Smart Money refers to capital controlled by professional investors, market makers, banks, and financial institutions.
Based on this principle, the Smart Money Concept (SMC) refers to the trading strategies of institutional investors and major financial entities.

The Smart Money (SMC) trading style identifies optimal entry and exit points through market structure analysis, liquidity dynamics, and institutional trading behaviors.
This methodology's primary goal is to align with Smart Money movements and take advantage of trading opportunities created by large institutions.
Five Key Smart Money (SMC) Terms
This section introduces five essential SMC terms that form the foundation of this trading strategy:
- Break of Market Structure (BMS/BOS): Key level breakout, signaling a trend change
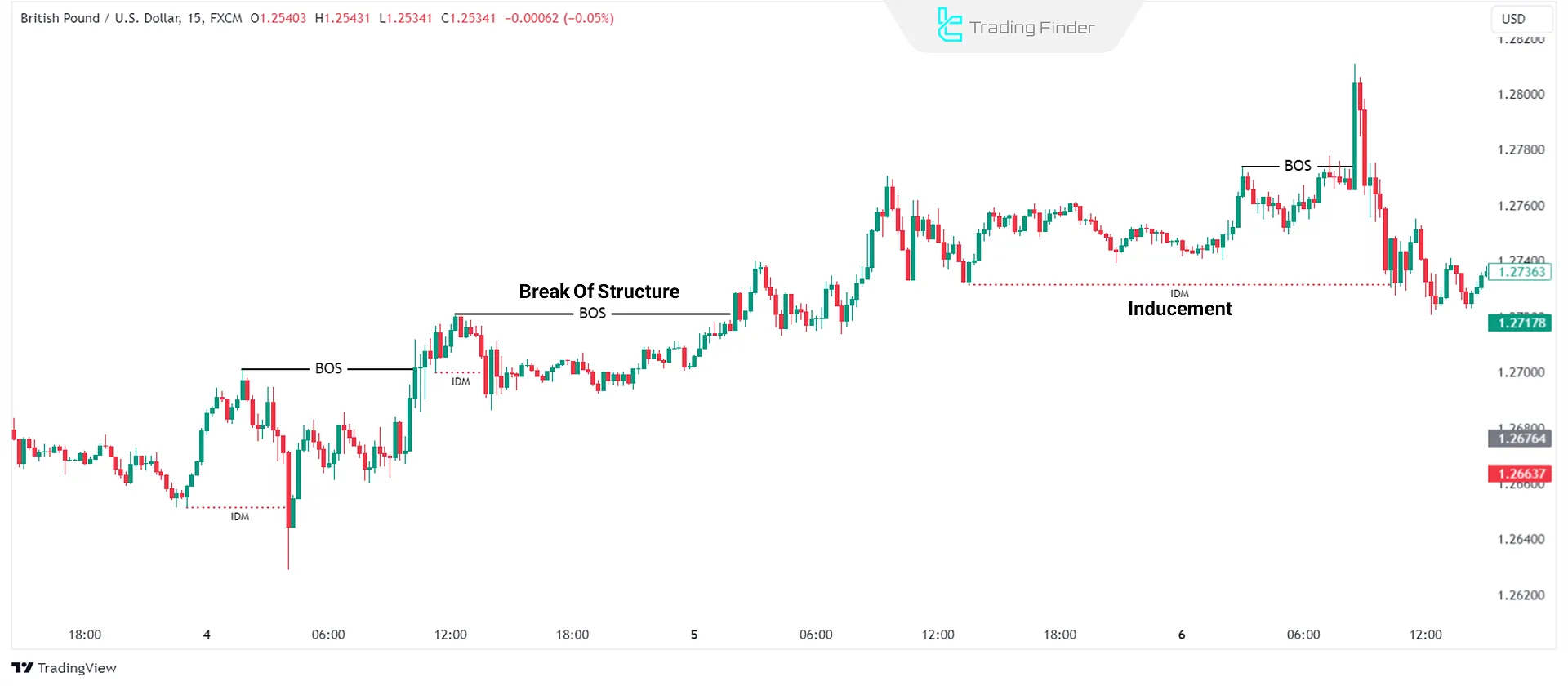
- Change of Character (CHoCH): Sudden market trend reversal, indicating weakness in the current trend and a possible shift in market direction
- Order Block (OB): Smart Money zone where institutional orders are placed for entry or exit
- Liquidity Pool (LQ): Zone containing many buy or sell orders, including stop-loss orders
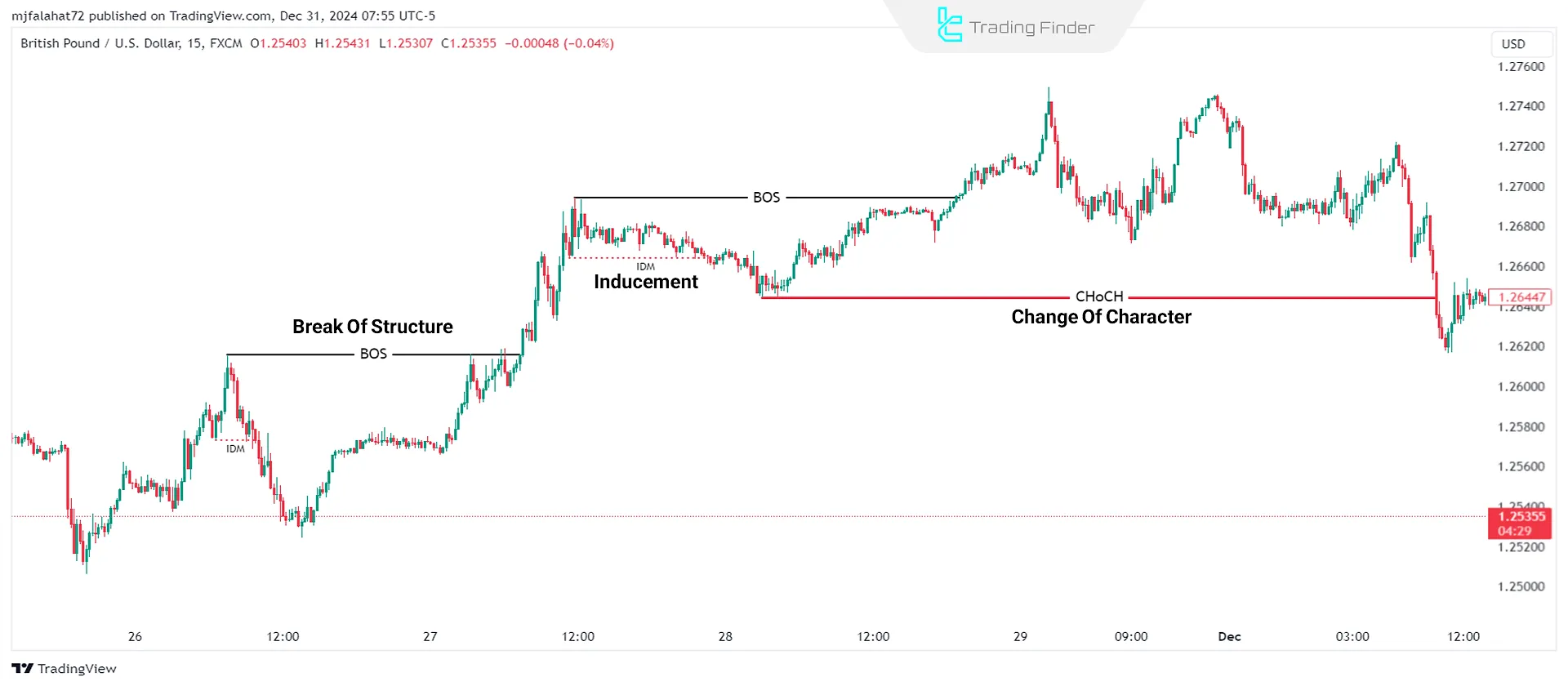
- Inducement (IDM): When Smart Money deliberately moves prices in a specific direction to trap retail traders into taking incorrect positions.
