Forex trading interest in India has expanded alongside rising disposable income and a growing retail trading community, but participation remains constrained by a complex regulatory environment.
Domestic financial authorities such as SEBI and RBI impose strict limits on the Forex products that locally regulated institutions can offer, which narrows access to global currency markets.
 | ActivTrades | |||
 | IC Markets | |||
 | TMGM | |||
| 4 |  | FXCM | ||
| 5 |  | Go Markets | ||
| 6 |  | FxPro | ||
| 7 |  | FBS | ||
| 8 |  | JustMarkets | ||
| 9 |  | Tickmill | ||
| 10 |  | Moneta Markets |
Trustpilot Score of Forex Brokers in India
The table below provides the Trustpilot rating of the Forex brokers in India.
Broker | Trustpilot Rating | Number of Reviews |
| IC Markets | 4.8/5 ⭐ | +49000 |
| FXCM | 4.6/5 ⭐ | +800 |
Go Markets | 4.5/5 ⭐ | +700 |
| FBS | 4.3/5 ⭐ | +7500 |
Moneta Markets | 4.2/5 ⭐ | +400 |
TMGM | 4.1/5 ⭐ | +800 |
3.9/5 ⭐ | +1000 | |
| FxPro | 3.8/5 ⭐ | +800 |
| JustMarkets | 3.7/5 ⭐ | +3500 |
| Tickmill | 3.6/5 ⭐ | +1000 |
Minimum Spreads of Forex Brokers in India
Trading fees are a core factor in evaluating Forex brokers, as spreads represent the direct cost of entering and exiting trades. Traders can compare the lowest spread fees in the well-known Forex brokers in India by checking the table below.
Brokers | Minimum Spreads |
Tickmill | From 0.0 pips |
IC Markets | From 0.0 pips |
From 0.0 pips | |
From 0.0 pips | |
XM Group | From 0.0 pips |
Axi | From 0.0 pips |
Forex.com | From 0.0 pips |
Fusion Markets | From 0.0 pips |
From 0.2 pips | |
Capital.com | From 0.67 pips |
Non-Trading Fees in Forex Brokers for India Traders
Non-trading fees are a critical component of the total cost structure when evaluating Forex brokers available to Indian traders. Charges related to deposits, withdrawals, and account inactivity can directly affect capital efficiency, especially for long-term investors or low-frequency traders.
Broker | Deposit Fee | Withdrawal Fee | Inactivity Fee |
Global Prime | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| FBS | $0 | $0 | $0 |
FP Markets | $0 | No (Except for Skrill and Paysafe: 1%) | $0 |
Interactive Brokers | $0 | Varies | $0 |
Activ Trades | $0 | $0 | £10 |
Axi | $0 for up to $50,000 deposited funds | Free withdrawal above $50 | $10 |
Forex.com | $0 | $0 | $15 |
$0 | $0 | $15 | |
XM Group | $0 | $0 | $15 |
$0 | $0 | $30 |
Number of Tradable Instruments in Forex Brokers of India
The number of tradable instruments is a key indicator of market access and flexibility when comparing Forex brokers available to traders in India. A broader asset range allows exposure beyond major currency pairs into CFDs on indices, commodities, equities, cryptocurrencies, and ETFs.
Broker | Number of Tradable Assets |
Blackbull Markets | +26000 |
Forex.com | +7000 |
Capital.com | +6000 |
IC Markets | +2250 |
Go Markets | +2000 |
XM Group | +1400 |
ActivTrades | +1000 |
+600 | |
| JustMarkets | +260 |
AvaTrade | +250 |
Top 8 Best Brokers in India
The best Forex brokers in India operate under a highly regulated framework supervised by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), with strict rules on broker licensing, margin requirements, and investor protection. Retail leverage is tightly limited, and trading activity must comply with guidelines set by SEBI and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
Traders have access to hundreds of tradable instruments on famous trading platforms such as MT4, MT5, TradingView, and cTrader.
ActivTrades
ActivTrades, founded in 2001 and headquartered in London, operates under oversight from several regulatory authorities, including the FCA in the United Kingdom, alongside regional regulators such as SCB, CMVM, BACEN, and CVM.

The broker provides access to a broad range of CFD markets (over 10000 instruments), covering Forex pairs, indices, commodities, shares, ETFs, bonds, and selected cryptocurrencies.
Trading conditions are structured around floating spreads, market execution, and flexible account types designed to accommodate retail, professional, demo, and Islamic trading requirements who complete the ActivTrades registration process.
Trading services are supported across multiple platforms, including MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, TradingView integration, and the proprietary ActivTrader platform, each offering advanced charting, order management tools, and multi-asset support.
Client protection mechanisms include segregated accounts, negative balance protection, and compensation schemes.
