Scalping is a highly fast-paced trading strategy in financial markets where the period between opening and closing trades is only a few seconds to a few minutes.
As a result, risk management in scalping trades is of heightened importance, since the high trade volume means even the smallest slip can lead to significant losses.
Scalpers rely on short-term price fluctuations, aiming to trade on the market’s quickest reactions; in this approach, the high number of trades and substantial position sizes generate small but frequent profits.
Execution speed and the quality of market liquidity connection are also critical; for this reason, many scalpers use ECN/STP brokers with extremely low spreads and latency of less than 50 milliseconds.

Definition of Scalping
Scalping is a trading style that focuses on very short time frames. Entry and exit occur quickly within limited time intervals.
Traders using this style are known as scalpers, who open multiple trades throughout the day with the goal of capitalizing on momentary price movements.
In this method, real-time market analysis, immediate decision-making, and quick reactions to price changes are mandatory.
Alongside these factors, managing emotions, mental discipline, and adhering to the trading strategy is essential for success in this style.
Main Features of Scalping
Scalping has distinctive technical features for technical traders that make it a unique tool:
- Ultra-Short-Term Trades: Executing positions in time frames ranging from a few seconds to a few minutes;
- Increased Position Volume: Using large trading volumes to achieve small and consecutive profits;
- High Number of Positions Within a Trading Day: Using multiple opportunities for quick entry and exit from the market;
- Reacting to Momentary Price Fluctuations: Focusing on immediate and short-term changes to gain profits from fast market movements.
For a deeper understanding of the scalping trading strategy, you can also refer to the article mastering quick profits in the market with scalping strategy training on investopedia.com.
Differences Between Scalping, Day Trading, and Swing Trading
Choosing a trading style is not merely a personal preference it’s a strategic decision determined by factors such as risk tolerance, investment horizon, mental processing speed, and psychological capacity.
The following table compares Scalping, Day Trading, and Swing Trading:
Comparison Criteria | Scalping | Day Trading | Swing Trading |
Trade Time Horizon | A few seconds to a few minutes | A few minutes to several hours (positions closed the same day) | A few days to several weeks |
Number of Trades | Very high (dozens to hundreds per day) | Moderate (a few trades per day) | Low (a few trades per week) |
Risk Management | Very tight stop-losses, repeated risk exposure | Medium stop-losses, daily risk control | Larger stop-losses, smaller position sizes |
Need for Speed and Focus | Very high – instant execution is critical | Moderate – continuous chart monitoring throughout the day | Low – periodic reviews are sufficient |
Psychological Pressure | Very intense | Moderate | Relatively low |
Lifestyle Suitability | Suitable for individuals with free time and momentary focus | Suitable for full-time traders | Suitable for those with jobs or side activities |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Scalping
Advantages and disadvantages of scalp trading are noted below:
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Lower Risk Compared to Long-Term Trading | High Transaction Fees Due to Large Volume and Frequency |
More Trading Opportunities in a Short Time Frame | Need for Constant Market Analysis |
Potential to Profit from Low-Volatility Markets | Requires More Precision in Analysis |
Reduced Risk and Impact of Macroeconomic News | Time-Consuming and Demands More Focus on the Market |
Continuous Small Profits in a Short Time | Advanced Capital and Risk Management Needed |
No Need for Large Capital | Scalping May Be Prohibited by Some Brokers |
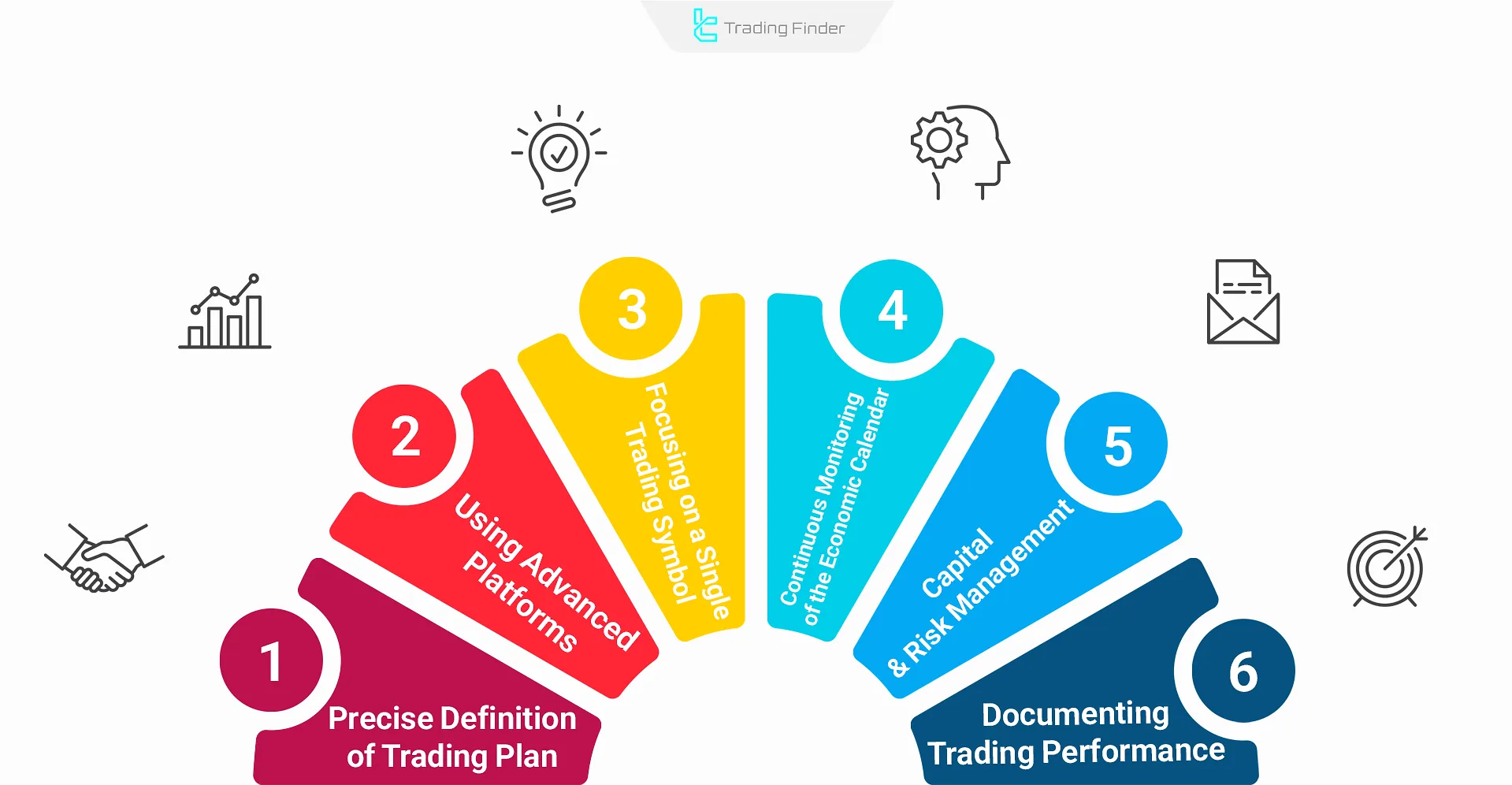
Basic Principles of Scalping
Ignoring basic principles in implementing the scalping style increases risk and reduces decision-making accuracy.
