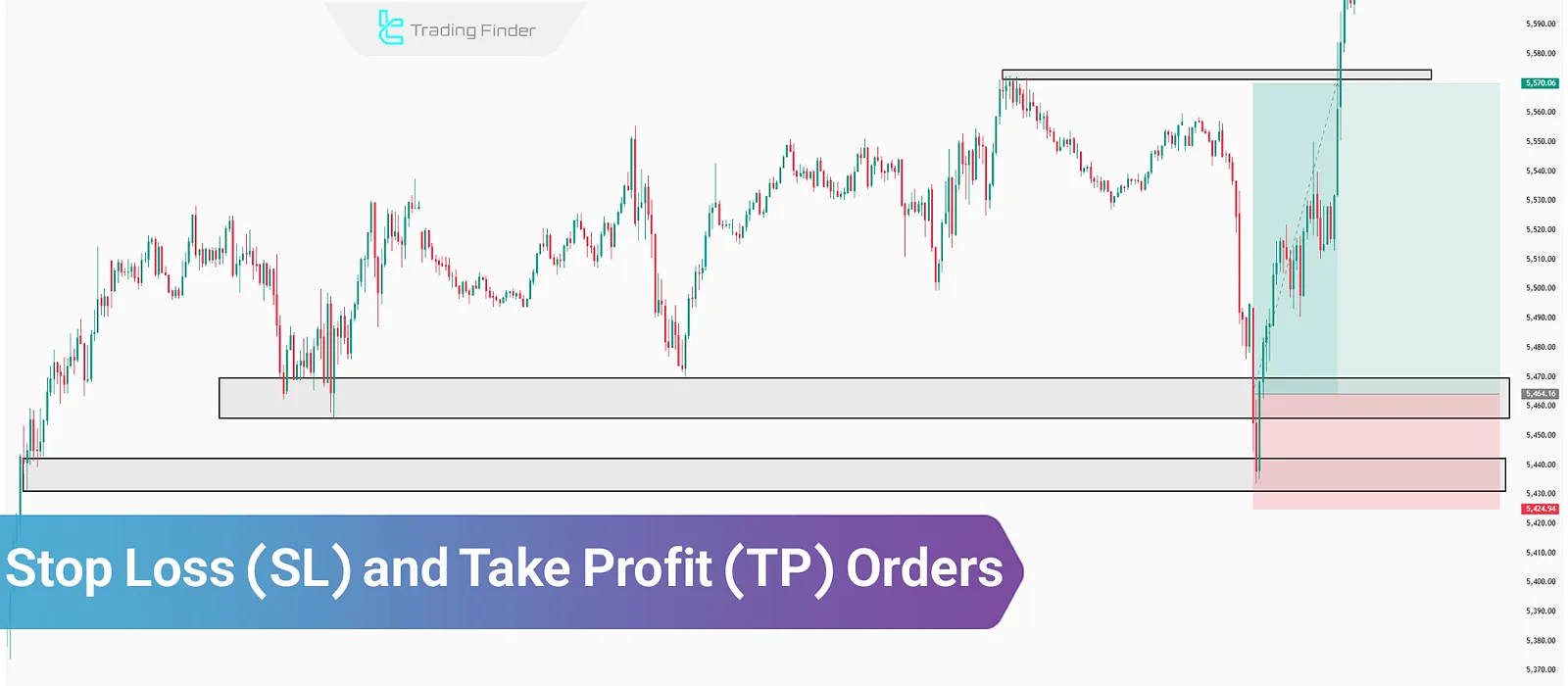
Placing stop loss and take profit orders on the trading platform helps determine the right time to exit a trade under different market conditions.
When a trade is in profit, a take profit (TP) order is used to exit the market at a favorablelevel. Conversely, when the market moves against the trade, a stop loss (SL) order is triggered to prevent further losses.
There are various methods for calculatingSL and TP levels depending on the trading strategy.
What Is Stop Loss?
Stop loss is a risk management tool that closes a trade when the price moves against the initialanalysis, preventing further loss.
In the Stop-Loss Order educational article on the Investopedia website, this concept is fully explained.
Types of Stop Loss
Depending on the trading strategy technical, time-based, fundamental, etc. various methods are used to set stop loss orders, each suited to specific market conditions and price action behavior.