Account Types | $0 |
Regulating Authorities | Bank Wire Transfer, Credit and Debit Cards (Visa, MasterCard), E-wallets (Skrill, Neteller), Local Payment Methods |
Minimum Deposit | Bank Wire Transfer, Credit and Debit Cards (Visa, MasterCard), E-wallets (Skrill, Neteller), Local Payment Methods |
Deposit Methods | Up to 1:400 (entity and client classification dependent) |
Withdrawal Methods | MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), ActivTrader, TradingView |
Maximum Leverage | Yes |
Trading Platforms & Apps | Live Chat, Phone Call, Ticket System |
ActivTrades Pros and Cons
Here are the important benefits and drawbacks of ActivTrades.
Pros | Cons |
Regulated by multiple authorities, including FCA, SCB, CMVM, BACEN, and CVM | Leverage limits vary depending on the regulatory entity |
Segregated client funds and negative balance protection across entities | Support services are available 24/5 rather than 24/7 |
Additional client insurance coverage beyond standard regulatory protection | - |
Access to MT4, MT5, TradingView, and proprietary ActivTrader platform | - |
IC Markets
IC Markets is a globally active Forex and CFD broker built around a high-performance execution model and extensive multi-asset market access.

Established in 2007, the broker operates through several regulated entities under authorities such as CIRO, CySEC, and the FSA, which define leverage limits, client eligibility, and regional investor protection frameworks.
Trading is offered primarily via CFDs, covering Forex pairs, indices, commodities, bonds, cryptocurrencies, and a deep equity CFD offering exceeding 2,100 instruments.
IC Markets supports 10 base account currencies, including USD, EUR, GBP, AUD, and CAD, with a standardized minimum deposit requirement of $200.
Across its global operations, the broker applies core safeguards such as segregated client funds, external audits, and strict anti-money-laundering controls.
IC Markets offers a clearly defined account lineup designed to match different pricing and execution preferences. The Standard account applies a spread-only pricing model, with minimum spreads starting from 0.8 pips on major Forex pairs. For traders seeking institutional-grade conditions, the Raw Spread account provides pricing from 0.0 pips, with trading costs separated into a fixed per lot commission, reflecting direct access to aggregated liquidity.
In addition, IC Markets supports an Islamic swap-free account, which removes overnight interest charges while maintaining the same execution model and market access across Forex and CFD instruments. Traders also have the option to to lower trading costs by using the IC Markets rebate services via TradingFinder IB.
Account Types | Standard, Raw Spread, Islamic |
Regulating Authorities | CIRO, CySEC, SCB, FSA, CMA |
Minimum Deposit | $200 |
Deposit Methods | Bank Cards (Visa, MasterCard), Bank Wire Transfer, E-wallets (Skrill, Neteller, PayPal), Local and regional payment solutions |
Withdrawal Methods | Bank Cards, Bank Wire Transfer, E-wallets (Skrill, Neteller, PayPal) |
Maximum Leverage | Up to 1:500 (subject to trading conditions) |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), cTrader, cTrader Web, IC Markets Mobile |
Pros and Cons of IC Markets for Indian Users
The following table contains the benefits and drawbacks of trading with the IC Markets broker for traders residing in India.
Pros | Cons |
Regulated by CIRO, CySEC, SCB, FSA, CMA | Minimum deposit of $200 may be less suitable for very small or entry level accounts |
Access to a wide multi-asset CFD offering, including Forex, indices, commodities, cryptocurrencies, and 2,100+ equity CFDs | Does not provide PAMM or managed investment account structures |
Supports a comprehensive platform range, including MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, cTrader, cTrader Web, and IC Markets mobile app | Raw Spread accounts apply a commission per traded lot |
Raw Spread accounts deliver institutional-style pricing with spreads from 0.0 pips | - |
JustMarkets
JustMarkets is a multi-asset Forex and CFD broker established in 2012, serving a global client base across more than 160 countries. The broker provides access to five core markets, including Forex, commodities, indices, cryptocurrencies, and stocks, primarily through CFD instruments.

Trading conditions are designed to accommodate different experience levels, with four main account types that support position sizes from 0.01 lots and leverage reaching up to 1:3000, depending on the regulatory entity and client classification.
From a regulatory perspective, JustMarkets operates under a multi-jurisdiction framework that includes oversight by CySEC, FSA, FSCA, and FSC, which all require traders to complete the JustMarkets verification for KYC and AML purposes.
Client funds are held in segregated accounts with Tier 1 banking partners, and negative balance protection is applied across entities, giving traders ease of mind for finalizing the JustMarkets Registration process.
Platform support centers on MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, and mobile applications, alongside analytical tools such as an economic calendar, VPS access, and market analysis resources.
The JustMarkets dashboard functions as the central interface for account management, funding, and trade monitoring.