The following are essential requirements for effective scalping execution:
- Precise Definition of a Trading Plan: Determining entry points, exit strategy, take-profit, and stop-loss levels before executing a trade;
- Using Fast and Advanced Platforms: Selecting trading tools with fast order execution, such as Metatrader 5, Metatrader 4, and TradingView;
- Symbol Focus: Continuously analyzing and tracking a specific asset’s technical behavior for real-time decision-making;
- Constantly Monitoring The Economic Calendar: Monitoring the economic calendar to anticipate major price moves using tools like TradingFinder's Calendar;
- Capital & Risk Management: Precisely determining position size based on account risk management;
- Documenting Trade Performance: Recording trade details (journaling) for ongoing strategy improvement based on past performance.
Exit Strategies in Scalping
Alongside a precise trading strategy, having a well-defined exit strategy is highly essential in scalping trades.
Timely exits in profit lead to consistent profitability, while timely exits in loss help prevent heavy and consecutive drawdowns. Types of exit strategies include:
- Time-based exit: closing the trade if it does not reach the target after a specific number of candles (for example, 5 M1 candles);
- Momentum-based exit: exiting upon detecting a momentary divergence or a noticeable slowdown in momentum within the entry timeframe;
- The “first mistake, last attempt” rule: stopping any further re-entry attempts after one consecutive stop-out in the same setup.
Types of Scalping Trades
Each method of scalping has its specific execution structure, focusing on high accuracy, speed, and market adaptation.
The choice of method depends on the trader's experience, market structure, and short-term trading objectives:
- News-Based Scalping: Capitalizing on significant price fluctuations due to economic data releases and major financial events;
- Liquidity-Based Scalping: Choosing assets with low spreads and appropriate market depth to minimize trading costs and ensure faster execution;
- Algorithmic Scalping: Using algorithms and automated trading systems to enter and exit the market quickly;
- Technical Analysis-Based Scalping: Executing quick trades using indicators, price levels, chart patterns, and other technical concepts;
- Trend-Based Scalping: Opening short-term positions in alignment with the market trend and prioritizing momentum;
- Tick Scalping: High-speed trades based on the smallest price movement unit (tick), suitable for high liquidity markets and momentary fluctuations.
Common Order Types for Executing Scalping Trades
In scalping, choosing the right type of order is highly important, as execution speed and risk control are crucial in this strategy.
The common order types used for executing scalping trades are compared with each other in the table below:
Order Type | Technical Definition | Application in Scalping | Key Advantage | Risk / Limitation |
Market Order | Immediate execution of a trade at the best available market price | Fast entry during range breakouts or rapid price movements | Very high entry speed | Possibility of slippage in highly volatile markets |