Trailing Stop Loss
In a trailing stop order, if the price moves in the anticipated profitable direction, the stop loss moves along with the price to lock in gains. However, if the price reverses, the stop loss remains fixed to close the trade at a defined level.
This type of stop loss allows trade management with out constant monitoring.
Fixed Stop Loss
In this strategy, a set percentage of capital is placed at risk for each trade. Before entering a position, the position size is calculated based on the predefined risk and the price level at which that amount would be lost is determined. A fixed stop loss is then placed at that level.
This helps ensure that no trade results in a loss greater than the predefined risk limit.
Time-Based Stop Loss
This method uses time analysis to determine optimal trading hours. Some trades must be closed before market peak hours, while others are only valid during high-liquidity sessions.
The time-based stop loss closes a trade at a specific hour or date regardless of price.of
What Is Take Profit?
Take profit (TP) order is triggered when the market moves in the anticipated direction. It automatically closes the trade at a favorable level and adds the realized profit to the trading account balance.
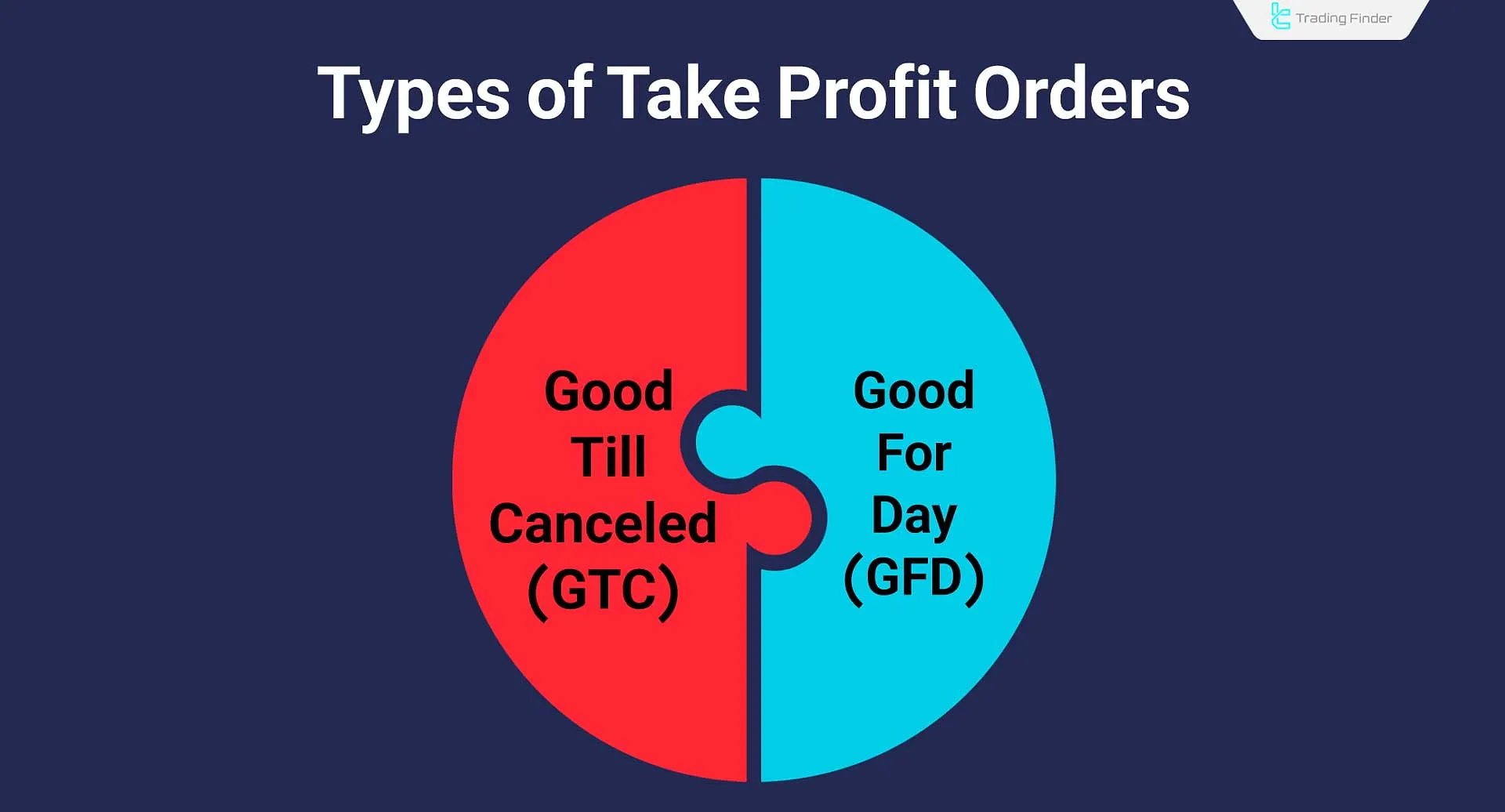
Types of Take Profit
Depending on the analysis and trade duration, take profit orders fall into two categories:
- Good for Day (GFD): If the target price is not reached by the end of the trading day, the position is closed automatically;
- Good till Canceled (GTC): The order remains active until the price target is reached or the trader cancels it manually.