Account Types | Standard Cent, Standard, Pro, Raw Spread |
Regulating Authorities | Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC), Seychelles Financial Services Authority (FSA), Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA), Financial Services Commission (FSC) |
Minimum Deposit | From $10 |
Deposit Methods | Bank transfer, E-payments, Credit/Debit cards, Crypto, Local banks |
Withdrawal Methods | Bank transfer, E-payments, Credit/Debit cards, Crypto, Local banks |
Maximum Leverage | Up to 1:3000 (depending on regulatory entity) |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), Mobile App |
JustMarkets Pros and Cons
Here are the advantages and disadvantages of using JustMarkets' services to trade Forex.
Pros | Cons |
Multi-jurisdiction regulation under CySEC, FSA, FSCA, and FSC | Limited number of tradable instruments compared to some global competitors |
Low entry requirement with a minimum deposit starting from $10 | $5 per month inactivity fee |
High leverage availability up to 1:3000 on non-EU entities | - |
Support for MT4, MT5, and mobile trading applications | - |
FxPro
FxPro is a global Forex and CFD broker with a long operating history and a strong emphasis on execution quality, platform diversity, and regulatory coverage.
FxPro provides access to more than 2,100 tradable instruments, including Forex pairs, equities, indices, commodities, metals, futures, and cryptocurrency CFDs after completing the FxPro registration.
Founded in 2006, the broker serves millions of client accounts worldwide through multiple regulated entities supervised by authorities such as the FCA, CySEC, FSCA, and SCB.
Trading is supported across a wide range of platforms, including MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, cTrader, WebTrader, and a dedicated mobile application available to download in the FxPro dashboard, enabling both manual and algorithmic trading strategies.
With a minimum deposit of $100 for many payment methods, including FxPro USDT TRC20 deposit, this broker positions itself as a multi-asset broker focused on flexible trading infrastructure, regulated market access, and execution driven conditions.
Account Types | Standard, Pro, Raw+, Elite |
Regulating Authorities | FCA (UK), CySEC (Cyprus), FSCA (South Africa), SCB (Bahamas) |
Minimum Deposit | $100 |
Deposit Methods | Visa, MasterCard, Bank Wire Transfer, Broker to Broker Transfer, Skrill, Neteller, PayPal |
Withdrawal Methods | Visa, MasterCard, Bank Wire Transfer, Broker to Broker Transfer, Skrill, Neteller, PayPal |
Maximum Leverage | Up to 1:500 (entity and client classification dependent) |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), cTrader, WebTrader, FxPro Mobile App |
FxPro Pros and Cons
Here are some of the pros and cons of trading with the FxPro broker as an Indian trader.
Pros | Cons |
Regulated by multiple authorities including FCA, CySEC, FSCA, and SCB, providing multi-jurisdictional oversight | Inactivity fees may apply after extended periods without trading activity ($15+$5/mo) |
Access to 2,100+ tradable instruments across Forex, indices, shares, commodities, metals, futures, and crypto CFDs | Higher minimum deposits apply to Pro, Raw+, and Elite account tiers |
Wide platform support including MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, cTrader, WebTrader, and FxPro mobile app | - |
Multiple account types with different pricing models, including Raw+ accounts with spreads from 0.0 pips | - |
Tickmill
Tickmill operates as a global Forex and CFD broker with a strong emphasis on execution quality, cost efficiency, and regulatory coverage.
Founded in 2014, the broker serves more than 785,000 registered users across over 180 countries and reports an average monthly trading volume exceeding $129 billion.
Tickmill follows a No Dealing Desk execution model, routing orders directly to liquidity providers to support fast execution and competitive pricing.
The broker operates through multiple regulated entities under authorities such as the FCA, CySEC, FSA, LFSA, and the Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA).
Tickmill offers Classic and Raw account structures with spreads starting from 0.0 pips after finalizing Tickmill registration, plus support of six base currencies and a minimum deposit of $100.
Trading is available across MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, WebTrader, and mobile platforms, covering Forex, indices, commodities, bonds, cryptocurrencies, and equities. Note that traders who open an account with this broker using the TradingFinder exclusive link, become eligible for Tickmill rebates of up to $7.75 per lot.
Account Types | Classic, Raw |
Regulating Authorities | FCA (UK), CySEC (Cyprus), FSA (Seychelles), LFSA (Labuan), FSCA (South Africa) |
Minimum Deposit | $100 |
Deposit Methods | Bank Transfer, Credit and Debit Cards (Visa, MasterCard), Skrill, Neteller, UnionPay, Cryptocurrency Payments |
Withdrawal Methods | Bank Transfer, Credit and Debit Cards (Visa, MasterCard), Skrill, Neteller, UnionPay, Cryptocurrency Payments |
Maximum Leverage | Up to 1:1000 (depends on regulatory entity and client classification) |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), MetaTrader Web, Tickmill Mobile App |
Pros and Cons of Tickmill Broker
Like any other broker, Tickmill has its own pros and cons.