Limit Order | Execution of a trade at a specified price or better | Entry at support and resistance levels or in range scalping strategies | Control over entry price and risk | Possibility of order not being triggered during fast price movements |
Stop Market Order | Trade activation once price surpasses a set level, then executed as a market order | Entry during breakouts | Ensures participation in sustained moves | High slippage during news or sharp price spikes |
Stop Limit Order | Activated when price reaches a specified level, but executed at the limit price or better | Sensitive breakout entries with price control | Reduced price slippage and precise entry control | Risk of missing the move in fast markets |
Trailing Stop | Dynamic stop-loss that moves with the price in favor of the trader | Protecting profits in short-term trades | Locks in profits and enables dynamic exit management | Early exit during false or temporary fluctuations |
OCO (One Cancels Other) Order | Combines two simultaneous orders; execution of one cancels the other | Range scalping or bidirectional movements | Simultaneous management of buy and sell scenarios | More complexity in setup and management |
Offline / Advanced Orders (Algo & Conditional Orders) | Includes conditional (If-Then), algorithmic, or automated arbitrage orders | Suitable for professional traders using scalping bots or API | Automated and fast execution without manual monitoring | Requires technical expertise and thorough strategy testing |
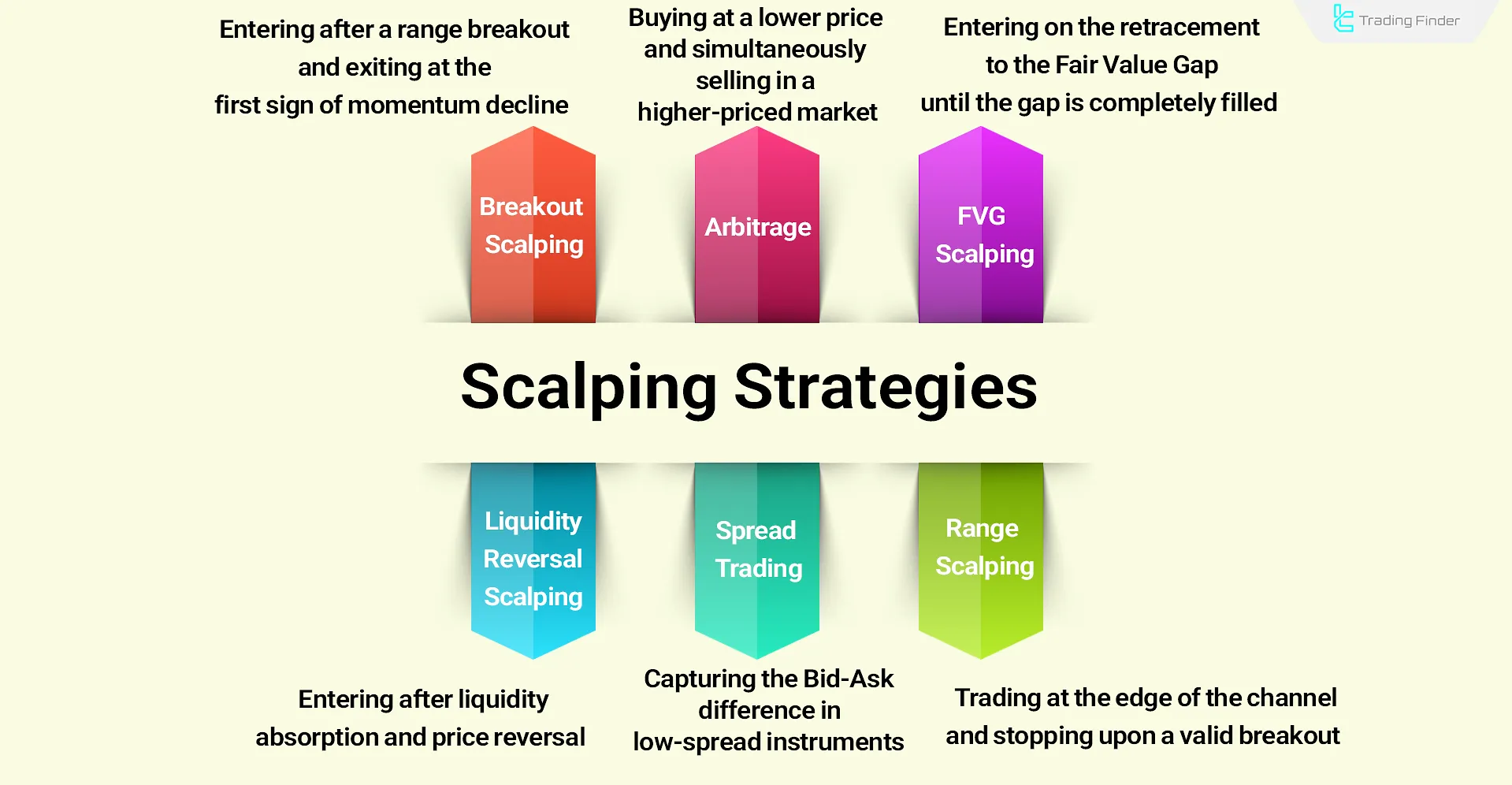
Practical Scalping Strategies
The following section introduces six practical scalping strategies that cover the full spectrum of approaches, including classical price action, range trading, market making, arbitrage, and advanced liquidity-based methods:
Strategy | Nature | Entry / Exit | Stop Loss | Main Risk |
Breakout | Capturing momentum after price exits a defined range | Stop-market entry on highs/lows, exit on momentum slowdown | Behind the range | False breakout without sufficient volume |
Range | Buying/selling at the edges of a neutral channel | Limit orders at the boundaries, stop upon valid breakout | Behind channel edge | Fake-out or sudden breakout |
Spread Trading | Exploiting the Bid/Ask spread | Two-way orders on narrow spreads | — | Sharp slippage during news or low market depth |
Arbitrage | Simultaneous buying in the cheaper market and selling in the more expensive one | Fast execution with low fees | — | Price discrepancy may vanish before completion |
Liquidity Sweep | Entering after stop-hunts and subsequent price reversal | Along with inflow of new liquidity | — | Partial reversal or lack of liquidity |
Fair Value Gap (FVG) | Filling the Fair Value Gap in lower timeframes | Entry on retrace to the gap, exit on complete fill | Small stop within the gap | Slow fill or unfilled gap |
These strategies not only enable traders to maximize their gains from instant market fluctuations but also, through dynamic risk management and multilayered order book analysis, significantly enhance the effectiveness of short-term trades.
Scalping Strategies at a Glance:
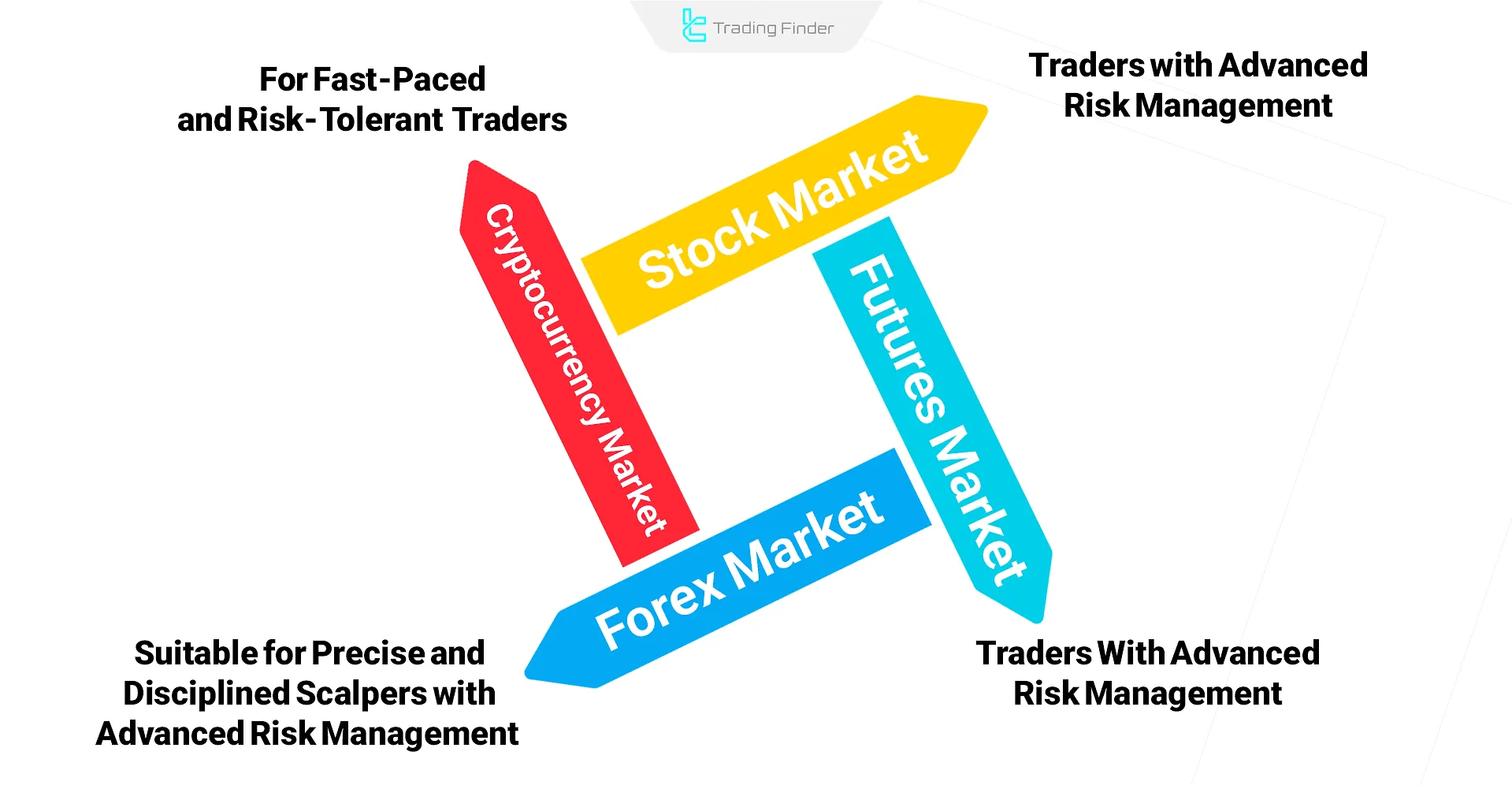
Scalping in Different Markets
The best scalping strategy in each market, with its unique characteristics, creates distinct conditions of opportunity and risk.
