The ICT trading style is a price action-based methodology developed by Michael J. Huddleston. This strategy focuses on analyzing major financial institutions' behavior and market makers' role.
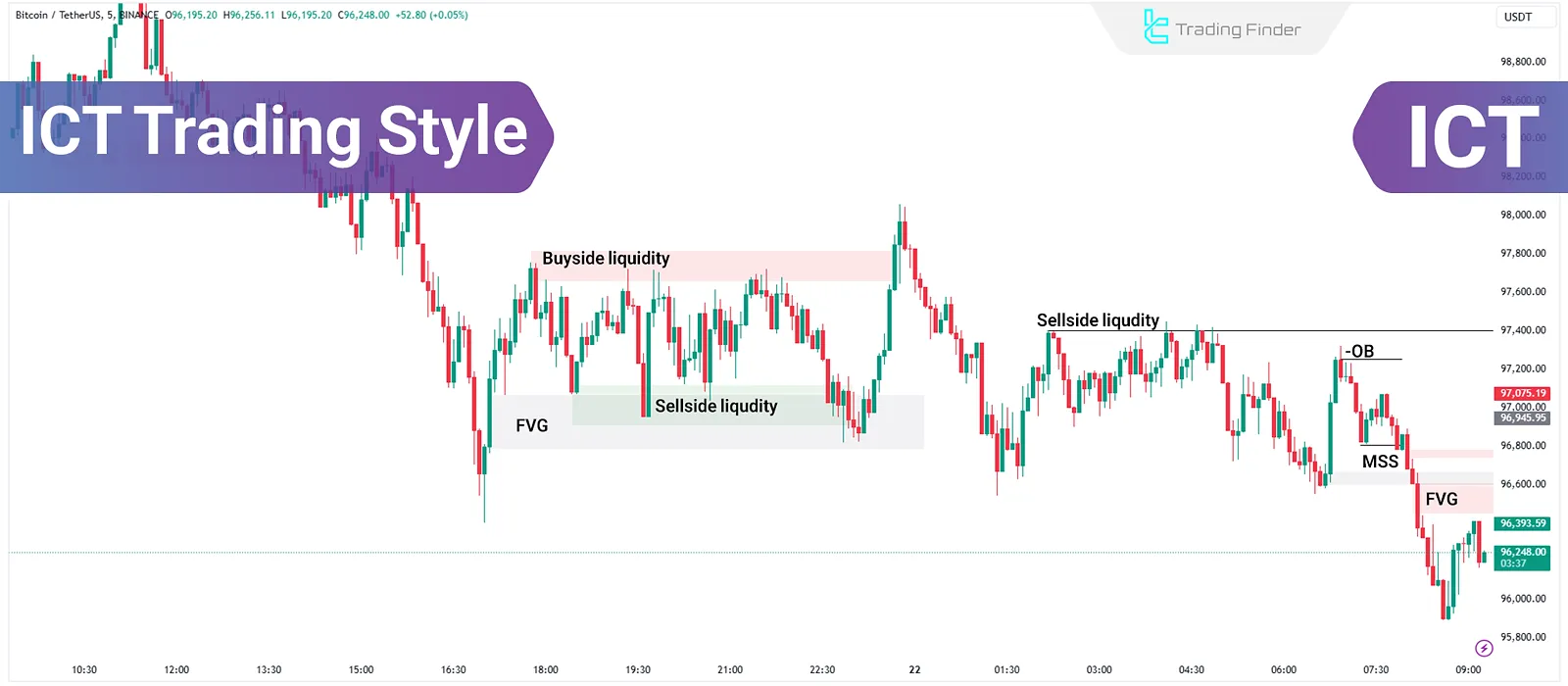
Using this style, traders can assess market movements from the perspective of large players like banks and identify key entry and exit points.
If you are new to this method, it is essential to understand its core concepts, such as Liquidity,Fair Value Gaps (FVG), and Market Maker Levels.
In this article, we'll thoroughly explore the key terms and concepts of the ICT trading style to help you apply this approach to your trades.
What is the ICT Style? An Overview of This Strategy
The ICT style is a price action-based trading methodology designed to identify and track the movements of large investors, known as "Smart Money."
This strategy enables traders to predict market maker (MMXM) traps and align their trades accordingly.