Types of Take Profit and Stop Loss in Order Types (Trailing Stop, Stop Limit, and Regular Stop Loss)
In most trading platforms such as MT4 and cTrader, various tools exist for setting automatic take profit and stop loss levels.
A stop loss order is an immediate stop instruction that, once triggered, closes the trade at the nearest market price. This type of order is one of the main foundations in stop loss forex trade management and helps prevent major losses.
A Stop Limit order provides greater flexibility and is executed when the price crosses a specified level, but only within a user-defined range.
Finally, a trailing stop moves automatically with the price trend, helping traders in both bullish and bearish markets to secure maximum profits without exiting prematurely. This process, combined with the concept of tp in trading, enables smarter decision-making.
what is SL and TP Advantages and Disadvantages
Using stop loss and take profit orders enables effective risk and capital management in trading. However, these orders can also cap the maximum potential profit of a trade.
The table below outlines the pros and cons of using SL and TP orders:
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Enhanced risk and capital management | Limits the profit potential of winning trades |
Facilitates long-term performance tracking | Prone to stop hunting |
Protects against large losses | May be triggered at inaccurate prices during high volatility |
Defines risk-to-reward ratios | SL may trigger even if price doesn’t reach the specified level precisely |
How to Calculate Stop Loss and Take Profit
The calculation of stop loss and take profit levels depends on the trading strategy and type of analysis used such as fundamental or technical.
On The Moving Average YouTube channel, the method of setting take profit and stop loss levels is explained in a detailed video:
Calculation Based on Fundamental Analysis
In fundamental analysis, various factors of an asset are evaluated to estimate its intrinsic value. If the current price deviates significantly from this intrinsic value, a trade may be initiated. The SL and TP levels are then determined based on this calculated fair value.
Calculation Based on Technical Analysis
In technical analysis, the market is examined through liquidity behavior. By identifyingsupport and resistance levels, traders can set appropriate stop loss and take profit orders aligned with market structure.
Training on Setting Take Profit and Stop Loss Based on Support and Resistance Levels
Support and resistance levels are among the most fundamental concepts in technical analysis and play a crucial role in choosing exit points for trades. In buy positions, the stop loss is usually placed slightly below the support level to prevent early activation.
In sell positions, the stop loss should ideally be set slightly above the main resistance.
Conversely, the take profit can be placed at the next resistance level or within the supply zone. This method, when combined with price action, provides high accuracy for logical exits and simplifies the understanding of take profit stop loss.