Market Structure Terminologies in Smart Money Concepts (SMC)
This section includes terminologies related to market structure, which help traders identify trends and key market shifts.
- Market Structure (MS): The overall market structure consists of trends, support and resistance levels, and price patterns
- Internal Market Structure (iMS): The minor structure of the market, including short-term trends and support/resistance levels on lower timeframes
- Fractal Market Structure: More detailed market structure displaying repetitive price patterns across different timeframes
- Break of Structure (BOS): Breakout of a key level, indicating a trend shift
- Break of Market Structure (BMS): Structural shift in the market, confirming a change in overall trend direction
- Internal Break of Structure (iBOS): Minor structure break, signaling a short-term market reversal
- Fractal Break of Structure (iiBOS): Fractally confirmed structure break, reflecting short-term market shifts
- Market Structure Shift (MSS): Directional shift in market trends, whether short-term or long-term
- Change of Character (CHoCH): Sudden market shift, signaling trend weakness and potential reversal
- Internal Change of Character (iCHoCH): Minor market structure shift, indicating weakness in the current trend and a potential short-term reversal
Key Price Zones & Blocks in Smart Money (SMC)
This section explains critical price zones and order blocks, which traders use to define high-probability trade areas.
- Supply Zone: Zone where Smart Money sell orders are concentrated, representing resistance in the market
- Demand Zone: Zone where Smart Money buy orders accumulate, acting as market support
- Order Block (OB): Smart Money zone where institutional orders are placed for entry or exit