Key Features
This style is built on several essential elements, including:
- Focusing on price behavior and order flow;
- Identifying key zones for entry and exit by major capital holders;
- Using concepts like Order Blocks, Liquidity, and Market Structure Shifts;
- Avoiding reliance on complex indicators;
- Utilizing patterns of market manipulation.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Every strategy has pros and cons; knowing them helps traders decide if ICT suits their goals.
Advantages | Disadvantages |
It provides deeper insights into market behavior | requires significant time and practice |
Focuses on strategic, knowledge-based decisions | Contains complex and diverse concepts |
Reduces reliance on technical indicators | Risk of misinterpreting signals without experience |
Access to extensive educational resources by Huddleston | - |
Detailed Analysis of ICT Trading Terms and Concepts
Mastering its associated terms and concepts is essential to effectively use the ICT style. Below, we'll delve into the following ICT-related terms:
- Order Block
- Smart Money
- Liquidity
- Market Structure Shift (MSS)
- Fair Value Gap (FVG)
- Inducement
- Balanced Price Range
Order Block
Order Blocks are one of the most critical ICT concepts. These are areas on the chart where large institutional orders are placed, often acting as strong support or resistance zones. Identifying these areas can help predict future price movements.
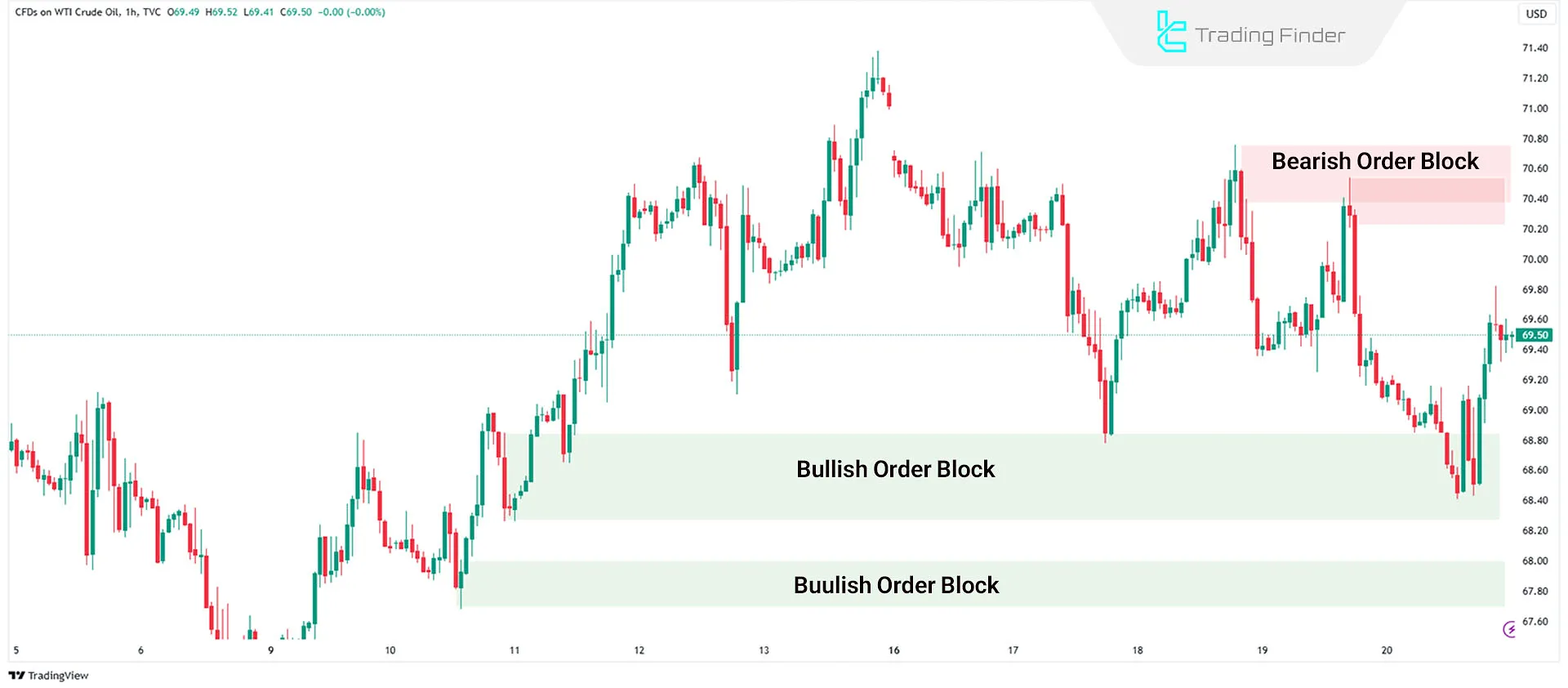
To identify Order Blocks, traders should look for large, high-volume candles that often appear before a significant trend reversal.