- Forex Market: Ideal for precise and consistent scalpers;
- Cryptocurrency Market: Attractive for fast-paced and risk-tolerant traders;
- Stock Market: Offers limited opportunities during specific hours and requires intense focus;
- Futures Market: Perfect for advanced risk-managed scalpers.
Scalping in Forex
The Forex market, due to its high liquidity and extremely low spreads, is one of the best options for scalping.
Forex scalpers typically aim for a few pipsin the fastest time possible. Important Points in Forex Scalping:
- High Liquidity: Major pairs usually offer high liquidity and volume for fast trade execution;
- Very Low Spreads: Low spreads allow scalpers to make more profit from their trades;
- Sensitivity To News: Significant economic events greatly increase market volatility.
Those interested in price action–based scalping in the Forex market can also benefit from Al Brooks’ scalping tutorial video on YouTube:
Scalping in Crypto
Scalping in Cryptocurrency trading has significant appeal due to the 24/7 nature of the market. However, unexpected volatility is a major challenge for scalpers.
Key Points in Crypto Scalping:
- Non-Stop Market: Scalping is available 24 hours a day, seven days a week;
- High Volatility: Even major coins like BTC and ETH experience high volatility in the short term;
- Suitable Coins: Popular cryptocurrencies for scalping are high-volume pairs such as BTC/USDT or ETH/USDT, which have low spreads.
Scalping in the Stock Market
Scalping in stock market trading is limited to official exchange hours and is usually performed on high-volume and volatile stocks.
Key points in stock scalping:
- Specific Trading Hours: Trades can only be made during official stock exchange hours;
- Impact of Company News: Financial reports, management changes, and other news can create optimal scalping opportunities;
- Transaction Costs: High fees and taxes for very short-term trades can erode scalpers' profits.
Scalping in Futures Market
Futures, due to the ability to use high leverage and access to various assets (indices, commodities, currencies, and cryptocurrencies), provide an ideal environment for professional scalpers. Important points for future scalping:
- High Leverage: Allows controlling larger positions with small capital and requires precise management;
- Fast Movements: Sharp price fluctuations in small time frames, such as indices like S&P500 or Dow Jones;
- Risk Of Liquidation: Using high leverage without stop-loss can result in complete account liquidation.
Psychology of Scalping
The psychology and mental health of the trader are crucial for mastering the market and executing precise scalping trades.
The most important psychological aspects of scalp trading are:
- Emotional Control: Managing fear, greed, and stress arising from trades in the market;
- Quick And Decisive Decision-Making: Entering trades without hesitation and confidently executing the analysis;
- Stress Management: Avoiding emotional decisions and limiting the number of trades per day by taking regular breaks to prevent mental exhaustion;
- Adherence to the Trading Plan: Discipline in executing entries and exits as per the trading plan without changing decisions impulsively;
- Statistical Mindset: A Realistic understanding of overall trading performance, accepting that profit and loss are inevitable, and avoiding emotional reactions to losing trades.
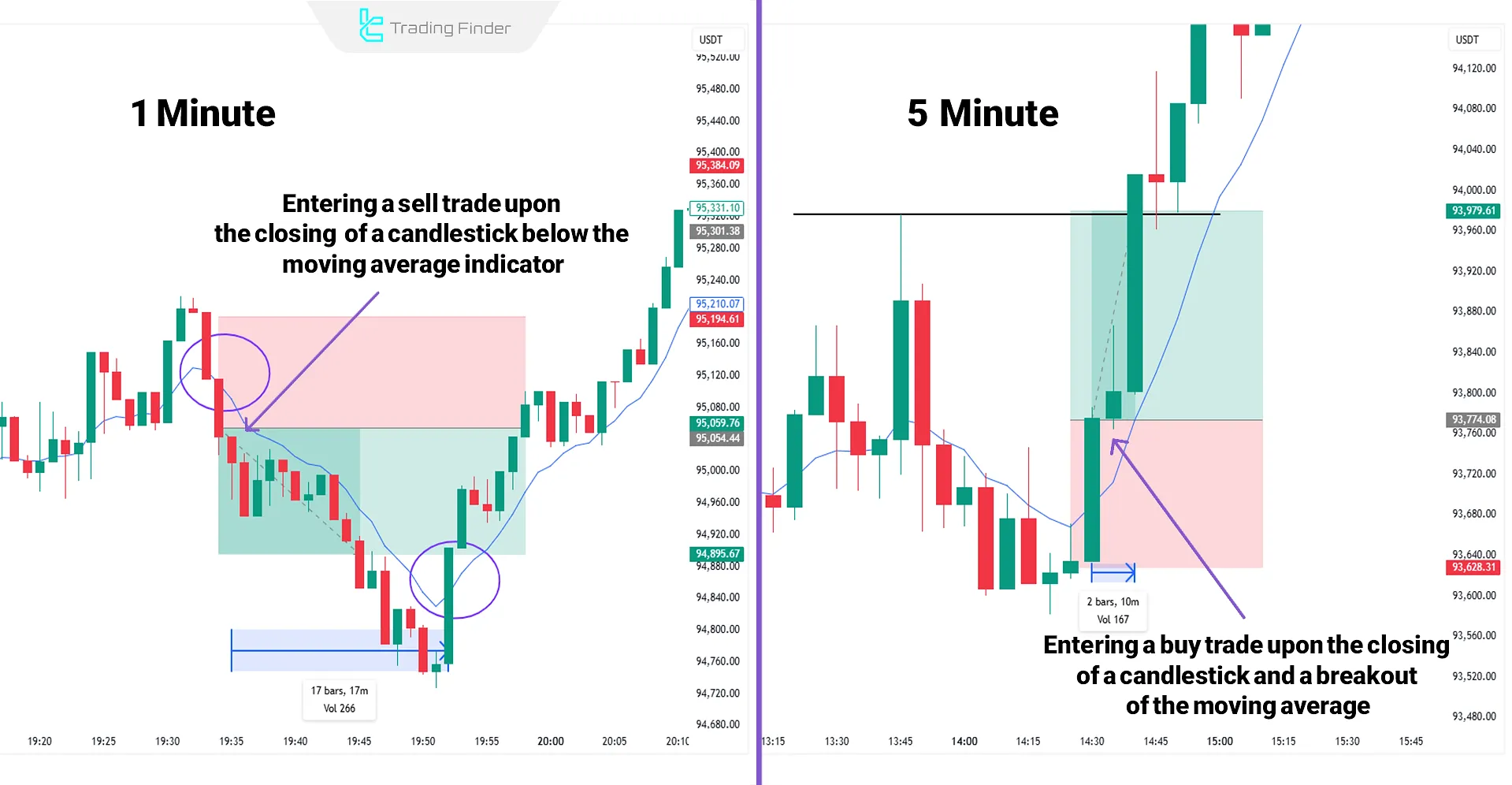
Best Time Frames for Scalping
The best time frames for scalping are typically 1 minute and 5 minutes, as these intervals allow for quick entries and exits, capitalizing on momentary fluctuations.