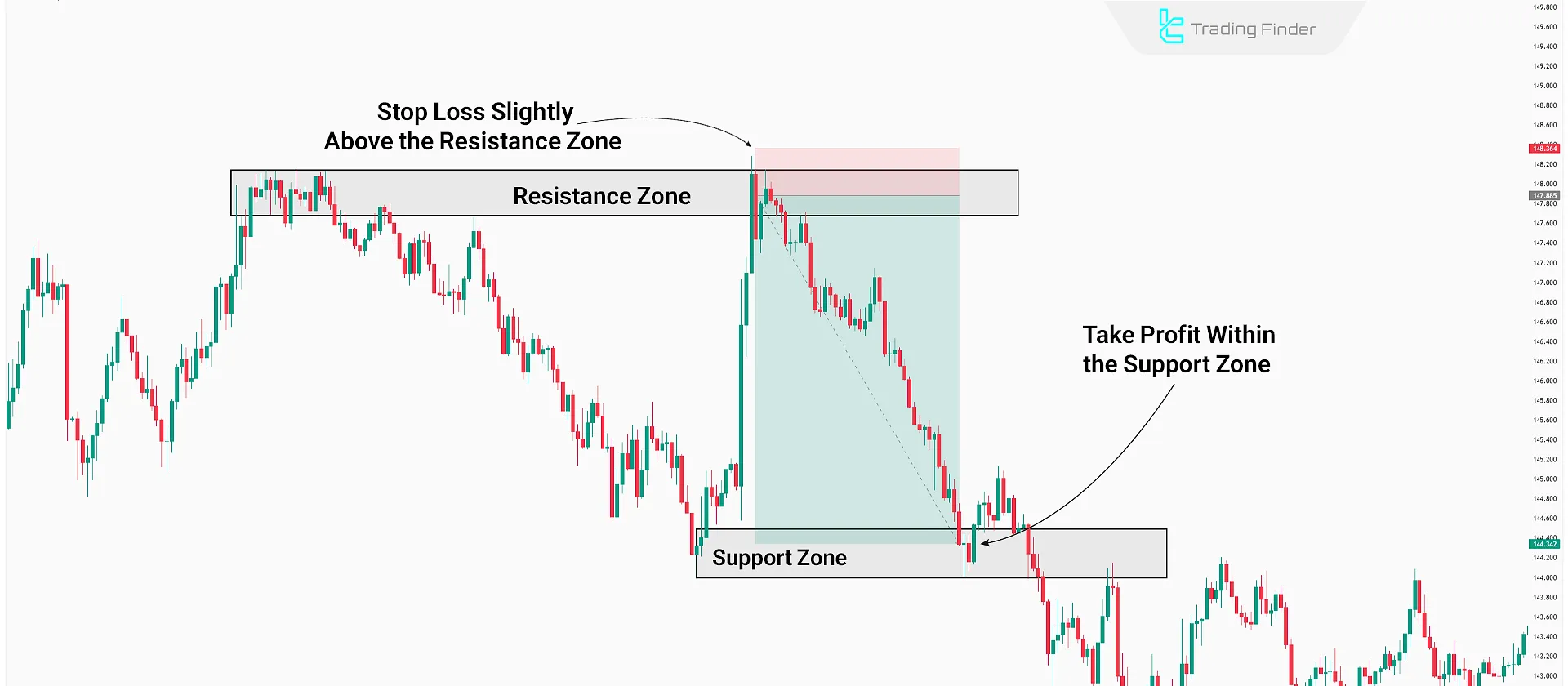
Practical Examples of Setting Stop Loss and Take Profit
In the example below, price moves toward a resistance zone after forming a range. A candlestick pattern confirms a reversal into a downtrend.
In this setup, the stop loss is placed above the resistance zone and the wick of the last bullish candle. The take profit target is set inside the first valid support zone.
what is SL and TP Importance and Application
The primary function of stop loss and take profit is to support risk and capital management. By setting SL and TP levels, the risk-to-reward ratio of each trade is defined, which helps maintain a consistently growing account over time.
Capital Management
Stop loss and take profit orders determine how much of the total capital is at risk in each trade and how much will be added to the account if the trade is profitable.
Managing these amounts allows traders to evaluate their long-term performance effectively.
Risk Management
Since financial markets are inherently uncertain, it’s essential to manage the risk exposure of each trade using a stop loss.
Without risk control, long-term performance tracking becomes unreliable.
Defining Risk-to-Reward Ratio
The risk-to-reward ratio is calculated using the following formula:

Based on the win rate of different trading styles, it's advisable to avoid trades with a risk-to-reward ratio below 1.1.
Set and Forget Trading System
TheSet and Forget strategy involves entering a trade after market analysis and then stepping away from the market without further monitoring.
In this system, both stop loss and take profit orders are defined at the time of entry. The trade remains active until the price reaches either SL or TP whichever comes first.
There is no active trade management during the position, making it a popular method among traders who prefer low-intervention strategies.
The Relationship Between Trade Win Rate and Risk-to-Reward Ratio
A proper understanding of the relationship between win rate and risk-to-reward ratio is highly important. For example, if your trading system has a success rate of only 40 percent, the risk-to-reward ratio must be at least 1 to 2 to remain profitable in the long run.
Professional traders never enter a position with a ratio lower than 1 to 1.1, as the probability of long-term loss becomes very high.
In markets such as Forex, the concept of stop loss and take profit forex is one of the key components in profitability analysis, and without it, calculating real returns is impossible.