Pros | Cons |
Regulated by multiple authorities, including FCA (UK), CySEC (Cyprus), FSA (Seychelles), LFSA (Labuan), and FSCA (South Africa) | Classic and Raw are the only live account types, with no Pro or multi-tier account segmentation |
No Dealing Desk (NDD) execution model with direct routing to external liquidity providers | The number of Forex pairs and equity CFDs is lower compared to brokers with 2,000+ share CFDs |
Raw accounts offer spreads from 0.0 pips with transparent commission per lot pricing | Social Trading (Tickmill Social) availability is limited to specific entities, such as the Seychelles-regulated branch |
Supports MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, MetaTrader Web, and the Tickmill mobile app | Advanced platforms such as cTrader or proprietary trading terminals are not supported |
FXCM
FXCM, founded in 1999, operates through several licensed entities supervised by Tier 1 and Tier 2 regulators, including FCA, ASIC, CySEC, FSCA, and ISA.
FXCM provides access primarily through CFD instruments covering Forex pairs, indices, commodities, equities, and cryptocurrencies. Account structures include CFD, Active Trader, and Corporate accounts, with a minimum deposit threshold of $50 for all FXCM registrations.
Pricing is based on floating spreads starting from 0.2 pips on major currency pairs, with standard CFD trades offered on a commission-free basis. The trading costs can be lowered by leveraging various options, including promotional plans or the FXCM rebate.
Trading infrastructure supports multiple platforms, including MetaTrader 4, TradingView, TradeStation, and FXCM’s proprietary Trading Station, enabling manual trading, algorithmic strategies, and social trading integrations such as ZuluTrade and Capitalise AI.
Leverage availability varies by entity, reaching higher levels under selected jurisdictions while remaining tightly capped in the EU and Australia.
Account Types | CFD Account, Active Trader Account, Corporate Account |
Regulating Authorities | FCA, ASIC, CySEC, FSCA, ISA |
Minimum Deposit | $50 |
Deposit Methods | Credit and debit cards (Visa, MasterCard), bank wire transfer, Skrill, Neteller |
Withdrawal Methods | Credit and debit cards, bank wire transfer, Skrill, Neteller |
Maximum Leverage | Up to 1:1000 (entity dependent) |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MetaTrader 4, TradingView, TradeStation, FXCM Trading Station |
FXCM Pros and Cons
The table below helps traders outline the key advantages and disadvantages of trading with the FXCM broker.
Pros | Cons |
Operating history dating back to 1999, reflecting long-term participation in global Forex and CFD markets | Bank wire withdrawals may incur a $40 processing fee, depending on the region |
Access to several advanced trading platforms such as MetaTrader 4, TradingView, TradeStation, and FXCM Trading Station | Cryptocurrency CFD offering is more limited compared to crypto-focused multi-asset brokers |
Spread-based pricing model with floating spreads from 0.2 pips on major Forex pairs and zero commission on standard CFD trades | Cryptocurrency CFD offering is more limited compared to crypto-focused multi-asset brokers |
Support for additional trading tools, including ZuluTrade, Capitalise AI, demo accounts, and Islamic swap-free options | - |
FBS
FBS is a multi-asset Forex and CFD broker that has been operating in the online trading industry since 2009. The company serves a global client base and provides access to more than 550 tradable instruments across Forex, indices, commodities, metals, shares, and cryptocurrencies, and a wide variety of features in the FBS dashboard.
FBS uses a floating spread model where pricing adjusts in real time based on market liquidity and volatility conditions. On the Standard account, spreads generally begin from around 0.7 pips, with trading costs incorporated directly into the bid-ask spread rather than charged as a separate commission. Trading costs can be lowered by leveraging FBS rebates up to 25%.
From a regulatory standpoint, FBS operates through multiple legal entities. Its European operations are regulated by the Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC) under license 331/17, while other branches fall under the Financial Services Commission (FSC) and ASIC for region-specific services.
Client funds are held in segregated accounts, and negative balance protection is available across supported entities, although investor compensation schemes apply mainly under the EU regulated structure.
FBS supports MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, and a proprietary mobile application that includes more than 90 technical indicators for all traders who complete the FBS registration. Account access is simplified, with a low minimum deposit threshold and position sizing starting from 0.01 lots.
Account Types | Standard |
Regulating Authorities | Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC), Financial Services Commission (FSC), Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) |
Minimum Deposit | From $5 |
Deposit Methods | Bank transfers, payment systems, credit/debit cards |
Withdrawal Methods | Bank transfers, payment systems, credit/debit cards |
Maximum Leverage | Up to 1:3000 (depending on regulatory entity) |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), FBS Mobile App |
FBS Pro and Cons
Here’s a detailed table of the benefits and drawbacks of FBS for Indian traders.
Pros | Cons |
Multi-jurisdiction regulation under CySEC, FSC, ASIC | Limited number of tradable instruments compared to some global competitors (550 assets) |
Low entry requirement with a minimum deposit starting from $5 | Higher than average spreads |
High leverage availability up to 1:3000 | - |
Support for MT4, MT5, and mobile trading applications | - |
TMGM
TMGM, operating under the name TradeMax Global Markets, is an Australian-based Forex and CFD broker with a growing international presence and a product offering designed for multi-asset trading. The broker operates through several regional entities, with its primary license held by ASIC, supported by offshore regulation from VFSC, FSC, and CMA for all TMGM registrations.