- Bearish Order Block (OB-): Order blocks reinforcing a bearish move
- Bullish Order Block (OB+): Order blocks supporting a bullish move
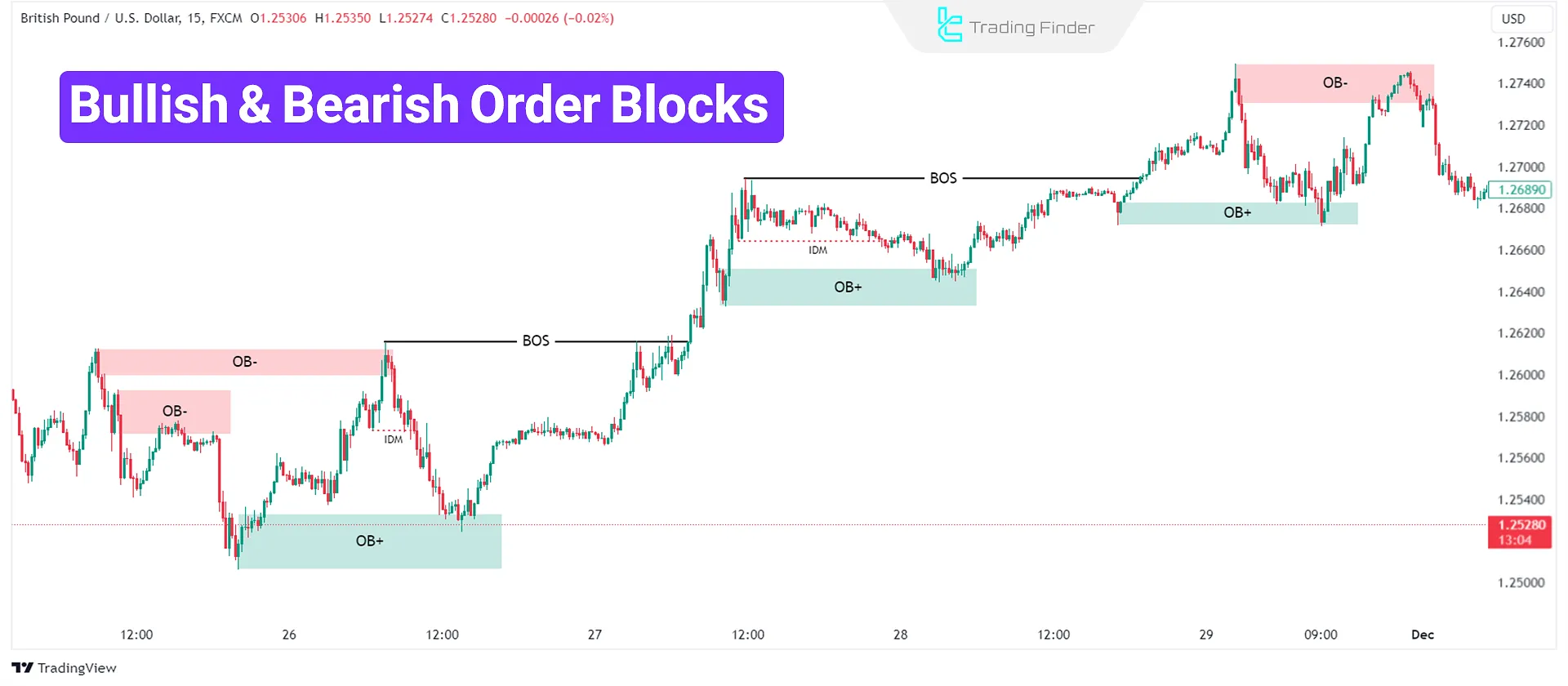
- Mitigation Block (MB): Block representing Smart Money actions to reduce risk and improve trade positioning
- Bullish Mitigation Block (MB+): Mitigation block functioning in an uptrend
- Bearish Mitigation Block (MB-): Mitigation block appearing in a downtrend
- Breaker Block (BB): Former order block, now acting as support or resistance
- Bullish Breaker Block (BRK+): Breaker block supporting a bullish move
- Bearish Breaker Block (BRK-): Breaker block confirming bearish momentum
- Rejection Block (RB): Block where price aggressively rejects a level, often leading to trend reversals
- Vacuum Block (VB): Zone with no executed trades, where price moves rapidly
- Reclaimed Order Block (ROB): Order block that price revisits and reactivates
- Propulsion Block (PB): Block responsible for strong and sustained price movements in one direction
- Mean Threshold (MT): Midpoint of an order block, often used as a retracement level
- Return to Order Block (RTO): When the price returns to an order block
- Return to Breaker (RTB): When the price revisits a breaker block
- Point of Interest (POI): Key price level where traders anticipate significant market reactions
- Decisional Zone: Zone where Smart Money makes key trade decisions, often leading to major moves
- Extreme Zone: Last significant area where Smart Money executes positions, representing the final entry or exit point
Liquidity and Imbalance Terminologies in Smart Money (SMC)
This section includes terms related to liquidity and price imbalances, which help traders identify areas with high order concentration and trading opportunities.