Combining Stop Loss and Take Profit with Other Technical Analysis Tools
To refine the placement of stop loss and take profit, traders can use various technical indicators. These tools help identify SL and TP levels based on liquidity behavior and historical price movement averages.
Using Moving Averages to Set SL and TP
A moving average line acts as dynamic support or resistance, depending on the price’s position relative to it.
When price moves below the moving average, the stop loss is typically set above it. When price is above, the SL is set below the moving average line.
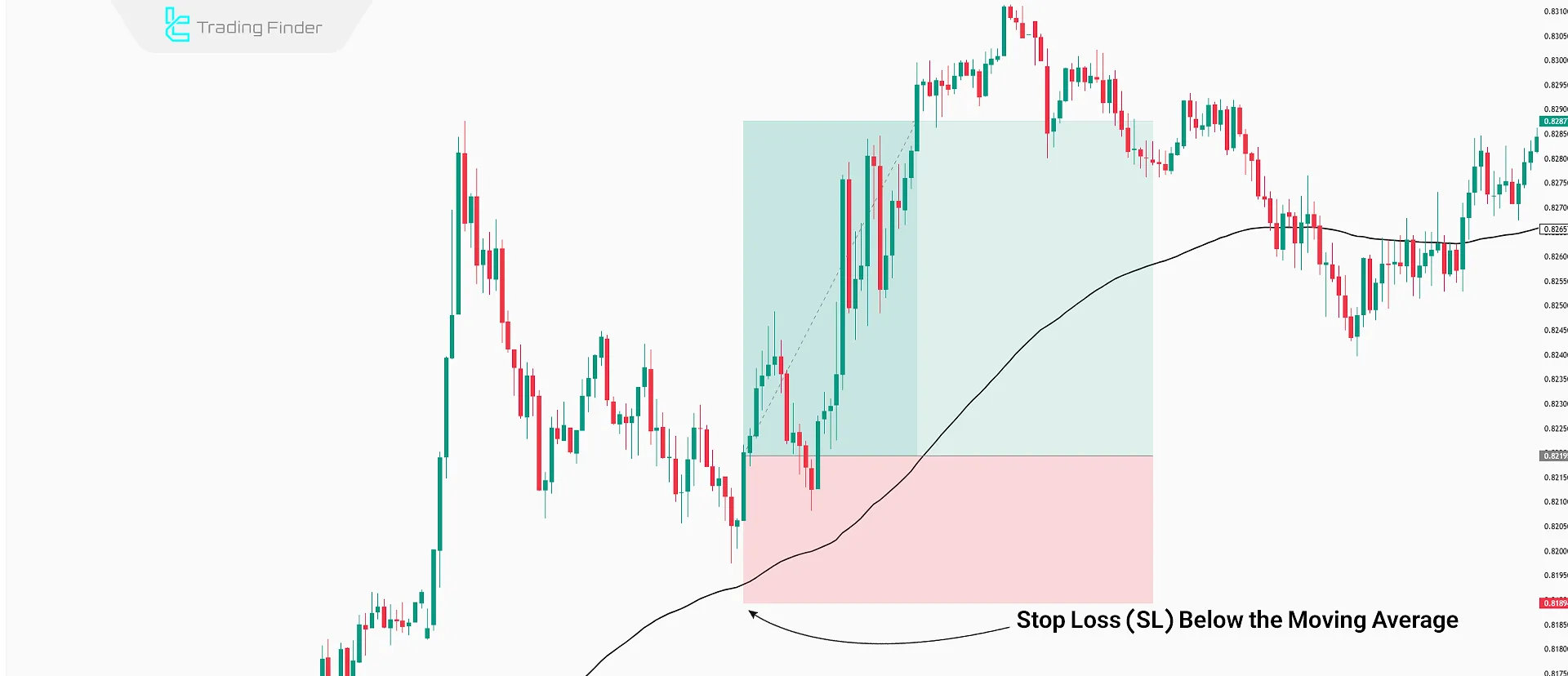
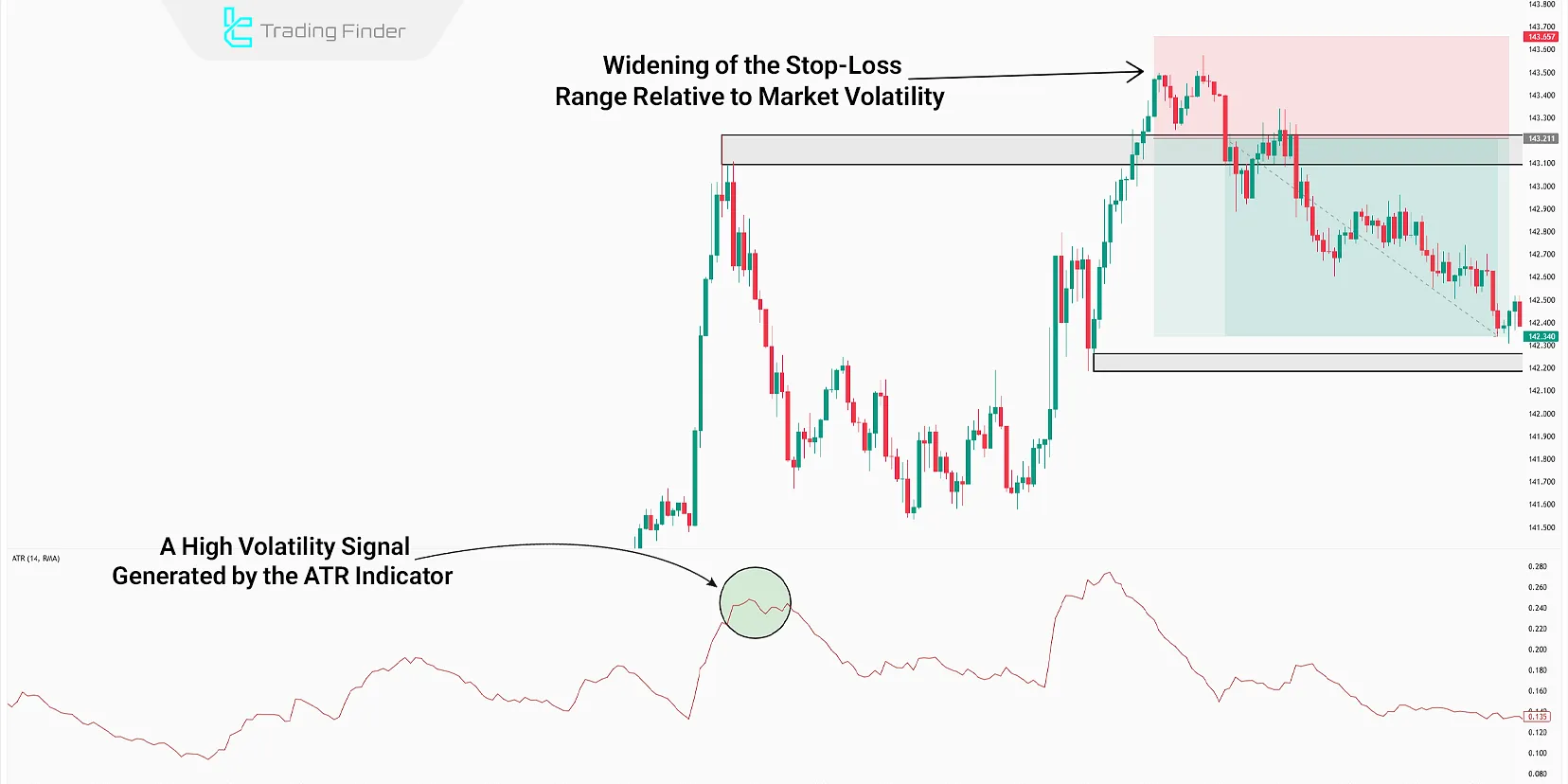
Using the ATR Indicator to Set SL and TP
The Average True Range (ATR) indicator measures the market’s current volatility.
If the ATR shows high volatility, it indicates longer price swings. As a result, the distance between the entry point and SL/TP should be wider than usual.
Common Mistakes in Setting Stop Loss and Take Profit
Accurately placing stop loss and take profit orders requires experience with specific trading styles, deep understanding of market structure, and detailed observation of liquidity behavior.