This regulatory structure defines leverage limits, client eligibility, and investor protection levels across jurisdictions, while core safeguards such as segregated client funds and professional indemnity insurance remain in place
TMGM provides access to more than 12,000 tradable instruments, spanning Forex pairs, global equities, indices, commodities, energies, and cryptocurrency CFDs. Trading is supported via MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, IRESS, and the proprietary TMGM mobile app, enabling both retail and institutional style execution.
Account structures include EDGE (ECN) and Classic accounts, each requiring a minimum deposit of $100, with pricing models ranging from raw spreads plus commission to spread-only execution. This broker also supports a wide variety of payment methods, including TMGM USDT TRC20 deposit and withdrawal options.
Additional features include copy trading and social trading, Islamic swap-free accounts, and 24/7 multilingual customer support in the TMGM dashboard.
Account Types | Classic, EDGE (ECN) |
Regulating Authorities | ASIC (Australia), VFSC (Vanuatu), FSC (Mauritius), CMA (Kenya) |
Minimum Deposit | $100 |
Deposit Methods | Bank Transfer, Credit and Debit Cards (Visa, MasterCard), Skrill, Neteller, Local Payment Methods |
Withdrawal Methods | Bank Transfer, Credit and Debit Cards (Visa, MasterCard), Skrill, Neteller, Local Payment Methods |
Maximum Leverage | Up to 1:500 (depends on regulatory entity and client classification) |
Trading Platforms & Apps | MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), IRESS, TMGM Mobile App |
TMGM Pros and Cons
Indian traders must consider the following benefits and limitations before choosing TMGM as their broker.
Pros | Cons |
Regulated by multiple authorities, including ASIC, VFSC, FSC (Mauritius), and CMA (Kenya), providing multi-jurisdictional oversight | Investor protection standards and leverage limits vary significantly depending on the regulatory entity |
Access to a very broad multi-asset offering with 12,000+ tradable instruments across Forex, equities, indices, commodities, energies, and crypto CFDs | IRESS platform access may require higher capital thresholds depending on account type |
Supports MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, IRESS, and the TMGM mobile app, covering both retail and institutional trading workflows | - |
EDGE (ECN) accounts provide raw pricing with direct liquidity access and a commission-based cost structure | - |
Is Forex Trading Legal in India?
Forex trading is legal in India, but it is subject to strict regulatory limitations imposed by domestic financial authorities.
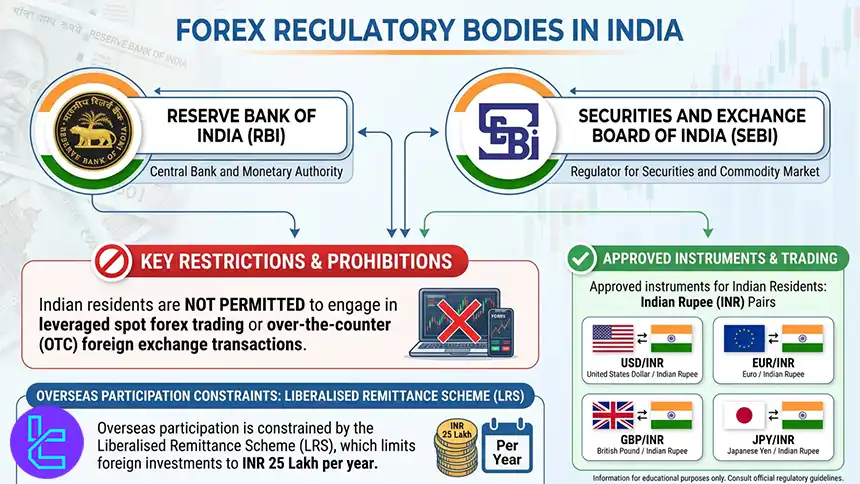
The primary regulators governing this area are the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), with legal oversight defined under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA).
Indian residents are not permitted to engage in leveraged spot forex trading or over-the-counter foreign exchange transactions.
Instead, legal participation is limited to exchange-traded currency derivatives, such as futures and options, offered on SEBI-regulated exchanges including the National Stock Exchange (NSE) and the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE). Approved instruments are mainly currency pairs benchmarked against the Indian Rupee (INR), such as USD/INR, EUR/INR, GBP/INR, and JPY/INR, along with a small number of non INR pairs.
While many offshore brokers provide access to CFD-based forex trading, where no physical currency delivery occurs, these platforms are not regulated by SEBI.
The RBI has issued repeated warnings regarding the risks of using unregulated foreign brokers, particularly around fund transfers and investor protection.
Additionally, overseas participation is constrained by the Liberalised Remittance Scheme (LRS), which limits foreign investments to INR 25 lakh per year.