However, to obtain higher-quality signals and filter market noise, using higher time frames, such as 30 minutes and 1 hour, is effective for analyzing key levels.
The multi-timeframe analysis approach in scalping is a professional and efficient structure for scalpers.
When and for Whom is Fast Scalping Suitable?
Fast Scalping is a subcategory of scalping in which trades are opened and closed at very high speed usually within a few seconds to less than a minute.
Suitable times for fast scalping:
- High-liquidity sessions such as London and New York, featuring low spreads and sufficient volatility;
- Moments before and after economic news releases with sharp movements (requires professional risk management);
- Trending markets with strong momentum for capturing quick price moves.
This method is not suitable for all traders and is only appropriate for those with low latency and automated execution systems.
Traders suitable for fast scalping:
- Traders with quick decision-making ability and instant reaction time;
- Those equipped with fast infrastructure, including stable internet and a low-ping VPS;
- Individuals proficient in price action, liquidity analysis, and short-term risk management;
- Disciplined and risk-averse traders to prevent consecutive losses.
Best Time for Scalping in Forex and Crypto
The most suitable time periods for scalpers include the London session, New York session, kill zones, and moments during the release of important economic news.
During these periods, the market experiences the highest trading volume (liquidity) and sharp volatility, providing optimal conditions for fast short-term trades.
Tools Suitable for Scalping
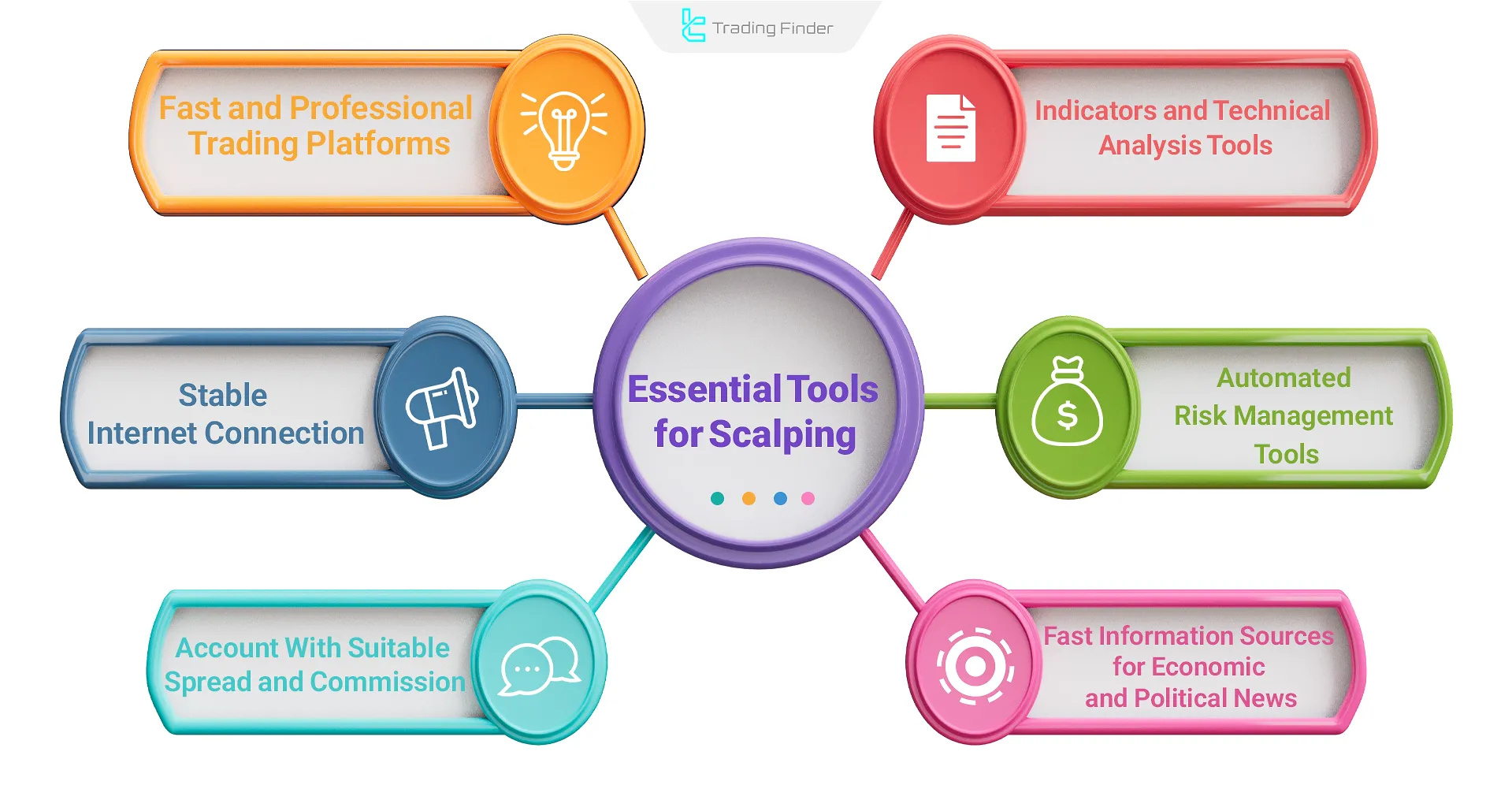
In scalping, quick decision-making is critical, and achieving profit depends on choosing the right analytical tools. Essential tools for scalping include:
- Fast And Professional Trading Platforms;
- Stable Internet Connection;
- Trading Account With Low Spread And Suitable Commission;
- Indicators And Technical Analysis Tools;
- Fast Information Sources For Economic And Political News;
- Automated Risk Management Tools (Expert Advisors And Others).