Some common mistakes that lead to premature stop-outs even with correct analysis include:
- Using a single time frame for analysis
- Failing to assess liquidity direction
- Entering trades emotionally, without final confirmation
- Placing SL too close to the entry point
- Positioning SL within key zones such as support or resistance
Comparison of Take Profit and Stop Loss Determination Methods
Ultimately, traders can choose one of the following methods to set take profit and stop loss levels depending on their market type and trading style. The table below compares the advantages and limitations of each method:
Determination Method | Accuracy and Reliability | Suitable Market | Main Advantage | Weakness |
Support and Resistance Levels | High | Forex, Stocks | Simple and fast | Requires precise level identification |
ATR Indicator | High | All Markets | Scientific and numerical | Delayed response in volatile markets |
Moving Average | Medium | Trending Markets | Logical exit adjustment | Slow reaction to changes |
Price Action | High | All Markets | Alignment with market structure | Requires high experience |
Fixed Pip Method | Low | Calm Markets | Ease of use | Low accuracy in high volatility |
In many Forex strategies, a dedicated stop loss tool is used to minimize human error and automatically record entry and exit points.
Take Profit & Stop Loss Calculator Indicator
The Take Profit & Stop Loss Calculator indicator is one of the most practical trading tools on the MetaTrader 4 platform, allowing traders to calculate the exact potential profit or loss of each position before entering a trade.
This indicator appears in an interactive panel and displays key information such as the risk-to-reward ratio (R/R), trade volume in lots, and the time remaining until the next bar closes. It is ideal for those who want to calculate stop loss and take profit accurately.
Within the MetaTrader 4 environment, users can manually set or input R/R values for both Buy and Sell positions to define their take profit and stop loss levels.
This feature makes risk control and capital management simpler and more precise under any market condition. On charts of currency pairs like USD/CAD or assets like ETH, the lines for “Open Position”, “TP”, and “SL” are displayed in different colors, making it easier to identify active positions.
In practice, using take profit and stop loss in these charts helps traders gain better visibility over open trades.
In many professional strategies, traders use take profit orders as an automatic exit method to close trades at optimal times. These orders, combined with stop loss and support-resistance levels, complete the capital management structure.
Across various trading environments, particularly in the Forex market, tools are designed to calculate sl and tp in forex, helping traders precisely adjust their risk-to-reward ratios when opening new trades. This capability also applies to other markets and enhances analytical accuracy.
When a strategy is based on market volatility, using sl and tp in trading can simplify decision-making. Combining these concepts with trade volume and technical analysis helps traders control emotions during sharp price movements.
In modern training materials, many analysts use tp and sl in trading as performance measurement tools for trading systems. By evaluating entry and exit accuracy through these ratios, one can assess the quality of a strategy over time.
With advanced indicators, users can calculate stop loss numerically and determine the exact exit point without relying on guesswork or extensive experience. This functionality forms the foundation of effective risk management.
In the Forex market, many professional traders analyze profit zones using the forex take profit concept to identify potential reversal points and capture maximum profit from each trade. This method is typically combined with volume data and confirmation indicators.
Ultimately, the concept of trading stop loss and take profit acts as a key framework across all trading strategies. When implemented correctly, it significantly reduces trading risk and enhances long-term profitability.
This indicator is compatible with various trading styles including scalping, swing, and intraday trading, and performs efficiently across all financial markets such as Forex, cryptocurrency, stocks, commodities, and indices.
Features like quick line removal, light/dark theme switching, and position size adjustment increase analytical and execution efficiency.
By using this indicator, traders can fine-tune their stop loss and take profit levels relative to entry points, achieving a better balance between risk and return.
For beginner MetaTrader 4 users, this tool serves as a practical risk management tutorial and, combined with complementary indicators such as the Position Size Calculator and Live Spread, helps optimize trading strategies.
Overall, the Take Profit & Stop Loss Calculator is a precise and intelligent tool for informed decision-making and emotion control in financial markets, elevating trade management to a professional level.
- Download Take Profit & Stop Loss Calculator Indicator for MetaTrader 4
- Download Take Profit & Stop Loss Calculator Indicator for MetaTrader 5
Conclusion
A stop loss order is placed at a specific price level to close a losing trade; If the market moves against the analysis, thereby limiting further losses.
A take profit order, on the other hand, is executed at a predefined level when the market moves in favor of the trade, securing the profit into the trading account.
Using stop loss and take profit orders enables traders to evaluate the long-term performance of their trading strategies.
Different types of SL and TP orders such as trailing stops and time-based stops are essential tools for managing risk and capital. By defining SL and TP for each trade, traders can calculate the risk-to-reward ratio, allowing for optimized trading decisions.