As a result, forex trading in India is legally permitted but tightly controlled, requiring careful consideration of regulatory compliance.
Which Financial Authority Regulates Forex Brokers in India?
Securities and Exchange Board of India, established in 1988 under the SEBI Act of 1992, is responsible for regulating the securities and derivatives markets.
In the context of Forex trading, SEBI licenses and supervises brokers that offer exchange-traded currency derivatives, such as futures and options, on recognized Indian exchanges, including the National Stock Exchange (NSE) and the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE).
These brokers must comply with both SEBI regulations and RBI guidelines to operate legally.
While SEBI oversees market intermediaries, investor protection, and exchange operations, the RBI retains authority over banking institutions, payment systems, and foreign exchange transfers.
How to Verify SEBI Regulation?
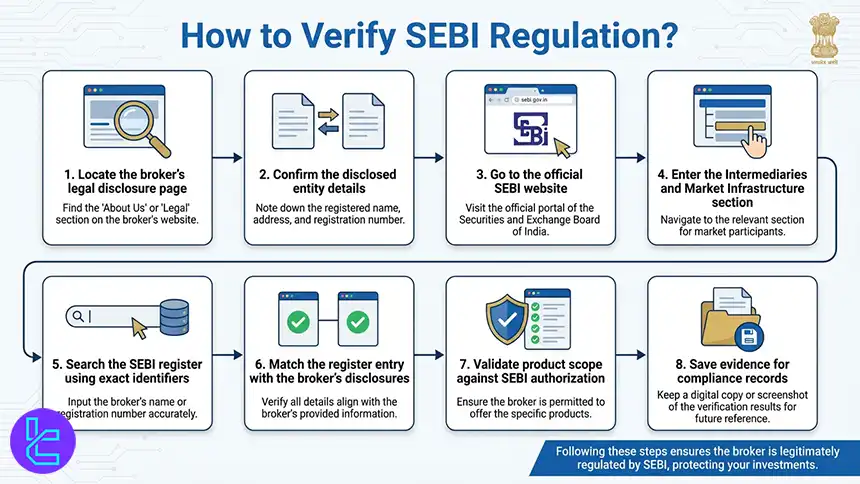
To verify a broker’s license from SEBI, traders must follow the steps listed below:
- Locate the broker’s legal disclosure page: Check the website footer or the Legal section for regulatory and company information;
- Confirm the disclosed entity details: Record the legal company name, SEBI registration number, registered office address, and official contact details;
- Go to the official SEBI website: Open sebi.gov.in and use the site navigation rather than third party directories;
- Enter the Intermediaries and Market Infrastructure section: Access SEBI’s public registers for licensed market participants and intermediaries;
- Search the SEBI register using exact identifiers: Search by the broker’s legal entity name or SEBI registration number to avoid brand name mismatches;
- Match the register entry with the broker’s disclosures: Verify that the registration number, entity name, and address match what the broker publishes;
- Validate product scope against SEBI authorization: Confirm the broker is licensed for exchange traded currency derivatives if it claims India based Forex access via NSE or BSE;
- Save evidence for compliance records: Keep screenshots or PDFs of the SEBI register entry and the broker’s disclosure page for future reference.
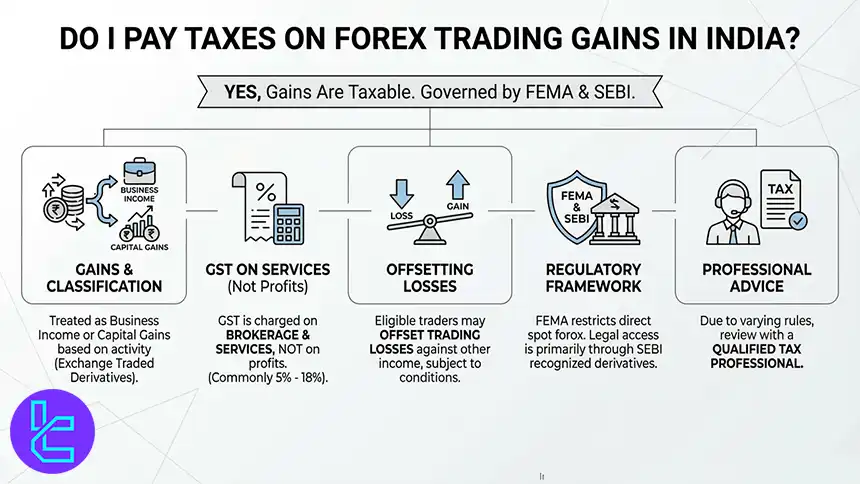
Do I Pay Taxes on My Forex Trading Gains in India?
Yes, forex-related trading gains are generally taxable in India because investments and trading profits fall under Indian tax rules.
Instead, legal participation is
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is usually not applied to trading profits themselves, but it can be charged on brokerage and related financial services connected to trading, with rates commonly ranging from 5% to 18%.