Smart Money
"Smart Money" refers to the substantial capital flows by institutional investors, which can influence market movements. One of the primary objectives of ICT traders is to track and follow the behavior of these major players.
ICT traders believe that by understanding Smart Money patterns and aligning their trades, they can achieve more favorable outcomes and identify traps set by large market participants.
Liquidity
Liquidity refers to zones where large clusters of buy or sell orders are concentrated. In ICT, liquidity is divided into two main types:
- Buy Liquidity: Levels where sell-side stop losses are positioned.
- Sell Liquidity: Levels where buy-side stop losses are positioned.
ICT traders operate on the assumption that markets tend to reverse after crossing liquidity levels.
Market Structure Shift (MSS)
Mrket structure shift refers to a significant change in the chart's overall trend. For example:
- In an uptrend, prices consistently form higher highs and higher lows.
- A shift occurs when a lower high or lower low is established, signaling a potential trend reversal.
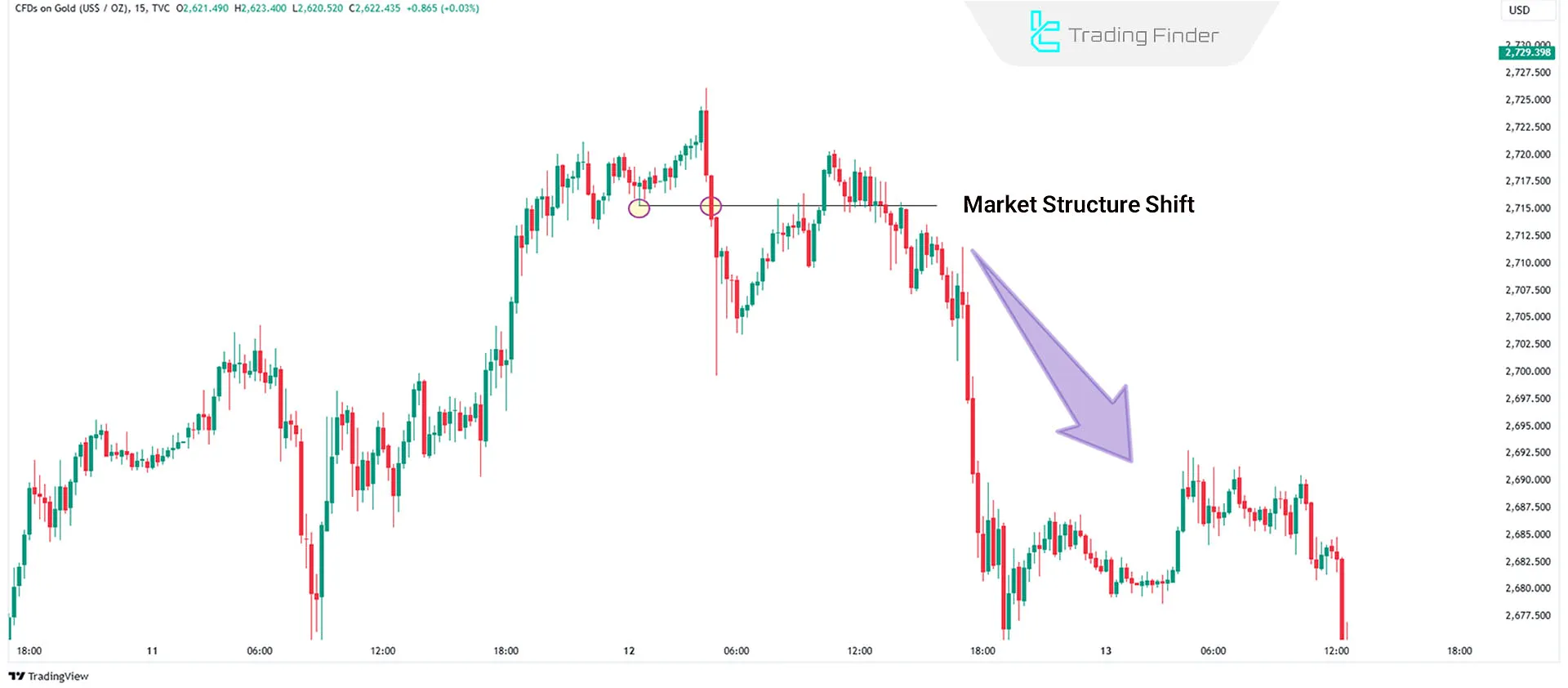
MSS is highly significant in ICT as it indicates potential changes in Smart Money behavior and creates trading opportunities.