Capital Management in Scalping
Due to the high speed of trades, precise and conservative capital management is essential in scalping.
The smallest mistake in this process can lead to heavy losses or even the complete loss of the trading account.
Important principles of capital management inscalping:
- Fixed Risk Per Trade: Apply a maximum of 1% risk of capital per trade;
- Correct Position Sizing: Calculate position size considering the stop-loss distance and the allowable risk amount;
- Small Stop-Losses: To achieve quicker profits, the stop-loss should be short for scalp trades;
- Small Profit-To-Loss Ratio: Unlike swing trading, the profit-to-loss ratio in scalping is smaller (e.g. 1:1);
- Limiting The Number of Trades: Avoid over-trading and limit yourself to 3-5 trades per day.
Calculation of Trading Costs and Breakeven Point in Scalping
Calculating trading costs and determining the breakeven point in scalping is highly important, as the profit margin in this strategy is extremely limited, and even the smallest additional cost can reduce the final profit.
In scalping, all direct and indirect costs must be considered, including the following:
Spread: the difference between the bid and ask price, the most significant cost in short-term trades.
- Commission: a fixed fee in ECN or RAW accounts per lot;
- Swap: usually negligible in short-term scalping but important for overnight trades;
- Slippage: the difference between the order price and the actual execution price, more severe during news releases;
- Platform or VPS fee: the cost of using a dedicated server or professional trading tools.
Formula for Calculating the Cost of Each Trade
The general formula for calculating the cost of each trade in scalping is as follows:
Note: Swap is added as a cost or profit if a position is carried over to the next day. In scalping, it is usually zero.