Indian tax rules may also allow eligible traders to offset trading losses against other income or gains, subject to set-off and carry-forward conditions.
Because tax treatment can vary by instrument type and regulatory updates, traders often review their reporting approach with a qualified tax professional.
Maximum Trading Leverage in India
Leverage in the Indian forex market is deliberately conservative and structured around risk containment rather than aggressive capital amplification.
Indian residents trading permitted currency derivatives are subject to clearly defined leverage ceilings that limit position size relative to account equity.
For widely traded currency pairs linked to the Indian Rupee, leverage typically does not exceed 1:50, while other eligible instruments may carry even lower ratios.
These limits are embedded into exchange-level margin requirements and apply uniformly to retail participants.
Outside India, leverage conditions can differ significantly. Brokers operating in certain offshore jurisdictions may advertise much higher leverage ratios, sometimes reaching 1:5000. While this can increase short-term exposure, it also raises the probability of outsized losses.
For many traders, especially those prioritizing consistency and capital protection, modest leverage levels remain a practical choice regardless of what higher leverage alternatives may be available elsewhere.
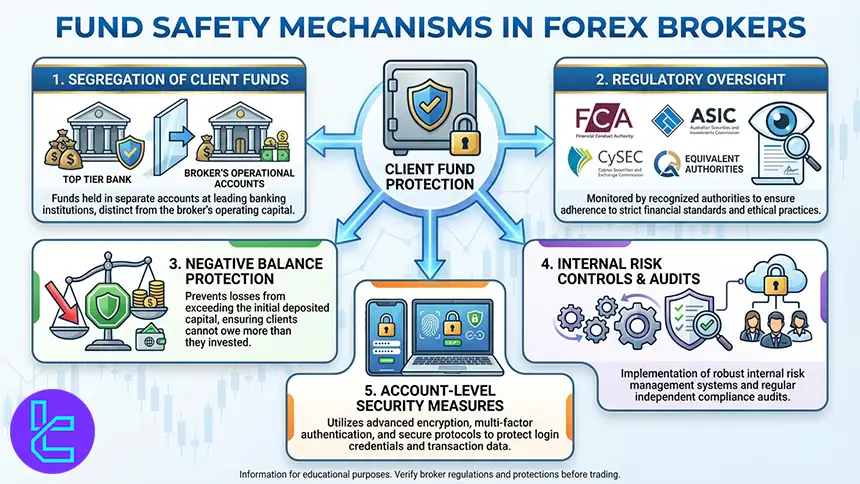
How Secure are My Funds When Trading with Forex Brokers in India?
Fund security is a critical consideration for Indian traders, particularly when accessing Forex and Contract for Difference markets through international brokers.
While market risk cannot be eliminated, capital protection largely depends on the regulatory standards and internal safeguards applied by the broker.
Reputable Forex brokers operate under strict compliance with SEBI frameworks (which is a 2nd tier authority based on TF scores) that are designed to protect client money from operational and financial risks.
One of the most important protection mechanisms is the use of segregated funds. Under this structure, client deposits are held in separate bank accounts that are legally isolated from the broker’s own operating capital.
This separation reduces exposure in the event of insolvency or financial mismanagement and aligns with global best practices enforced by Tier 1 regulators.
- Segregation of client funds in top-tier banking institutions;
- Oversight by recognized regulators such as the FCA, ASIC, CySEC, or equivalent authorities;
- Negative balance protection to prevent losses exceeding deposited capital;
- Internal risk controls and regular compliance audits;
- Account-level security measures to protect login and transaction data.
Ultimately, while Forex trading carries inherent risk, choosing a broker that enforces strict fund segregation, transparent regulation, and robust financial controls significantly enhances the level of capital protection available to Indian traders.
How to Trade Forex in India
To begin trading currency pairs in India, traders must follow a simple process to create an account with a reputable broker and begin trading. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
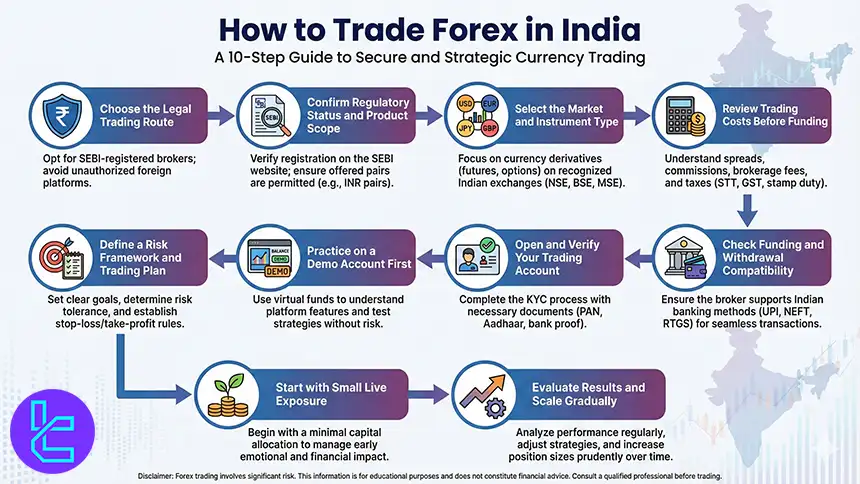
#1 Choose the Legal Trading Route
Decide whether you will trade SEBI-recognized exchange-listed currency derivatives or use a foreign broker offering margin based CFD trading.