Fair Value Gap (FVG)
Fair Value Gap FVG refers to gaps between two candlesticks, typically caused by significant price movements.
These gaps signify temporary supply-demand imbalances and are often revisited by price.
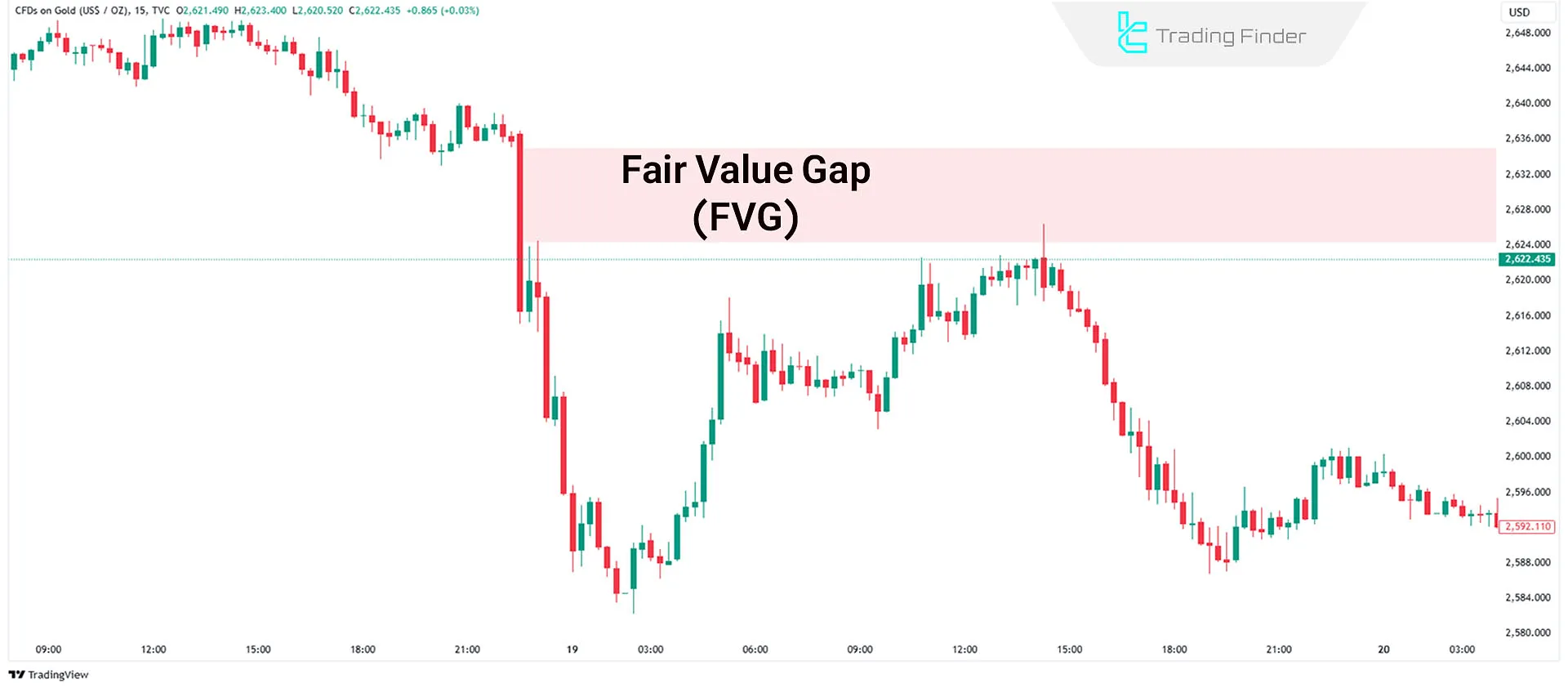
Inducement
Inducement describes short-term, deceptive price movements designed by market makers to lure retail traders into placing orders. These movements aim to generate liquidity by triggering stop-loss orders.