Example of Calculating Trade Cost in Scalping
In the following example, the trade costs are such that before reaching profit, the price must move at least $17 in your favor to reach the breakeven point:
- Spread: 0.8 pip
- Value per pip: $10
- Commission: $7 (round trip)
- Slippage: 0.2 pip
Formula for Calculating the Breakeven Point
fter estimating the total trading costs, the breakeven point can be calculated using the following formula:
Example of Calculating Breakeven Point in Scalping
This means the price must move at least 1.7 pips in your favor to reach the breakeven point, after which you start generating net profit.
Introducing the Best Indicators for Scalping in the Market
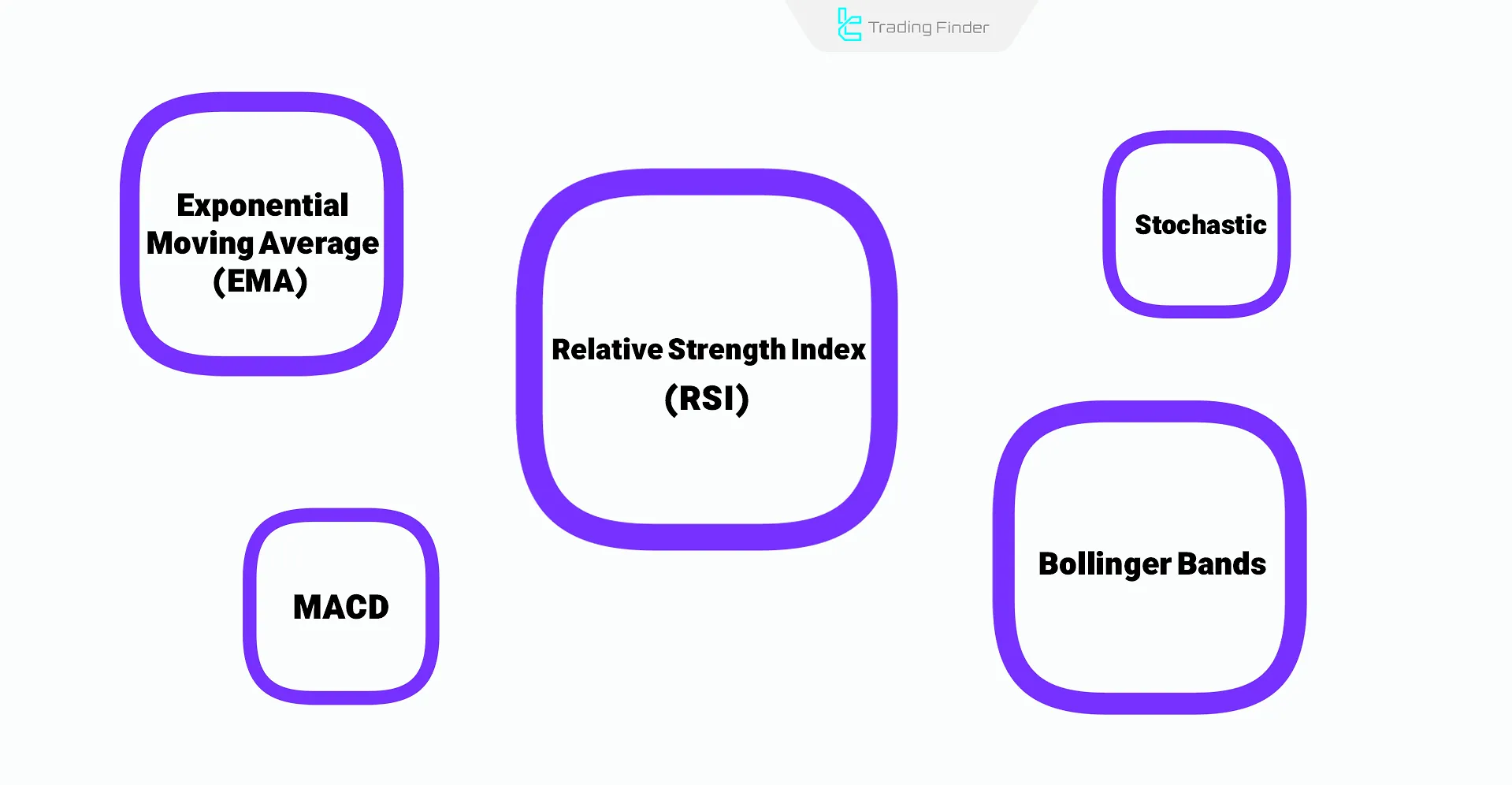
Scalpers use a variety of tools, such as indicators, to confirm trading signals. Below are some of the best indicators for scalping:
Indicator | Main Use | Scalping Tips |
Exponential Moving Average (EMA) | Identifying Trend Direction | Use 9 And 21-Period Settings For Entries in Small Pullbacks |
Relative Strength Index (RSI) | Identifying Overbought and Oversold Conditions | Use Shorter Periods (7 or 14) For Faster Reversal Signals |
Stochastic Oscillator | Reversal Signals | Look For Crosses In Overbought and Oversold Zones In 1-5 Minute Time Frames |
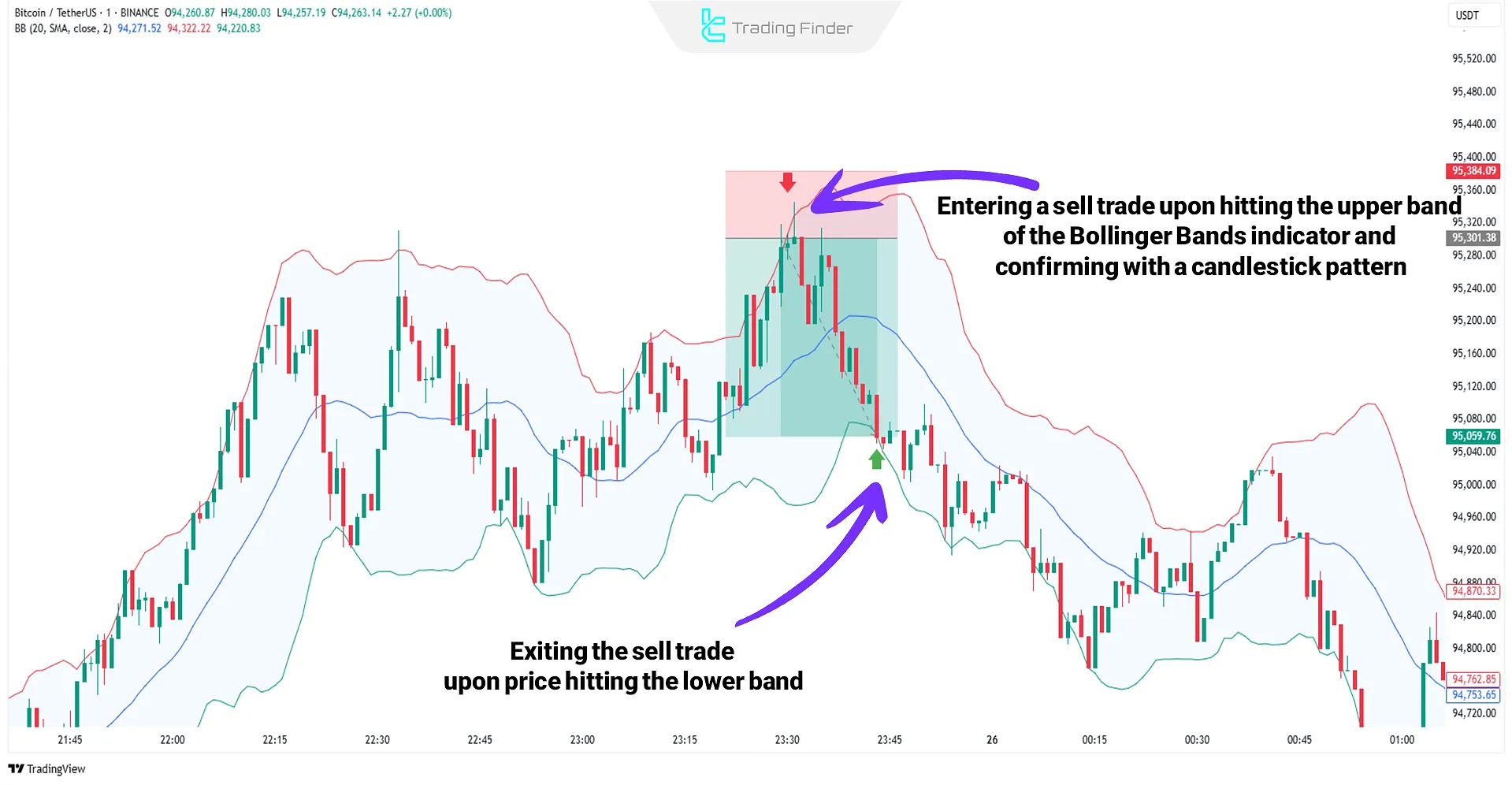
Bollinger Bands | Identifying Price Squeeze and Breakout | Trade Reversal or Breakout from Bands During Price Pressure Moments |
MACD | Crossovers to Start Trends | Use Faster Settings (5-13-1) For Quicker Reactions |
Personalizing and fine-tuning the indicators should be fully aligned with your trading strategy.
Before use in real market conditions, backtesting and optimizing parameters are essential to fully evaluate the indicator's performance under various market scenarios.
