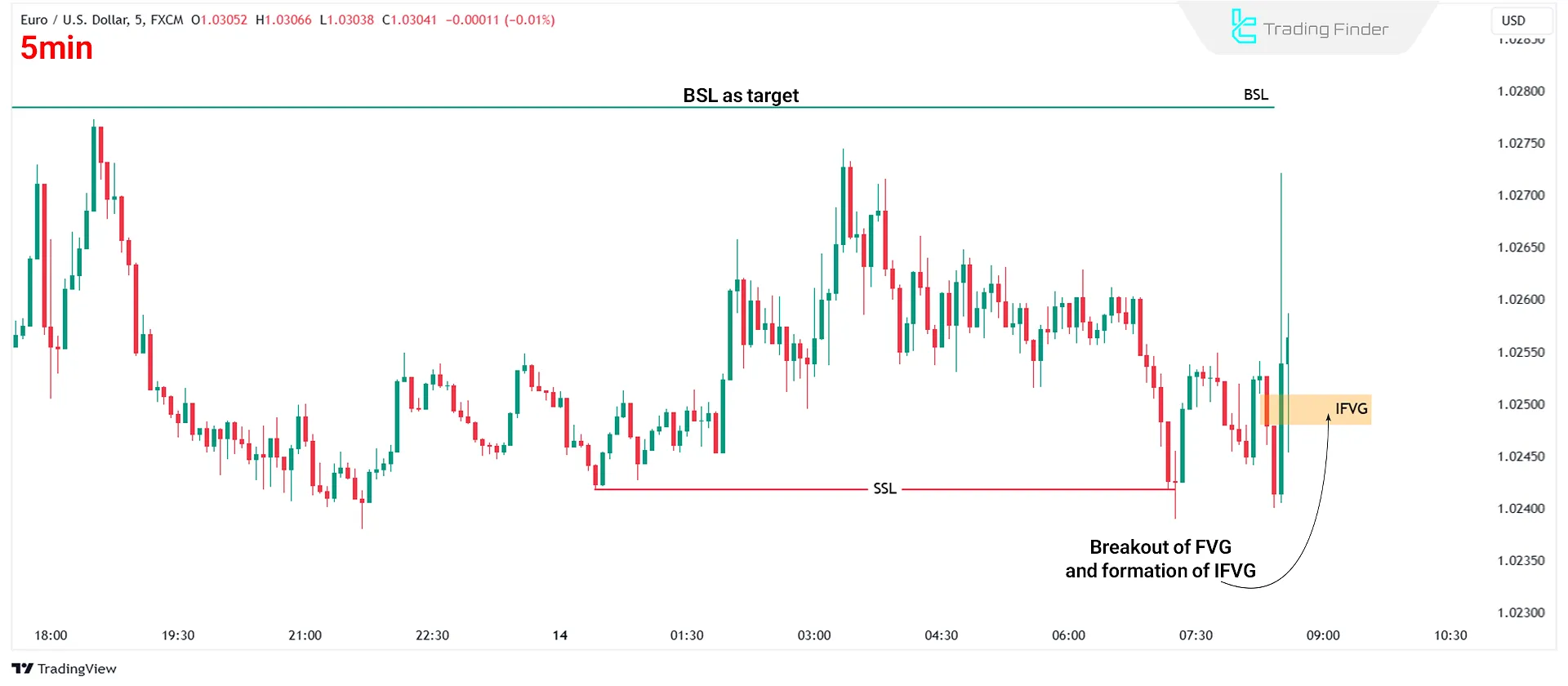
#3 Risk Management
Trading IFVG or any other strategy requires practical risk management tools. Use the following tips for stop-loss and take-profit placement:
- Stop Loss (SL): Place your SL below the nearest low or above the nearest high before the IFVG formation.
- Take Profit (TP): Set your TP at a significant high or low on the opposite side of the trade.