- Fair Value Gap (FVG): Three-candle price gap where the price has not yet returned
- Inversion Fair Value Gap (IFVG): Rapid price movement zone that has not been revisited, moving in the opposite direction
- Imbalance (IMB): Zone with a mismatch between buyers and sellers, often acting as a potential reversal area
- Inefficiencies: Market inefficiency zone caused by an imbalance between supply and demand, often serving as a reversal area
- Breakaway Gap (BAG): Gap forming at a key breakout level, indicating a structural market change
- Premium & Discount Array (PD Array): Price framework based on Fibonacci levels, classifying prices into Premium (above 50%) and Discount (below 50%) zones to highlight price imbalances
- Equilibrium (EQ): Midpoint of a PD Array, where the price balances between buying and selling pressures
- Liquidity (LQ): Ease with which an asset or security can be converted into cash without significantly affecting its price
- Trend Line Liquidity: Liquidity present along a trendline, often consisting of stop and pending orders
- Liquidity Void (LV): Price chart area with no executed trades, forming a vacuum zone
- Buy-Side Liquidity (BSL): Buy orders present in the market
- Sell-Side Liquidity (SSL): Sell orders present in the market
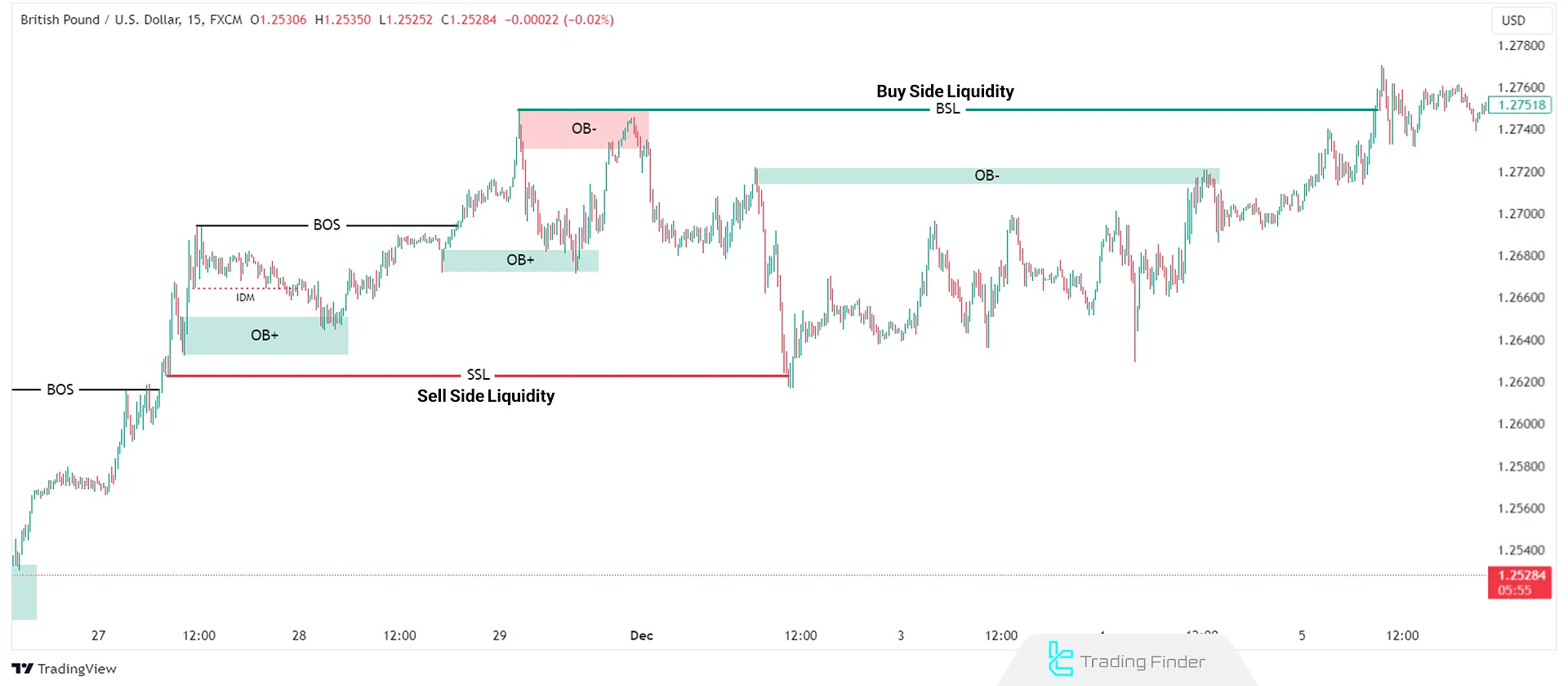
- External Range Liquidity (ERL): Liquidity present outside the current price range
- Internal Range Liquidity (IRL): Liquidity contained within the current price range
- Liquidity Pool (LP): Zone with a large concentration of buy or sell orders, including stop-loss clusters
- Draw on Liquidity (DOL): Price movement toward high-liquidity zones, where stop orders are triggered
- First Point of Liquidity (FPOL): Initial liquidity point, often serving as a key entry or exit level.