#2 Confirm Regulatory Status and Product Scope
Verify that the broker is SEBI registered for exchange-traded products, or regulated by a Tier 1 authority such as FCA, ASIC, or CySEC for offshore access.
#3 Select the Market and Instrument Type
Pick whether you will trade INR-linked currency derivatives, major Forex pairs via CFDs, or a mix of FX, indices, and commodities, depending on your broker’s offering.
#4 Review Trading Costs Before Funding
Compare spreads, commissions, overnight financing, and non-trading fees to estimate real costs per trade and long-term account impact.
#5 Check Funding and Withdrawal Compatibility
Confirm supported payment rails, settlement times, base currency options, and any conversion fees that affect INR deposits and cross-border transfers.
#6 Open and Verify Your Trading Account
Complete KYC, set account preferences such as platform, base currency, and leverage, then secure the account with strong authentication controls.
#7 Practice on a Demo Account First
Test order types, charting tools, and risk parameters on the chosen platform before placing live trades with real capital.
#8 Define a Risk Framework and Trading Plan
Set position sizing rules, maximum drawdown limits, stop loss placement logic, and a journal process for reviewing performance.
#9 Start with Small Live Exposure
Execute a limited number of trades using an amount you can afford to risk, focusing on a consistent process rather than short-term returns.
#10 Evaluate Results and Scale Gradually
Measure performance using metrics such as win rate, average R multiple, and maximum drawdown, then increase size only after stable execution.
How Does Forex Trading in India Compare to That in Other Countries?
Forex trading in India is shaped by a tightly controlled regulatory structure that prioritizes capital controls and investor protection over market flexibility. Oversight from domestic authorities such as the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) significantly limits how retail traders can access currency markets.
Compared to offshore jurisdictions or regions with liberal margin rules, India enforces strict restrictions on leverage and product availability.
Retail traders are generally confined to exchange-traded currency derivatives on SEBI-regulated venues like NSE and BSE, while higher leverage levels are typically only accessible through non Indian, internationally regulated brokers that accept Indian residents.
Comparison Factor | India | South Africa | ||
Primary Regulator | Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), Reserve Bank of India (RBI) | Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA) | Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC) under ESMA | Capital Markets Authority (CMA Kenya) |
Regulatory Framework | National regulation under SEBI | National regulation under FSCA (non-EU) | EU-wide MiFID II and ESMA compliance | National regulation under CMA Kenya |
Retail Leverage Cap (Forex Majors) | 1:50 | Not strictly capped; higher leverage commonly available | 1:30 | 1:400 |
Investor Protection Level | Moderate to high | High | Very high | Moderate |
Negative Balance Protection | Mandatory | Commonly applied by brokers | Mandatory | Applied by many brokers |
Client Fund Segregation | Required for SEBI-regulated brokers | Required under FSCA rules | Mandatory | Required under CMA rules |
Broker Transparency Requirements | Strict disclosure for SEBI-regulated Firms | Strong conduct and disclosure standards | Strict EU disclosure rules | Formal licensing and disclosure requirements |
Broker Availability | Limited to SEBI-regulated brokers on NSE and BSE; offshore brokers are widely used | Mix of FSCA-licensed and international brokers | Broad EU broker access via passporting | CMA licensed local and international brokers |
Access to International Brokers | Moderate to high | High (global brokers actively target ZA market) | Very high (EU passporting hub) | Moderate to high |
Typical Trading Platforms | MT4, MT5, TradingView, cTrader | MT4, MT5, cTrader, proprietary platforms | MT4, MT5, cTrader, TradingView | MT4, MT5, cTrader |
Maximum Loss Protection | Cannot lose more than the deposit | Often applied but entity-dependent | Cannot lose more than the deposit | Often applied but broker-dependent |
Tax Treatment of Forex Profits | Taxed as business income or capital gains under Indian tax law | Taxed as income or capital gains under South African tax law | Tax rules vary by residency | Tax obligations depend on the Kenyan tax law |
Conclusion
By comparing the best brokers in India, we can conclude that Forex.com, FxPro, FXCM, TMGM, ActivTrades, and IC Markets are the best available options.
Traders who are looking for a top-tier regulated broker with minimal spreads, low commissions, various instruments, and deposit/withdrawal methods can consider the options mentioned earlier and begin their trading journey.
All the brokers have been evaluated based on the Forex methodology considering various factors, including regulation, spreads, minimum deposits, leverage, trading platforms, and more.