Scalping Futures Indicator
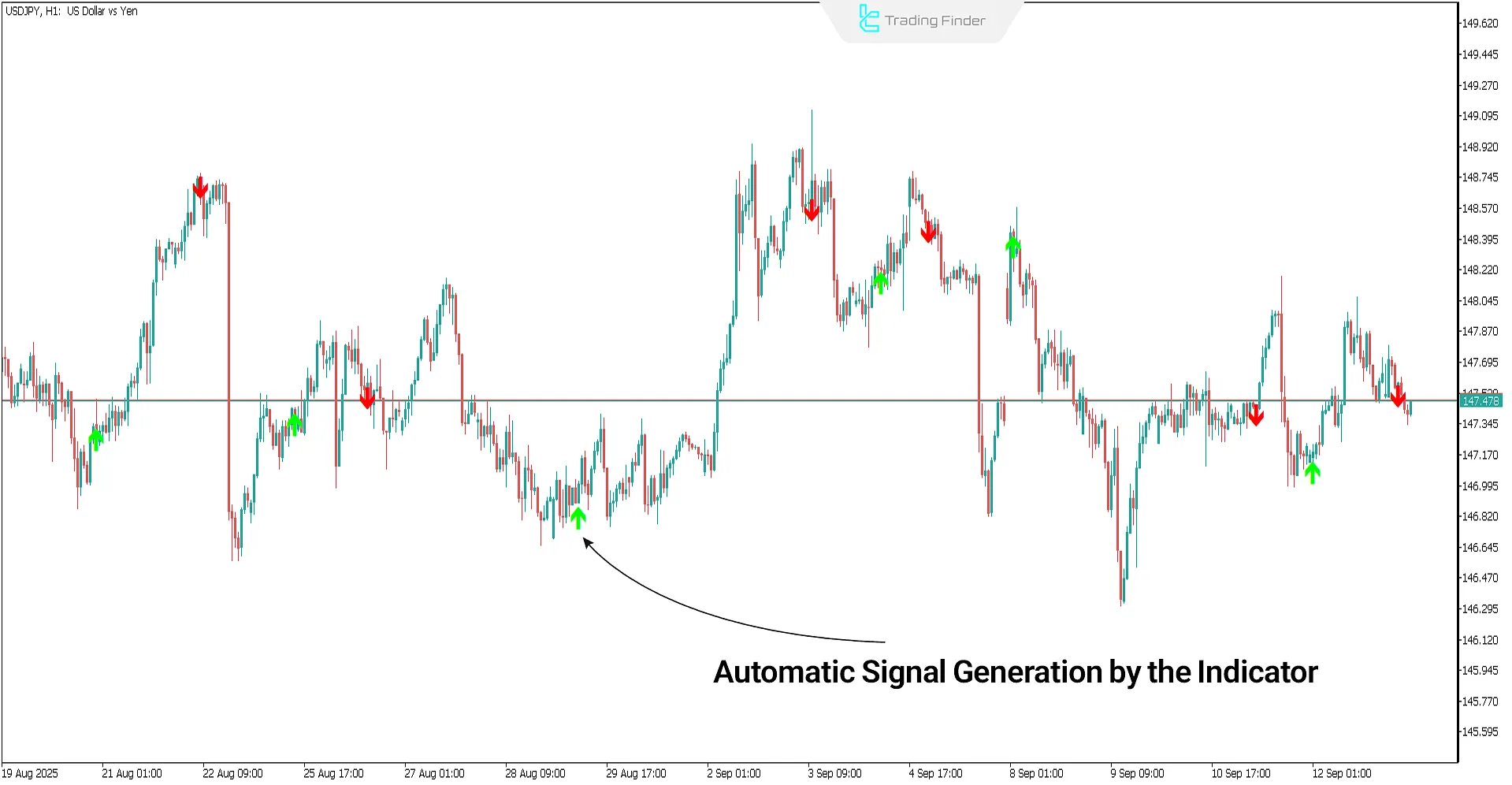
The Scalping Future indicator is one of the most popular and specialized tools for scalpers, designed to identify buying and selling pressure and determine the short-term direction of the market.
This indicator runs on MetaTrader 4 and 5 platforms and displays green and red arrows on the chart to visually indicate the strength of buyers and sellers.
In addition to the arrows, a textual BUY or SELL signal appears in the corner of the chart, providing additional confirmation for entries and exits.
- Download Scalping Future Indicator for MetaTrader 5
- Download Scalping Future Indicator for MetaTrader 4
This tool falls under the category of signal and forecasting indicators and is designed for beginner traders and those seeking quick decision-making in lower timeframes.
The Scalping Future indicator supports multiple timeframes and can be used across various markets, including Forex, cryptocurrencies, global stock indices, commodities, and company stocks.
It is optimized for short-term and intraday trading strategies. Instead of complex algorithms, it provides simple yet accurate signals:
- Green arrow: indicates buying pressure and a potential start of an upward trend;
- Red arrow: signals selling pressure and a possible beginning of a downward move or price correction;
- Textual BUY/SELL signal: displays a BUY or SELL label on the chart for visual confirmation.
In this tool, after a short correction, a green arrow is activated and a BUY signal is generated, indicating a buy entry opportunity. A red arrow appears when the price touches resistance and generates a SELL signal, marking a suitable selling point.
Multiple parameters can be adjusted in this indicator:
- FilterPeriod – defines the signal filtering period;
- SL_distance_pips – sets the stop-loss distance in pips;
- Activation of software alerts, email notifications, and push messages;
- Setting the time interval between messages.
These features allow the indicator to adapt to each scalper’s trading style.
Using the Scalping Future indicator on higher timeframes helps reduce false signals and increases accuracy in trading decisions.
Important Tips for Successful Scalping
For success and consistent profits in scalp trading, the following tips are essential:
- Focuson highly liquid symbols for fast and precise trade execution;
- Risk management and money management by defining clear stop-loss and profit targets are vital components of this trading style;
- Accepting small and consistent profits is the foundation of the scalping strategy, and it should not be confused with long-term profit goals;
- Scalping is designed for short-term, daily trades, and aiming for large profits with this method is not practical.
Common Mistakes in Scalping
Scalpers often encounter recurring mistakes that significantly reduce the efficiency of their trading strategy:
- Ignoring profitability and transaction costs like spread and commissions;
- Failing to commit to a trading strategy and making emotional trades;
- Hasty and impulsive decision-making;
- Not updating and optimizing the trading strategy;
- Failing to monitor trades and quick market changes;
- Misusing leverage and unnecessarily increasing risk;
- Not recording and evaluating trades through a trading journal or statement;
- Ignoring important news and events that create unexpected market volatility.

Conclusion
Short-term trades in the scalp trading strategy require speed, precision, and emotional control. This method is designed for experienced traders with high practical knowledge.
Successful implementation depends on precise capital management, disciplined trading, and adherence to market psychology principles
in this method, very low time frames, like 1 minute and 5 minutes offer the most effectiveness.
Scalpers typically use indicators like Bollinger Bands, moving averages, and others to confirm scalp trades. The main goal is to earn small consecutive profits from short-term fluctuations.
Not expecting large long-term profits is key to maintaining stability in this approach.