Price Level Terminologies in Smart Money (SMC)
This section includes key price level terms, helping traders identify crucial support and resistance areas.
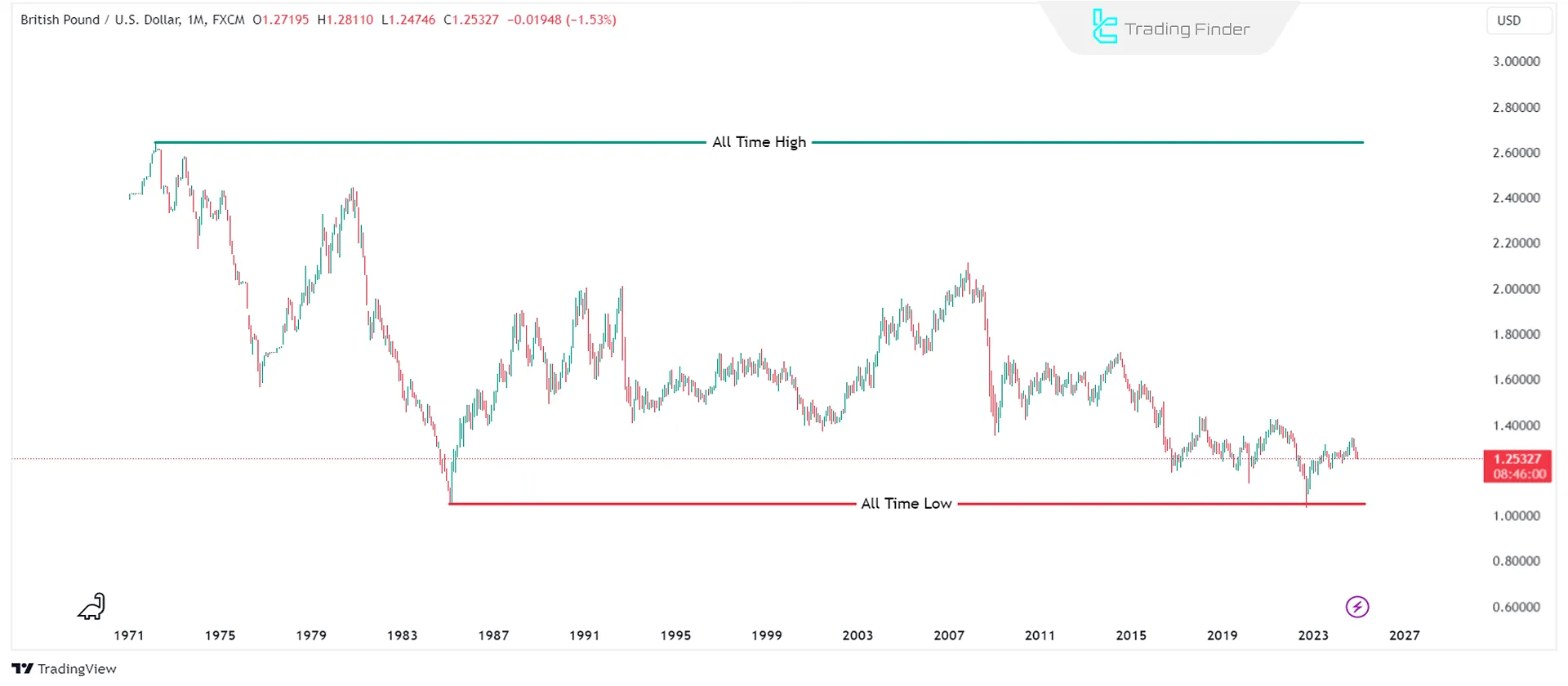
- All-Time High (ATH): Asset's highest price ever recorded
- All-Time Low (ATL): Lowest price ever recorded for an asset
- Higher Low (HL): Newly formed higher low in an uptrend
- Higher High (HH): Newly formed higher high in an uptrend
- Lower Low (LL): Newly formed lower low in a downtrend
- Lower High (LH): Newly formed lower high in a downtrend
- Swing High (SH): Highest price level in a given timeframe, acting as resistance
- Swing Low (SL): Lowest price level in a given timeframe, acting as support
- Equal Highs (EQH): Price formation where two or more highs align at the same level, indicating liquidity buildup
- Equal Lows (EQL): Price formation where two or more lows align at the same level, representing liquidity accumulation
- Support & Resistance (S/R): Key price levels where the price tends to reverse or break through
- Key Support & Resistance Levels: Major price levels that prevent or enable further price movement
Timeframe and Session Terminologies in Smart Money (SMC)
This section covers terms related to different timeframes and trading sessions, improving market timing and trade execution.