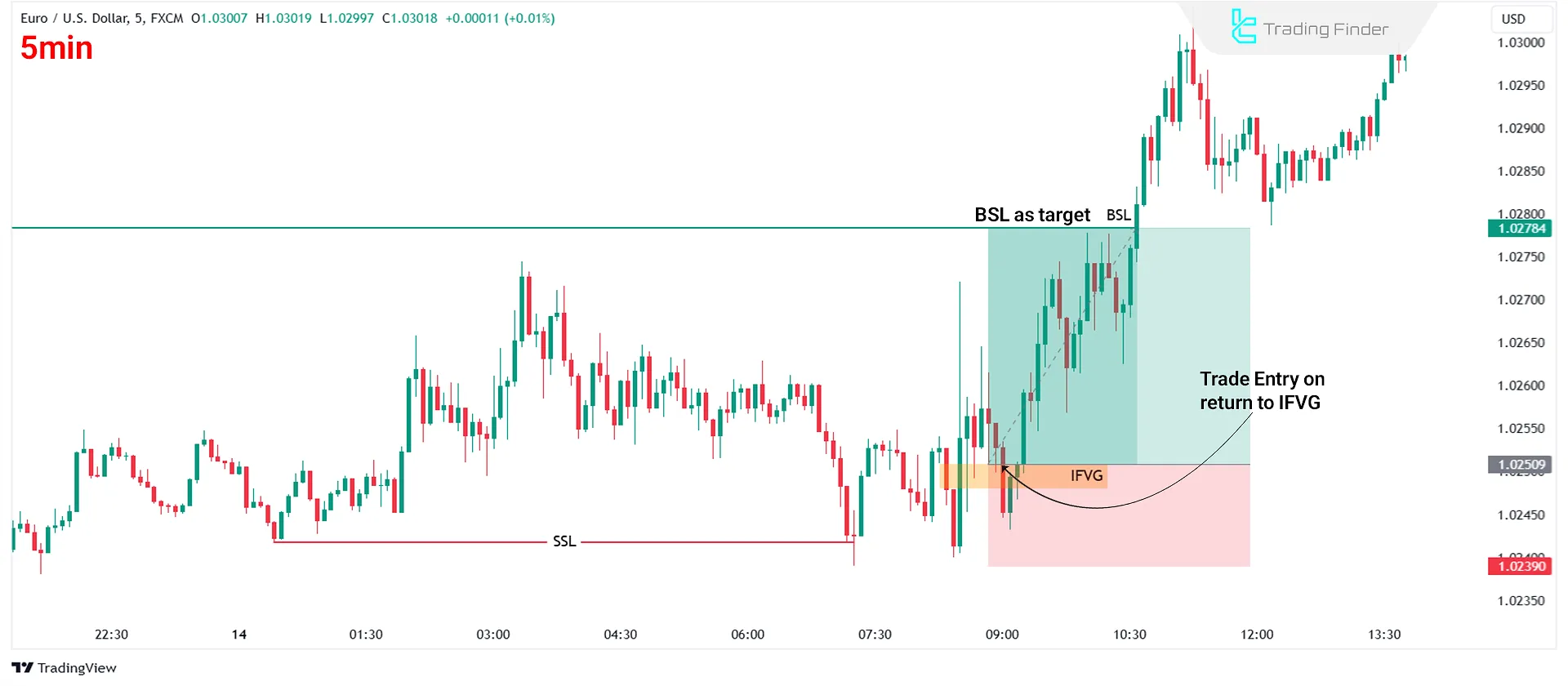
Conclusion
The ICT Inverse Fair Value Gap (IFVG) is an advanced analytical tool for identifying key entry or exit zones.
It forms when an FVG becomes invalidated in one direction and transforms into an effective zone in the opposite direction.
For optimal results, use IFVG alongside other ICT concepts like liquidity inducement, market structure shifts, premium/discount zones, and ICT kill zones.