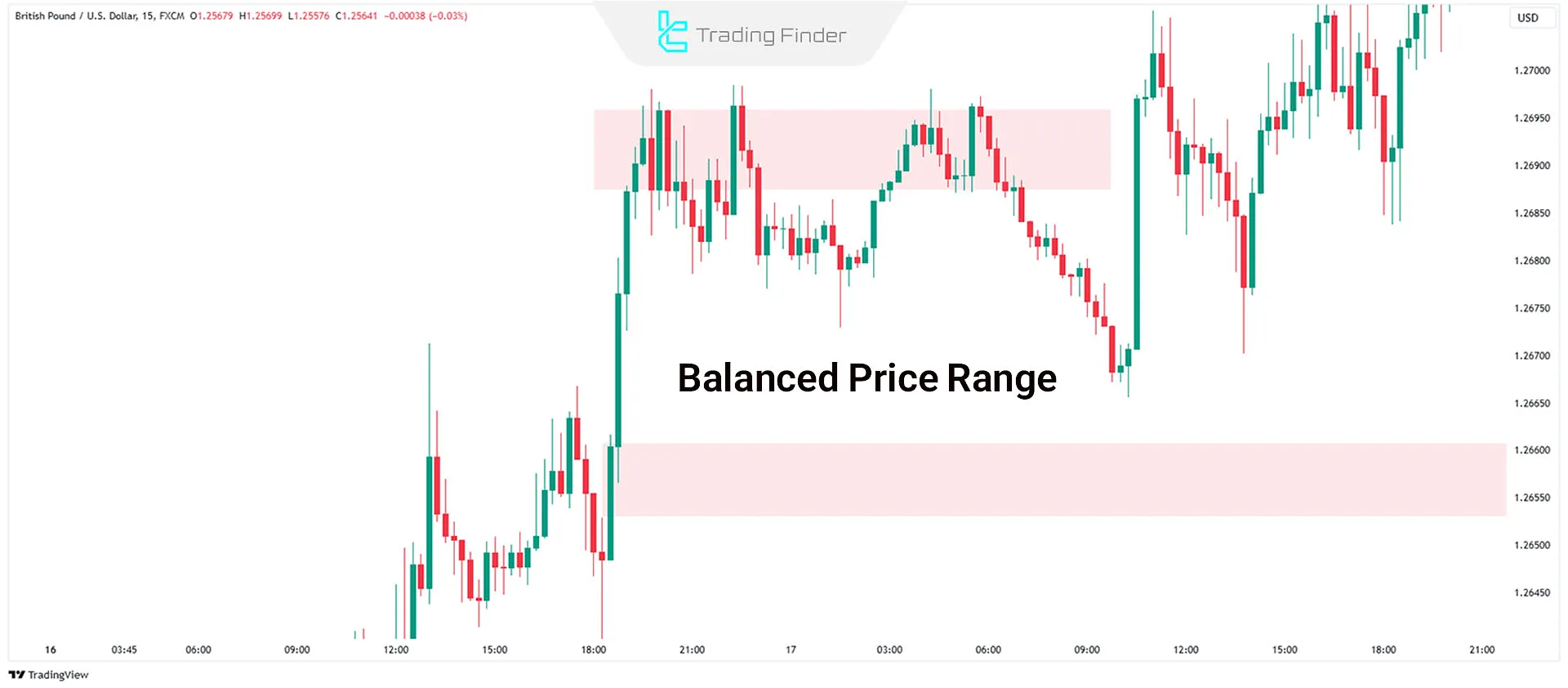
Balanced Price Range
A Balanced Price Range occurs when the price rapidly moves up and down (or vice versa), creating a range resembling a dual-sided FVG. These zones often signal potential market reversals.
Is the ICT Trading Style Suitable for Everyone?
ICT is ideal for traders who:
- Seek a deeper understanding of market behavior;
- Have patience for detailed chart analysis;
- Prefer a strategy with minimal reliance on indicators;
- Can manage Risk and control emotions effectively.
However, beginners or those seeking quick signals may find this method challenging. Mastery requires time and extensive practice.
Tips for Using the ICT Trading Style
Things to consider when using the ICT business style are as follows:
- Be patient: Understanding concepts like Order Blocks takes time and practice.
- Always use proper risk management.
- Continue learning: Keep your knowledge updated.
- Test your strategies: Use backtesting to evaluate their effectiveness.
Expert Advice and Conclusion
This article provides a comprehensive overview of ICT terminology and introduces the trading style. By leveraging this approach, traders can better analyze the behavior of large market players and potentially increase profits.
That said, ICT comes with its challenges and may not suit everyone, particularly beginners.