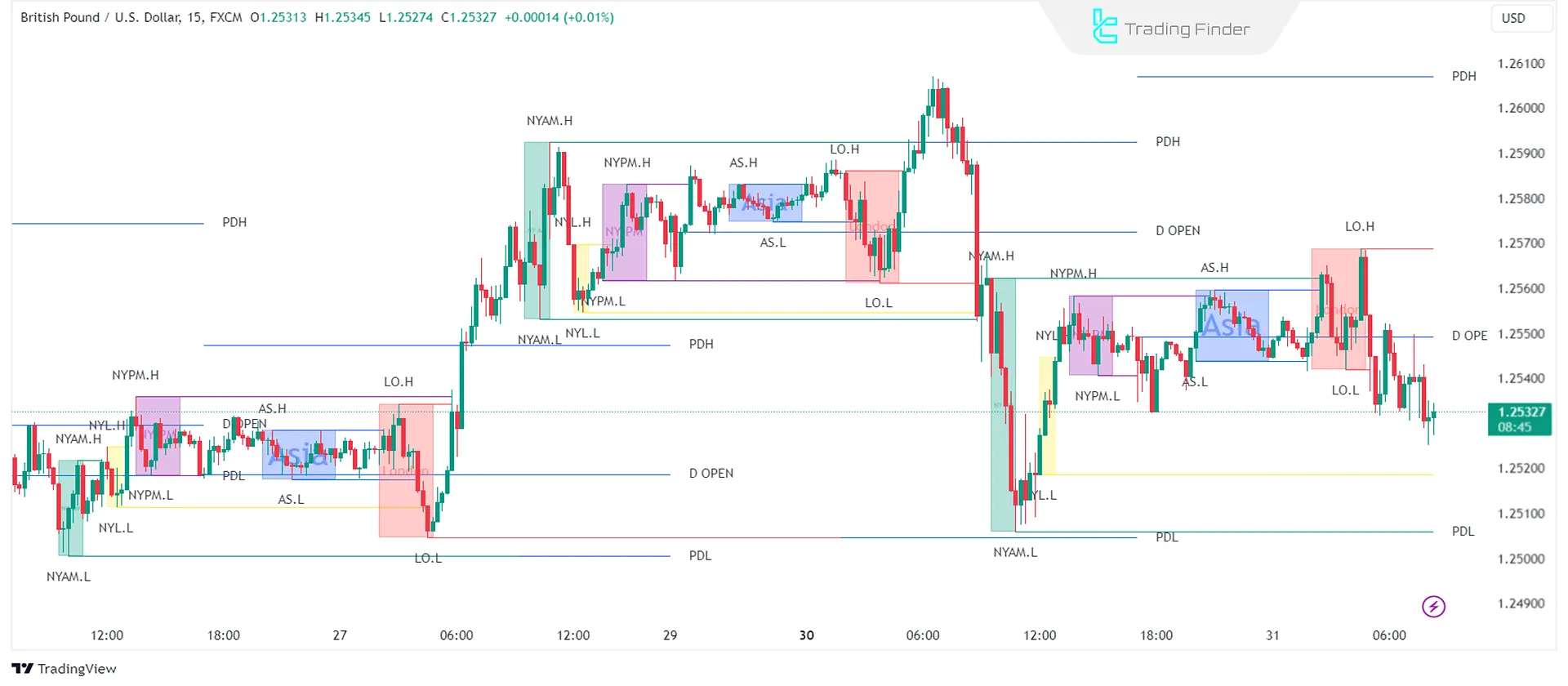
- Higher Time Frame (HTF): Longer-term timeframe used for macro market analysis
- Lower Time Frame (LTF): Short-term timeframe for precise trade entries and exits
- High of Day (HOD): Highest price reached during trading
- Low of Day (LOD): Lowest price reached during trading
- Previous Day Low (PDL): Lowest price recorded on the previous trading day
- Previous Day High (PDH): Highest price recorded on the previous trading day
- Previous Week High (PWH): Highest price recorded during the past week
- Previous Week Low (PWL): Lowest price recorded during the past week
- Previous Month High (PMH): Highest price recorded in the past month
- Previous Month Low (PML): Lowest price recorded in the past month
SMC Trading Models & Strategies
This section covers trading models and strategies in Smart Money (SMC), which traders use to refine their entry, exit, and market execution techniques.
- Accumulation, Manipulation, Distribution (AMD): Three-phase model Smart Money uses to control price movements
- Buy-Side Imbalance Sell-Side Inefficiency (BISI): Market condition where buy orders dominate sell orders, creating an imbalance
- Sell-Side Imbalance Buy-Side Inefficiency (SIBI): Market condition where sell orders exceed buy orders, leading to inefficiency
- Balanced Price Range (BPR): Zone where the price reaches equilibrium after an extended move
- Major Inducement: Significant liquidity inducement occurring within the main market structure
- Minor Inducement: Smaller liquidity inducement within internal market structures
- Institutional Order Flow (IOF): Large financial institutions executing major orders that influence liquidity
- Smart Money Technique (SMT): Methods used by Smart Money to manipulate price and market flow
- Smart Money Trap (SMT): Tactics used by Smart Money to deceive SMC traders into taking incorrect positions
- Smart Money Divergence (SMT Divergence - SMT Div): Divergence pattern created by Smart Money indicating price manipulation
Other General SMC Terminologies
This section includes common Smart Money terms and covers technical and fundamental analysis, risk management, and trade execution.
- Technical Analysis (TA): Study of price movements, chart patterns, and indicators to forecast price action
- Fundamental Analysis (FA): Examination of economic factors, financial reports, and macroeconomic data to assess an asset's value
- Price Action (PA): Market movement analysis based on price structure without using indicators
- Stop-Loss (SL): Predetermined price level where a trade is automatically exited to limit losses
- Take Profit (TP): Target price level where a trade is exited to secure profits
- Breakeven (BE): Price level where gains and losses in a trade are equal, ensuring no net profit or loss
- Risk-to-Reward Ratio (RR): Comparison of potential loss (risk) to expected gain (reward) in a trade
- Stop Hunt (SH): Market move designed to trigger stop-loss orders, often used by institutions to accumulate liquidity
- Drawdown (DD): Percentage decrease in account balance due to consecutive losses
- Dealing Range (DR): Specific price range where market movement is confined
- Average Daily Range (ADR): Asset's average price movement range in a single trading day
- Average True Range (ATR): Measure of market volatility, accounting for price gaps and extreme movements
- Commitment of Traders Report (COT): Report detailing institutional trading positions, offering insights into market sentiment
Conclusion
The Smart Money (SMC) trading methodology refers to the strategies used by institutional investors and large financial institutions. SMC helps traders identify institutional liquidity movements and align their trades accordingly.
Key SMC concepts include Break of Structure (BOS), Order Blocks (OB), Liquidity (LQ), Market Structure Shifts (MSS), and Fair Value Gaps (FVG).













